Unit 5: AP Human Geo. - AGRICULTURE
1/68
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
69 Terms
agriculture
the purposeful tending of crops and livestock in order to produce food and fiber

subsistence agriculture
level of farming in which a person raises only enough food to feed his or her family

First Agricultural Revolution
The period roughly 10,000 years ago during which humans first began domesticating crops and animals

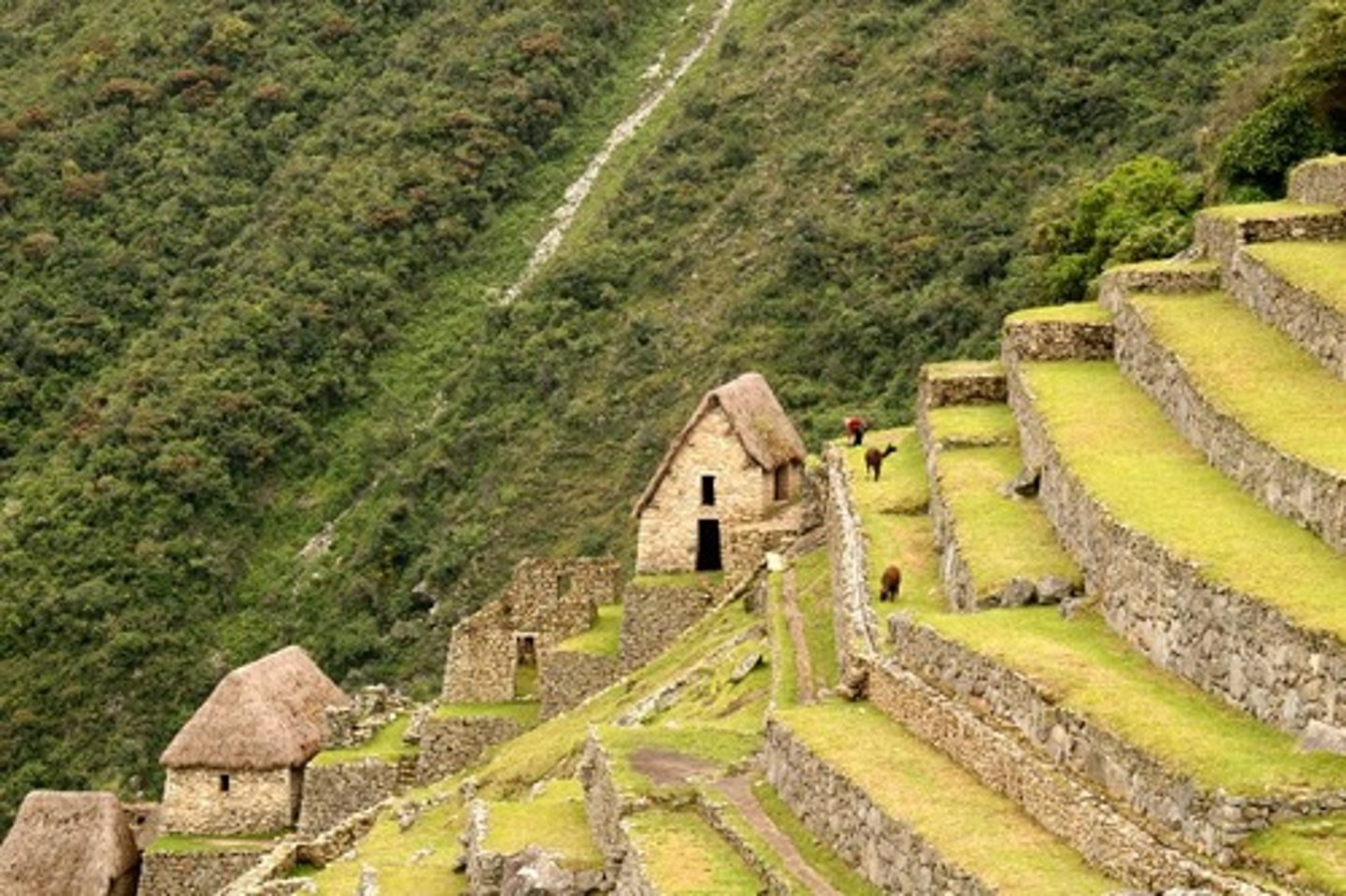
terrace farming
cutting of "steps" into the mountains that allowed for more agriculture

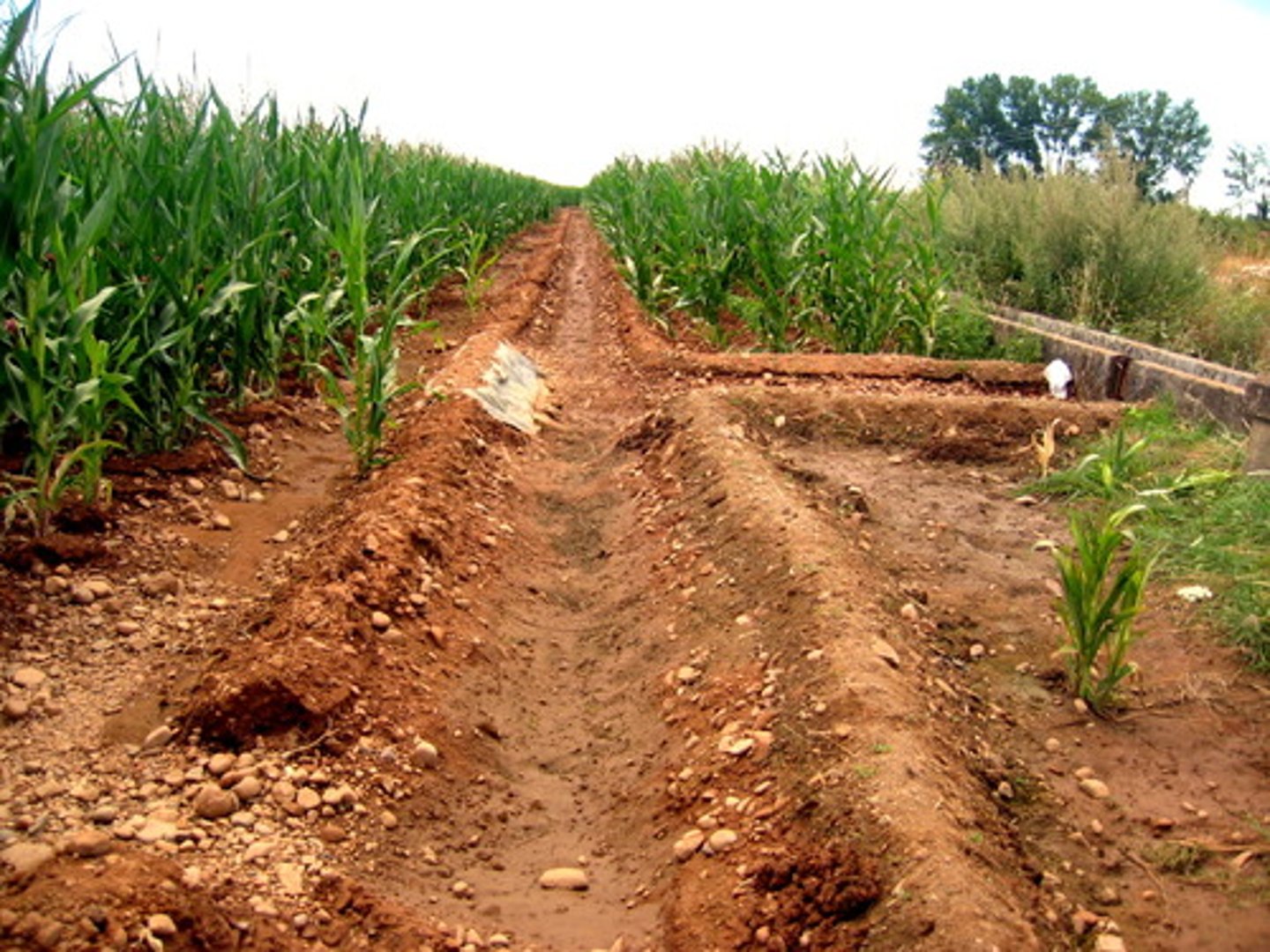
irrigation
a system that supplies dry land with water through ditches, pipes, or streams

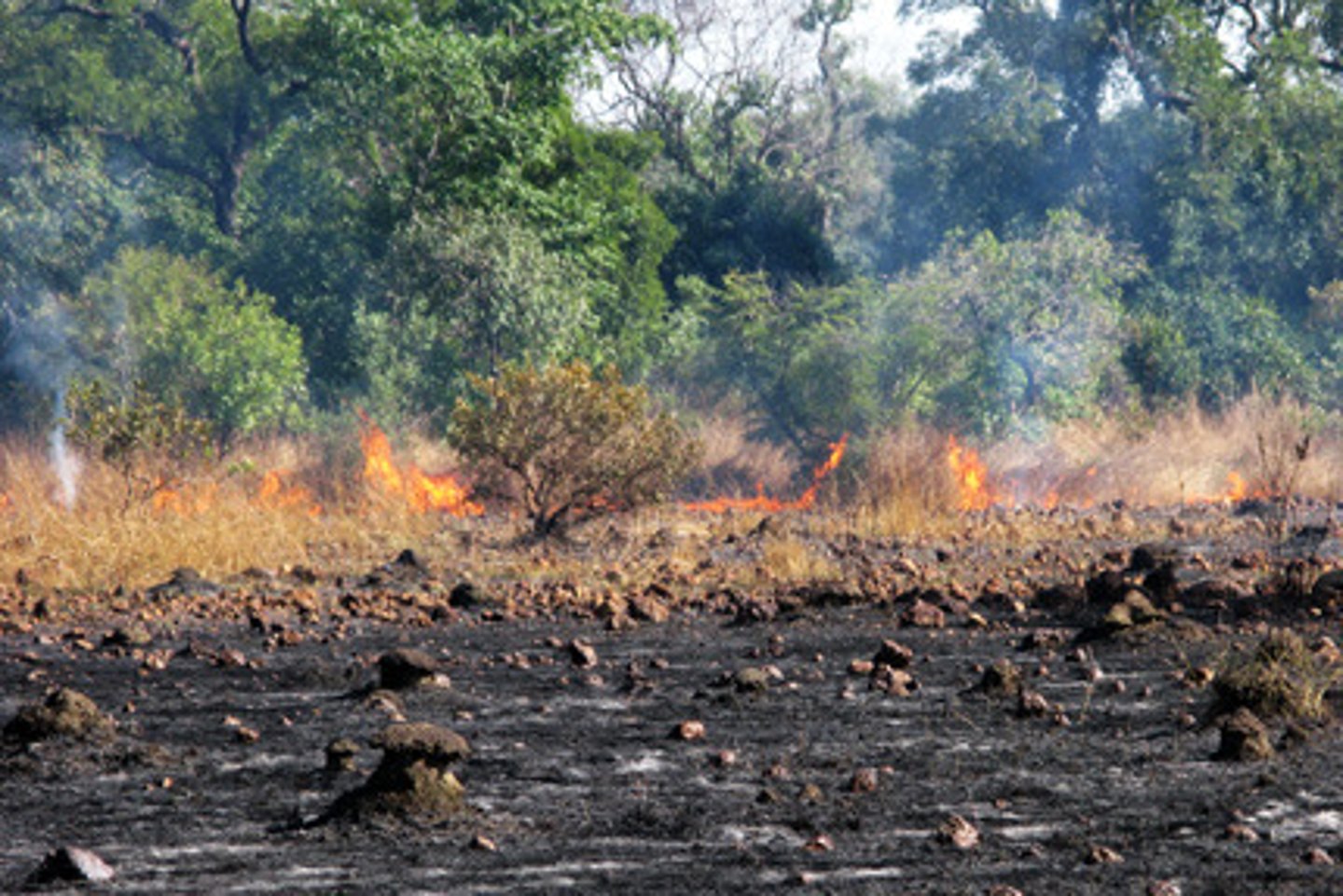
slash-and-burn
a farming technique in which trees are cut down and burned to clear and fertilize the land - associated with Shifting Cultivation

deforestation
the loss or destruction of forests, mainly for logging or farming
barbed wire
used for fencing and invented to keep cattle from trampling crops

Third Agricultural Revolution
'Green Revolution' Rapid diffusion of new agricultural techniques between 1970's and 1980's, especially new high-yield seeds and fertilizers. Has caused agricultural productivity at a global scale to increase faster than population growth.

GMOs
Crops that carry new traits that have been inserted through advanced genetic engineering methods

pastoral nomadism
A form of subsistence agriculture based on herding domesticated animals.

livestock ranching
An extensive commercial agricultural activity that involves the raising of livestock over vast geographic spaces typically located in semi-arid climates like the American West.

plantation farms
an estate where cash crops are grown on a large scale (especially in tropical areas)

truck farming
AKA - Commercial gardening and fruit farming, so named because truck was a Middle English word meaning bartering or the exchange of commodities.

milk shed
the circle around a dairy farm in which its products can be sold without spoiling

winter wheat
Kansas, Colorado, Oklahoma, a crop planted in fall and develops strong roots to survive the winter

spring wheat
a wheat crop that is planted in the spring and harvested in late summer
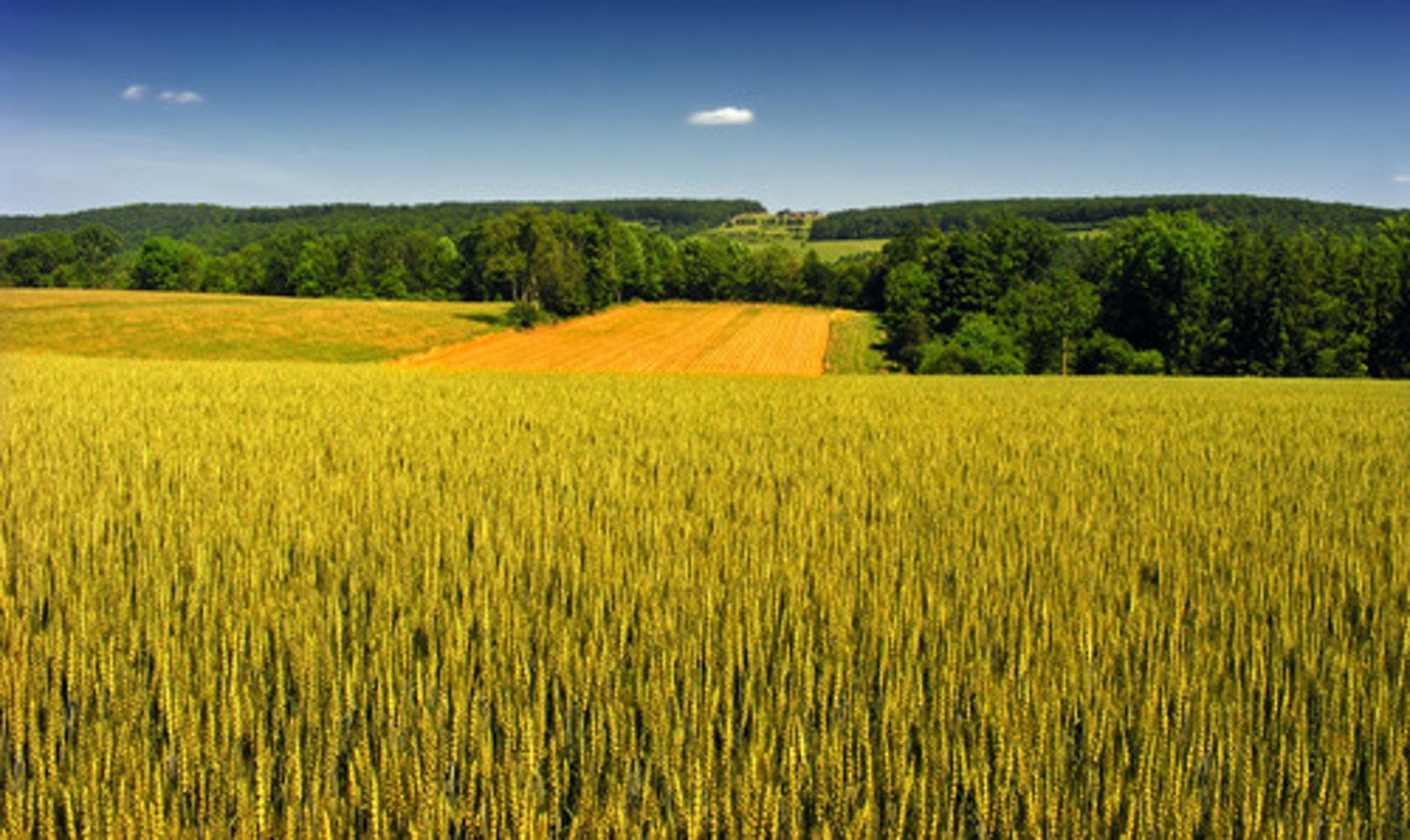

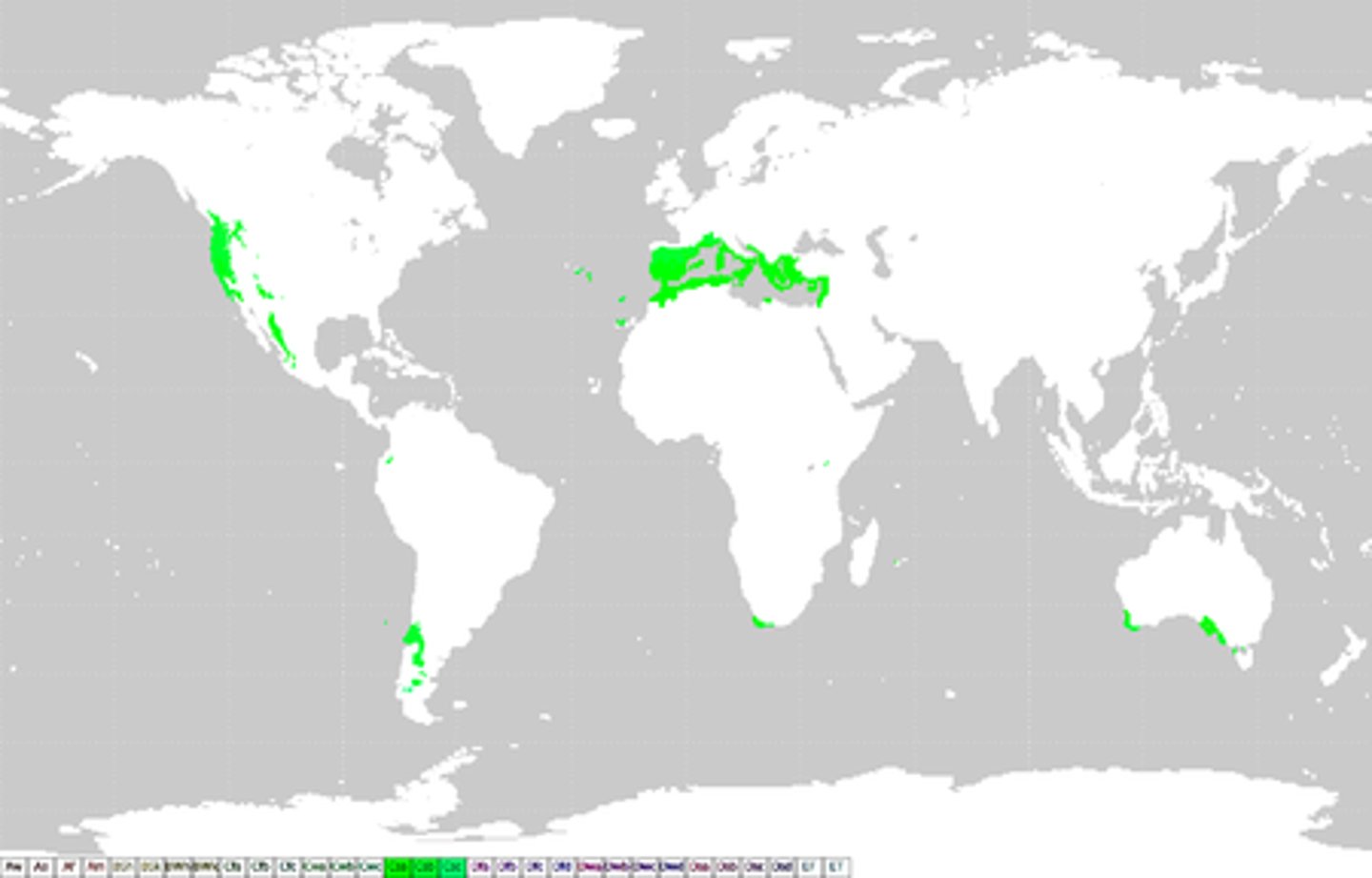
Mediterranean Agriculture
Specialized farming that occurs only in areas where the dry-summer Mediterranean climate prevails. Olives, olive oils, grapes, wheat, and tomatoes.
double-cropping
to plant and harvest on the same parcel of land twice per year
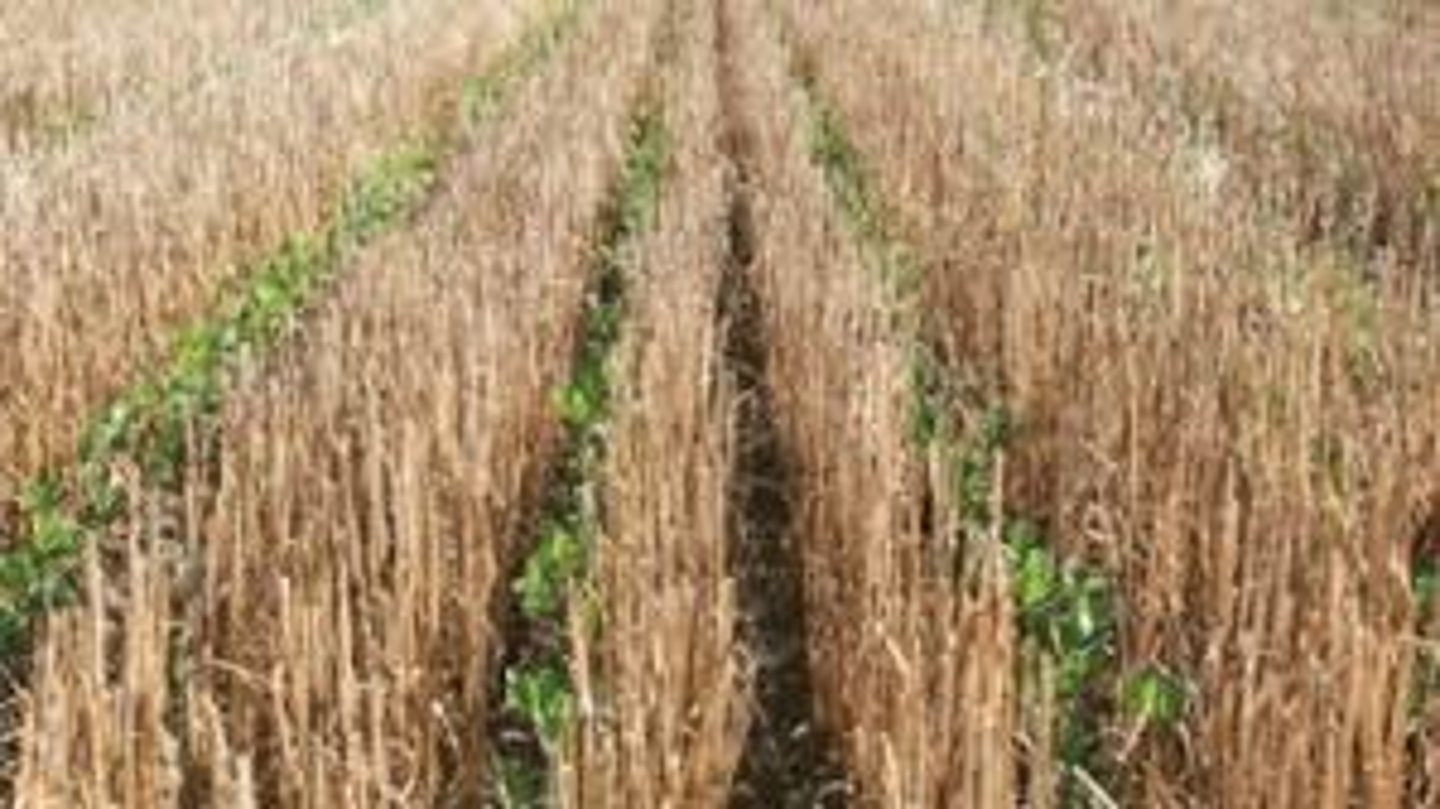

supply chain
the group of firms that make and deliver a given set of goods and services
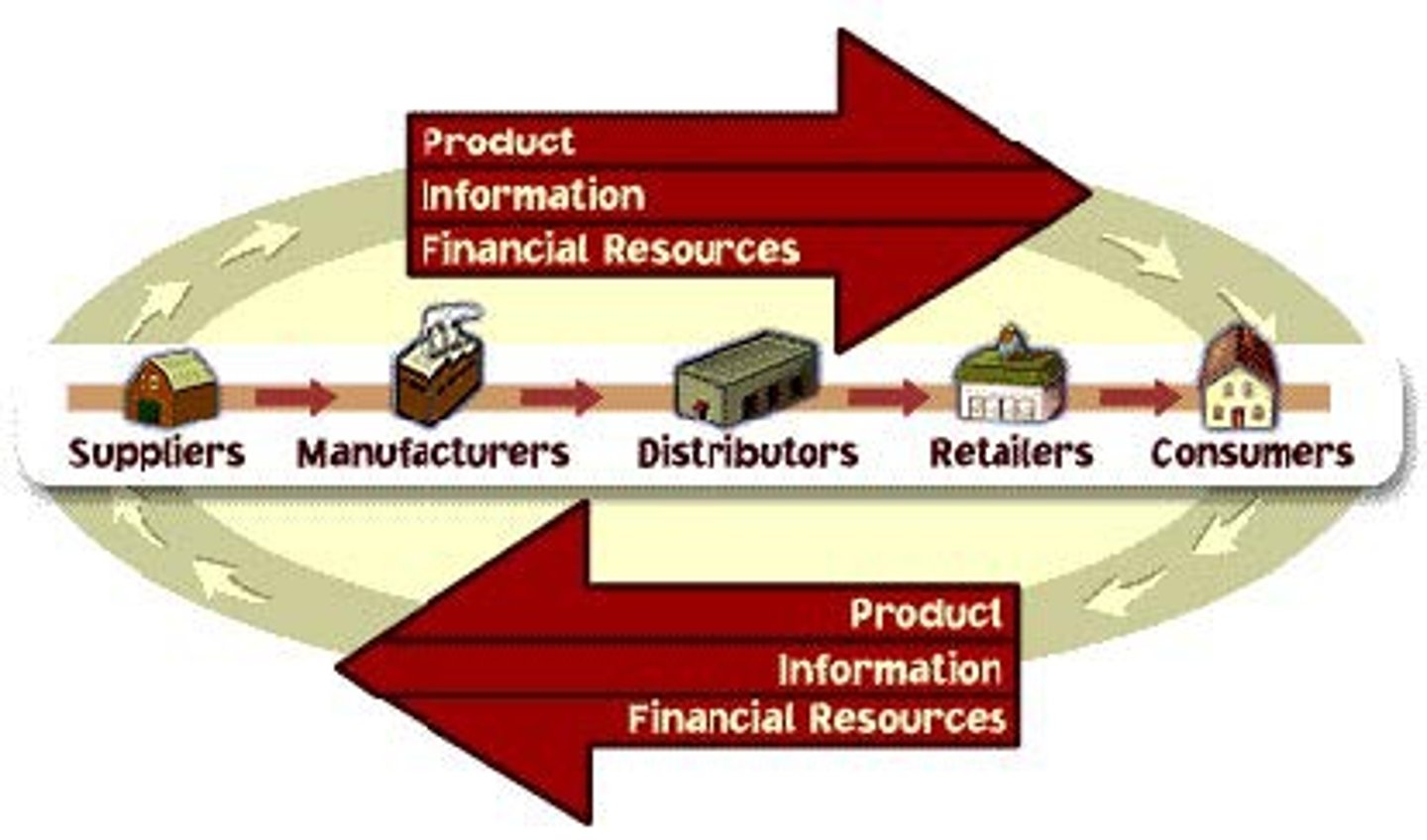
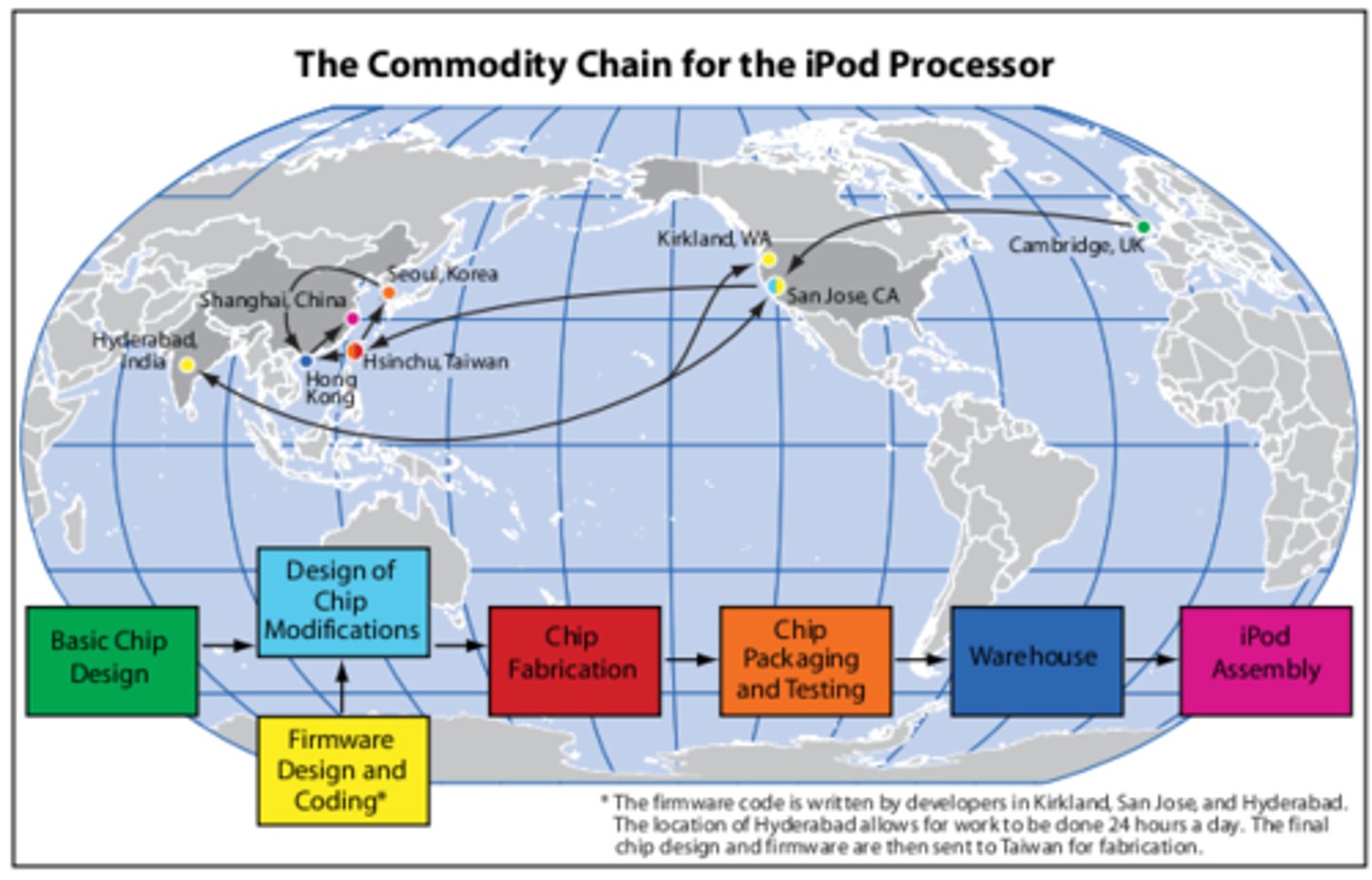
commodity chain
A chain of activities from the manufacturing to the distribution of a product
monoculture
farming strategy of planting a single, highly productive crop year after year

suitcase farm
In American commercial grain agriculture, a farm on which no one lives; planting and harvesting is done by hired migratory crews.

luxury crops
Non-subsistence crops such as tea, cacao, coffee, and tobacco

fair trade movement
an alternative method of international trade which promotes environmentalism, fair wages, alleviation of global poverty and a fair price for growers

subsidy
a sum of money granted by the government or a public body to assist an industry or business so that the price of a commodity or service may remain low or competitive.

infrastructure
the basic facilities that are necessary for a society to function and grow - roads, government buildings, electricity lines, railroads

dispersed settlements
A rural settlement pattern characterized by isolated farms rather than clustered villages.

French long-lot system
Linear settlements stretched out along a road or river.
von Thunen model
A model that explains the location of agricultureal activities in a commercial, profit-making economy. A process of spatial competition allocates various farming activities into rings around a central market city, with profit-earning capability the determining force in how far a crop locates from the market
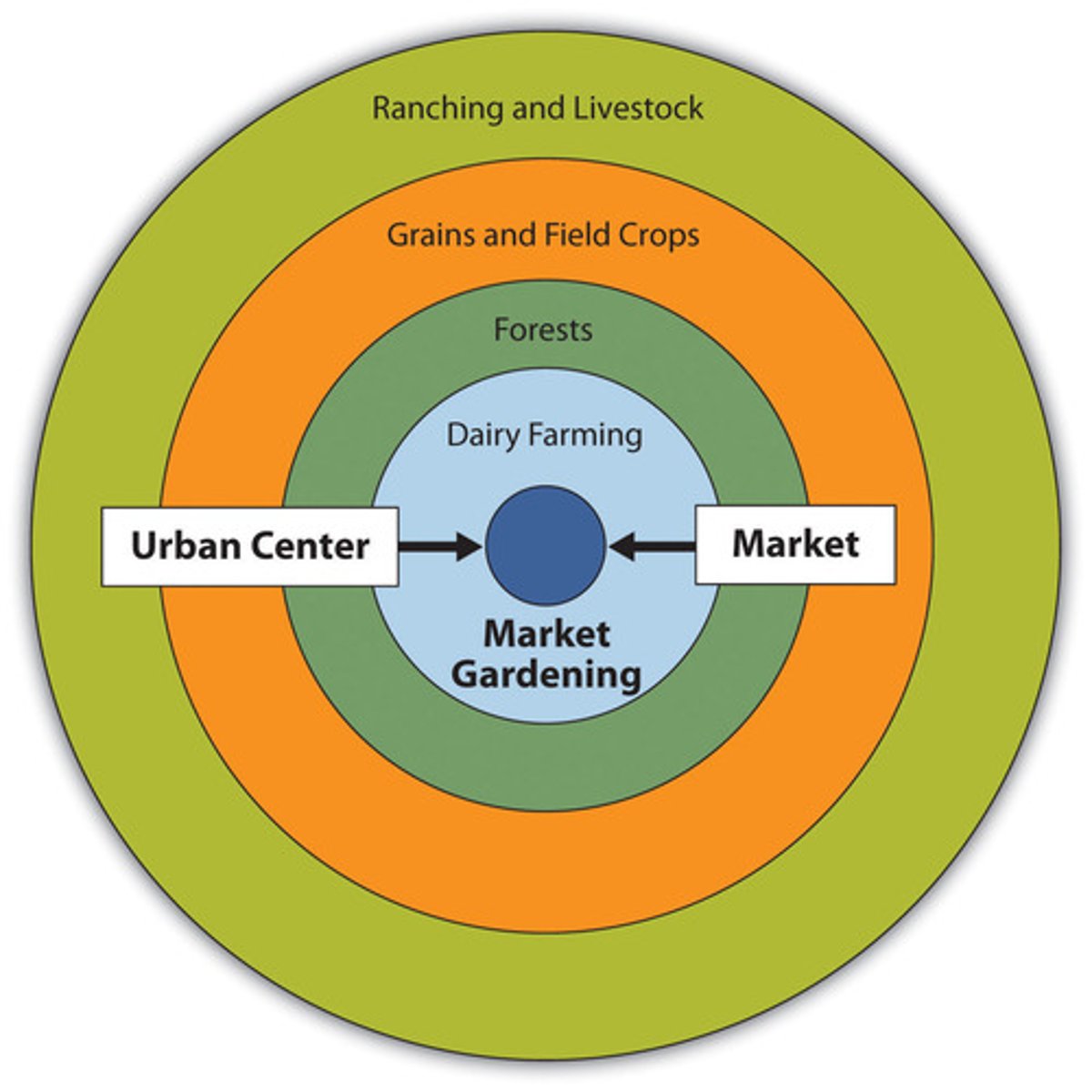
horticulture
The growing of fruits, vegetables, and flowers.

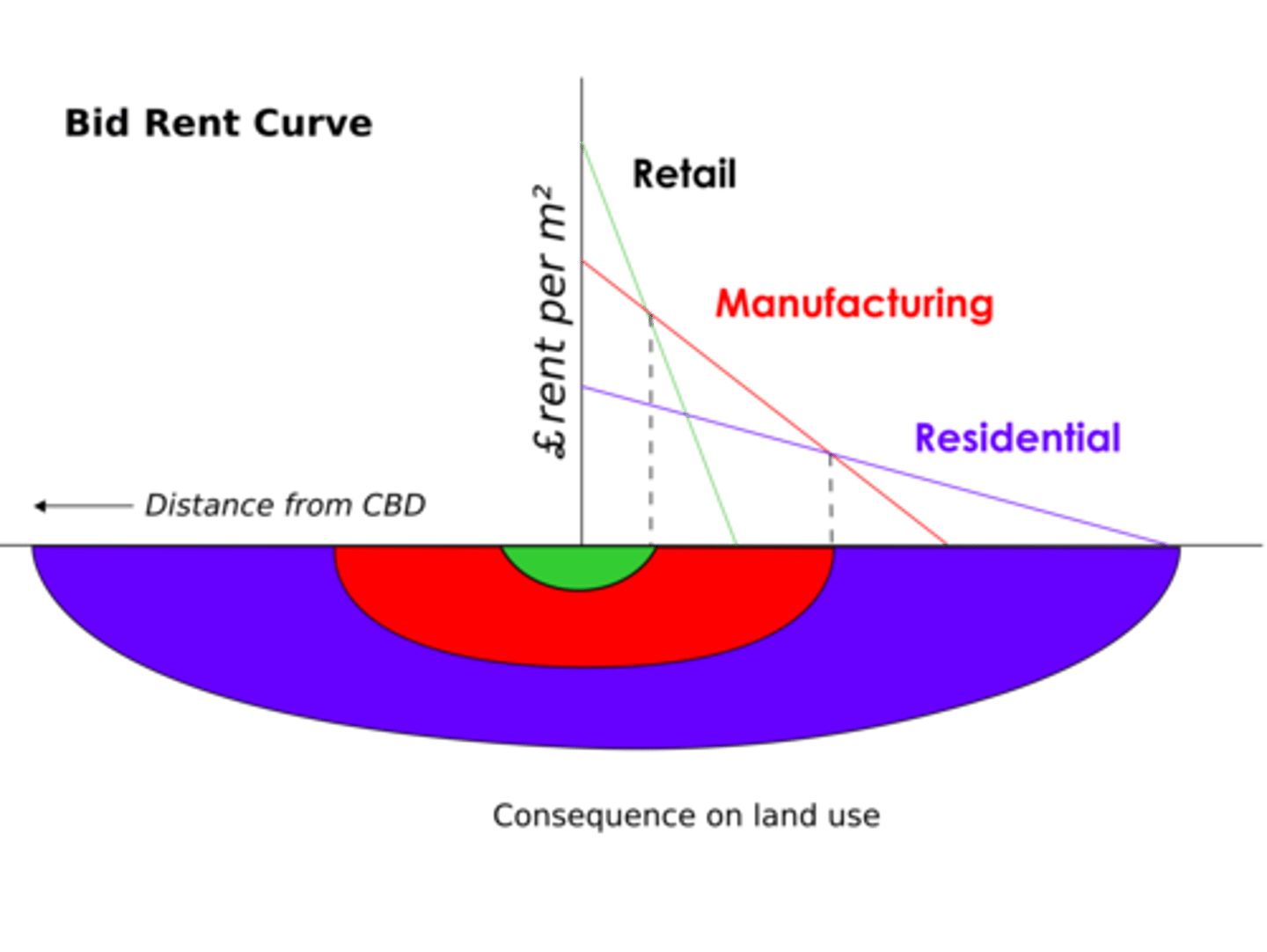
bid rent theory
geographical economic theory that refers to how the price and demand on real estate changes as the distance towards the Central Business District (CBD) increases.
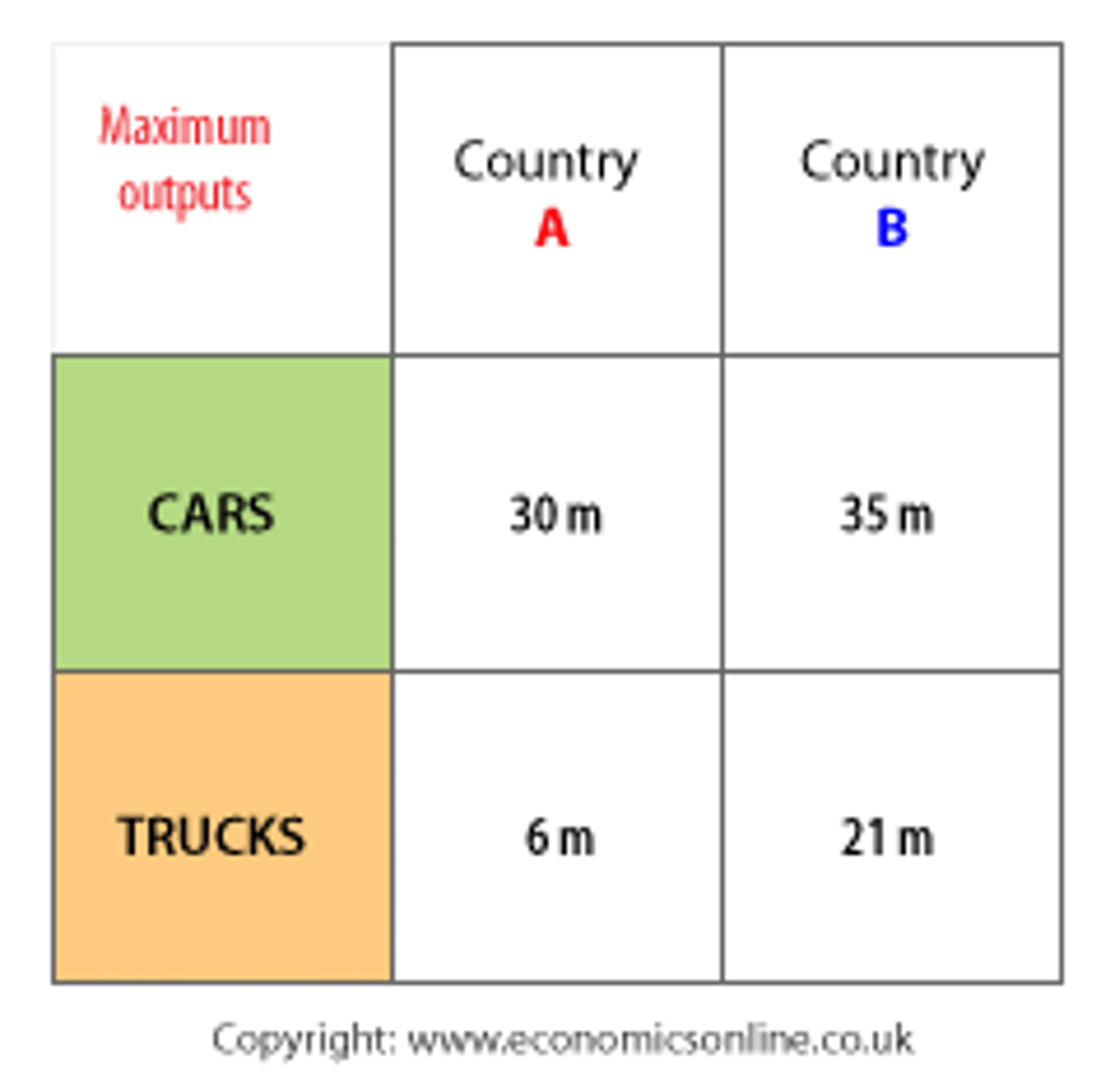
comparative advantage
the ability to produce a good at a lower opportunity cost than another producer
organic food
a type of food that is produced without pesticides, bioengineering, or high-energy radiation

overgrazing
the depletion of vegetation due to the continuous feeding of too many animals

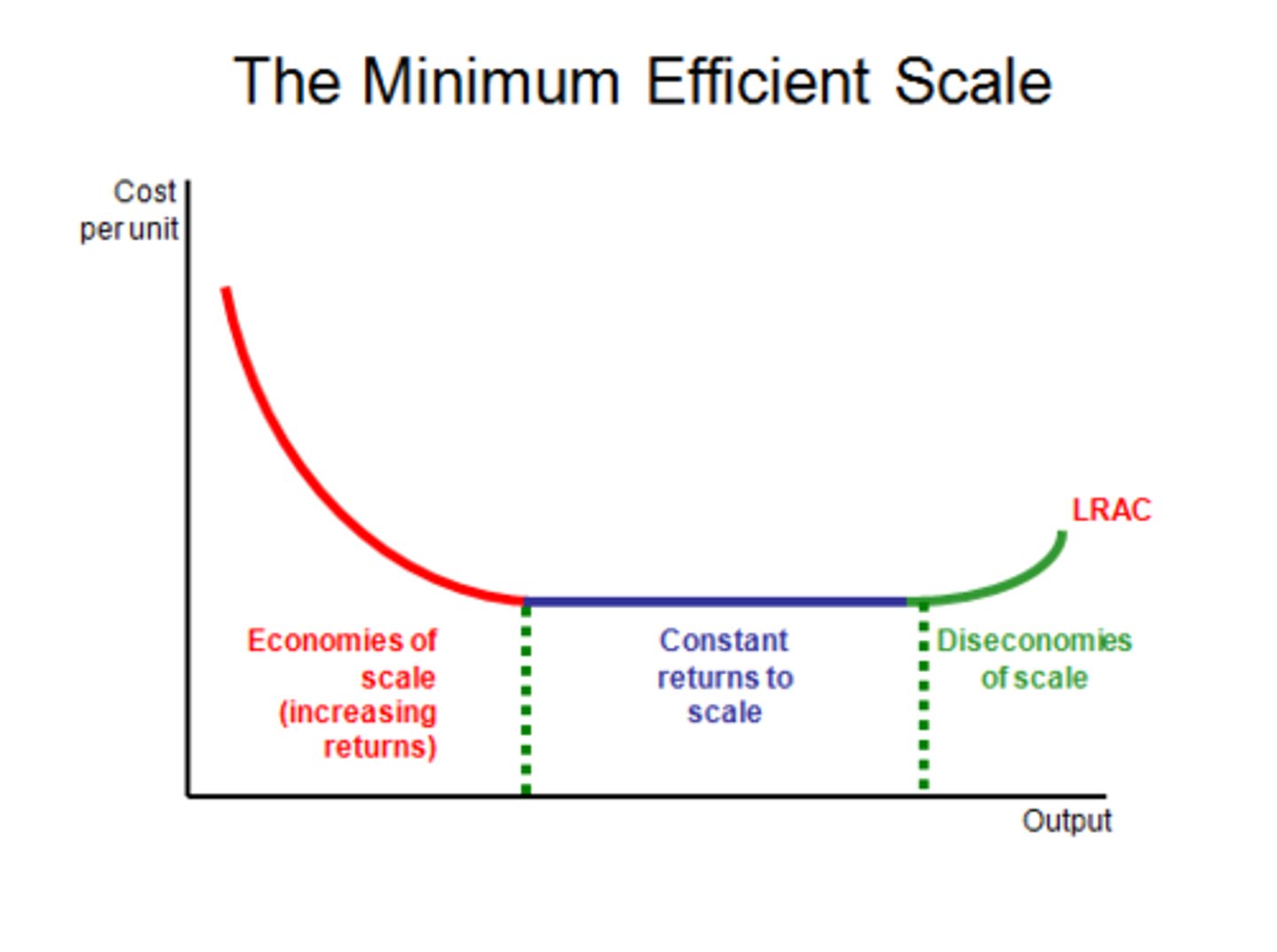
economies of scale
factors that cause a producer's average cost per unit to fall as output rises
Agrarian
characteristic of farmers or their way of life

Agribusiness
highly mechanized, large-scale farming, usually under corporate ownership

Agricultural industrialization
use of machinery in agriculture, like tractors

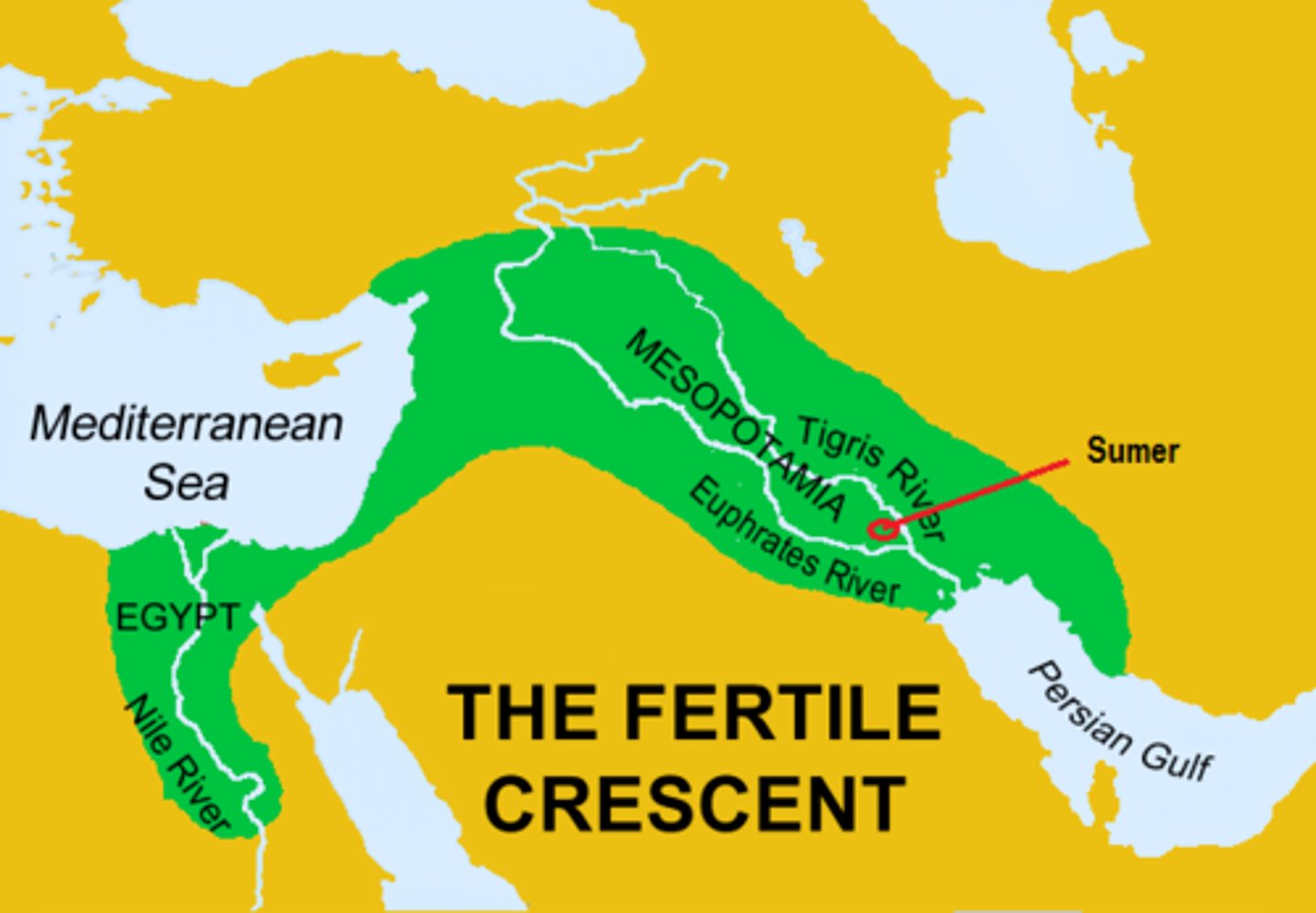
Agricultural origins
Includes but not exclusive to the Fertile crescent - originated in the hearths of humanity (Indus River, Central-South America, East-Southeast Asia)
Animal domestication
animals are tamed/bred and used for food and profit.

Aquaculture
the cultivation of aquatic organisms (as fish or shellfish) especially for food

Biotechnology
A form of technology that uses living organisms, usually genes, to modify products, to make or modify plants and animals, or to develop other microorganisms for specific purposes.

Commercial agriculture
term used to describe large scale farming and ranching operations that employ vast land bases, large mechanized equipment, factory-type labor forces, and the latest technology

intensive agriculture
A form of subsistence agriculture in which farmers must expend a relatively large amount of effort to produce the maximum yield from a parcel of land.

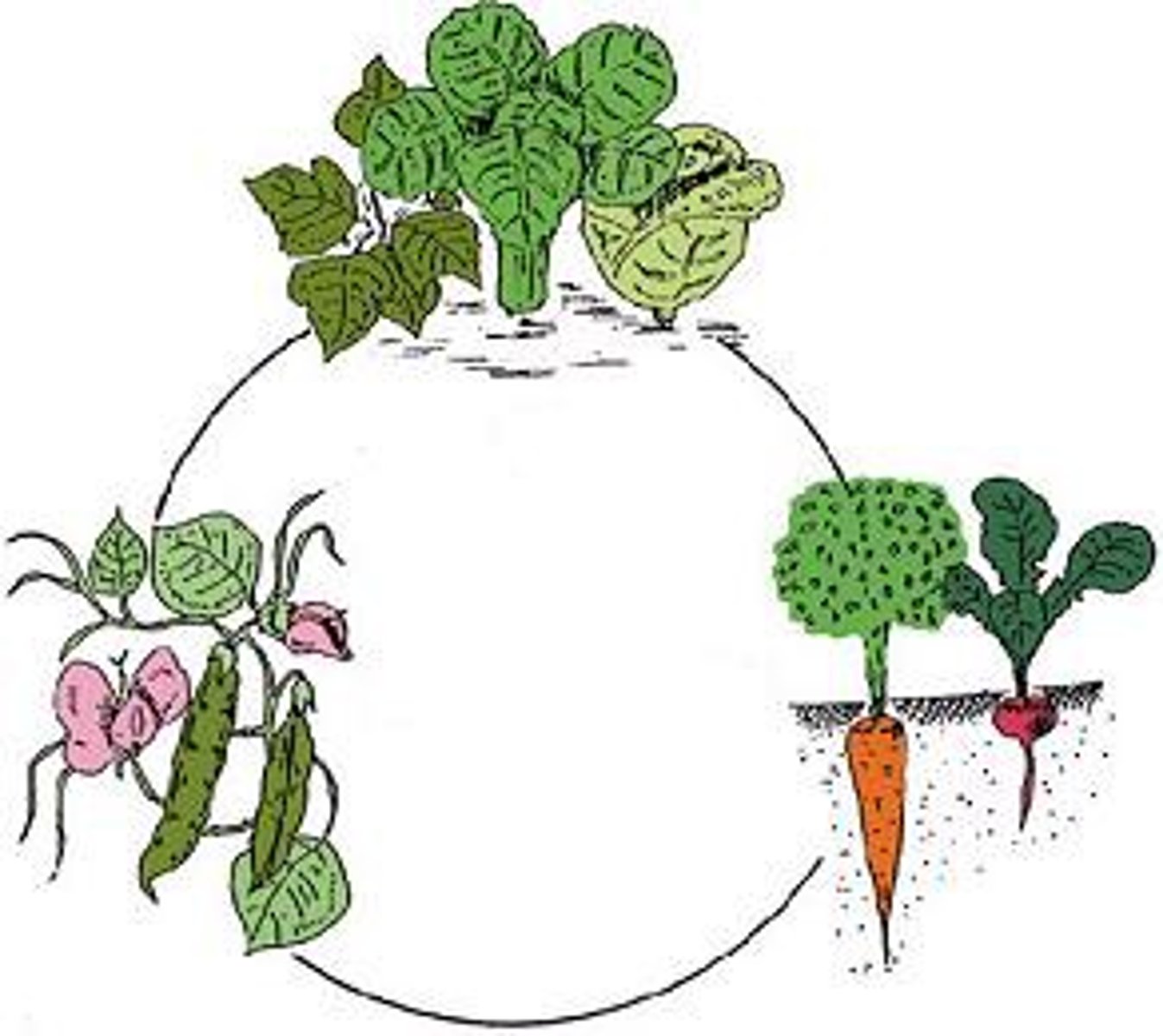
Crop rotation
the practice of rotating use of different fields from crop to crop each year, to avoid exhausting the soil

Dairying
raising female cattle, goats, or certain other lactating livestock for long-term production of milk

Double cropping
a second crop is planted after the first has been harvested

Primary Sector
The portion of the economy concerned with the direct extraction of materials from Earth's surface, generally through agriculture, although sometimes by mining, fishing, and forestry.

Pesticides
toxic substances released to kill living things

soil salinization
in arid regions, irrigation water evaporates, leaving salts behind

Desertification
the process by which fertile land becomes desert, typically as a result of drought, deforestation, or inappropriate agriculture.

Extensive subsistence agriculture
Using a large amount of land to farm food for the farmer's family to eat.

Shifting cultivation
A form of subsistence agriculture in which people shift activity from one field to another; each field is used for crops for relatively few years and left fallow for a relatively long period.

Slash-and-burn
A farming method involving the cutting of trees, then burning them to provide ash-enriched soil for the planting of crops
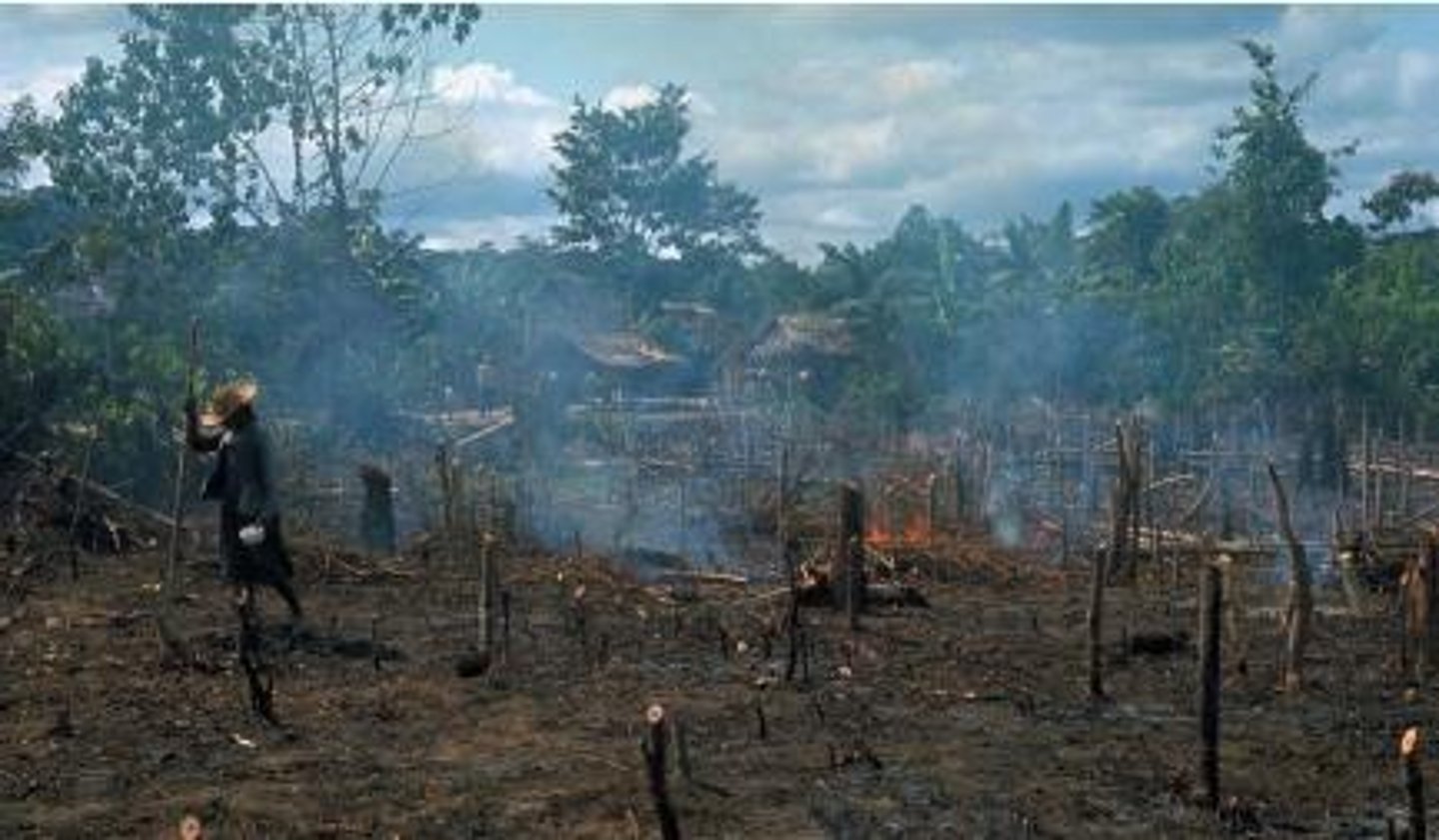

Swidden
Land that is prepared for agriculture by using the slash-and-burn method.
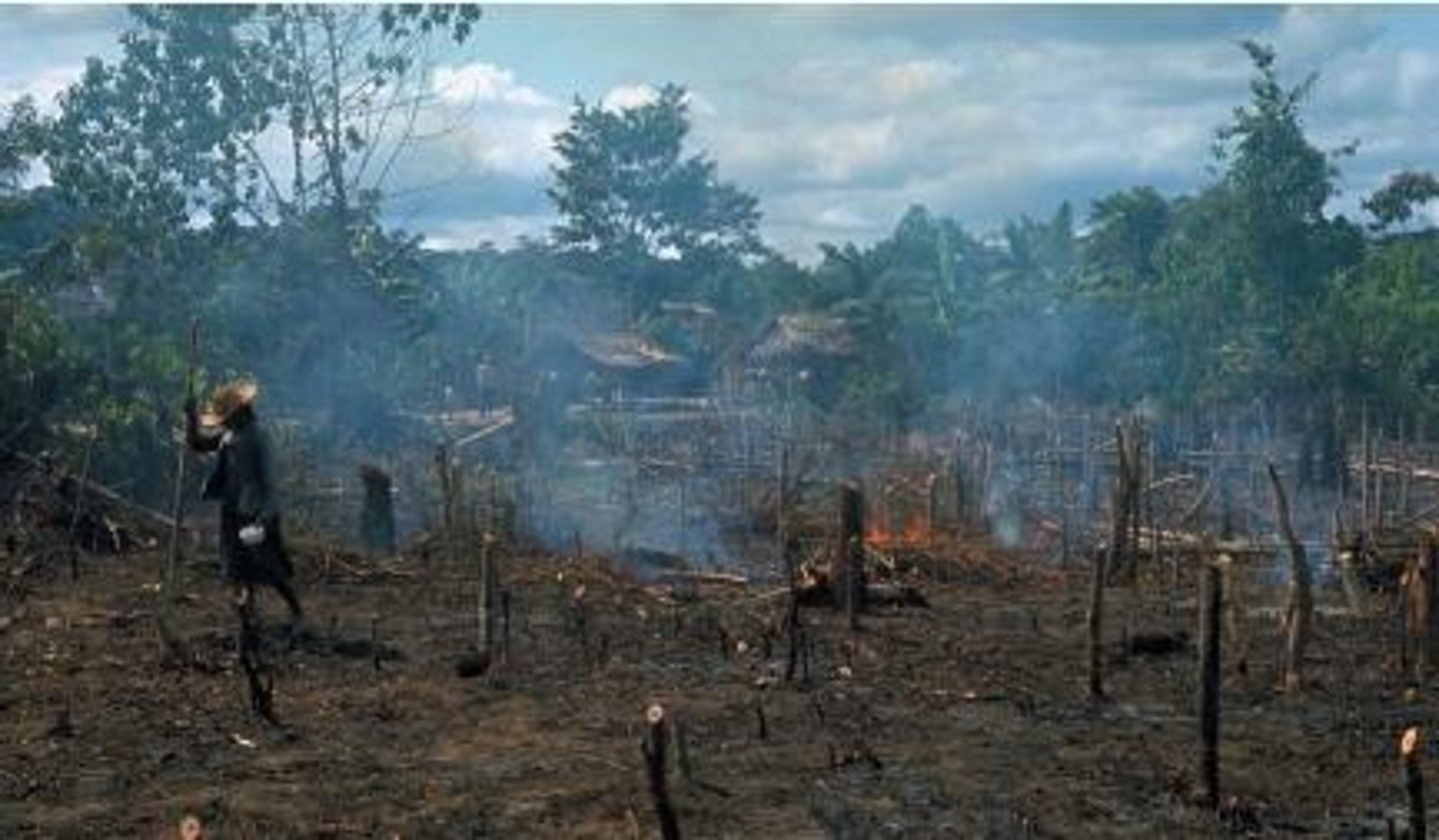

Feedlot
a plot of land on which livestock are fattened for market
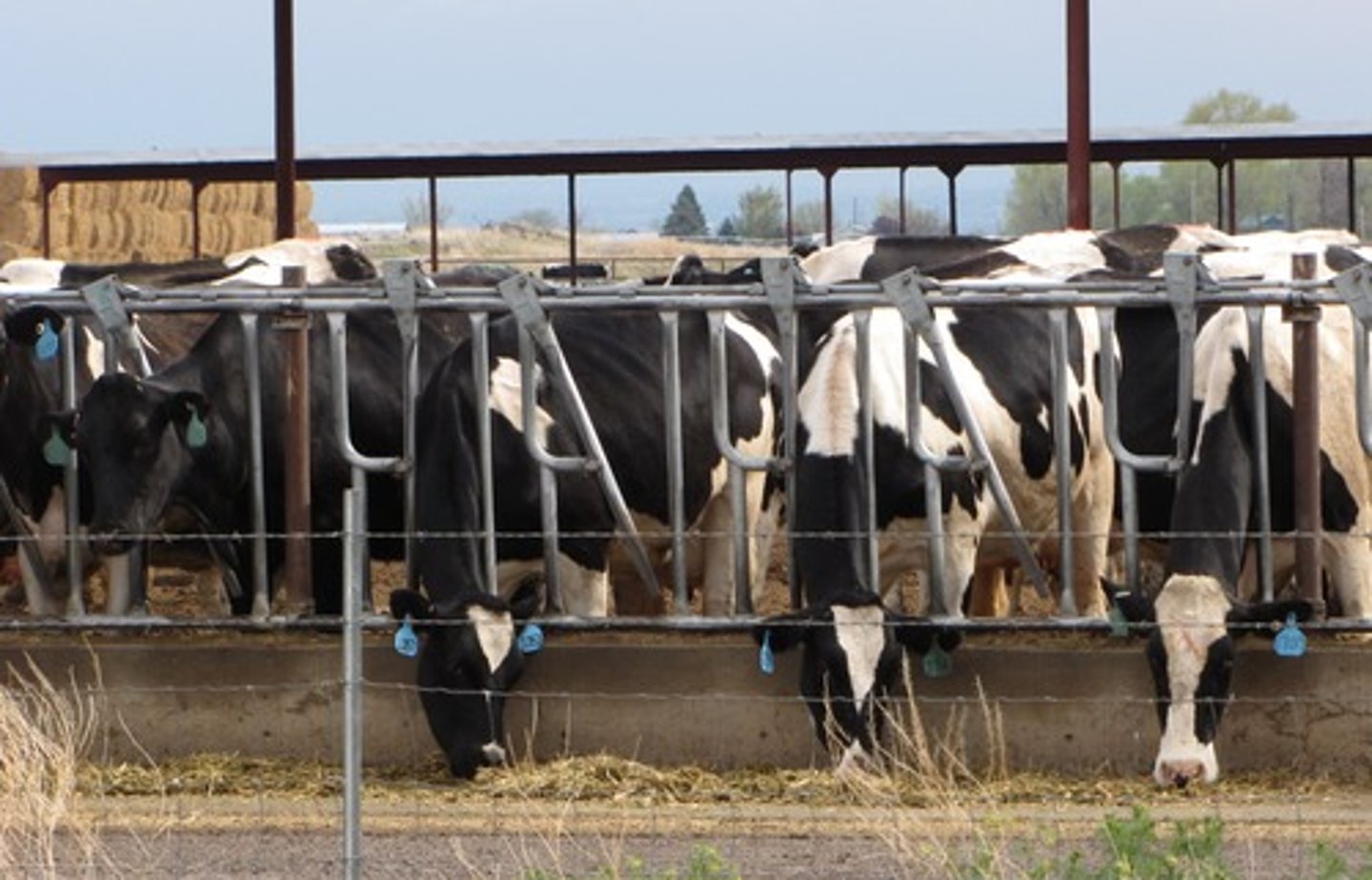

Hunting and gathering
The killing of wild animals and fish as well as the gathering of fruits, roots, nuts, and other plants for sustenance - Practiced a majority a human history, not much now.

Market gardening
the relatively small-scale production of fruits, vegetables and flowers as cash crops, frequently sold directly to consumers and restaurants

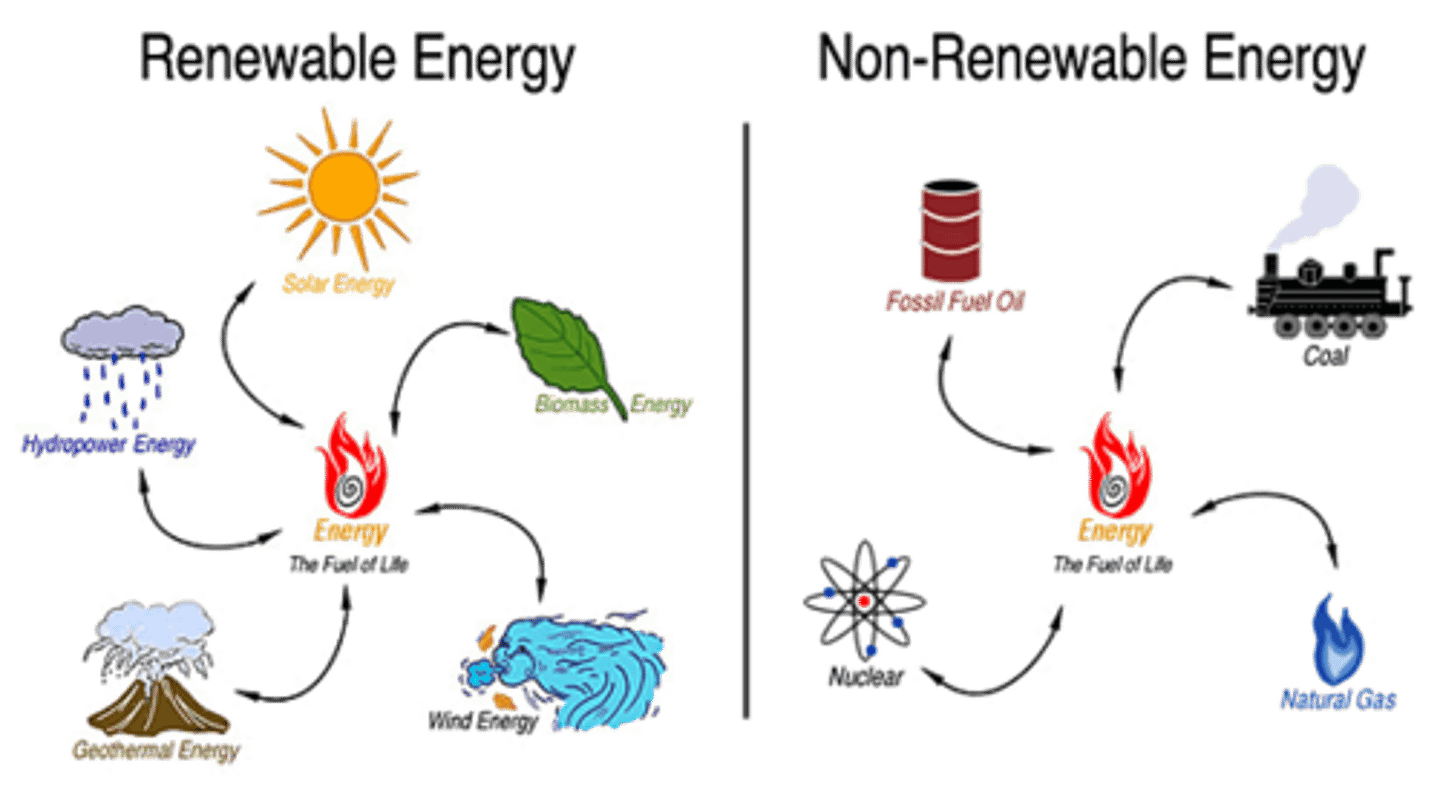
Renewable/non-renewable
a resource that can be used again or cannot be used again
Second agricultural revolution
Coinciding with the Industrial Revolution, it witnessed improved methods of cultivation, harvesting, and storage of farm produce

Staple Crop
the most important crop produced or consumed in a region

Transhumance
a seasonal periodic movement of pastoralists and their livestock between highland and lowland pastures

Commercial Agriculture
Agriculture undertaken primarily to generate products for sale off the farm.

Urban Farming Initiatives
Initiatives to bring fresh foods to urban areas. Small farms are created by and cared for by its residents.

Community Supported Agriculture (CSA)
A process in which consumers buy shares from local farmers in exchange for weekly produce

Local food movement
Purchasing food from nearby farms because you want to minimize the pollution created from the transportation of food around the world

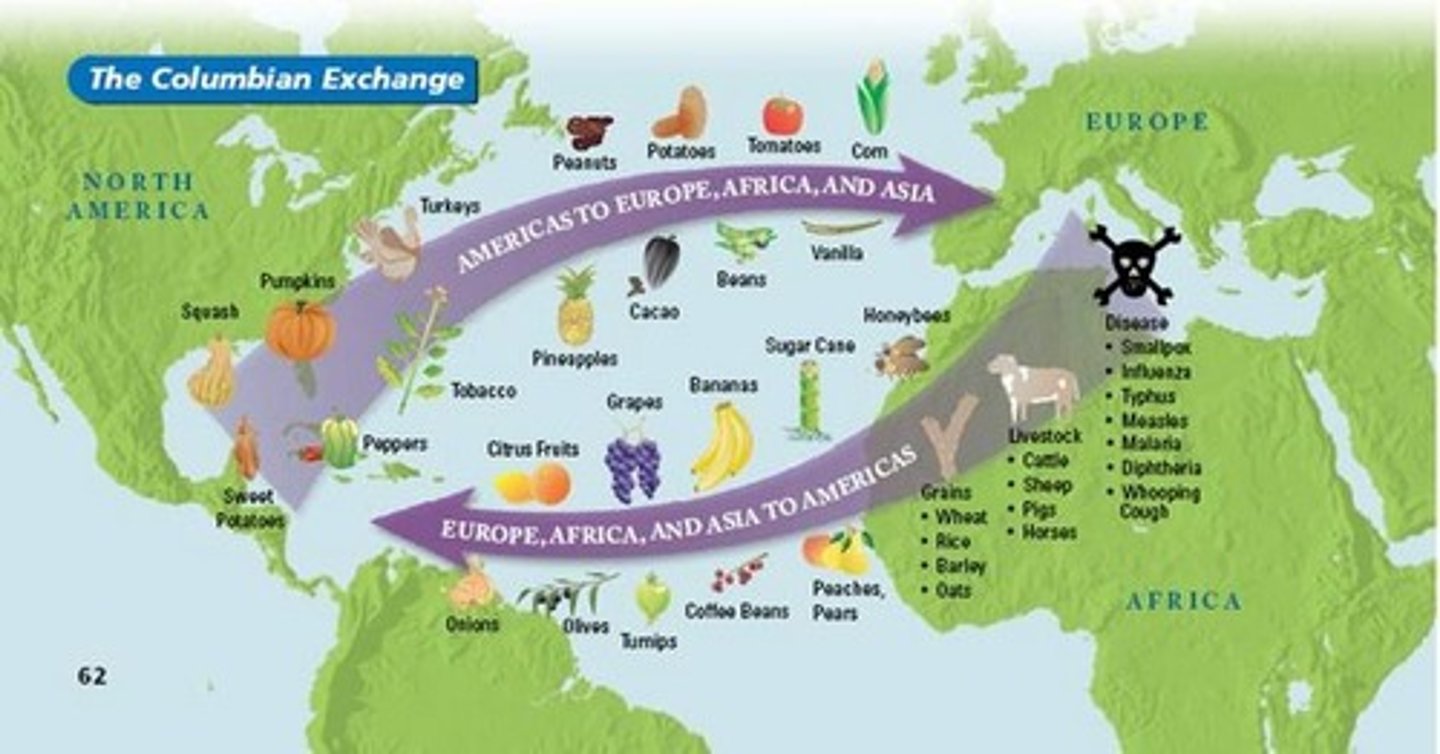
Columbian Exchange
The exchange of foods, goods, and ideas between Native Americans and Europeans following Colombus' exploration.
Pastoral Nomadism (herding)
A form of subsistence agriculture based on herding domesticated animals.
