Excitable Tissues: Muscle Physiology
1/43
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
44 Terms
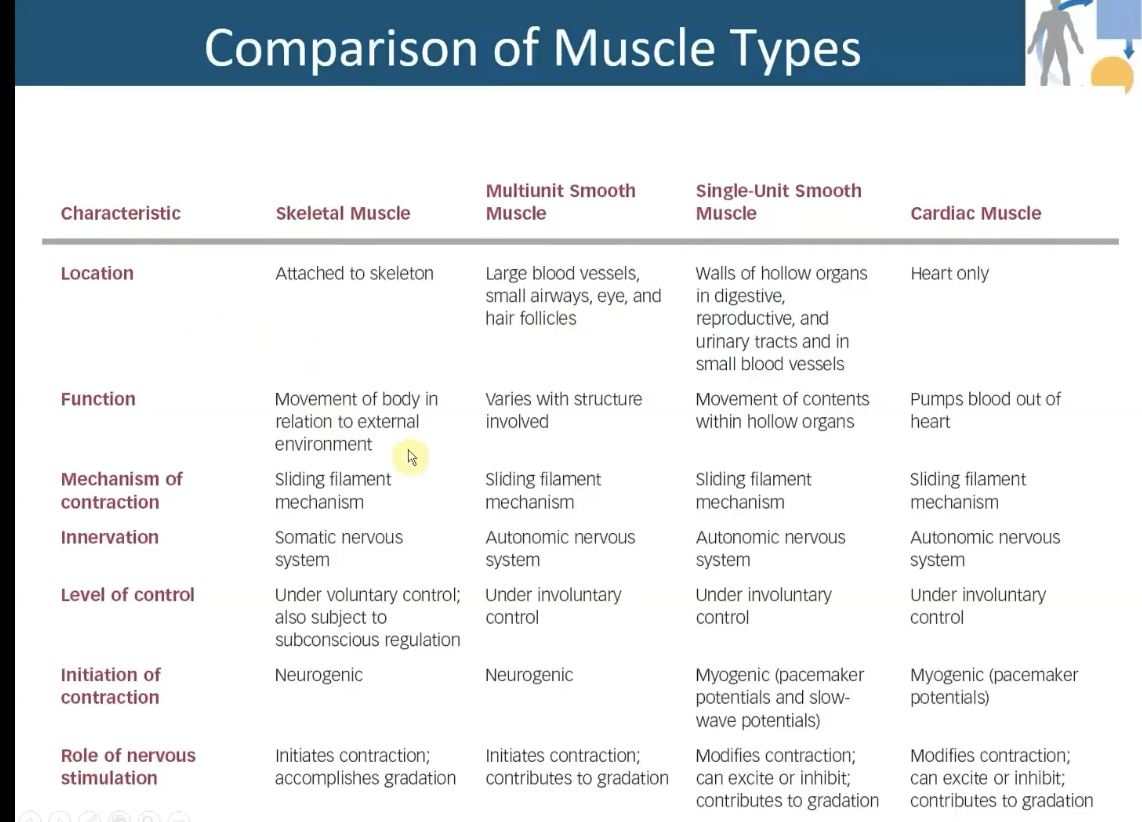
Skeletal Muscles
-Contract and allow body to perform variety of movements
-Striated
Cardiac Muscle
-Striated
-Contracts to generate pressure and move blood through vascular system
Smooth muscle
-Unstriated
-Found in walls of hollow organs and tubes
Regulates: Movement of blood; food; air; and urine out
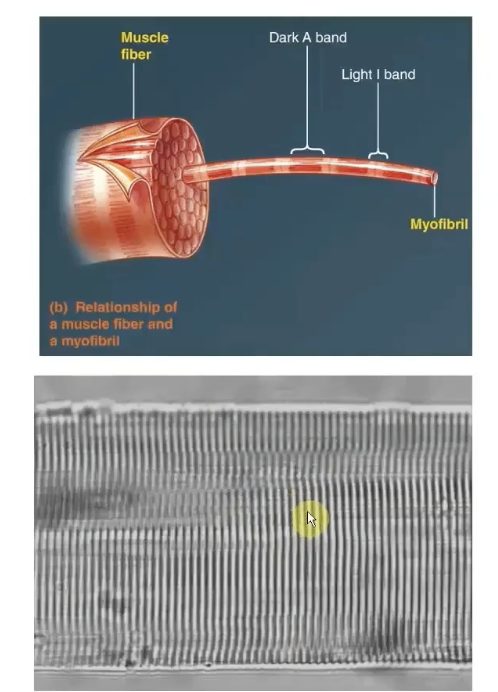
Muscle Fiber
-Single skeletal muscle cell
-Large, elongated, and cylindrical
skeletal muscle structure
microfilaments - made up of thick & thin filaments
thin=actin
thick=myosin
microfilaments → myofibrils → muscle fibers (endomysium)
→ fascicles (perimysium)
→ muscle bundle (epimysium)
→ muscle tissue
Fascicle
-Bundle of myofibrils held together (by perimysium)
Perimysium
-Outer layer of connective tissue in muscle tissue that surrounds the bundles of muscle fibers (fascicle)
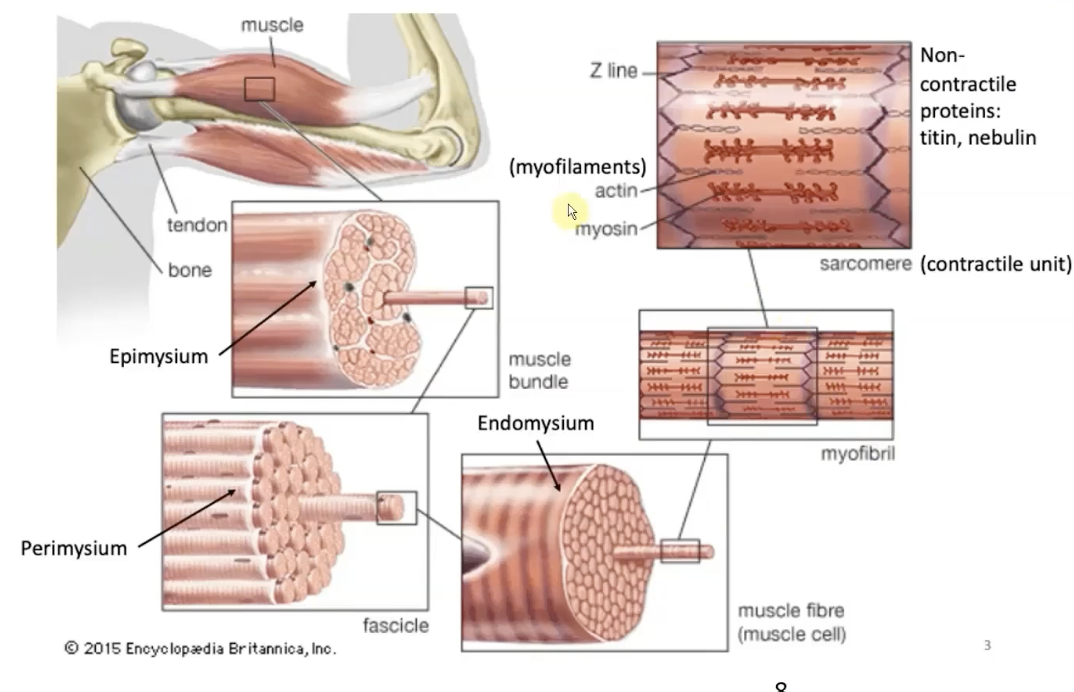
Endomysium
-Connective tissue surround an individual muscle fiber
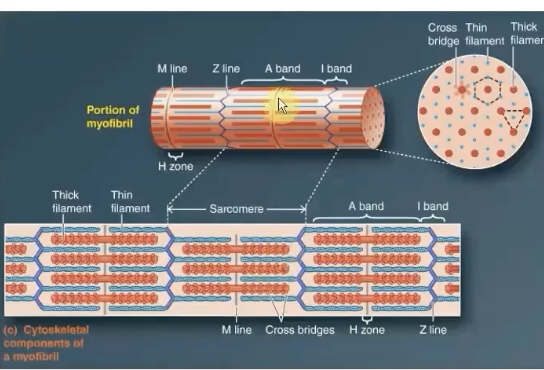
Myofibrils
-Cylindrical intracellular structures 1um in diameter that extend the entire muscle fiber length
-Specialized contractile elements that constitute 80% of muscle fiber volume
-dark A and light I bands are what make up the striations
Non-Contractile Proteins
-Titin
-Nebulin
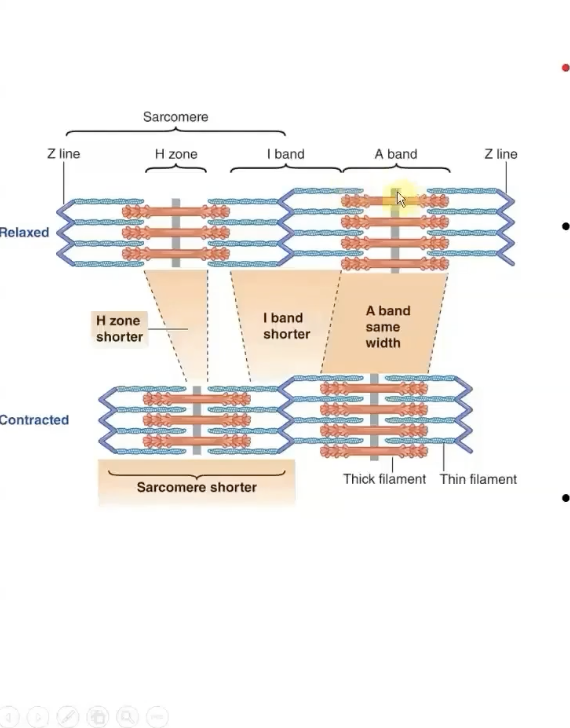
A Band
stacked thick filaments with portions of thin filaments that overlap on both ends of the thick filament
-Thick filaments lie ONLY within this band and extend its entire width
-HAS polarity
H zone
Lighter area in the middle of the A Band where thin filaments do not overlap
this lies in the center of thick filaments (A bands)
M line runs down the middle of it
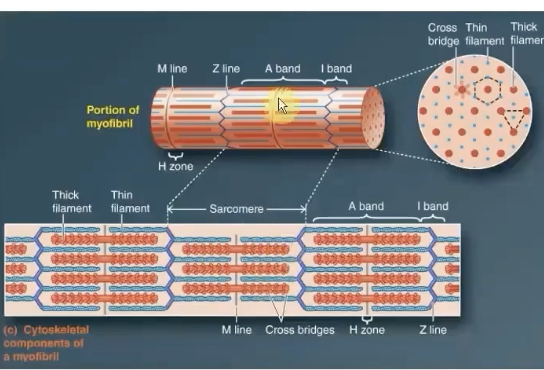
M Line
supporting proteins that hold the thick filaments
it extends down the middle of the A band within the center of the H zone
I Band
-Consists of remaining portion of thin filaments that do NOT projects into the A band
contains the Z line
ONLY thin filaments from two adjacent sarcomeres
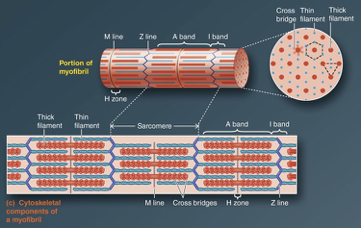
Z Line
middle of i band
flat, cytoskeletal disc that connects the thin filaments of two adjoining sarcomeres
Sarcomere
The area between two Z lines is called a sarcomere, which is the functional unit of skeletal muscle - smallest component of a muscle fiber that can contract
How do muscles grow?
new sarcomeres
Thick Filament Structure
contains many myosin molecules packed together
-Myosin has 2 identical subunits shaped like golf clubs
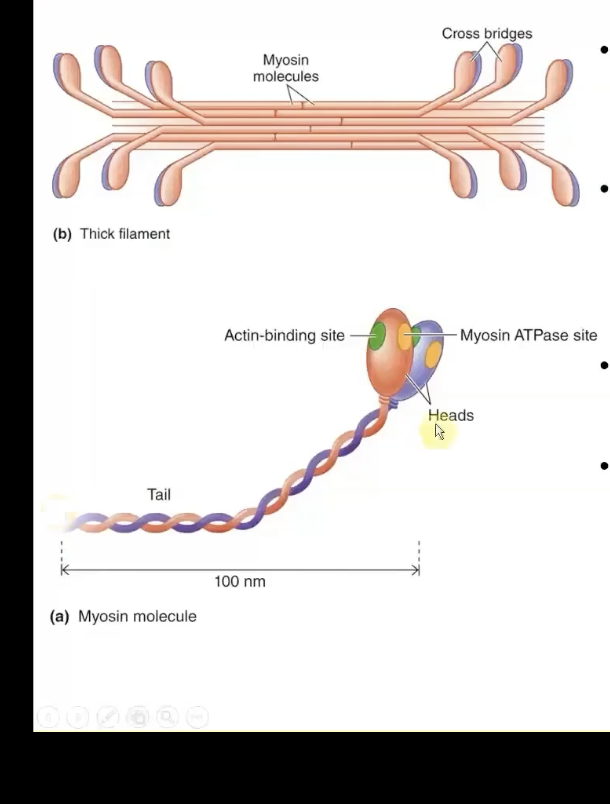
2 Sites for contractile process in Myosin
-Actin-binding site = binds to thin filament
-Myosin ATPase site = atp binds here, bproving energy for myosin
Crossbridges
-Formed from the heads of thick filaments from myosin protein between thick and thin filaments
myosin heads btwn the thick and thin filaments
Thin FIlament Structure
actin, tropomyosin,& troponin
-Actin: spherical, primary structure protein and forms backbone of this filament
-Filament is formed by actin molecules joined into 2 helix strands (String of pearls)
-Each actin molecule has a binding site for attaching with myosin crossbridge
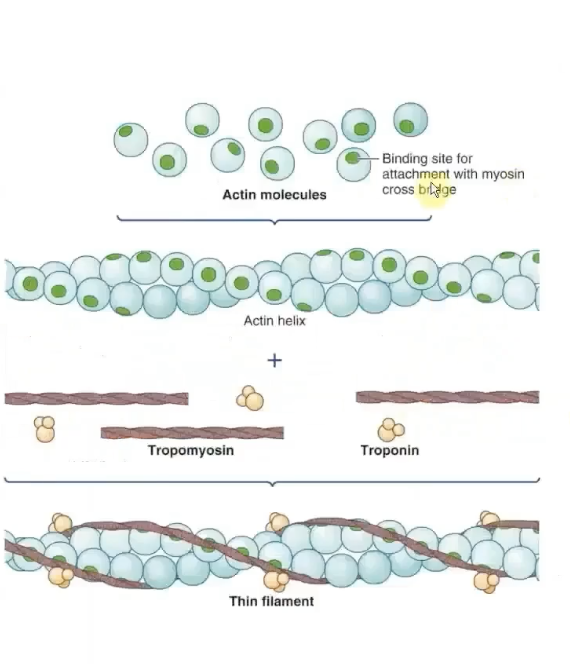
Tropomyosin
-Threadlike proteins that lie end to end alongside the groove of actin spiral
blocks the ability of crossbridges. in relaxed muscle.
regulatory system.
Troponin’s polypeptide units
made up of 3 polypeptide units:
-One binds to tropomyosin (TnT)
-One binds to Actin (TnI) = physcially holds tropomyosin over myosin binding ssites
-One binds with Ca2+ (TnC)
when NOT bound to Ca2+, this protein stabilizes tropomyosin in it's blocking position
Mechanism of Contraction
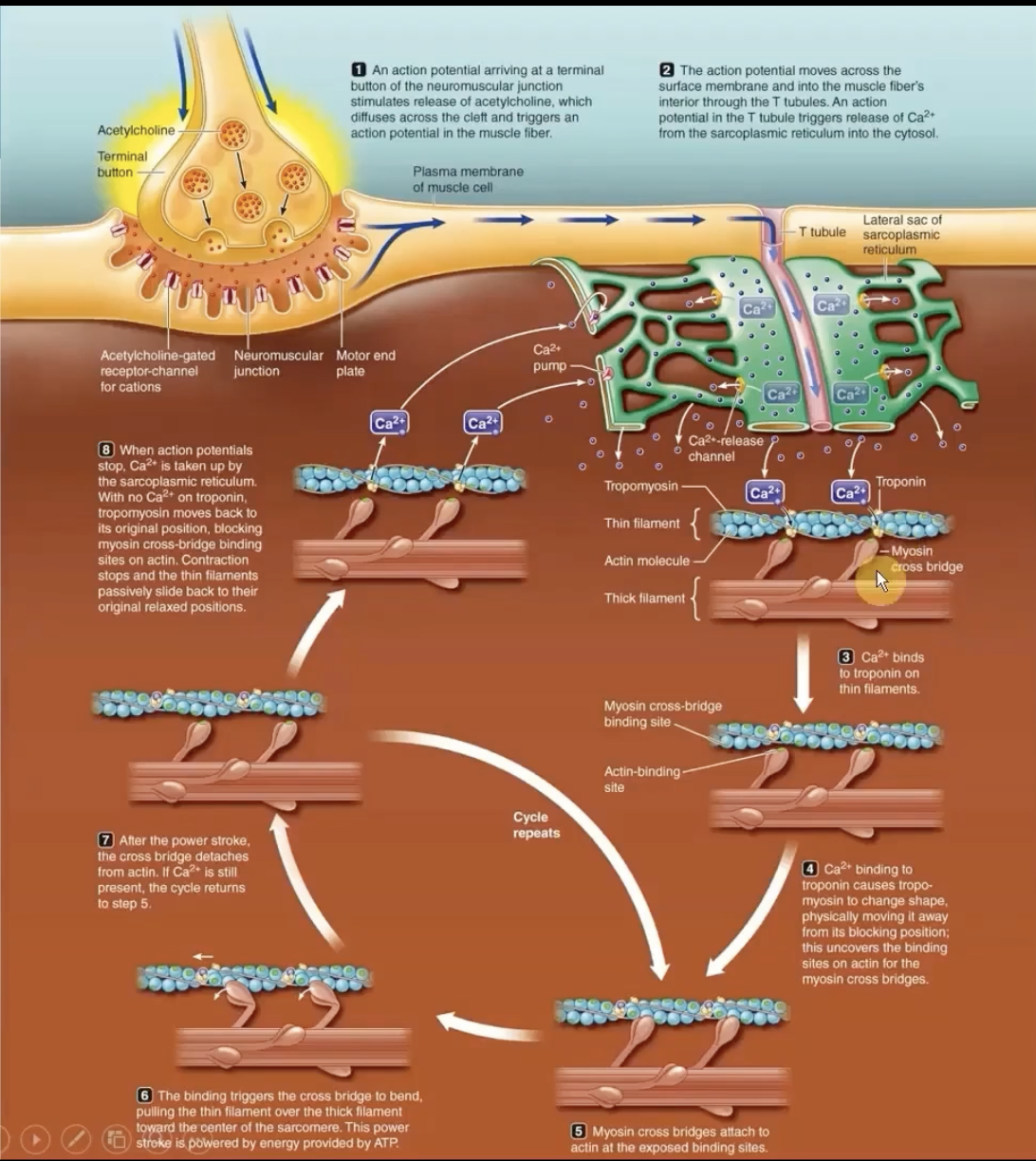
Ca2+ binds to troponin → tropomyosin moves away from its blocking position → actin/myosin allow crossbridge to pull thin filament towards center
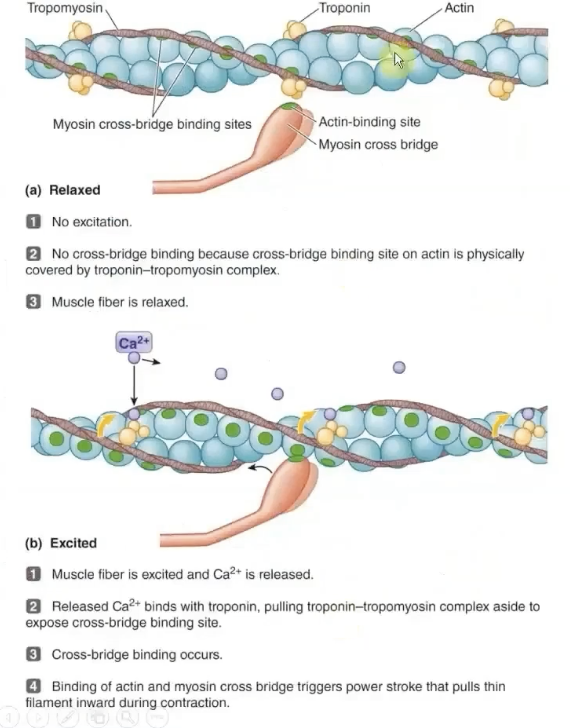
Regulatory Proteins of Muscle Contraction
-Tropomyosin and Troponin
they cover or expose the actin binding sites
Sliding Filament: Muscle contraction
Thin filament on each side of sarcomere slide inward over stationary thick filaments towards the A band's center
As they slide inward, the thin filaments pull the z lines closer so the whole sarcomere shortens
rigor mortis
atp is required to release the crossbridge, if no atp, myosin is just holding on and can’t let go. this leaves the muscles contracted.
Excitation-Contraction Coupling (T Tubule System)
tube system for action potential to travel down sarcoplasmic retirculum.
allows calcium release channels to open and release calcium into the cytoplasm
-Triggers opening of Ca2+ channels from the sarcoplasmic reticulum into the cytosol
-Ca2+ binds to troponin
sarcoplasmic reticulum stores calcium needed for muscle contraction.
T-tubules come into contact with these reticulum.
Length-tension relationship
At a specific "optimal" length, there is maximum overlap between actin and myosin filaments, allowing for the greatest number of cross-bridges to form and producing maximal tension.
When a muscle is shortened beyond its resting length, the actin filaments can overlap each other, and myosin filaments may bump against the Z-disks, limiting further contraction and reducing the force generated.
2 Factors to Accomplish Gradation of whole muscle tension
-Tension developed by each muscle fiber: Length, Stimulation frequency (twitch vs tetanus)
-The number of muscle fibers contracting within a muscle
Muscle twitch
One AP illicits a transient contraction, a muscle twitch
Tetanus
-Muscle is stimulated so rapidly that it does not have a chance to relax
maximum sustained contraction
Muscle Motor Unit
-The greater the number of fibers contracting, the greater the total muscle tension
more muscle fibers=more tension that can generate
A muscle fiber is innervated by ONE motor neuron. motor neuron can innervate multiple muscle fibers. these fibeers are innervated simultaneously = they are a motor unit
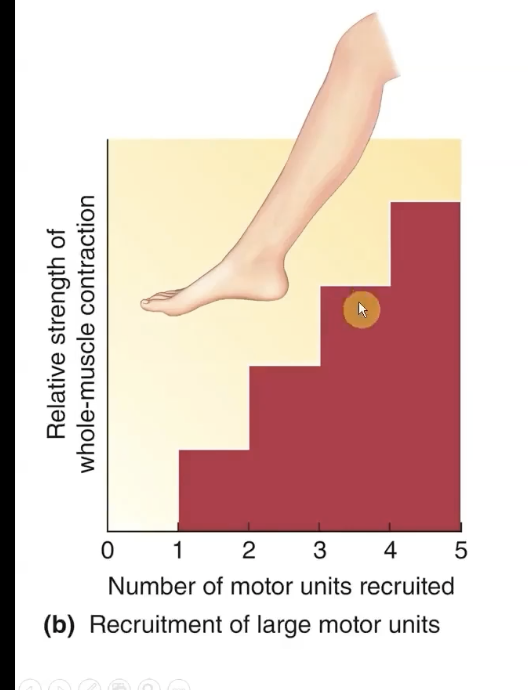
Motor Unit Recruitment
stronger and stronger contractions occur as more and more moto units fire off simultaneously = motor unit recruitment
if u want more force for a contraction, u recruit more motor units
bigger muscles have larger motor units!
Motor units for Muscles for Precise Movement
the more precise of a movement you need in an area, the less motor units there are
Motor units for Muscles of powerful controlled movement
more powerful contractions can happen, but there is going to be much less preciseness.
How does the body prevent fatigue in gravity resistant muscles?
asynchronous motor unit recruitment
shifts from one motor unit to the next to give other units an opportunity to rest
THIS CANNOT HAPPEN DURING MAXIMAL CONTRACTIONS
fatigue-resistant fibers are recruited first by the CNS to lift stuff, but if it is really heavy, then the larger fibers that fatigue quickly join in
Slow-Oxidative Fibers
-Most resistant to fatigue
-Slow contraction
lots of mitochondria
Fast-Oxidative Fibers
-Speed of contraction: Fast
resistance to Fatigue: Intermediate
Fast-glycolytic Fibers
-Speed of contraction: High
-Resistance to fatigue: Low
less mitochondria
Smooth Muscle Mechanism of Contraction
-Crossbridge is similar BUT:
-Activation is different: Myosin phosphorylation
-NO SARCOMERES
-SLOW but LONG lasting contractions (Non fatiguing)
no bare portion in the center of smooth muscle thick filament
E-C Coupling in Smooth Muscle
after topnonin and tropmyosin: what calcium does:
phosphorylation of myosin cross bridges in thick filament,
binding of actin and myosin at cross bridges
ACh is released at variscocities throughout the muscle instead of a NMJ
Excitation
-Rise in Ca2+ from extracellular matrix
-Biochemical events
-Phosphorylation of myosin cross bridges in thick filament
-Binding of actin & myosin at cross bridge
Multiunit Smooth Muscle
Multiple units that function independently of one another and must be separately stimulated by nerves to contract
-All of this type of smooth muscle is Tonic
Contracts only when stimulated by ANS in: Walls of large blood vessels; small airways; ciliary muscles; dilator/radial, constrictor/circular muscles; base of hair follicles (Goosebumps)
Single-unit/Unitary smooth muscle
-Most smooth muscle is this type
-Found in walls of hallow organs
-Contract as a single unit
-Does NOT require nervous stimulation for contraction (Myogenic) no true resting membrane potential
-Higher when muscle is active & lower when muscle is inhibited: Stretch, hormones & ANS input alter level of activation
-Always in a constant state of partial contraction or tone