Abdomen 2b: Gastrointestinal Tract - Dr. Inpanbutr
1/120
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
121 Terms
The gastrointestinal tract develops from a embryonic primitive gut tube called the what?
endoderm
Three parts of endoderm:
1.) foregut
2.) midgut
3.) hindgut
The foregut of the endoderm differentiates into (4)
1.) pharynx
2.) esophagus
3.) stomach
4.) first part of duodenum
The midgut of the endoderm differentiates into (5)
1.) distal part of duodenum
2.) jejunum
3.) ileum
4.) cecum
5.) larger part of the colon
The hindgut of the endoderm differentiates into (3)
1.) distal part of the colon
2.) rectum
3.) part of the urogenital tract
The gastrointestinal tract includes (3):
1.) stomach
2.) small intestines
3.) large intestines
Stomach
musculoglandular organ interposed between the esophagus and the small intestine
The stomach is the largest __________ of the GI tract
dilation
Function of the stomach (3)
1.) produce mucus and gastric enzymes
2.) produce muscular movements to mix ingesta and enzymes, aiding in digestion
3.) slowly move ingesta into the duodenum
Four parts of the stomach:
1.) cardiac
2.) fundus
3.) body
4.) pylorus
When the stomach is empty, is it hidden from palpation by what cranioventrally (2)?
liver and diaphragm
When the stomach is empty, is it hidden from palpation by what caudally?
intestinal mass
When the stomach is full, it protrudes beyond the...
costal arches
The full stomach can extend caudally to what point?
L3-L4 vertebrae
Rugae
folds of the stomach wall
Cardiac part of the stomach
the smallest part of the stomach situated near the esophagus
The cardiac part of the stomach is located at what intercostal space?
left 9th intercostal space
Fundus of the stomach
dome-shaped portion of the stomach that produces gastric juice
Where does the fundus of the stomach lie in relation to the cardiac part of the stomach?
to the left and dorsal to the cardiac part
Body of the stomach
large middle portion of the stomach that extends from the fundus on the left to the pyloric part on the right; produces gastric juice
Pyloric part of the stomach
distal third of the stomach that produces mucus
Three parts of the pyloric part of the stomach:
1.) pyloric antrum
2.) pyloric canal
3.) pylorus
pyloric antrum
thin walled part of pylorus that narrows into the pyloric canal
pyloric canal
narrow of the pyloric part of the stomach as it enters the duodenum
pylorus
sphincter between the pyloric part of the stomach and the duodenum
Which part(s) of the stomach produce gastric juices?
fundus and body
Which part(s) of the stomach produce mucus?
pyloric part of the stomach
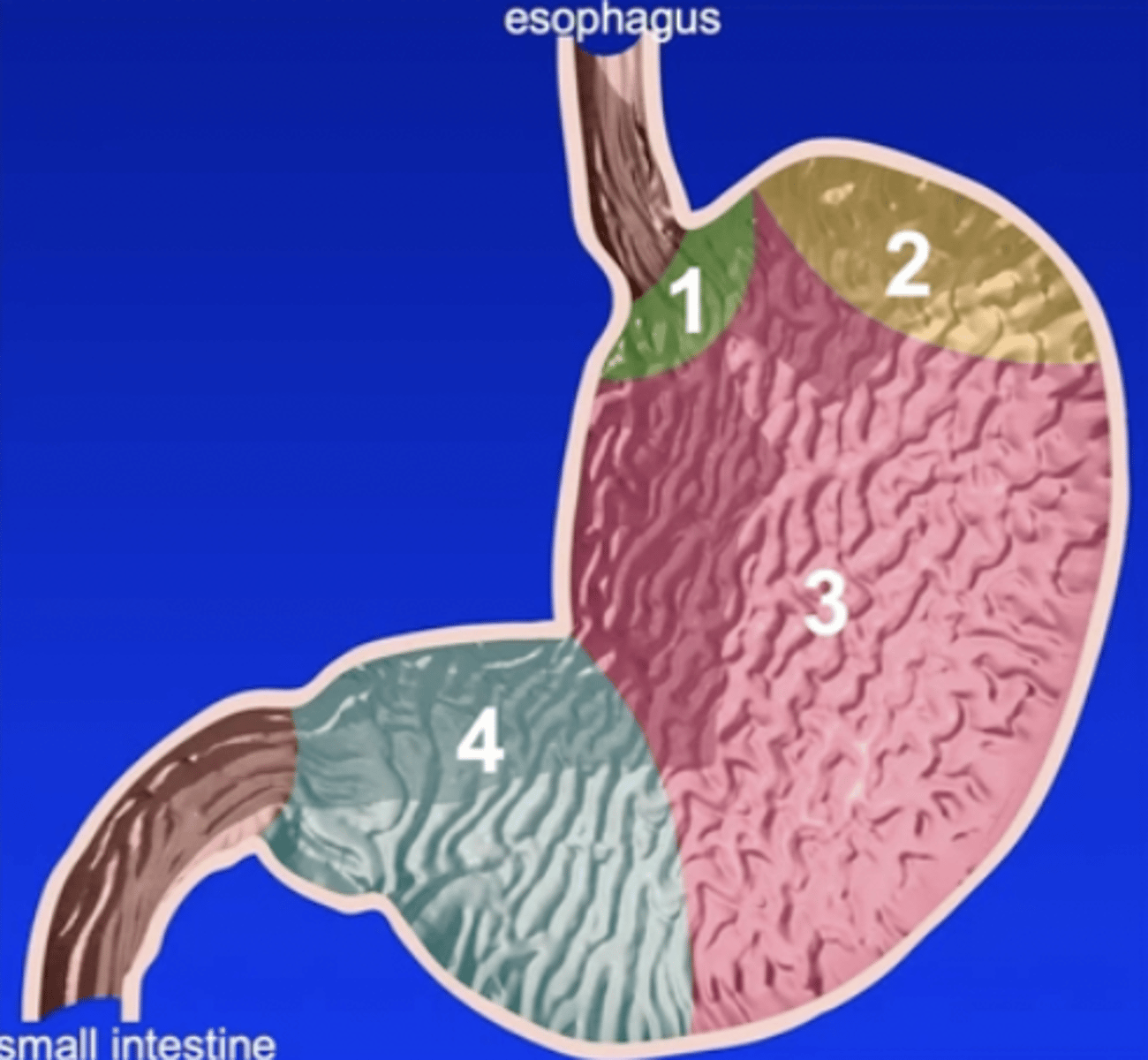
1
cardiac part of the stomach
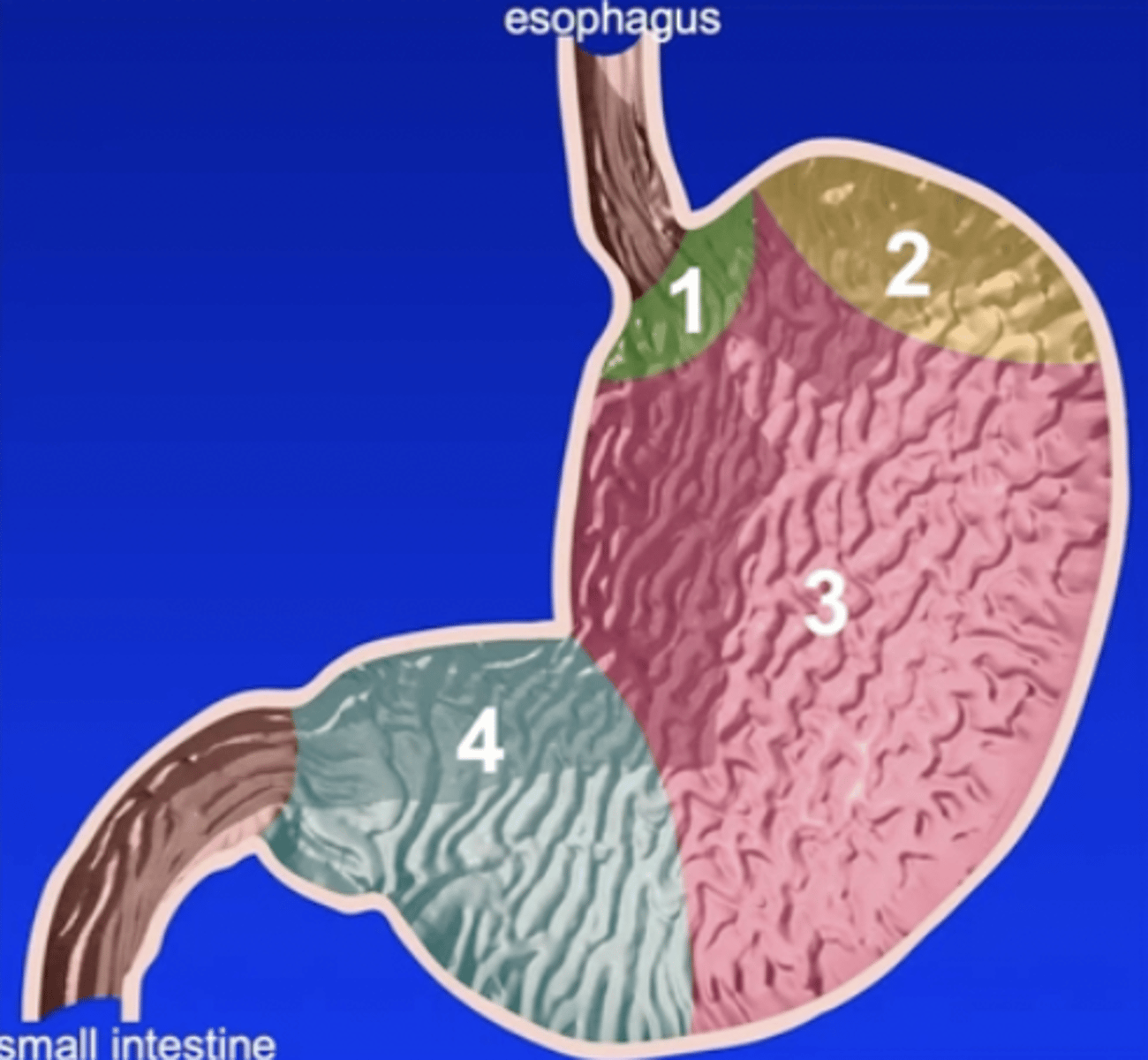
2
fundus of the stomach
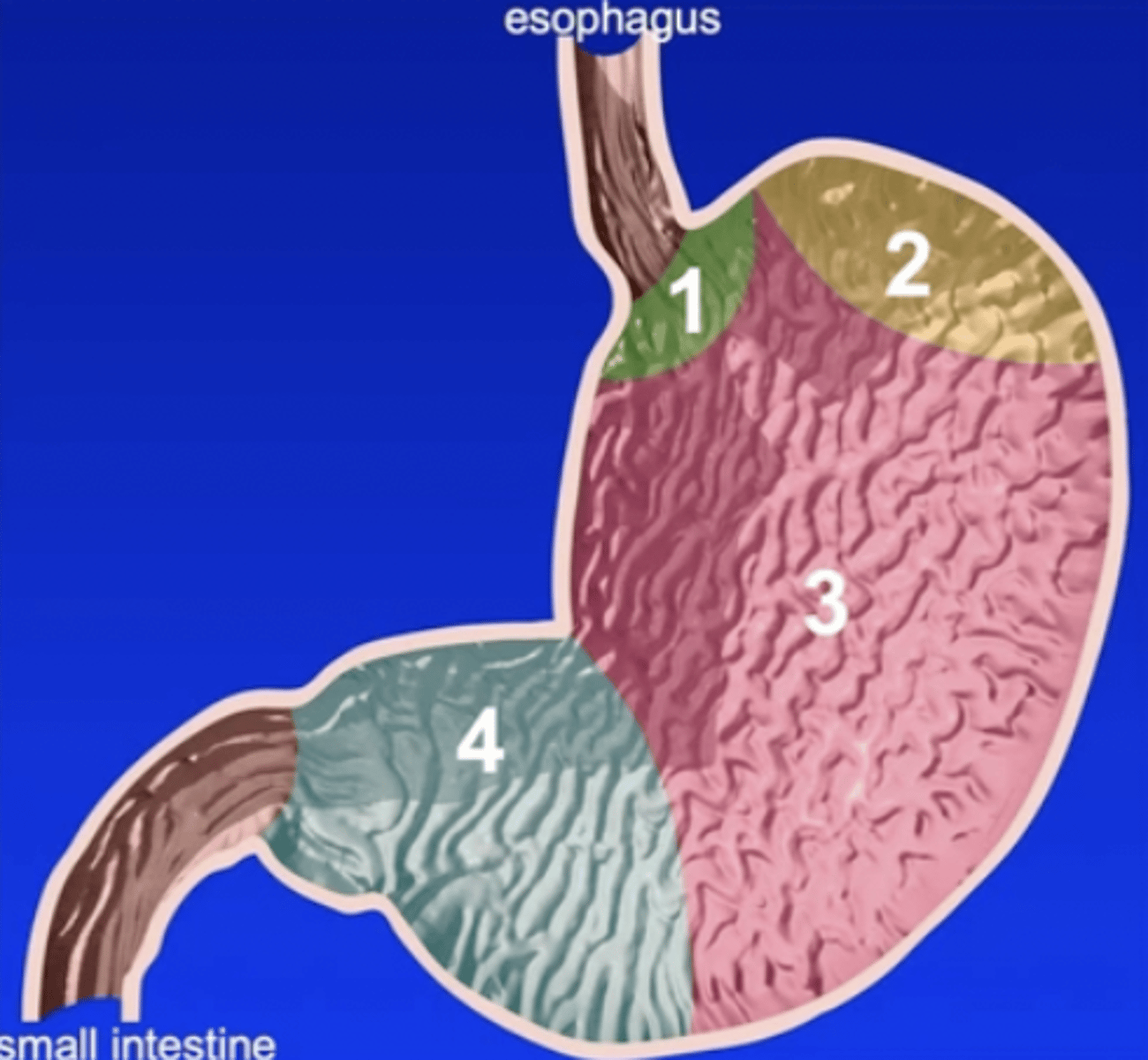
3
body of the stomach
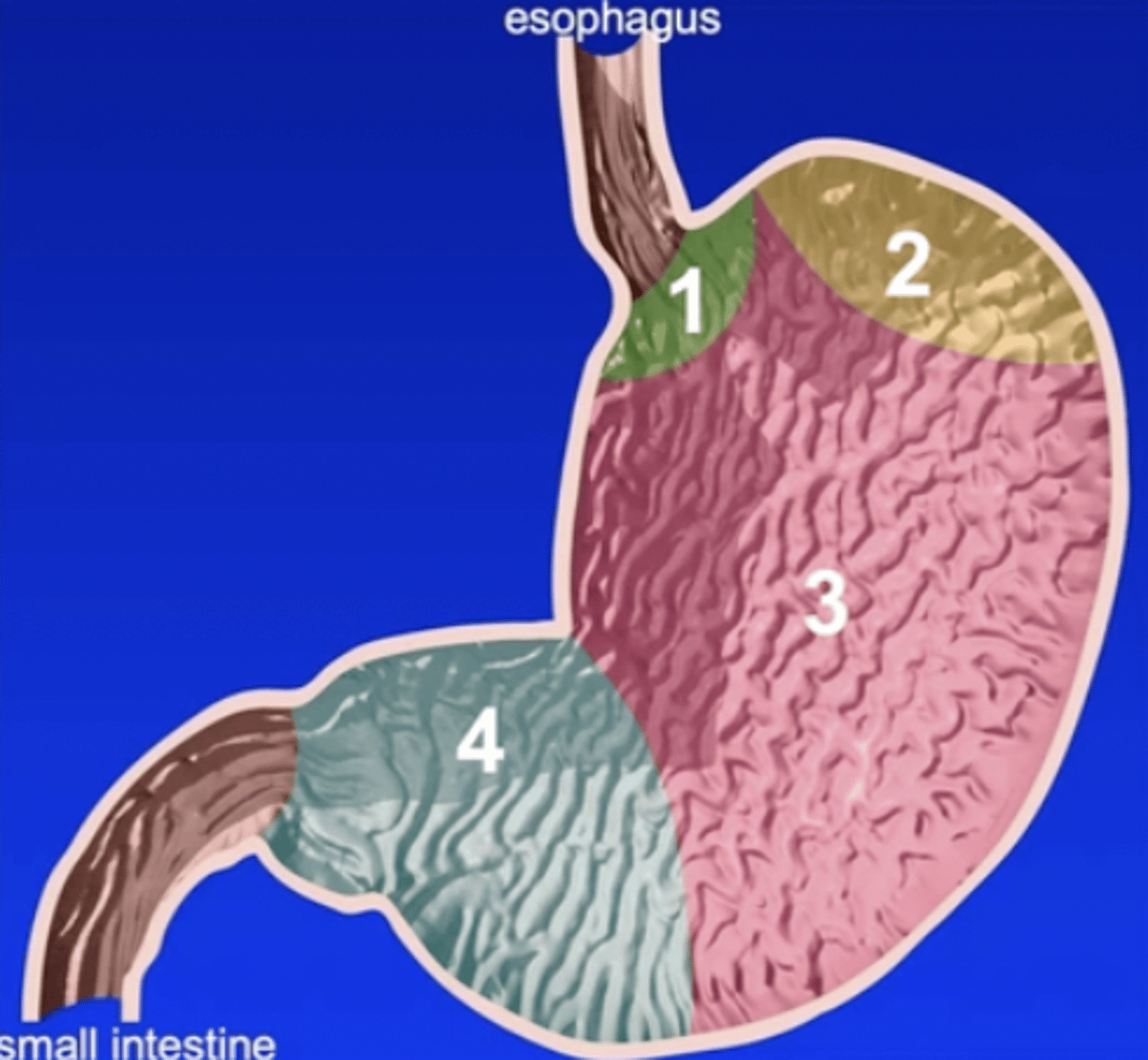
4
pyloric part of the stomach
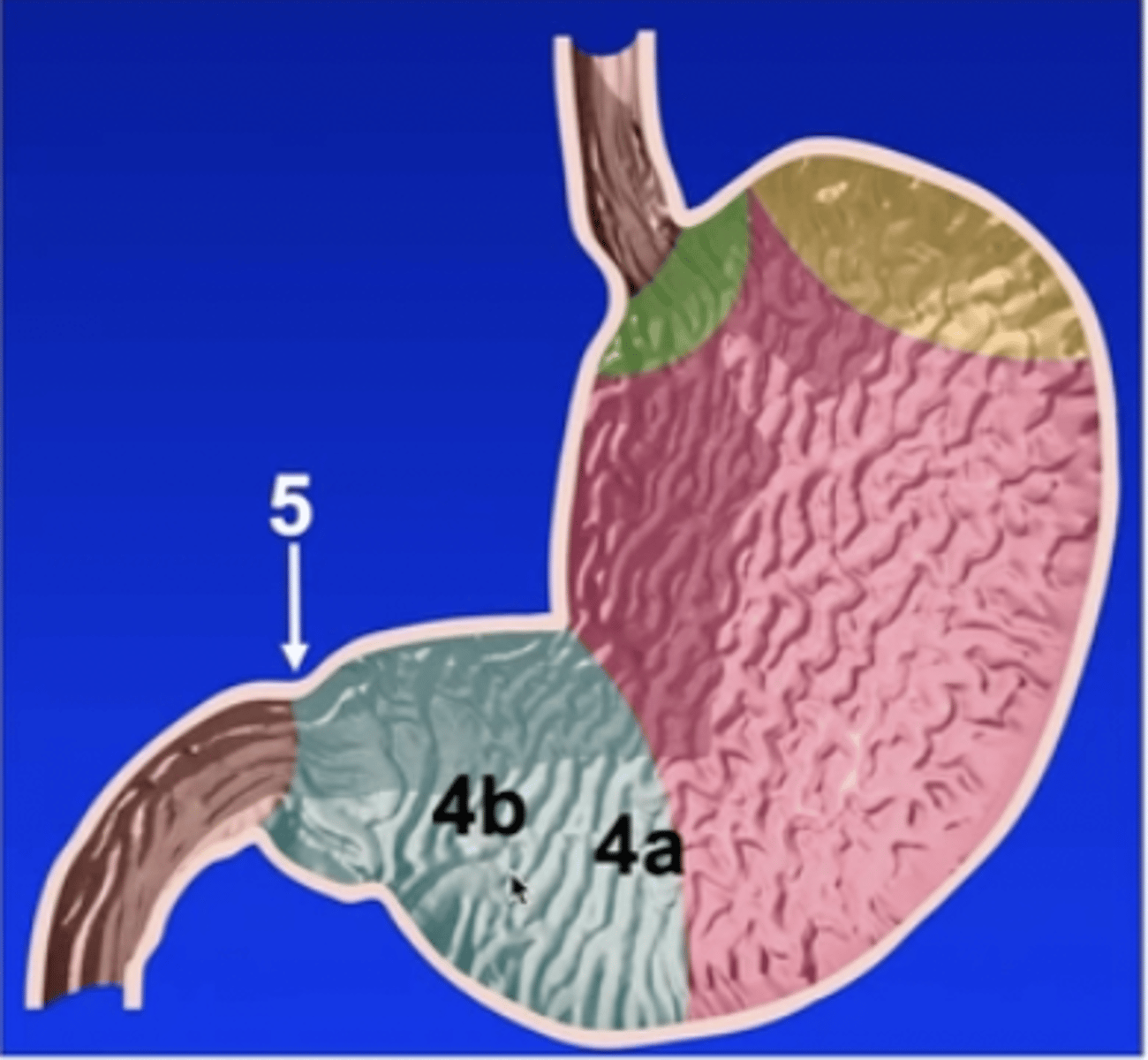
4a
pyloric antrum
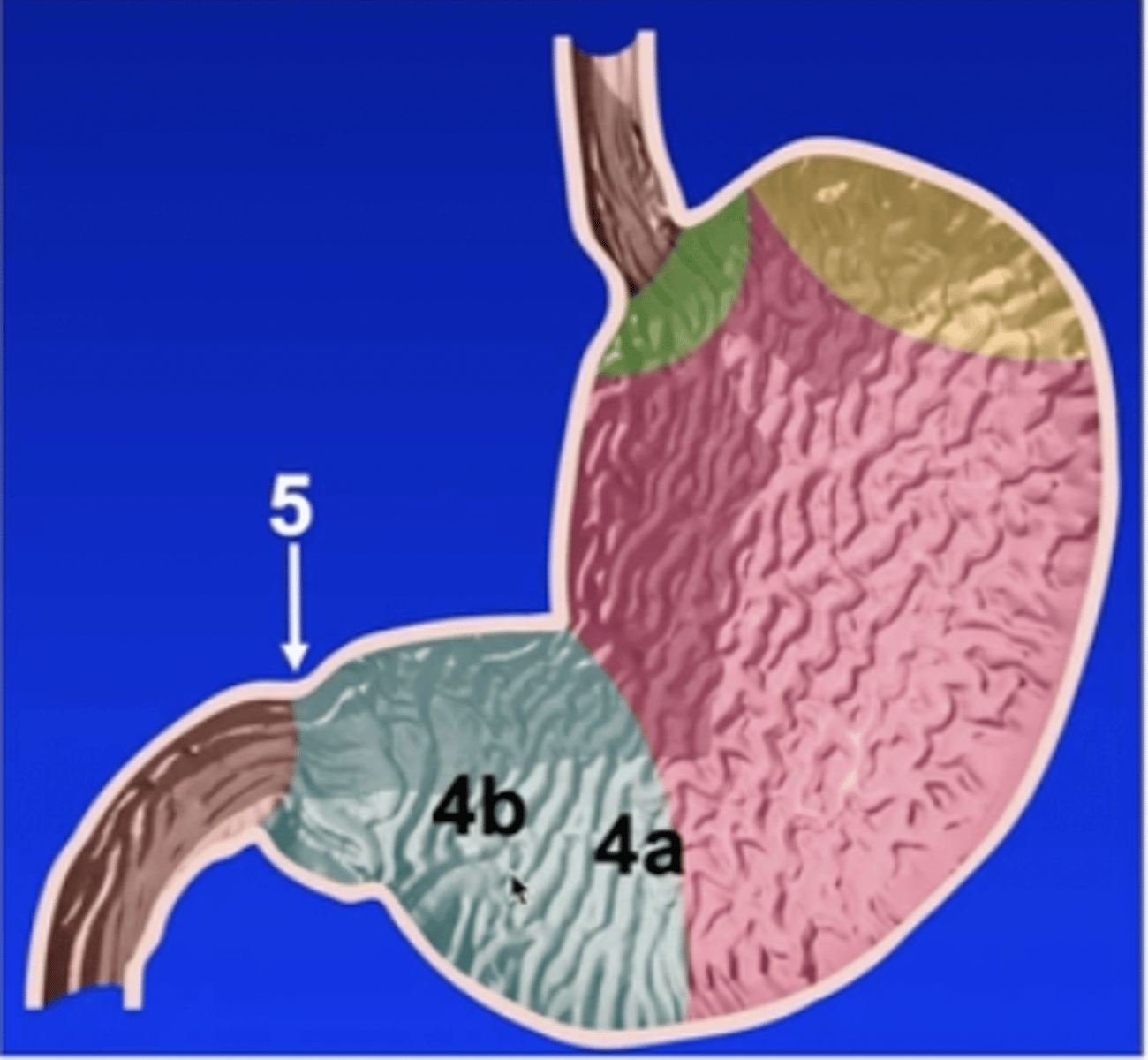
4b
pyloric canal
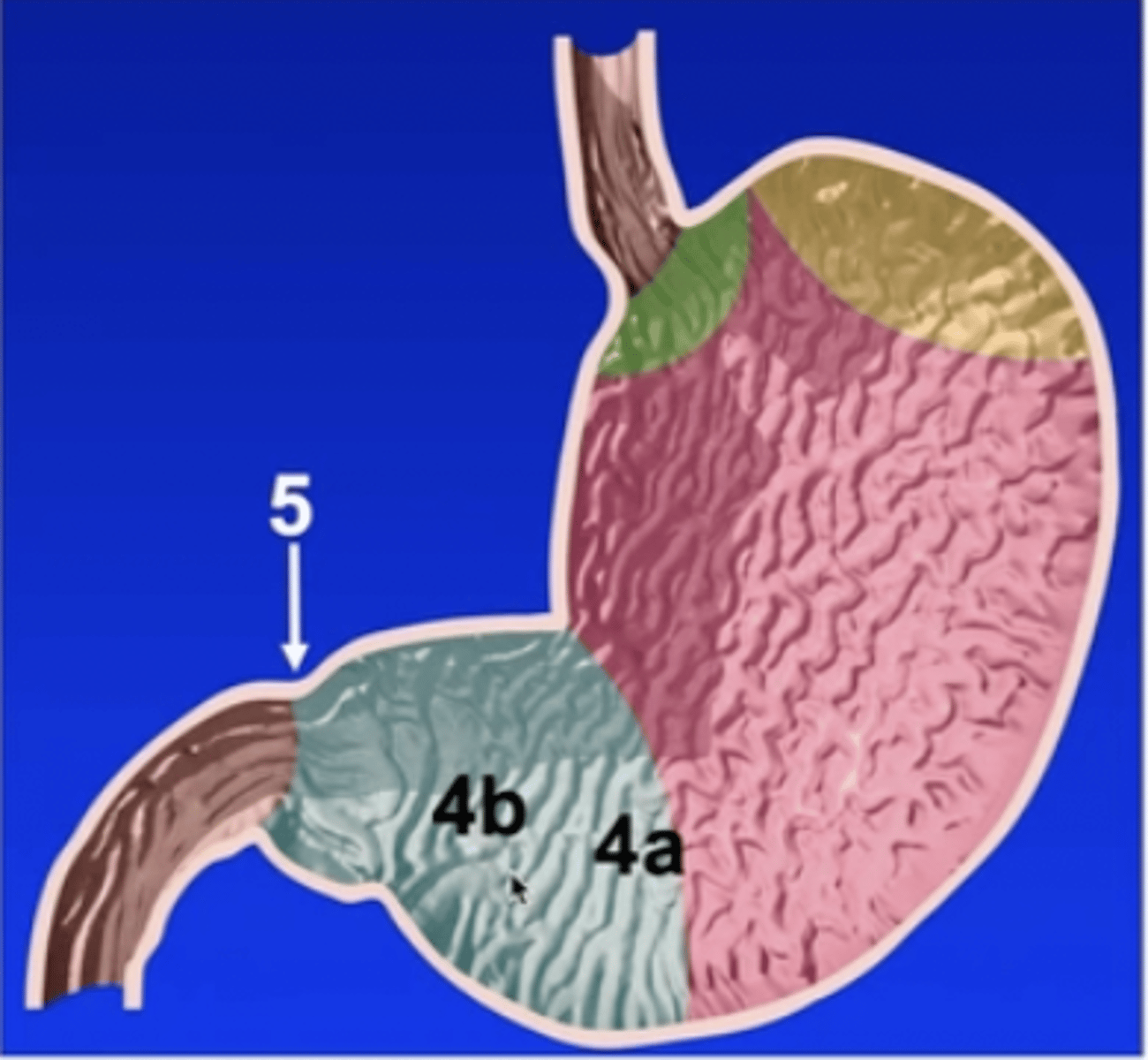
5
pylorus
Small intestines
principal site of digestion and absorption, extending from the pylorus of the stomach to the large intestine
three parts of the small intestines:
1.) duodenum
2.) jejunum
3.) ileum
Duodenum is the most _______ part of the small intestines
fixed
Since the duodenum is the most fixed part of the small intestines, does this make it more or less likely to be displaced?
less
The duodenum is divided into five segments:
1) cranial duodenal flexure
2) descending duodenum
3) caudal duodenal flexure
4) ascending duodenum
5) duodenojejunal flexure
cranial duodenal flexure
first bend of the duodenum near the pylorus
descending duodenum location
courses caudally on the right side of the abdominal cavity
the descending duodenum contacts the _________ part of the abdominal cavity
dorsolateral
The descending duodenum has three features:
1.) mesoduodenum
2.) major duodenal papilla
3.) minor duodenal papilla
mesoduodenum
mesentery that attaches the duodenum to the body wall
major duodenal papilla
opening of pancreatic & bile duct
minor duodenal papilla
opening of accessory pancreatic duct
caudal duodenal flexure
aka transverse duodenum; duodenum begins to travel towards the left side of the body
the caudal duodenal flexure occurs at the level of which vertebra?
L6 vertebra
ascending duodenum location
travels cranially on the left side of the root of the mesentery
duodenojejunal flexure
the junction between the duodenum and jejunum
The jejunum is the ________ part of the small intestine
longest
The jejunum occupies a large portion of the __________ abdomen
caudoventral
the jejunum is covered ventrally and laterally by what structure?
greater omentum
The jejunum is supported by the __________
mesojejunum
mesojejunum
mesentery that attaches the jejunum to the root of the mesentery
The mesojejnum spans from the __________ abdominal midline to the _________ lumbar vertebrae
dorsal abdominal midline; 2nd lumbar vertebra
The root of the mesentery is located at the
2nd lumbar vertebra
The root of the mesentery contains (3):
1.) cranial mesenteric artery
2.) nerves
3.) mesenteric lymph nodes
the ileum is the _________ part of the small intestine
shortest
The ileum opens into the ascending colon at the level of the
first or second lumbar vertebrae
Three features of the ileum:
1.) ileocolic orifice
2.) ileocolic sphincter
3.) ileocecal fold
ileocolic orifice
where the ileum empties into the colon
ileocolic sphincter
smooth muscle sphincter that regulates the flow of ingesta through the ileocolic orifice
The ileum is connected to the _______
cecum
The ileum is connected to the cecum through the...
ileocecal fold
The ileum is suspended by (2):
1.) mesentery
2.) mesocolon
Which artery is located parallel along the ileum?
antimesenteric ileal a.
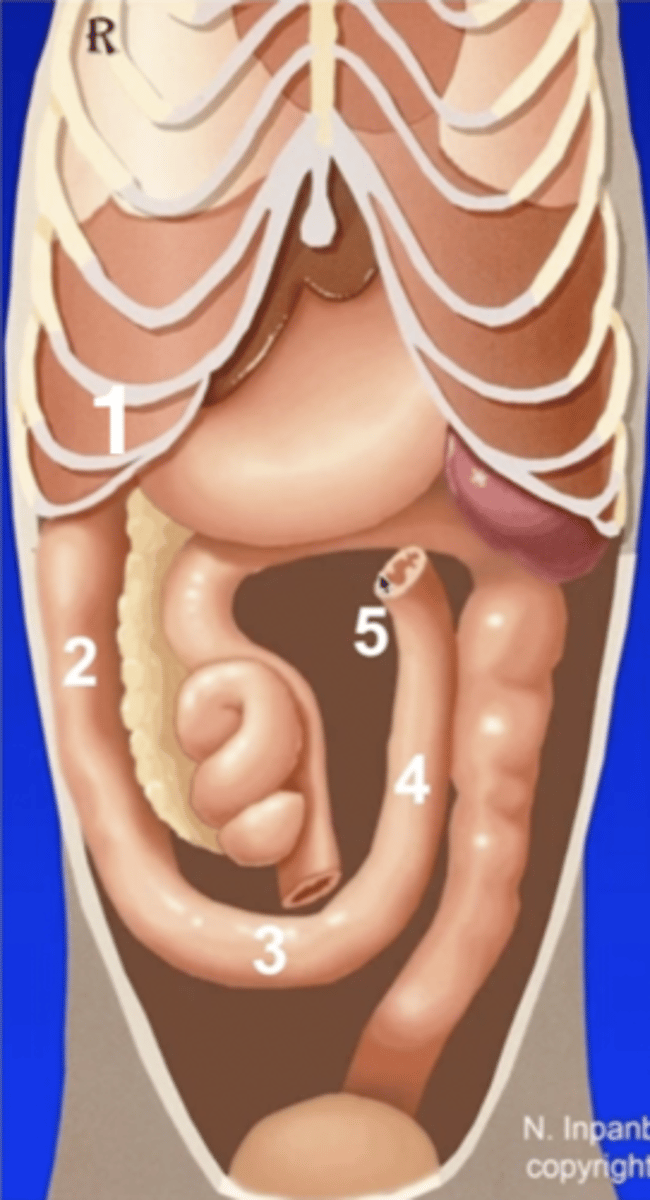
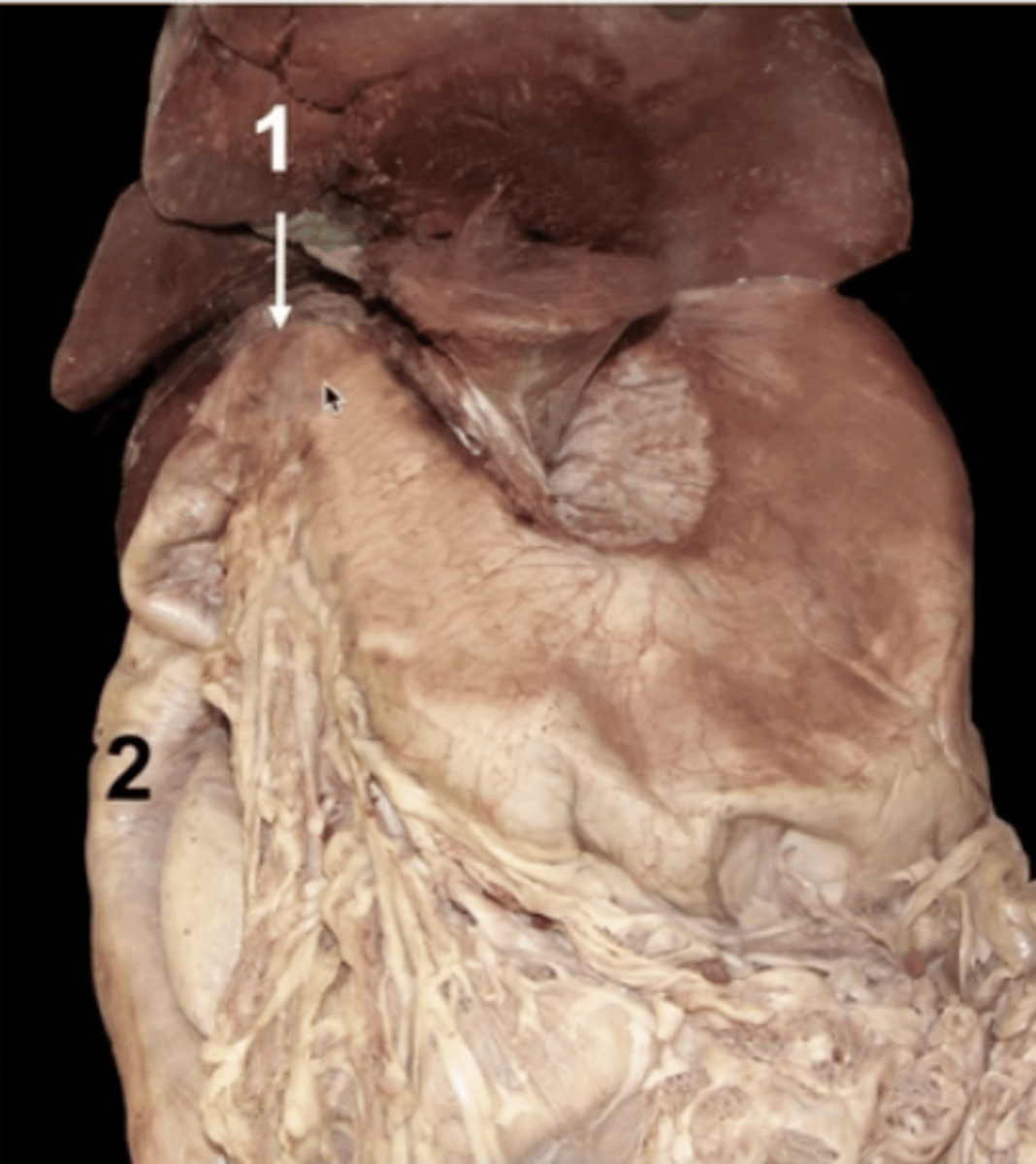
1 (behind ribs)
cranial duodenal flexure
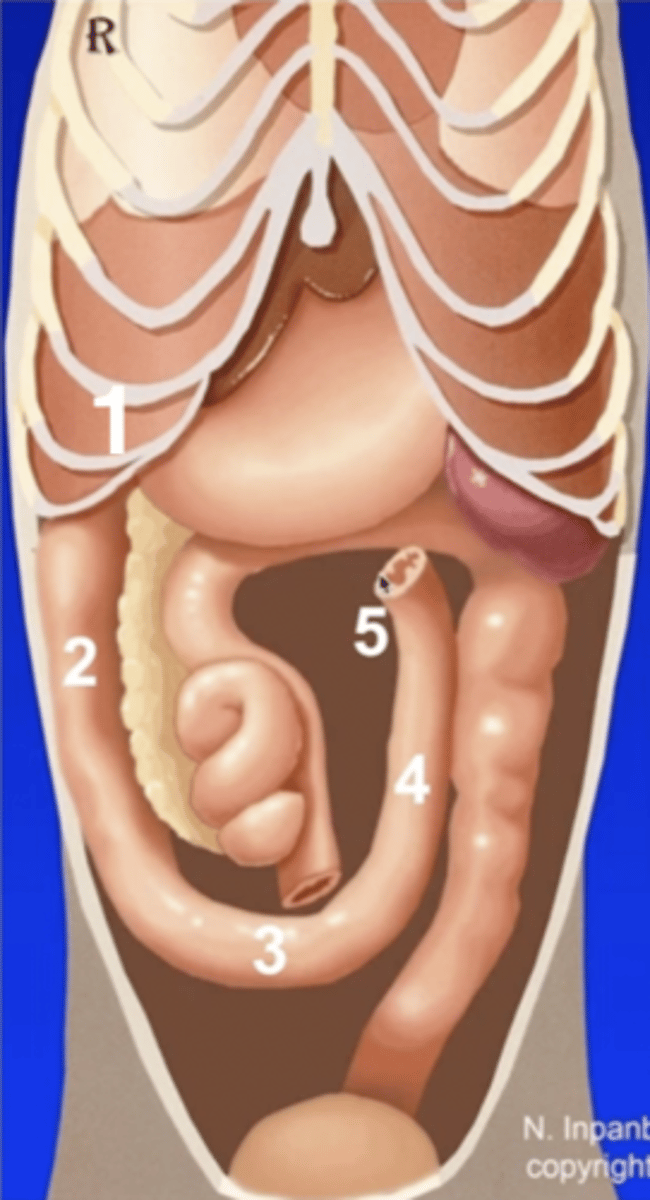
2
descending duodenum
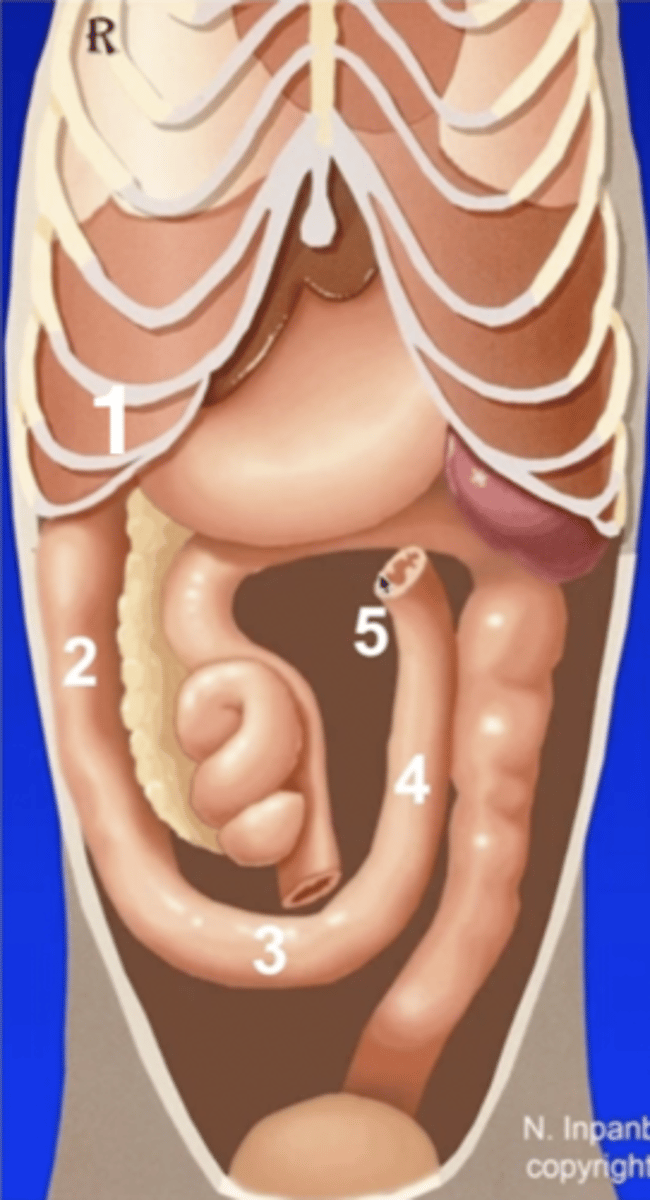
3
caudal duodenal flexure
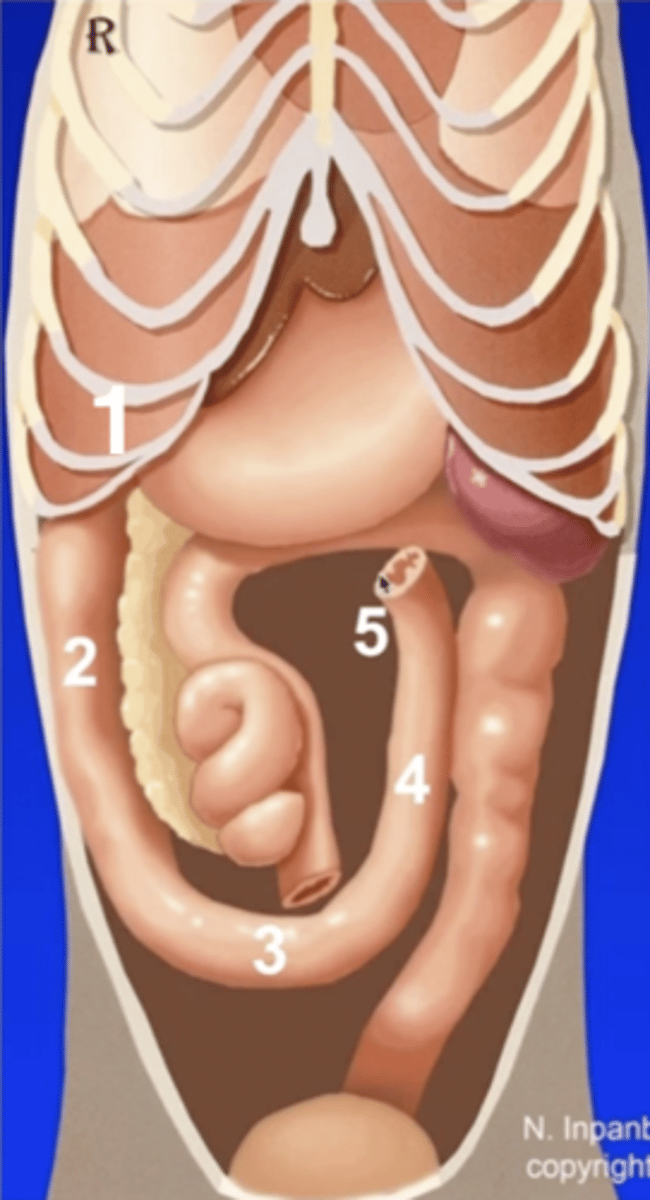
4
ascending duodenum
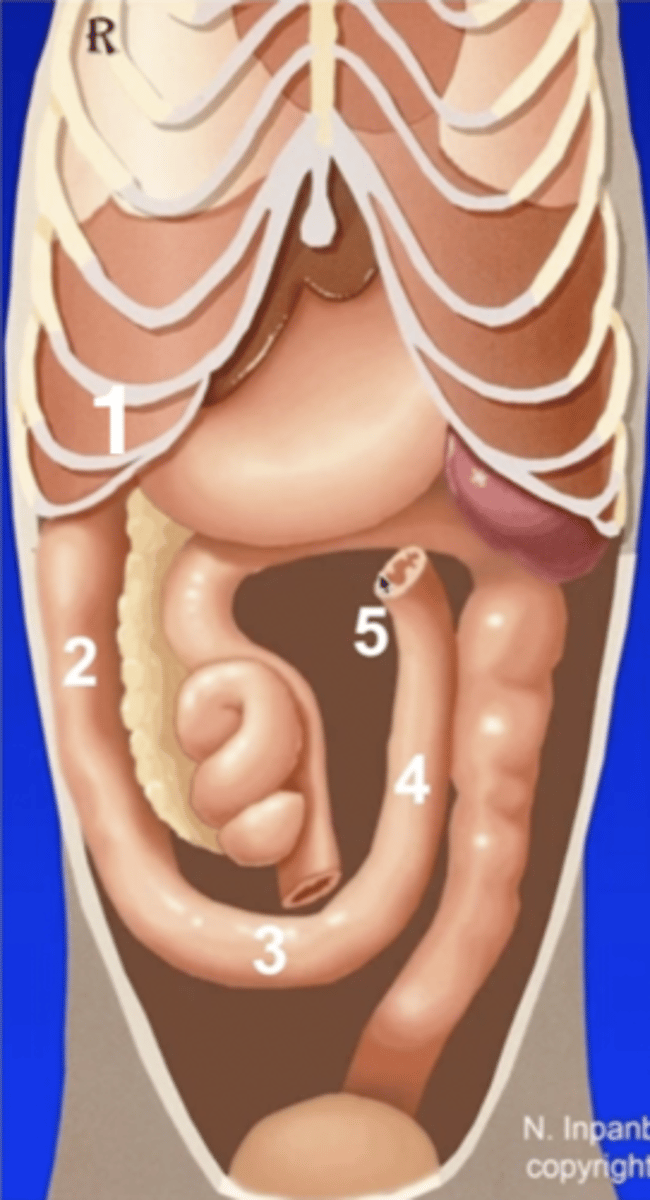
5
duodenojejunal flexure
1
cranial duodenal flexure
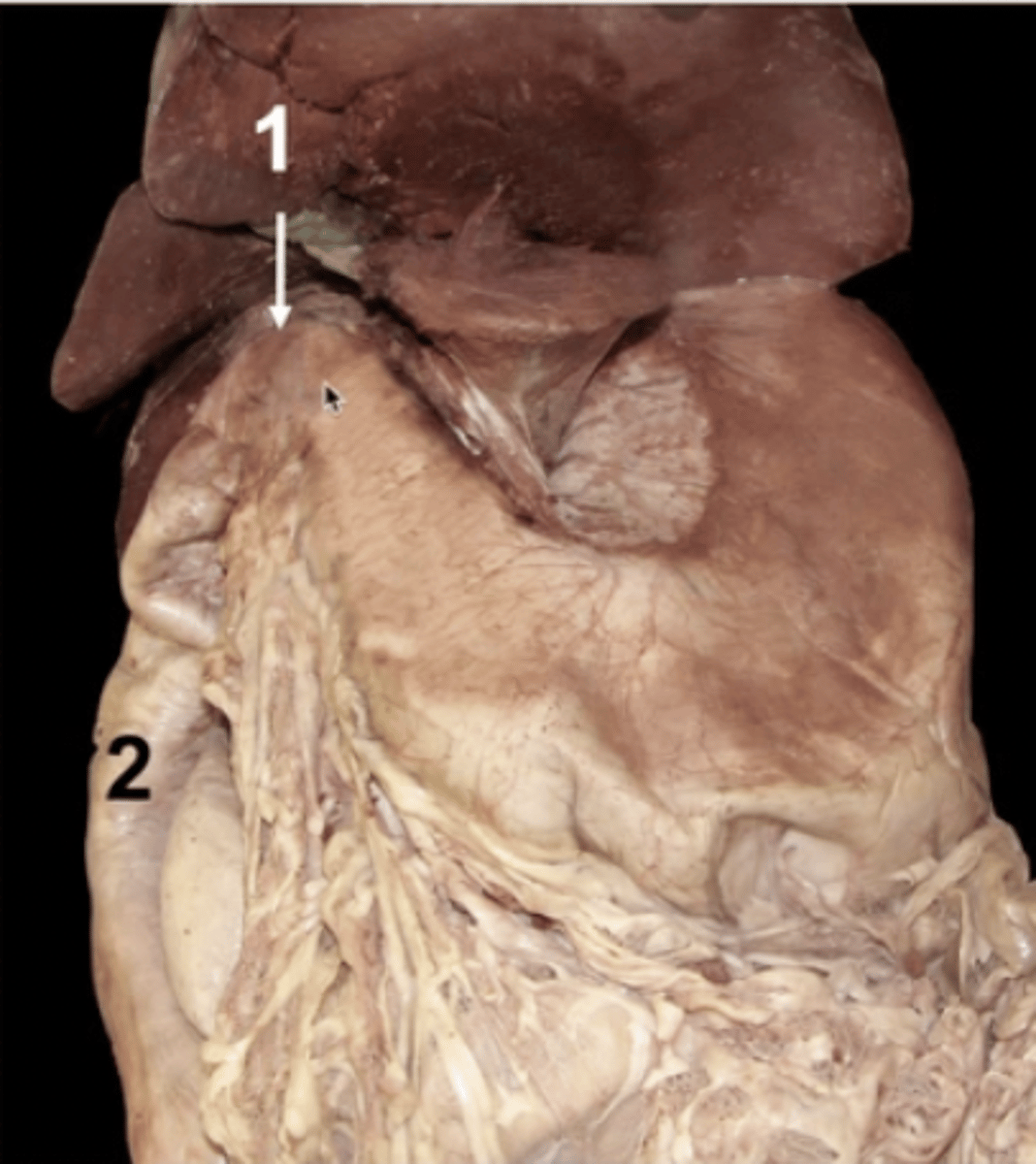
2
descending duodenum
1
jejunum
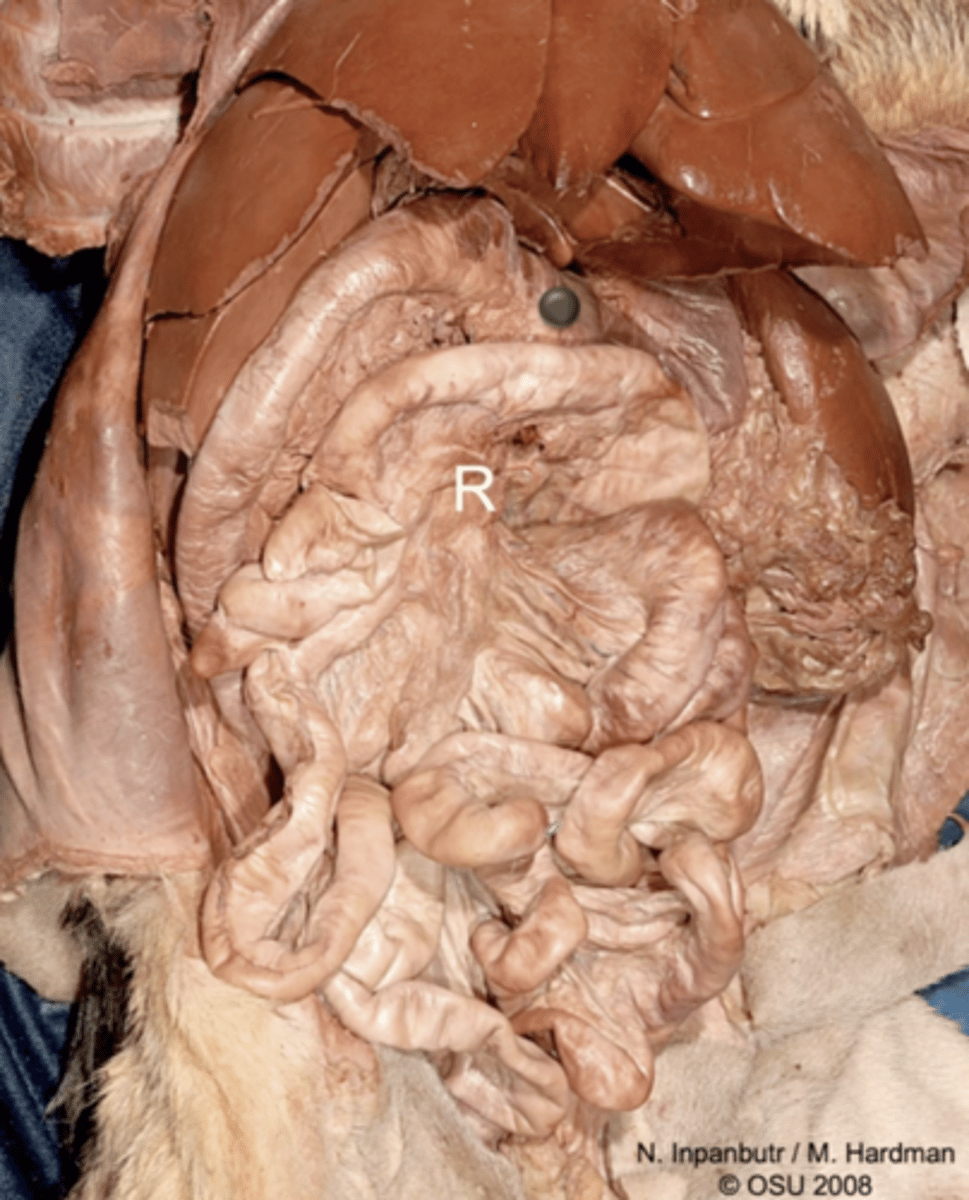
R
root of the mesentery
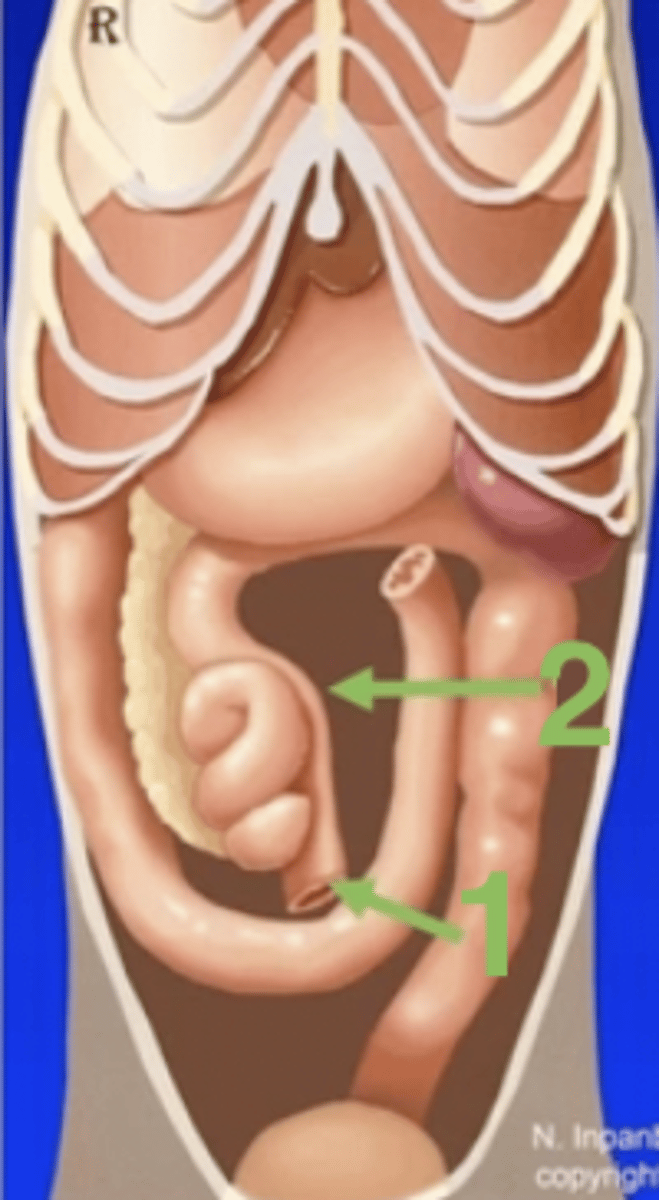
1
ileum
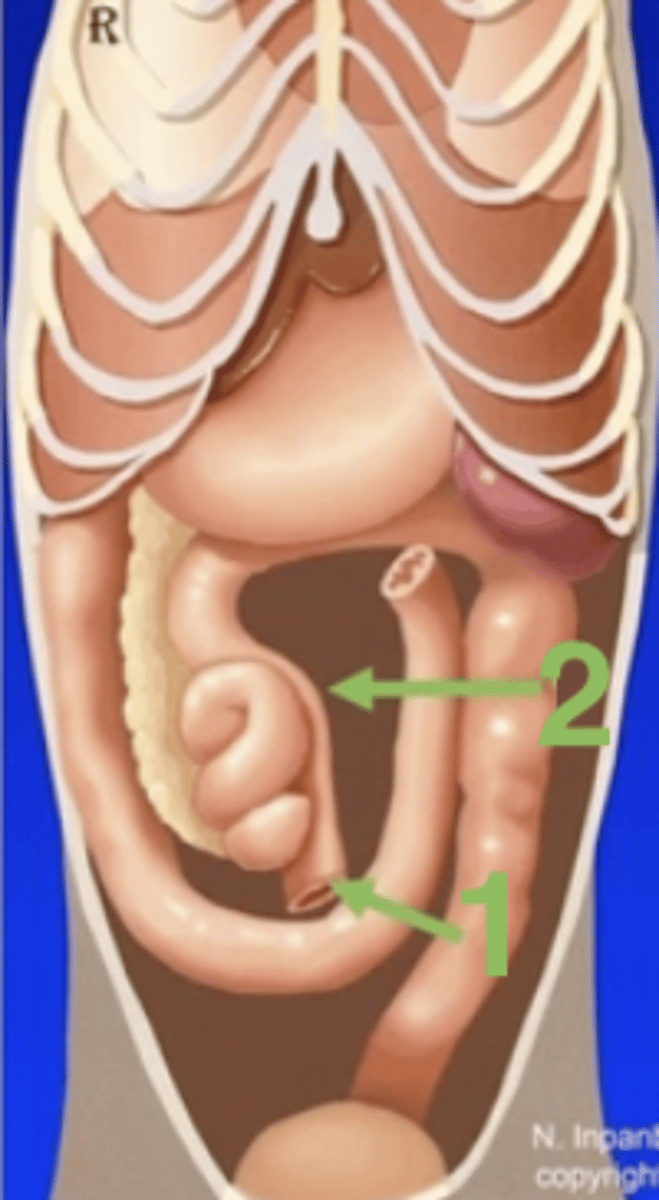
2
ascending colon
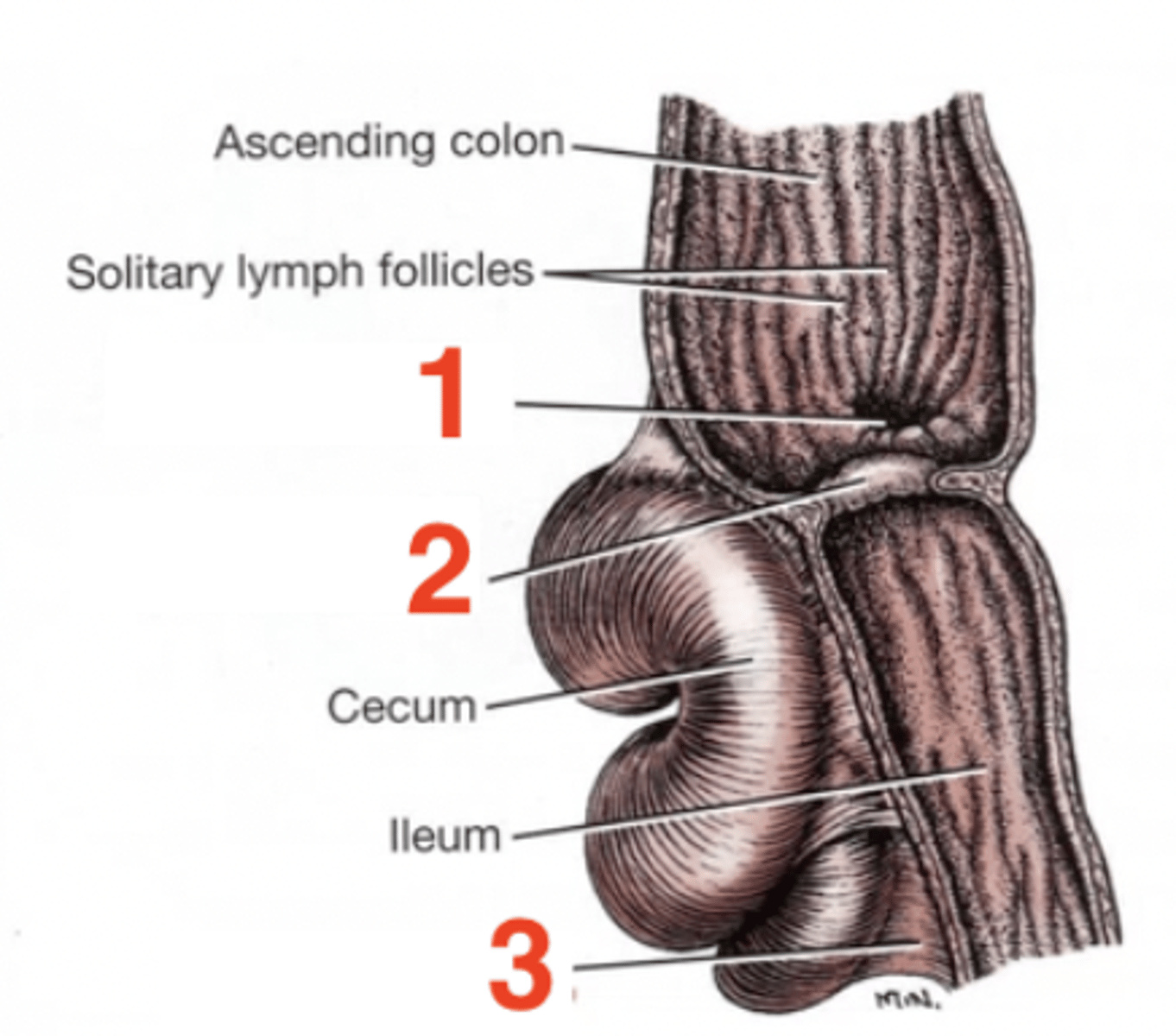
1
cecocolic orifice
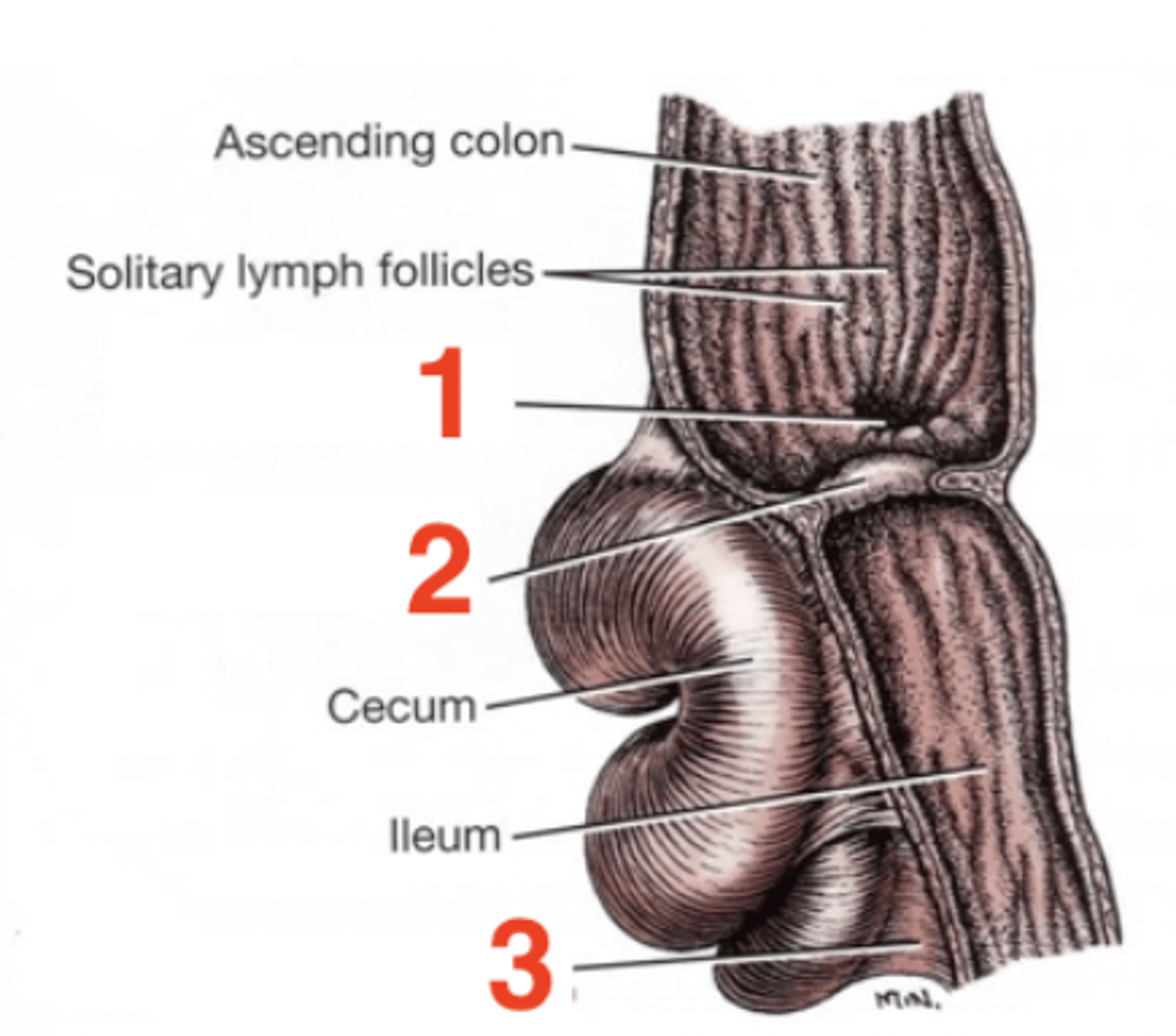
2
ileocolic orifice/ileocolic sphincter
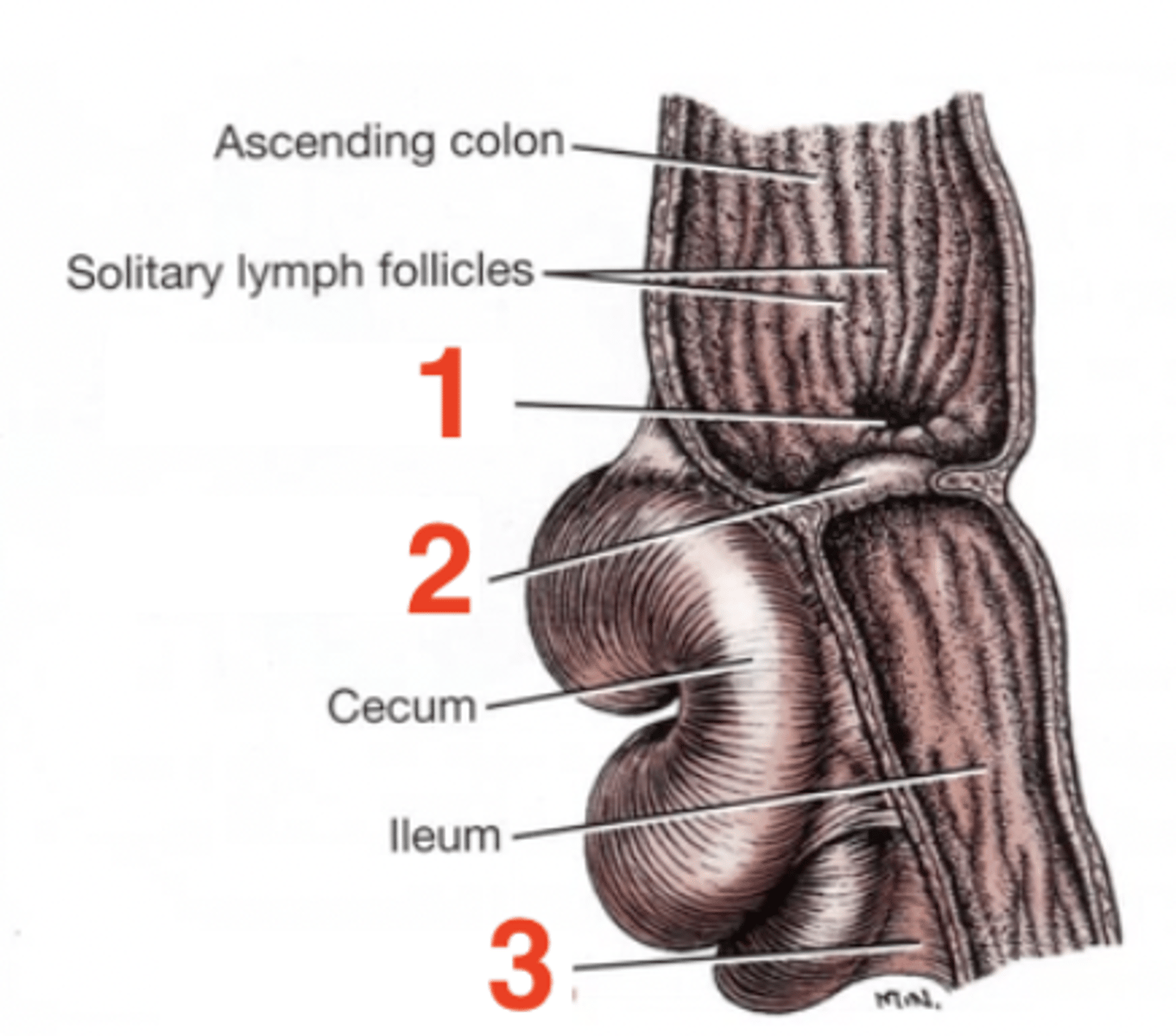
3
ileocecal fold
large intestines
extends from the ileum to the anus
large intestines function
dehydrate fecal contents by absorbing water
three parts of the large intestines
1.) cecum
2.) colon
3.) rectum
cecum
a blind diverticulum at the beginning of the colon
The cecum lies to the ________ of the root of the mesentery
right
What shape is the cecum in the dog?
"S" shaped
What shape is the cecum in the cat?
“comma” shaped
Two features of the cecum:
1.) cecocolic orifice
2.) cecocolic sphincter
cecocolic orifice
where the cecum communicates with the ascending colon
the cecocolic orifice is adjacent to the __________ orifice
ileocolic
cecocolic sphincter
regulates the passage of contents through the cecocolic orifice
The cecum in the cat can be palpated at the level of which vertebra?
4th vertebra
Colon
slightly wider section than the small intestine; located after the cecum
The colon is located _________ in the abdomen
dorsally
The colon is suspended by __________
mesocolon
The colon is divided into three parts:
1.) ascending colon
2.) transverse colon
3.) descending colon
Ascending colon location
to the right of the root of the mesentery
right colic flexure
bend between the ascending and transverse colon
Transverse colon location
lies cranial to the root of the mesentery