intro to inorganic chem
1/19
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
20 Terms
Define inorganic chem and what’s its importance in life? What other chem branches does it link to?
It deals with the study or inorganic and organometallic compounds and focused on properties and behaviours of them. Its the chemistry that isn’t carbon bases/ study of materials not carbon based.
Importance in life:
essential for various biological processes
Enables development of new materials
Crucial for energy production
Links to:
organic
Physical
Biological
Analytical
What are the applications of inorganic chemistry in chemical industry? What other applications does it have e.g drugs, diagnostic tools?
Chemical industry: catalysis, materials science, pigments, surfactants, coating, pharmaceuticals, fuels, agriculture
used in development of metal based drugs such as anticancer agents (cisplatin) rheumatoid arthritis treatments e.g gold compounds
Diagnostic tools like radio-pharmaceuticals. Key role in drug formulation inc. excipients, pH regulations e.g antacids
Application in chelation therapy to remove toxic metals from body
Whats an atom?
matter is anything that takes up space and has mas
All matter made of atoms
Atoms are building blocks of matter
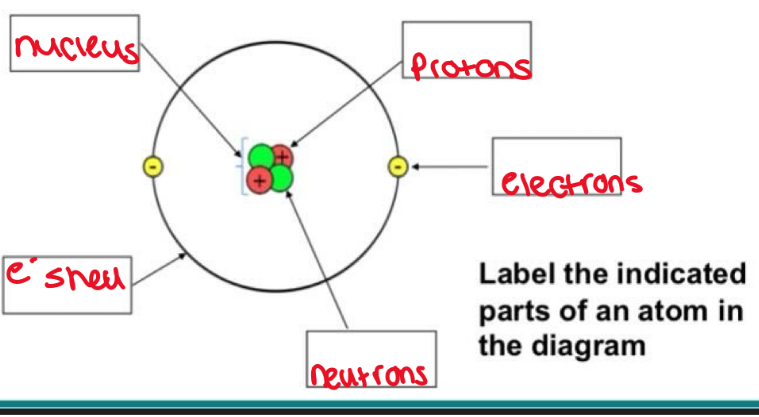
What are the sub atomic particles in atomic structure?
Protons - have positive charge and contribute to atoms mass
Neutrons - have no charge (neutral) and contribute to atoms mass
Electrons - negatively charged particles. Have very small mass compared to protons and neutrons
Label the parts
How does atomic size change down the group?
Atomic size increases down group as adding energy levels
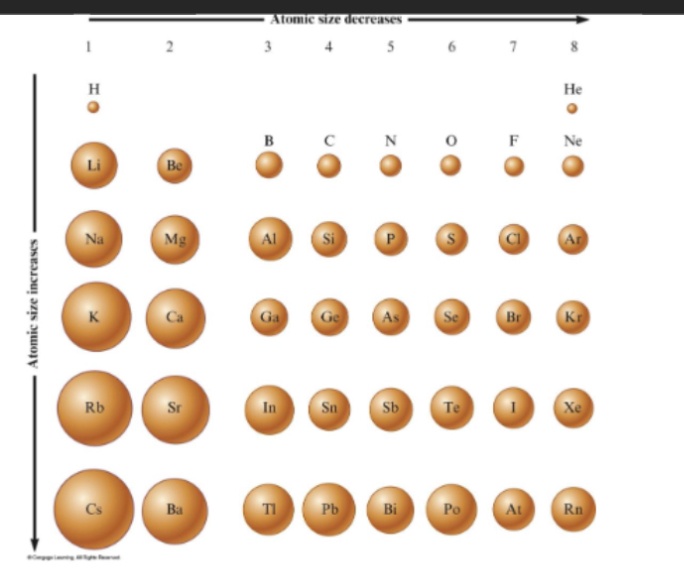
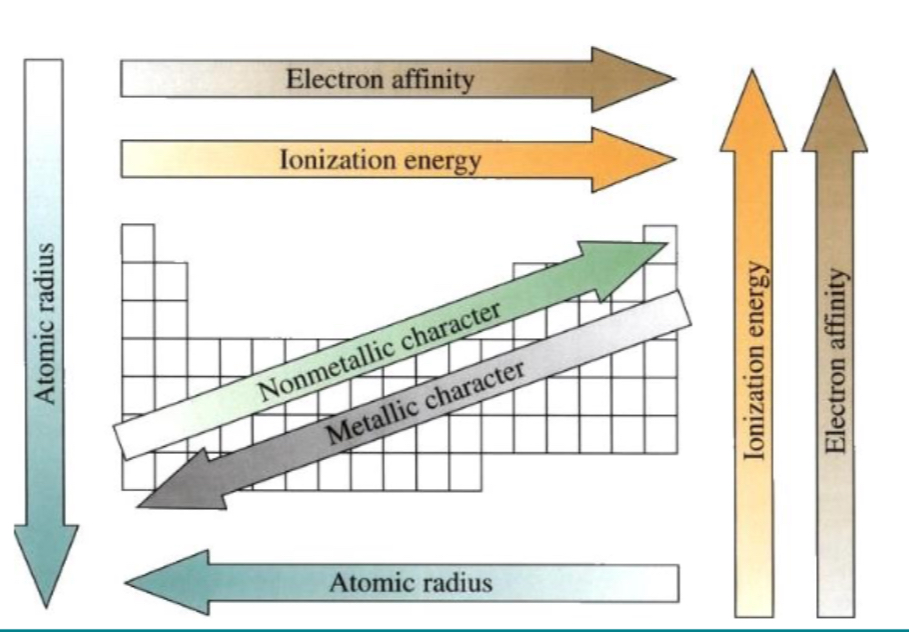
Whats atomic radius, ionisation energy, electronegativity, electron affinity, metallic character?
atomic radius = size of atom changes across periods and down group
Ionisation energy = energy required to remove e- from gaseous atom
Electronegativity = atoms ability to attract e- in chemical bond
Electron affinity = energy change when e- added to neutral atom
Metallic character = tendency of element to lose e- and form positive ions
What happens as you go across the period L-R?
Ionisation energy increase
Electron affinity increases
Non metallic character increases
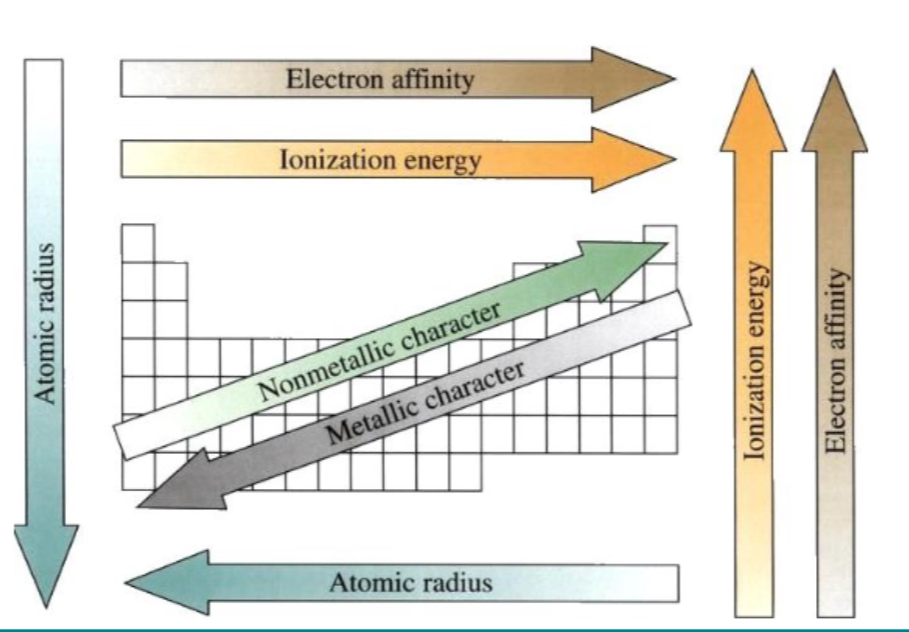
What happens as you go down the group?
Atomic radius decreases
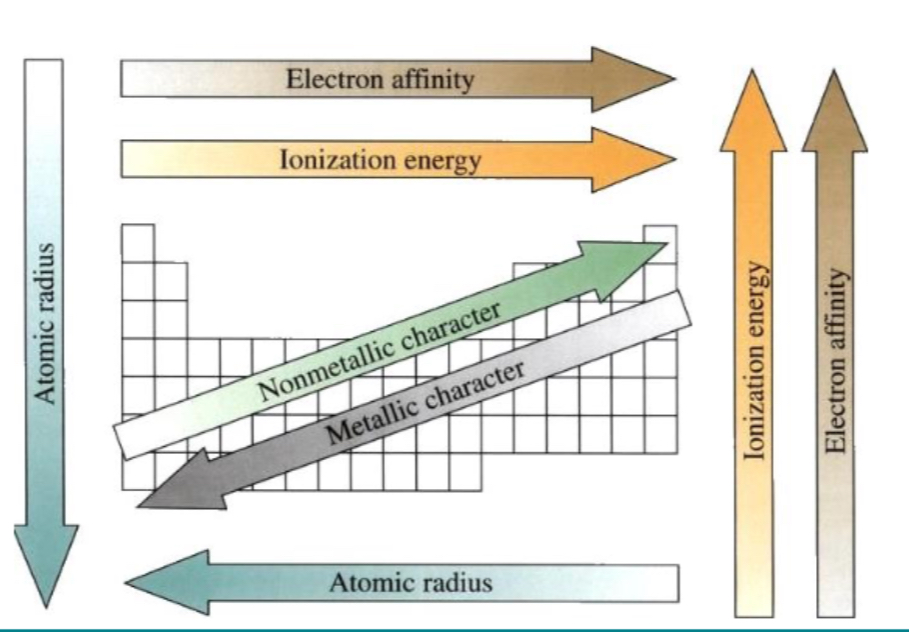
What happens as you go up group?
Ionisation energy increase
Electron affinity increases
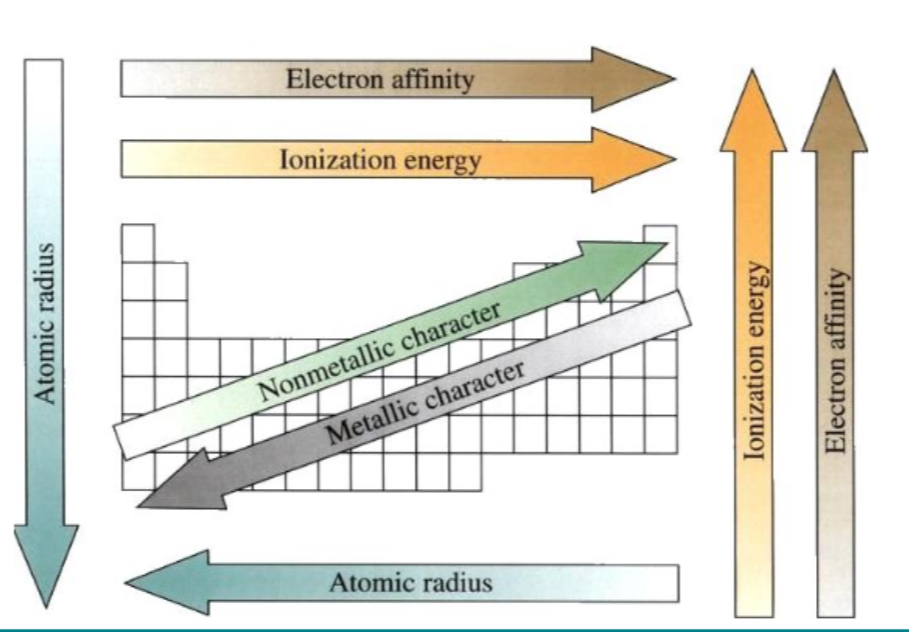
What happens as you go across period R-L?
Atomic radius increase
Metallic character increase
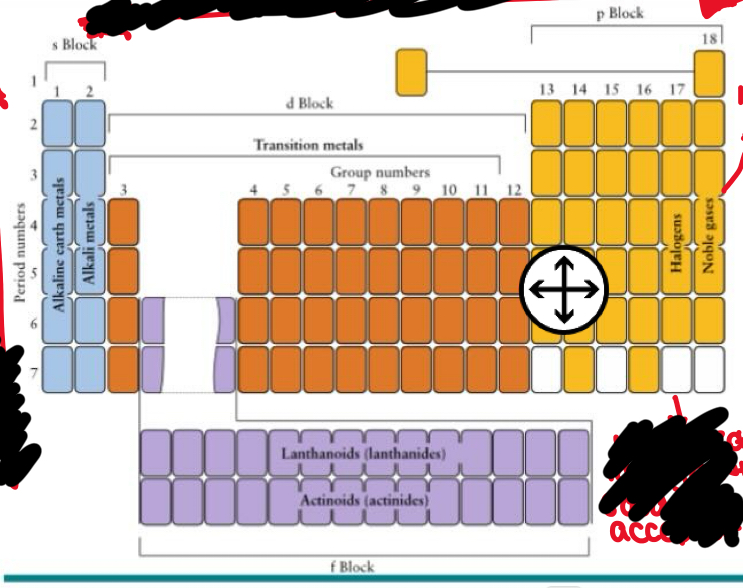
Name what each group is called in period table
Alkali metals
Alkaline earth metals
3-12 transition metal
5 - pnictogens
6 - chalcogens
7- halogens - high electronegativity good e- acceptor
8 - noble gases -inert
Bottom 2: lanthanides then actinides
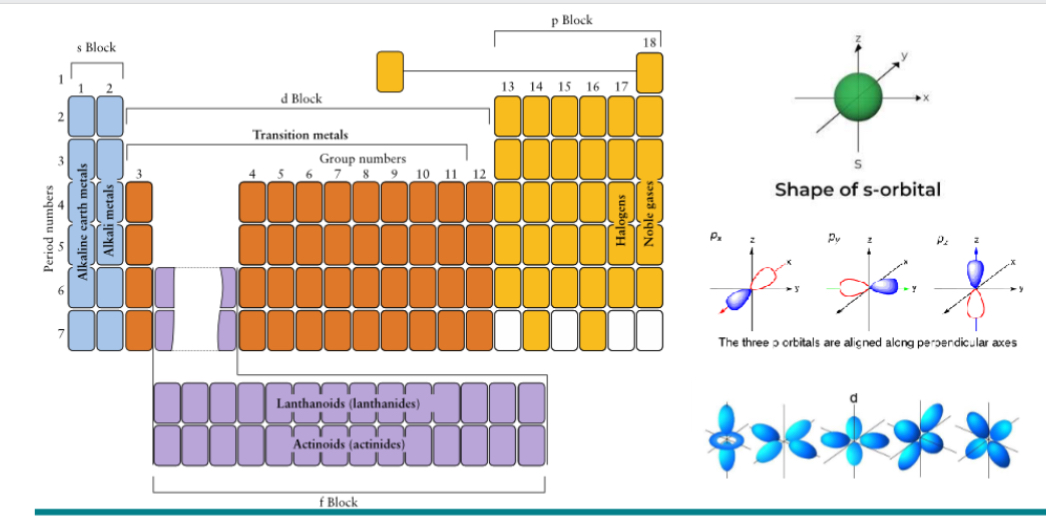
What are the 2 orbitals?
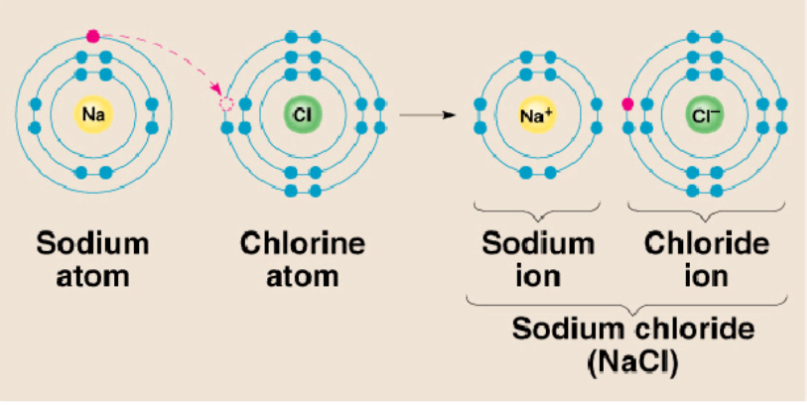
Whats ionic bonding? Give example and how it works in NaCl
Between atom of metal and non metal w/ different electronegative
Bond formed by transfer of e-
Examples: NaCl, CaCl2, K2O
Bonding in NaCl - involves Na e- transfer to Cl, causes charge imbalance in each atom, na becomes Na+ and Cl becomes Cl- charges particle or ion
What’s covalent bonding? Examples? Describe in Cl2
Between non metallic elements of similar electronegativity
Formed by sharing e- pairs
Eg. O2, CO2, C2H6, H2O, SiC
Bonding in Cl2: octet (max 8e-) achieved by each atom sharing e- pair in middle

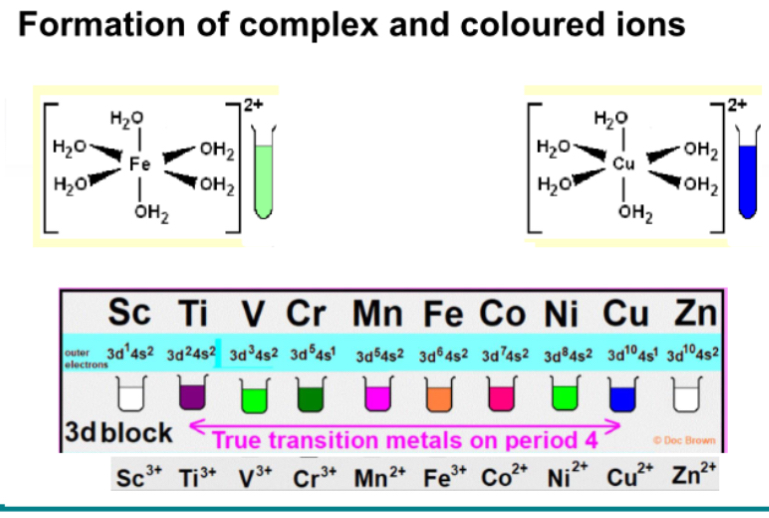
Whats a transition metal? Are all D block elements transition metals?
Also called D block elements - its elements with a partially filled d orbital
However not all D block elements are transition metals as some metals have a full d orbital
Characteristic properties of transition metals
variable oxidation states
Formation of complex ions
Catalytic behaviour
Magnetic properties
Coloured complexes - colour based on vacancy of d orbital
Uses of transition metals
iron for steel
Copper for wiring and pipes
Titanium for paint
Silver for photographic paper
Platinum for catalysts
Transition metal applications - drugs, diagnosis, materials?
metal based drugs - used to develop therapies for cancer, interactions and neurological disorders. Platinum complexes such as cisplatin for anticancer treatment
Diagnostic imaging -applied in contrast agents and radio pharmaceuticals - MRI contrast agents
Drug delivery - serve as barriers to enhance targeted delivery of therapeutics
Materials science application - important in detail implants and tissue engineering
Unique properties - ability to form stable bonds w/ biomolecules. Enable targeted interaction, diverse mechanism of action ad customisable drug design
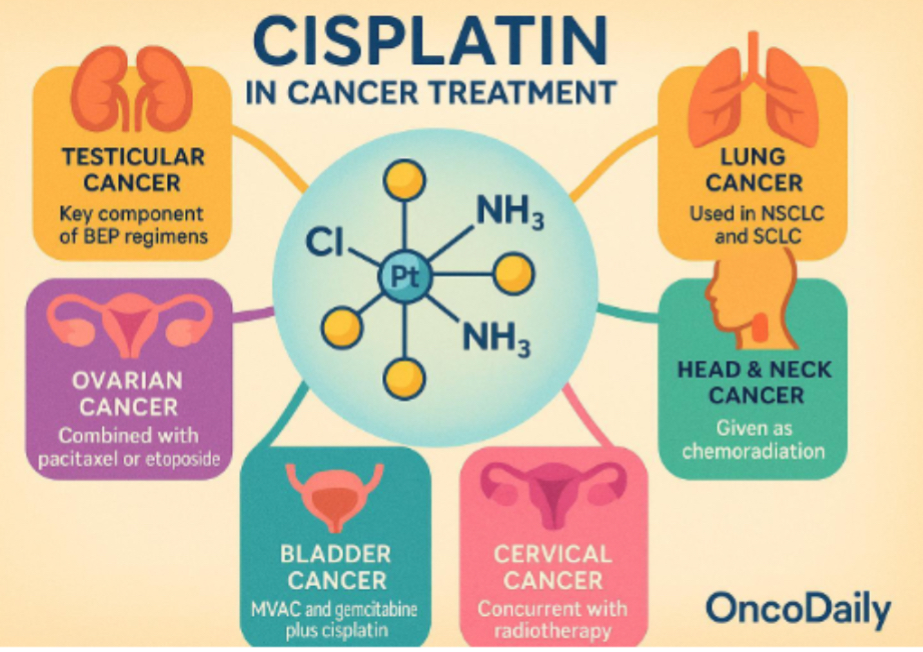
Clinical application of cisplatin in cancer therapy. How’s its dna unique? What cancers does it treat?
cisplatin discovered in 1960s and approved for clinical use in 1970
One of Most widely used platinum based chemotherapeutic agents
Unique DNA damaging mechanism makes it cornerstone in cancer therapy
Effectively treated solid tumours
Despite newer agents being developed, cisplatin remained essential in oncology
Continues to be included in standard of care protocols recommended by major oncology guidelines
Cancer research use platinum metallodrugs and it leads to apoptosis in cancer cells