PHSL 3051 renal physiology
1/58
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
59 Terms
function of the kidneys
regulation of water, inorganic ion balance, acid base balance
removal of metabolic waste products from the blood and their excretion in the urine
removal of foreign chemicals from the blood and their excretion in the urine
gluconeogenesis
production of hormones/enzymes
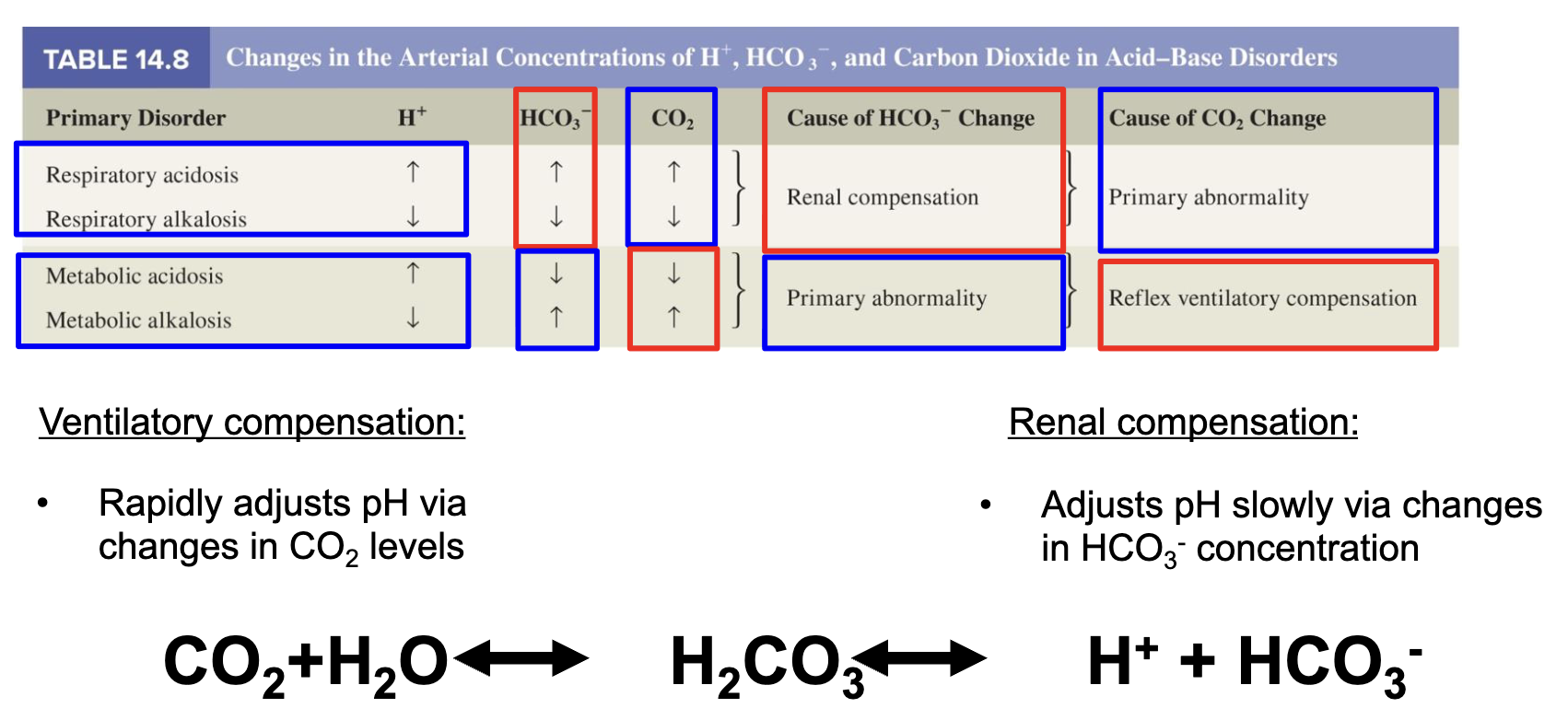
primary organs of the urinary system
kidney
ureter
bladder
urethra
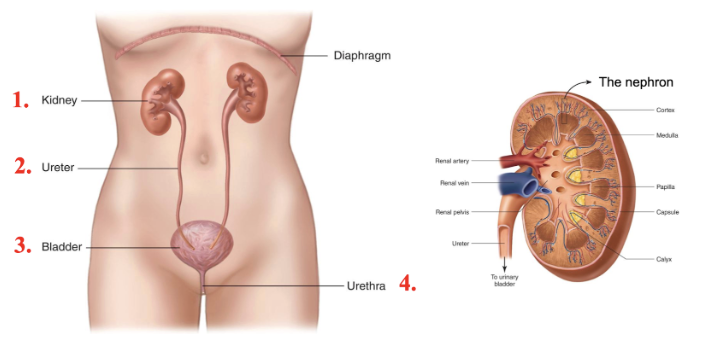
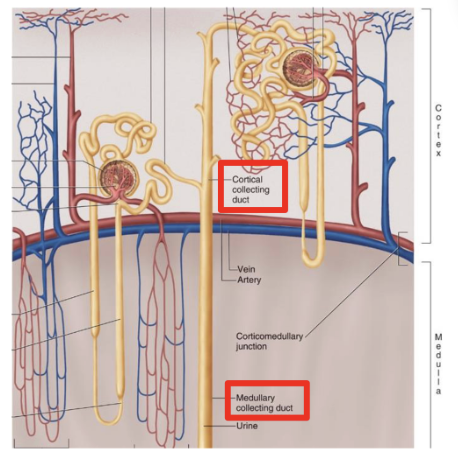
layers of the kidney
renal cortex = outer layer
contains renal corpuscles, convoluted tubules, cortical nephrons
renal medulla = inner layer
contains renal pyramids, long loops of henele, collecting ducts
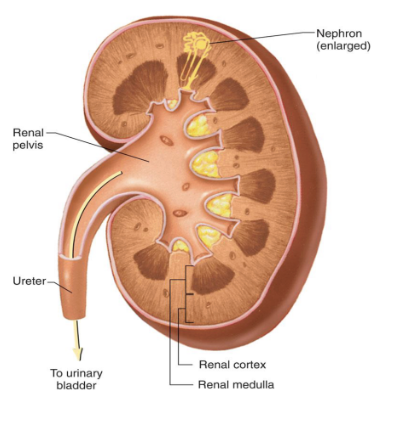
the nephron
the functional unit of the kidney
the nephron tubules
bowmans capsule (part of corpuscle)
proximal convulated/straight tubule
loop of henele
distal convulated tubule
collecting duct
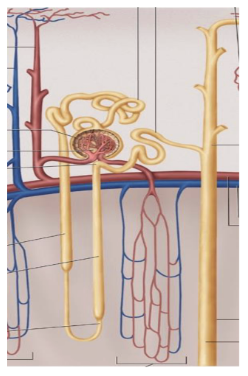
the nephron blood supply
a renal artery
afferent arteriole
glomerular capillaries
efferent arteriole
peritubular capillaries (possibly vasa recta, if in medulla)
a renal vein
portal system
an arrangement by which blood collected from one set of capillaries passes through a large vessel or vessels, to another set of capillaries before returning to the systemic circulation
the renal corpuscle =
glomerular capillaries + bowmans capsule
nephron =
glomerular (renal) corpuscle + renal tubule
segments of the nephron
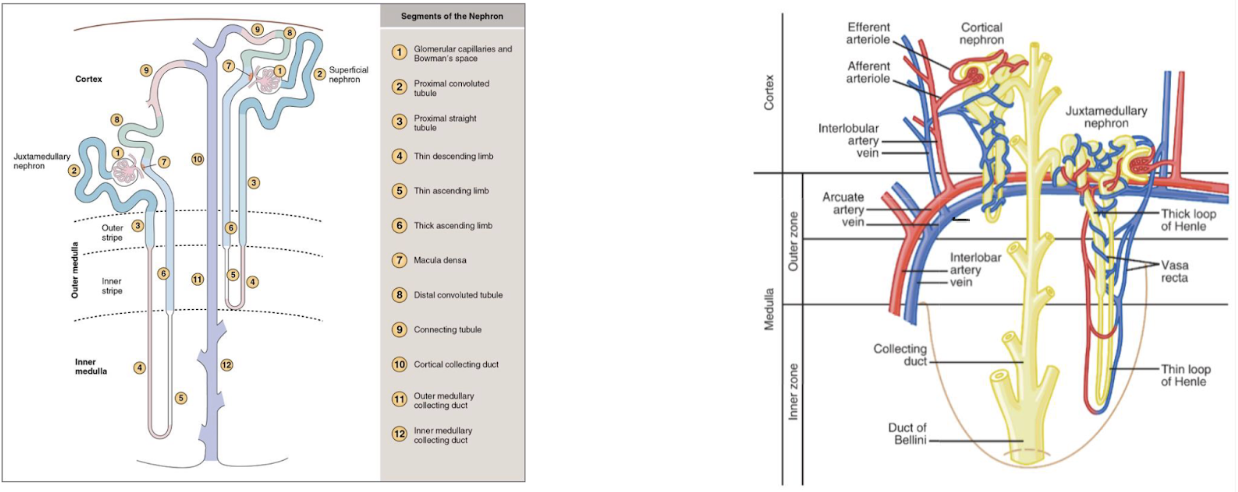
two types of nephrons
cortical (85%)
juxtamedullary (15%)
cortical nephron
short or no loops of henele
do not contribute to hypertonic medullary interstitium
change in volume and consumption of filtrate
juxtamedullary nephron
long loops of henele
generate gradient in medulla important for H2O reabsorption
peritubular capillaries are called the vasa rectua
concentrate the filtrate
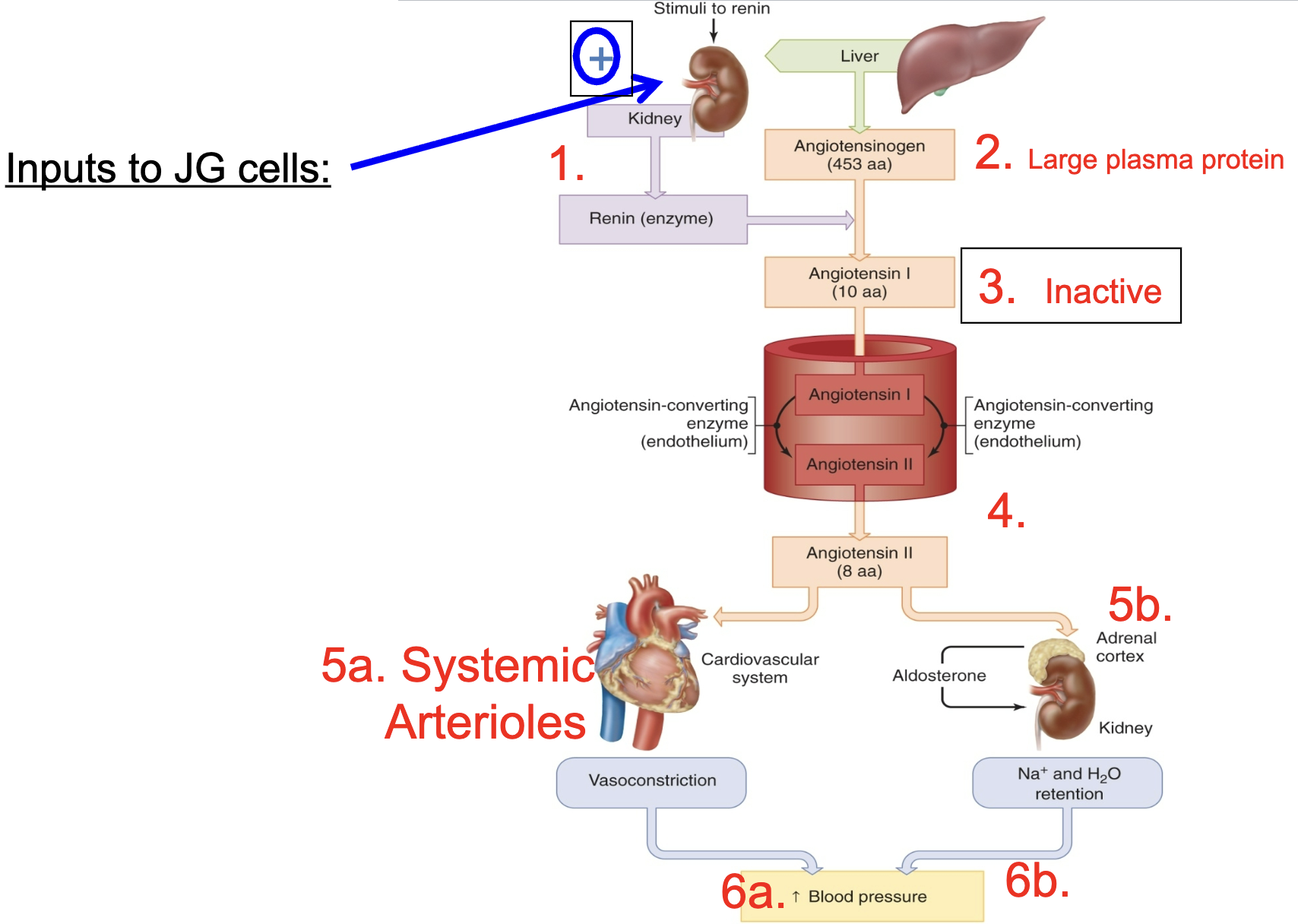
juxtaglomerular apparatus (JGA) composition
juxtaglomerular cell patch (afferent arteriole)
senses pressure and releases renin when it is low
macula densa cell patch (distal convoluted tubule)
senses flow (specifically Na+ and Cl- and sends paracrine signals to afferent arterioles)
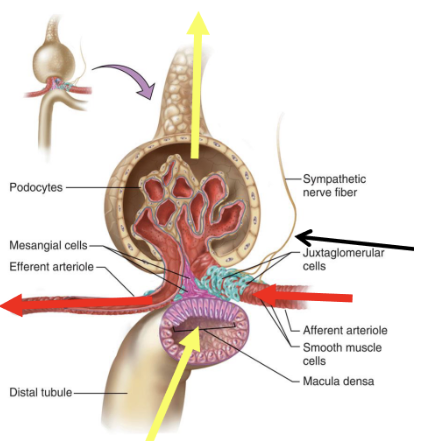
sympathetic nerve from CVCC
constricts afferent arteriole
causes renin secretion from juxtaglomerular cells (special secretory cells)
renin
an enzyme/hormone that is important for blood pressure regulation
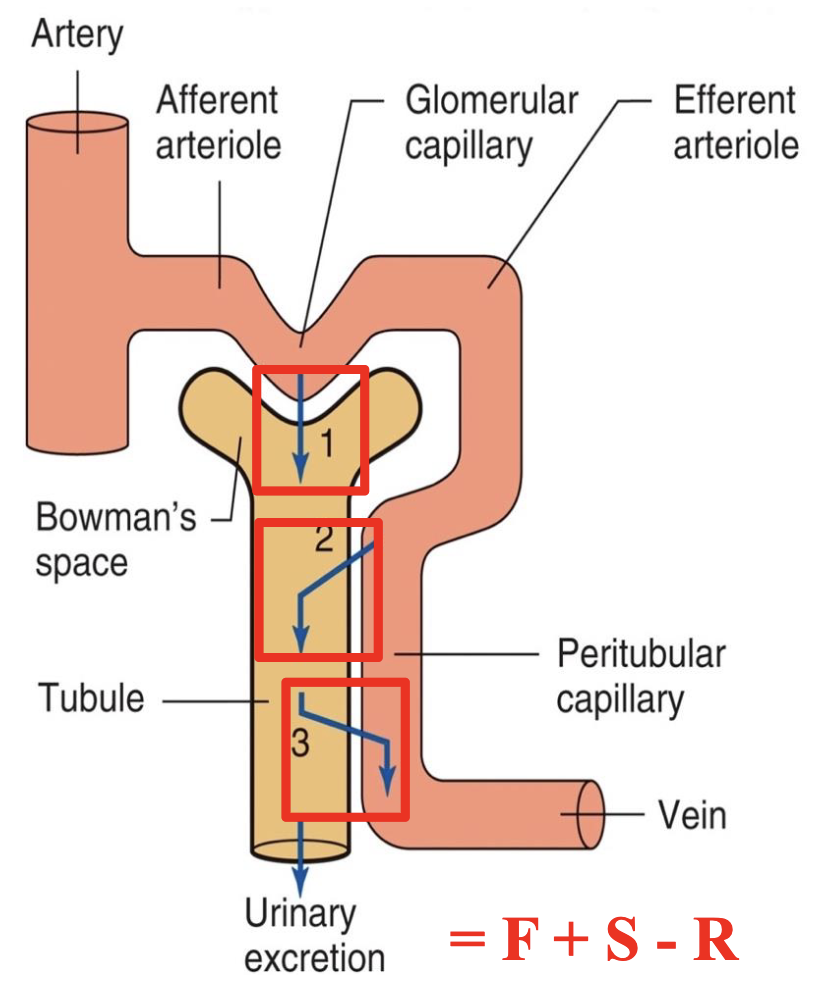
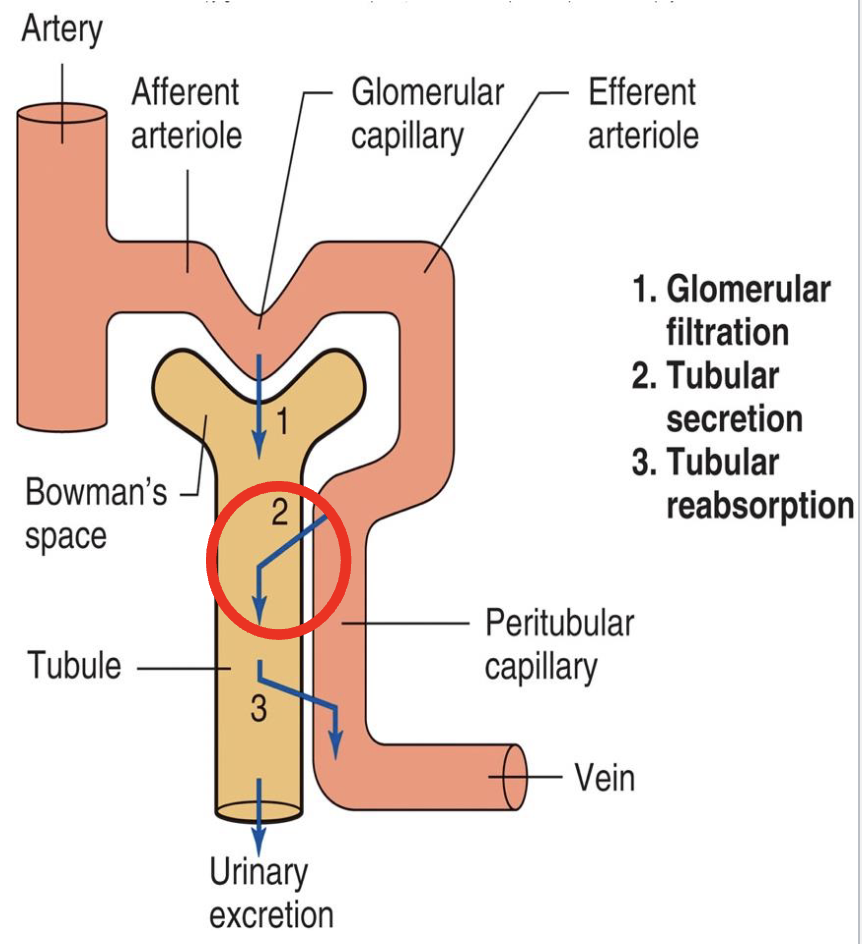
basic renal processes
glomerular filtration
20% of plasma is filtered, 80% continues into peritubular capillaries
tubular secretion
from 80% that wasnt filtered
tubular reabsorption
reabsorbs from filtrate and put back into plasma *prevents excretion in urine
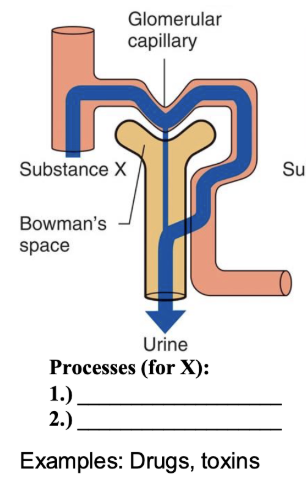
processes for X
freely filtered
100% secreted
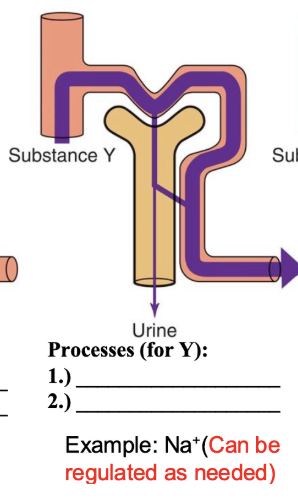
processes for Y
freely filtered
partially reabsorbed
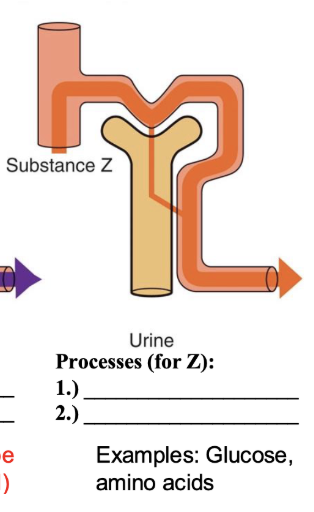
processes for Z
freely filtered
100% reabsorbed *more excreted in urine
glomerular filtration
20% of plasma is filtered, 80% continues into peritubular capillaries
plasma proteins and cells are too big for filtration
negatively charged membranes, also exclude plasma proteins
filtrate = blood plasma except for RBC and proteins
glomerular filtrate is plasma without cells or plasma proteins
useful molecules like nutrients are reabsorbed, while waste products and toxins are secreted
**GFR = 125 mL/min (180 L/day)
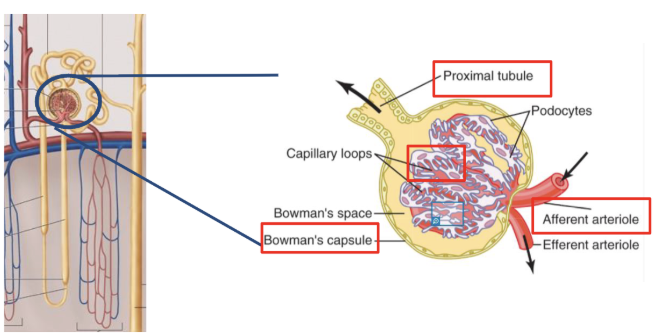
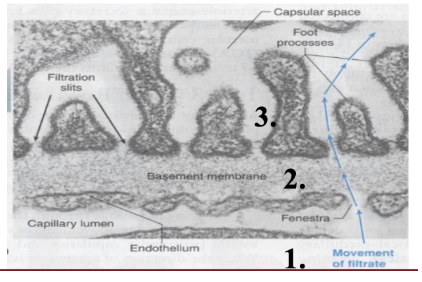
3 layers of GFR
capillary endothelium (50x more leaky than other typical capillary bed)
basement membrane (negative charge)
bowmans epithelium (i.e. podocytes
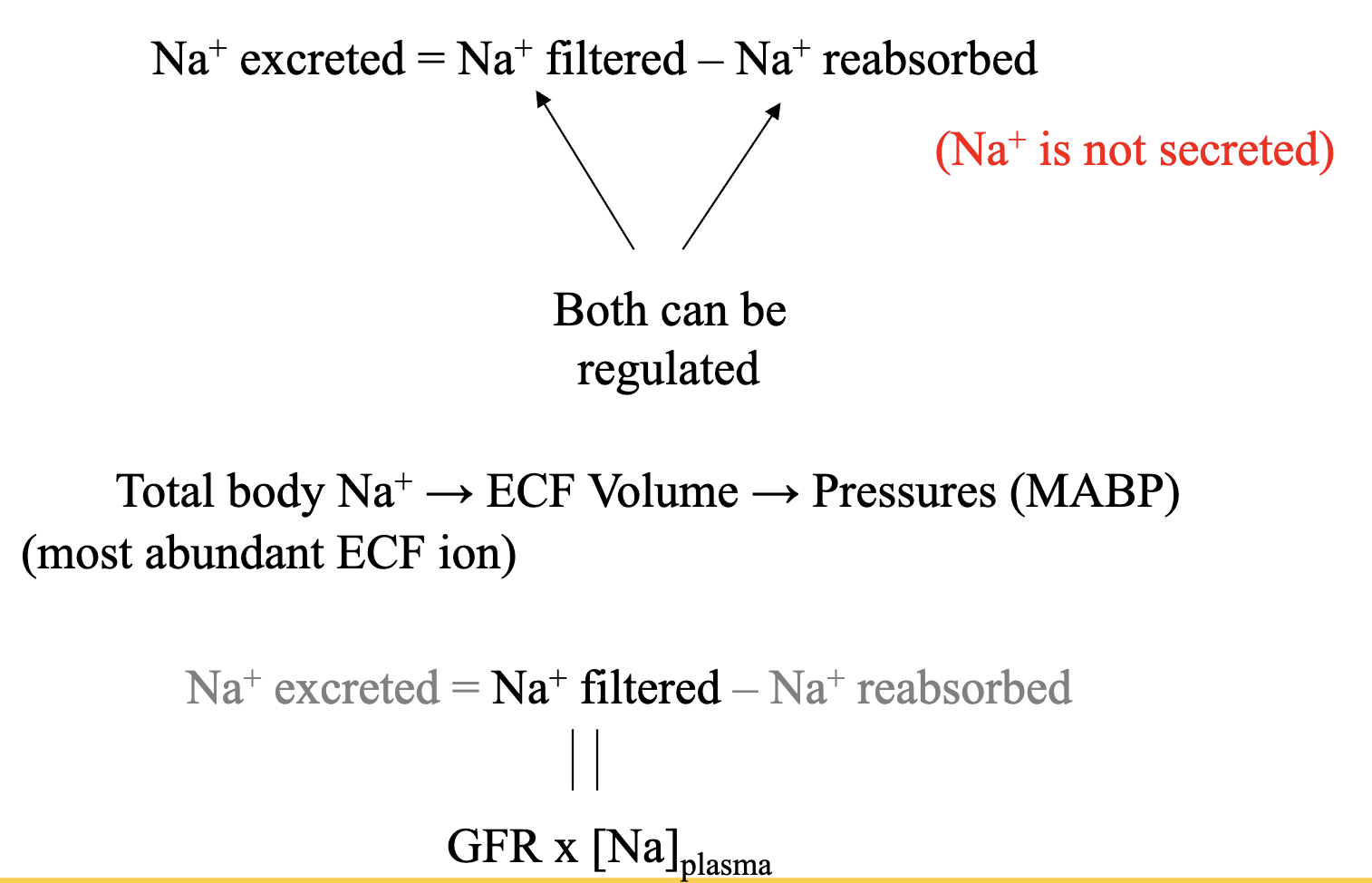
filtered load vs excreted load (3 important equations)
FL = GFR x [P]
FL = flow/min GFR = mL/min P = mg/mL
EL = V x [U]
EL = mg/min V= urine flow rate, mL/min U = mg/mL
if EL < FL, net reabsorption
if FL < EL, net secretion
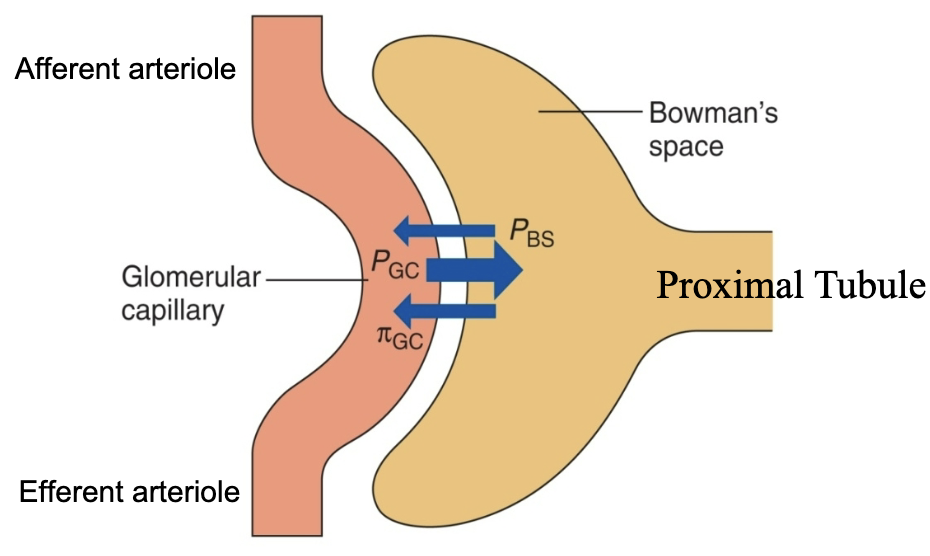
starling forces in glomerular filtration
favoring filtration
glomerular capillary blood pressure (PGC) → 60 mmHg
opposing filtration
fluid pressure in bowmans space (PBS) → 15 mmHg
osmotic force due to protein in plasma (πGC) → 29 mmHg
Net glomerular filtration pressure = PGC - PBS - πGC → 16 mmHg
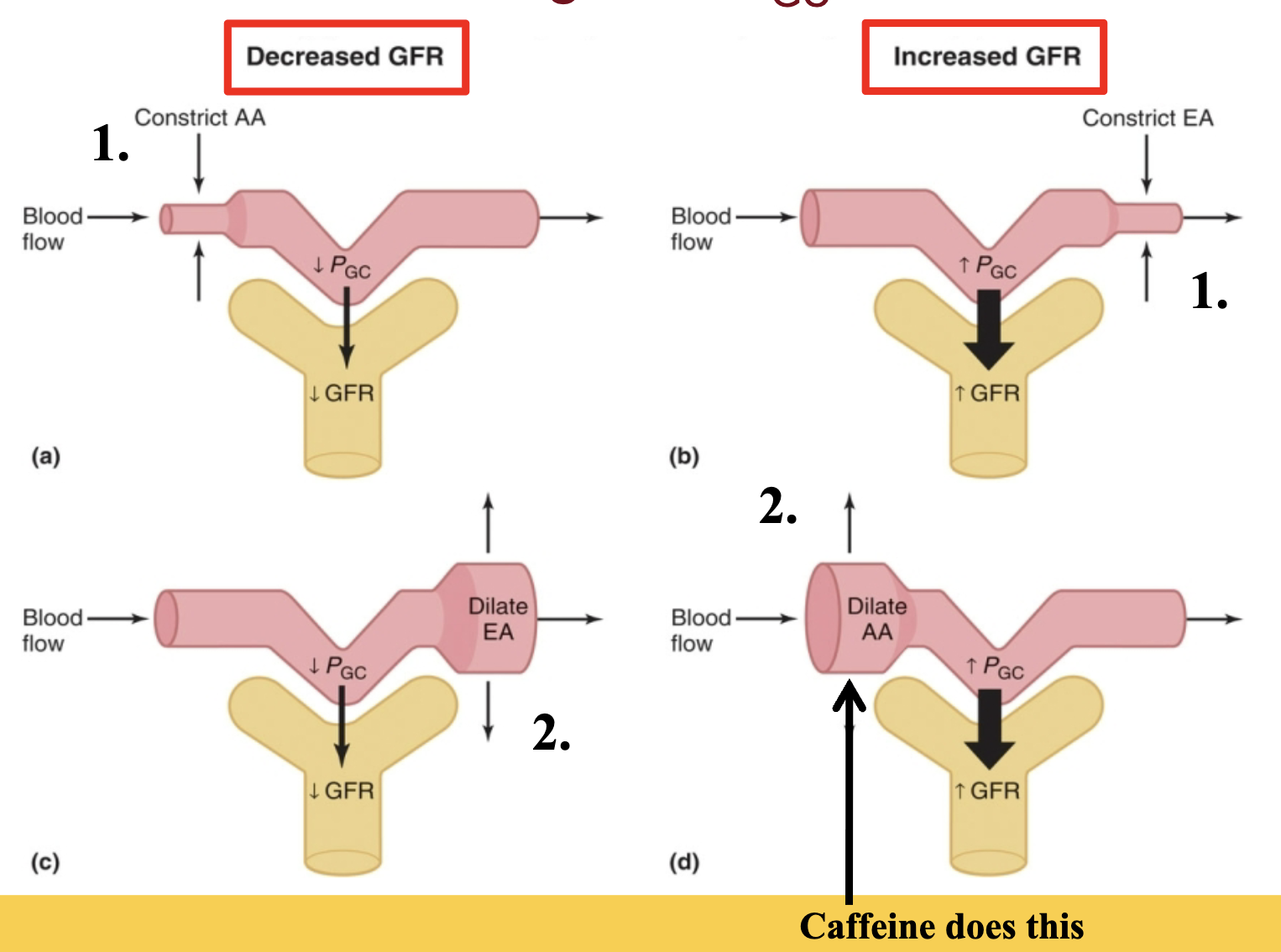
renal arterioles regulate PGC and thus GFR
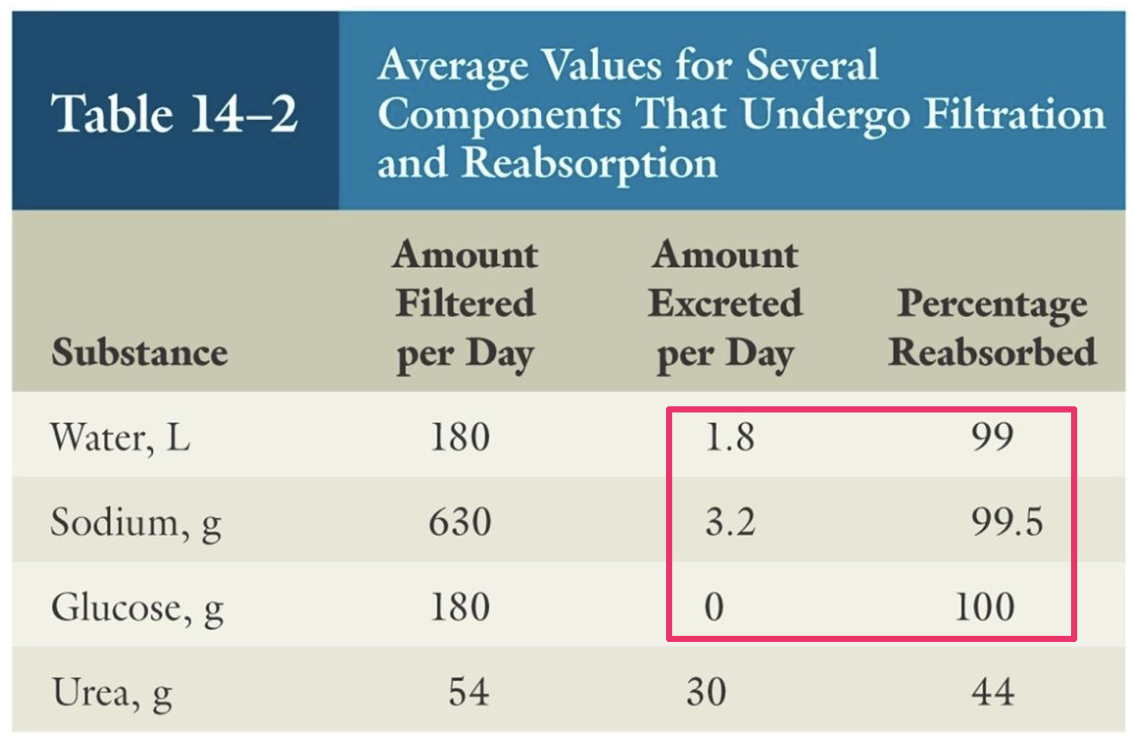
tubular reabsorption
filtered loads are HUGE (180 L/day of water)
reabsorption of water, ions, nutrients, etc. is almost complete
reabsorption of wastes is incomplete → excreted
modes and routes of tubular reabsorption
99% of filtrate volume is reabsorbed
*tight junctions vary by region
diffusion
lipid soluble substances that dont need carriers
meditated transport
large/charged substances (glucose)
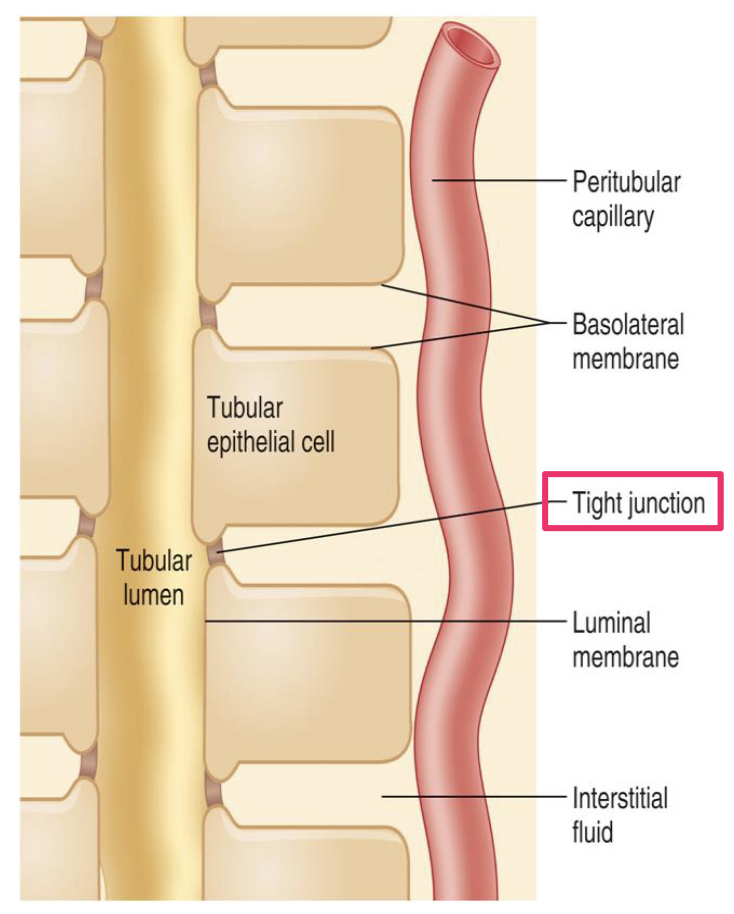
transcellular route
luminal membrane
basolateral membrane
renal interstitial fluid
peritubular capillaries
paracellular route
through tight functions
renal interstitial fluid
peritubular capillaries
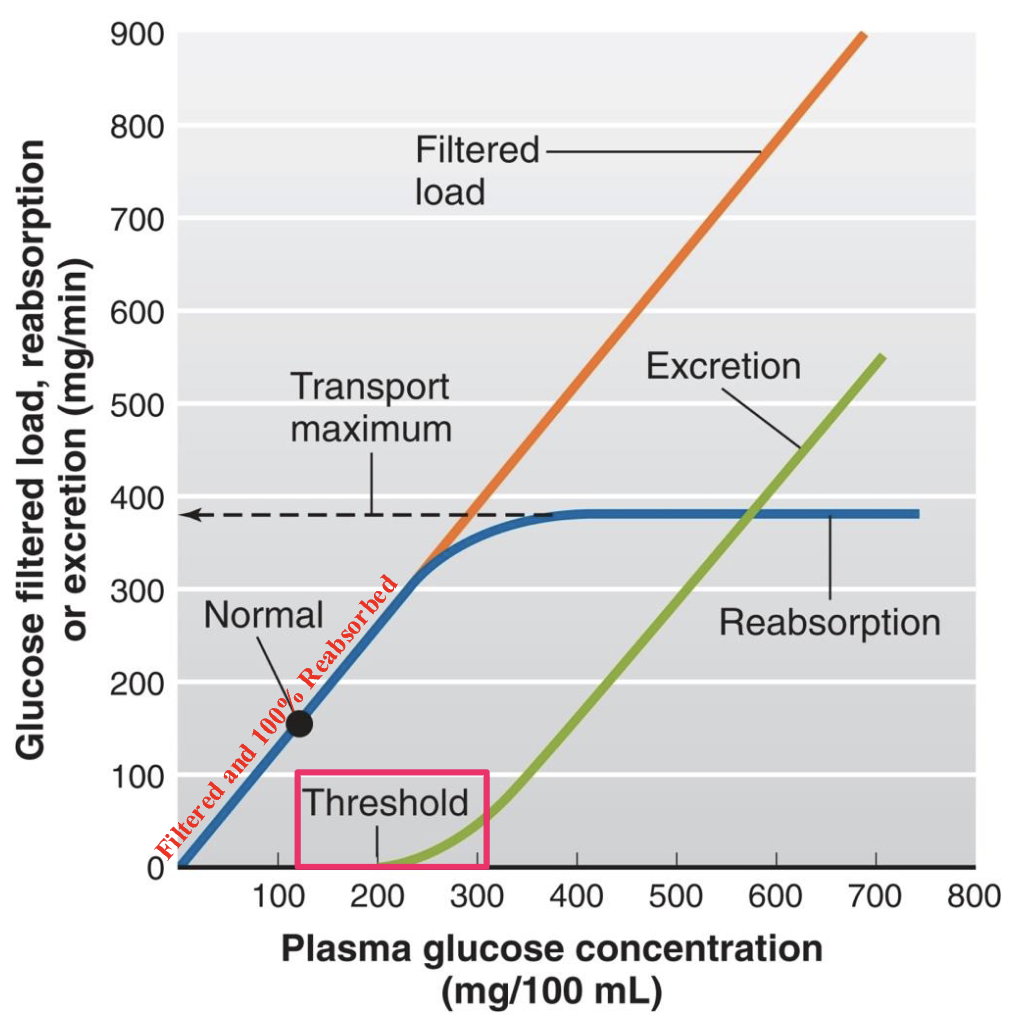
substances needing protein carriers have a transport maximum (Tm)
example: glucose
glucose is freely filtered, and in health, is fully reabsorbed in the proximal tubule - the plasma glucose of a healthy person almost never becomes high enough to cause glucose excretion in the urine
however, in uncontrolled diabetes mellitus, plasma glucose concentration may rise high enough to cause the filtered load of glucose to exceed the transport max, resulting in urinary glucose excretion
renal sodium regulation
Notes
when plasma volume drops, a decrease in GFR reduces Na+ and H2O loss
regulation of sodium reabsorption
renin/angiotensis/aldosterone system
renal sodium regulation steps
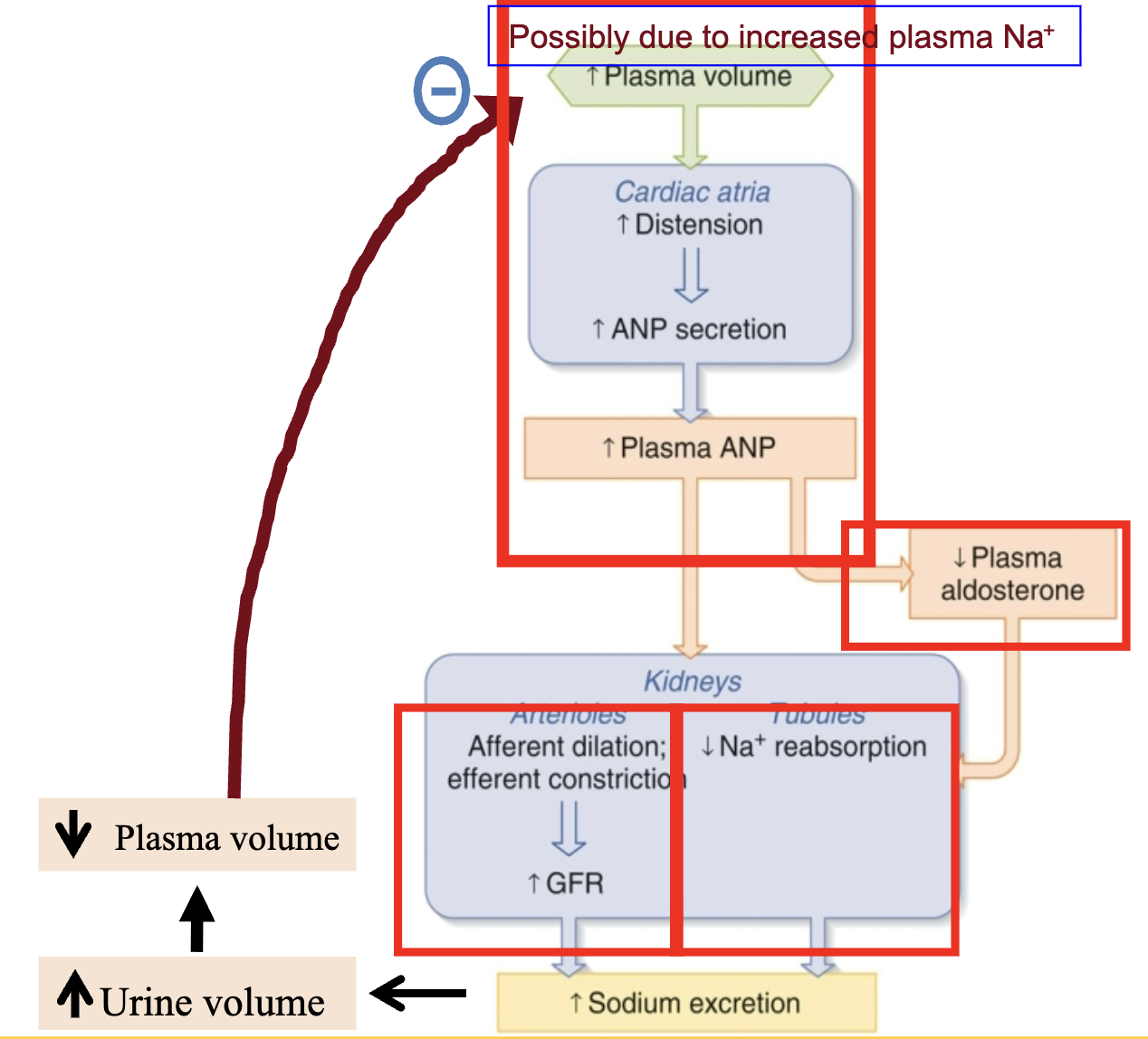
renal sodium regulation ANP
atrial natriuretic peptide
“the anti-aldosterone”
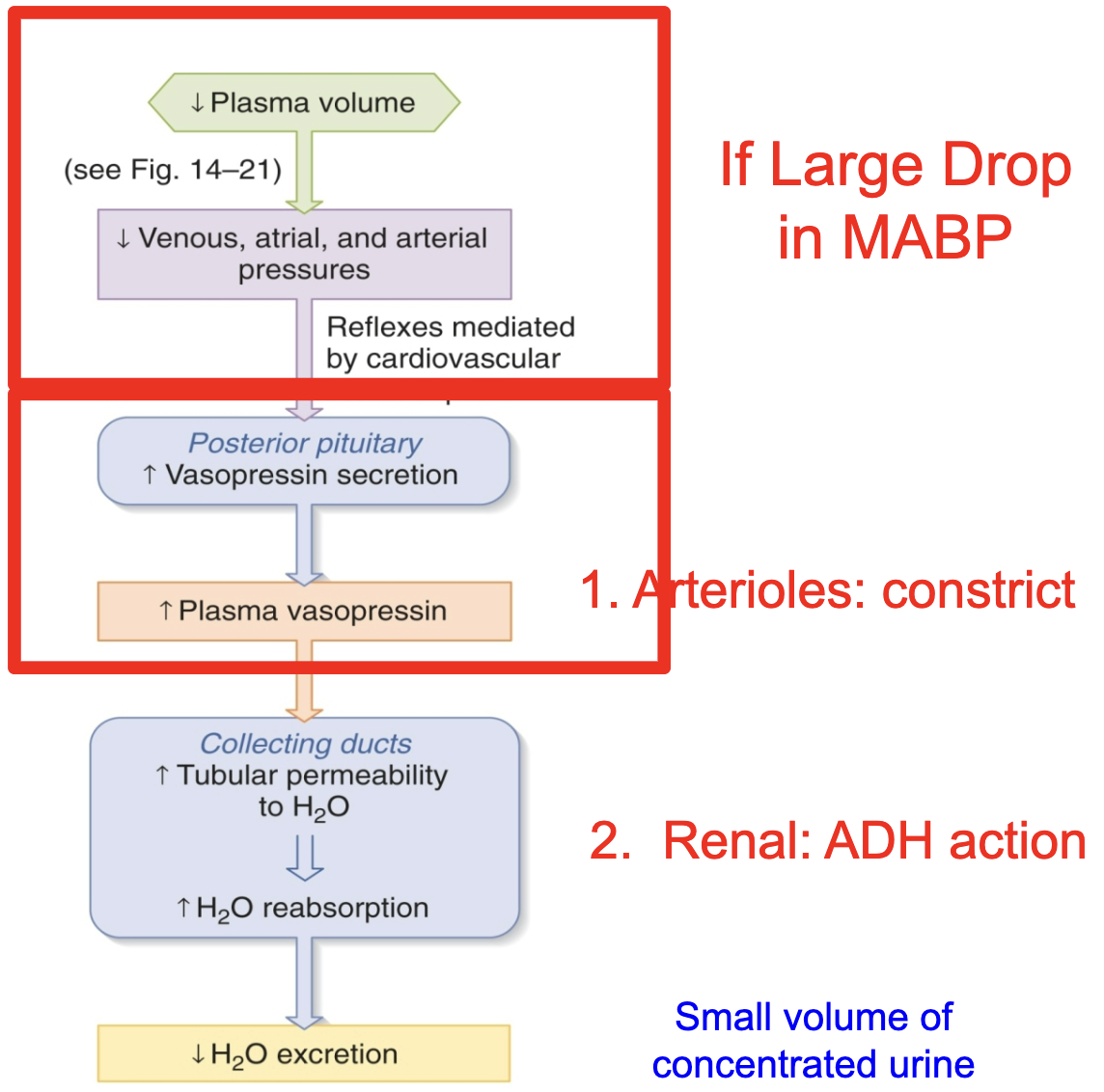
renal water regulation
there is also a baroreceptor reflex for
vasopressin/ADH secretion
although this reflex plays a lesser role under most physiological circumstances compared to the
osmoreceptor reflex
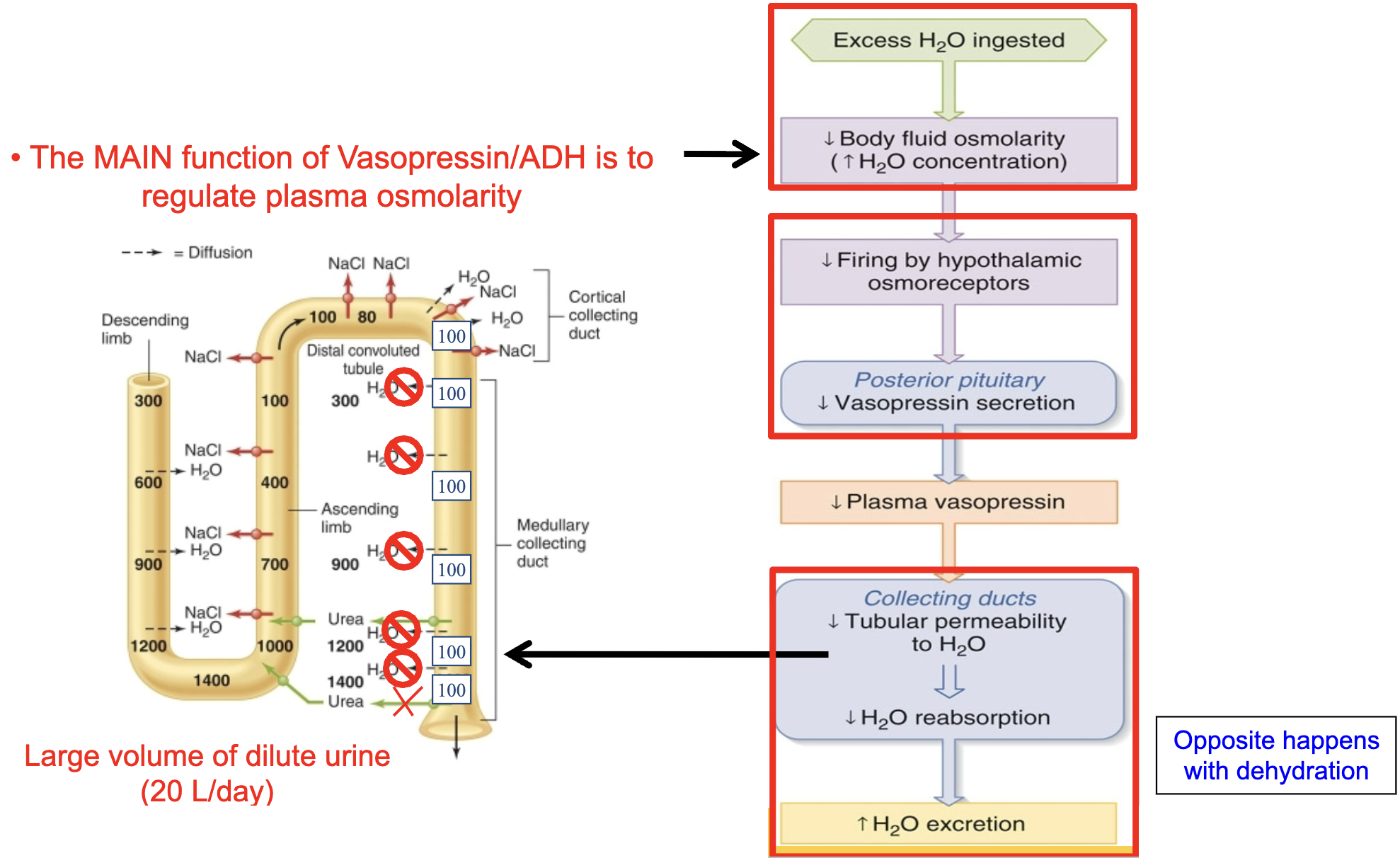
renal water regulation
tubular secretion
foreign chemicals and toxins
penicillin
usually involves active transport
coupled to Na+ reabsorption
i.e. secondary active transport
most secretion occurs into the proximal tubules
except K+ and H+ ions are mainly secreted into the distal tubule
secreted substances can have a Tm too
renal plasma clearance definition/equation
the volume of PLASMA per unit time from which all of a substance is removed/cleared by the kidneys and excreted in the urine
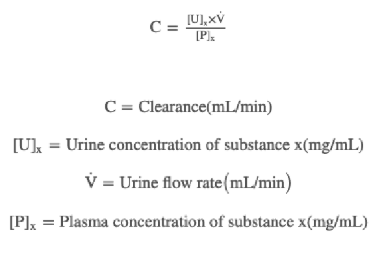
renal plasma clearance
RPC measurements can be used to determine how well the kidneys are functioning or how a substance is handled by the kidney
very important when figuring out dosing, developing new drugs, etc.
inulin (an exogenous substance) is freely filtered but not secreted or reabsorbed
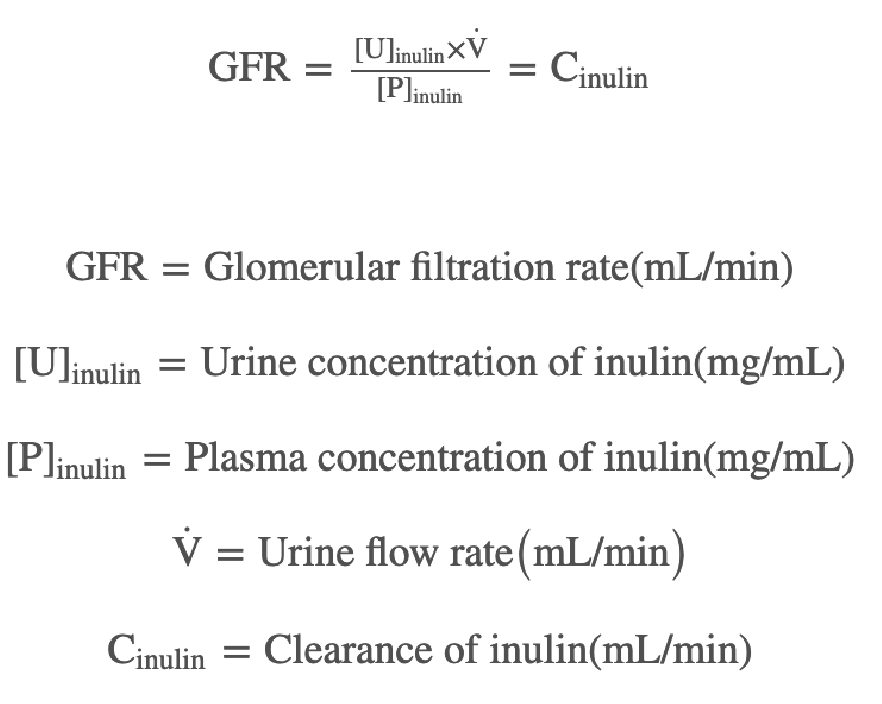
RPCinulin = GFR (typically 125 mL/min)
RPC of any new substance will show how that substance is handled by the kidneys
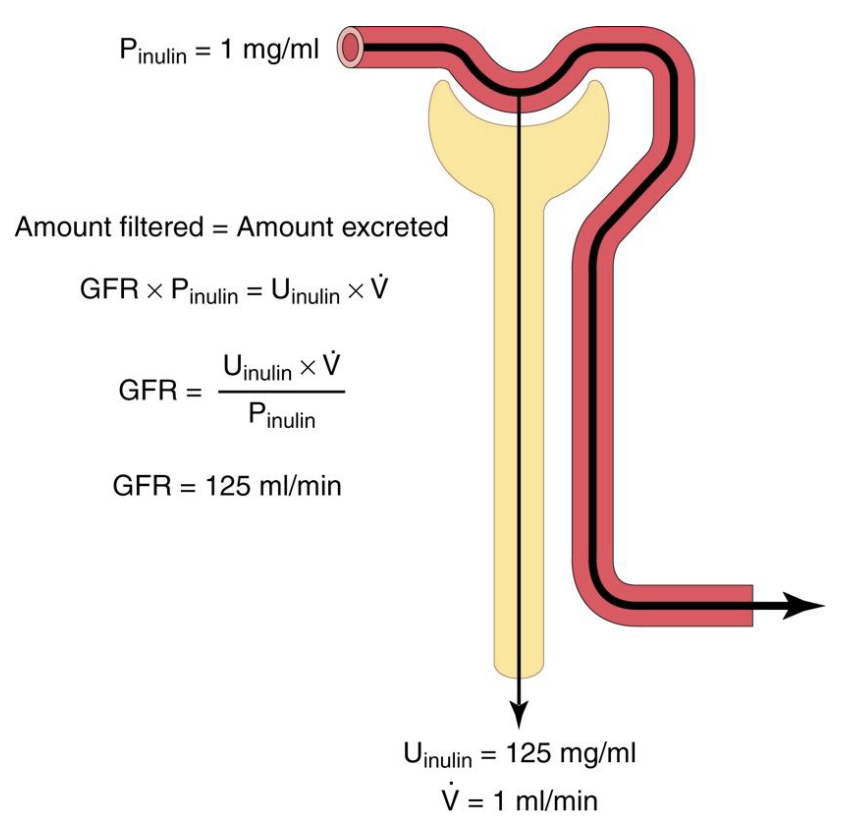
renal plasma clearance outcomes
RPC > GFR, substance is NET secreted
RPC < GFR, substance is NET reabsorbed (or partially filtered)
RBCinulin = GFR
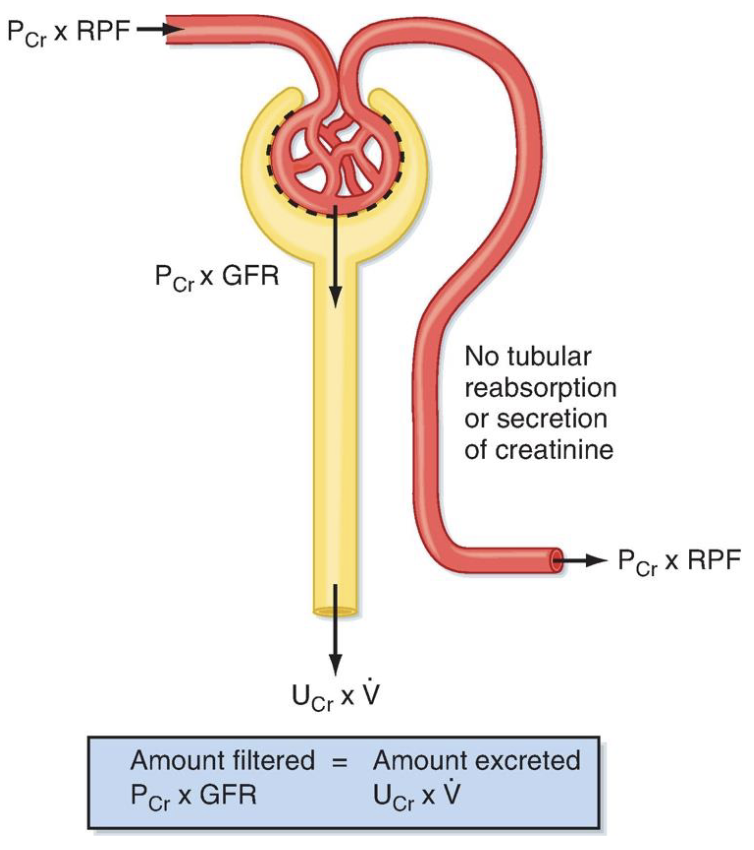
renal plasma clearance of creatinine
a more practical, less invasive way of determining GFR
produced by muscles at a constant rate (byproduct of normal skeletal muscle metabolism)
freely filtered
not reabsorbed
slightly secreted
RPCcr = to true GFR
renal plasma flow definition/equation
the volume of plasma going to the kidneys per minute
PAH is freely filtered and essentially 100% secreted
normal RPF is 625 mL/min
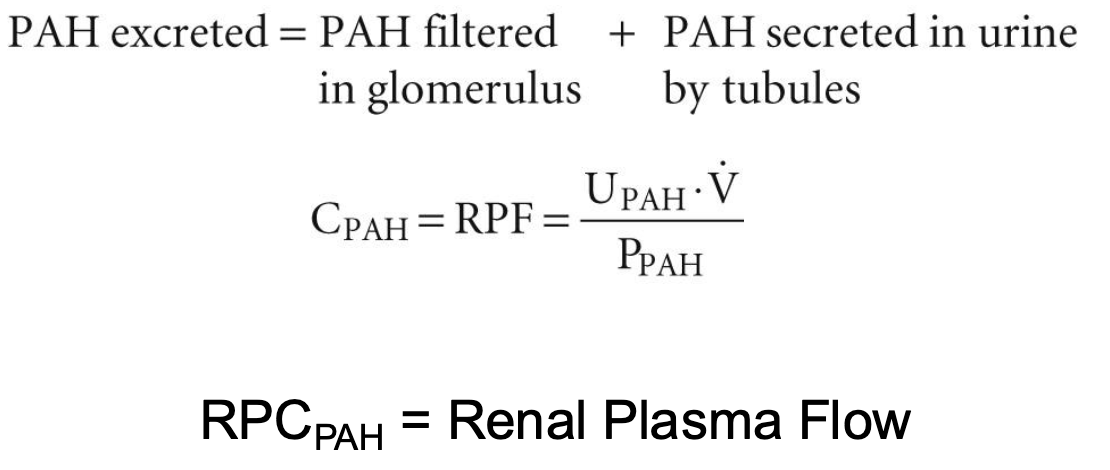
renal plasma flow
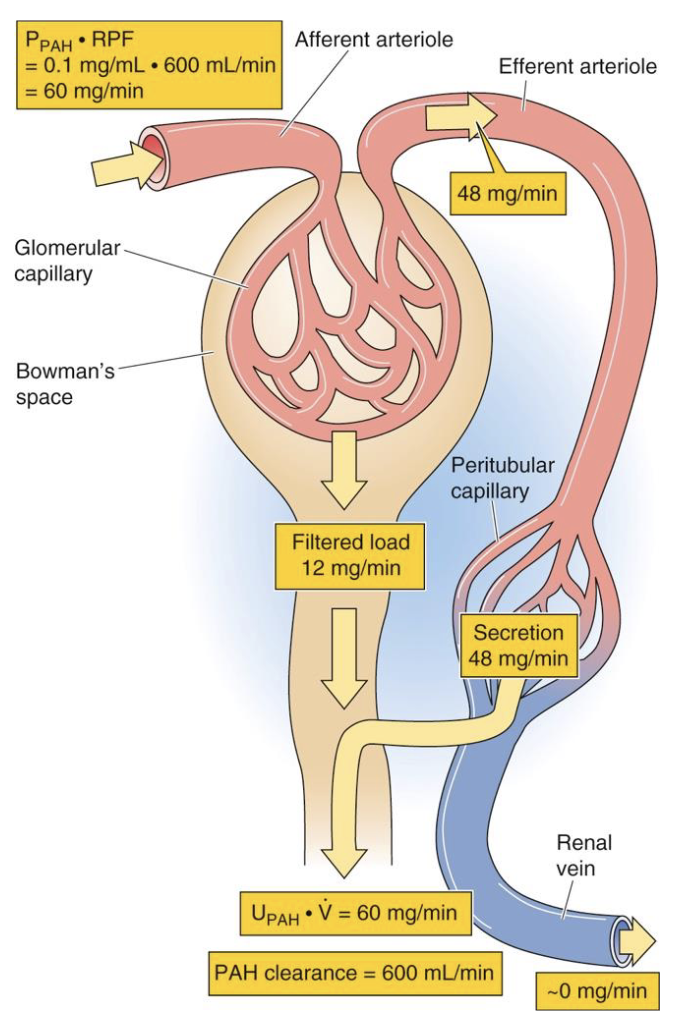
micturition (urination)
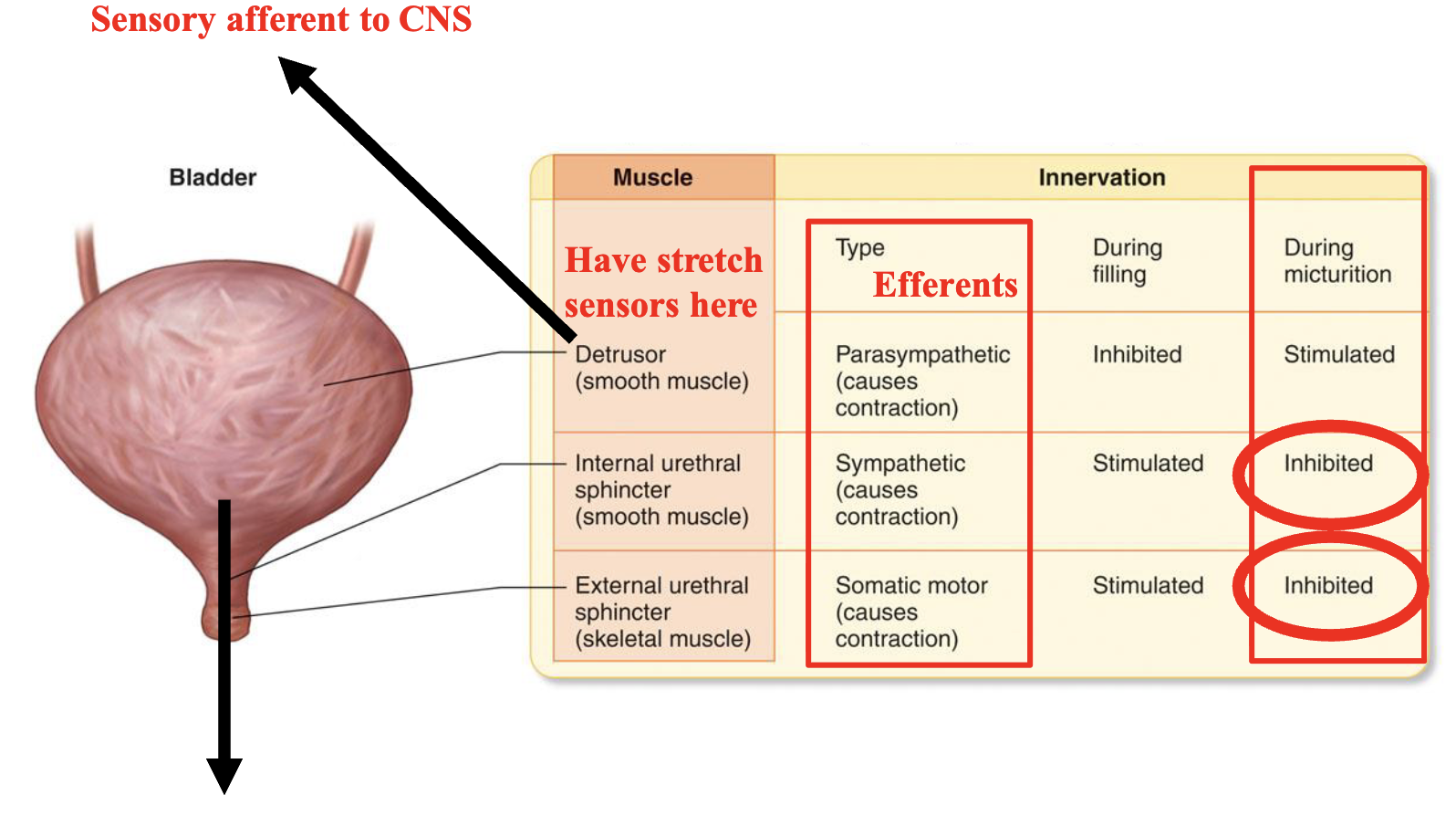
the micturition reflex is a single complete cycle of…
progressive and rapid increase of pressure
a period of sustained pressure
return of the pressure to the basal tone of the bladder
once a micturition reflex has occurred but has not succeeded in emptying the bladder, the nervous elements of this reflex usually remain in an inhibited state for a few minutes to an hour or more before another micturition reflex occurs
as the bladder becomes more and more filled, micturition reflexes occur more and more often and more powerfully
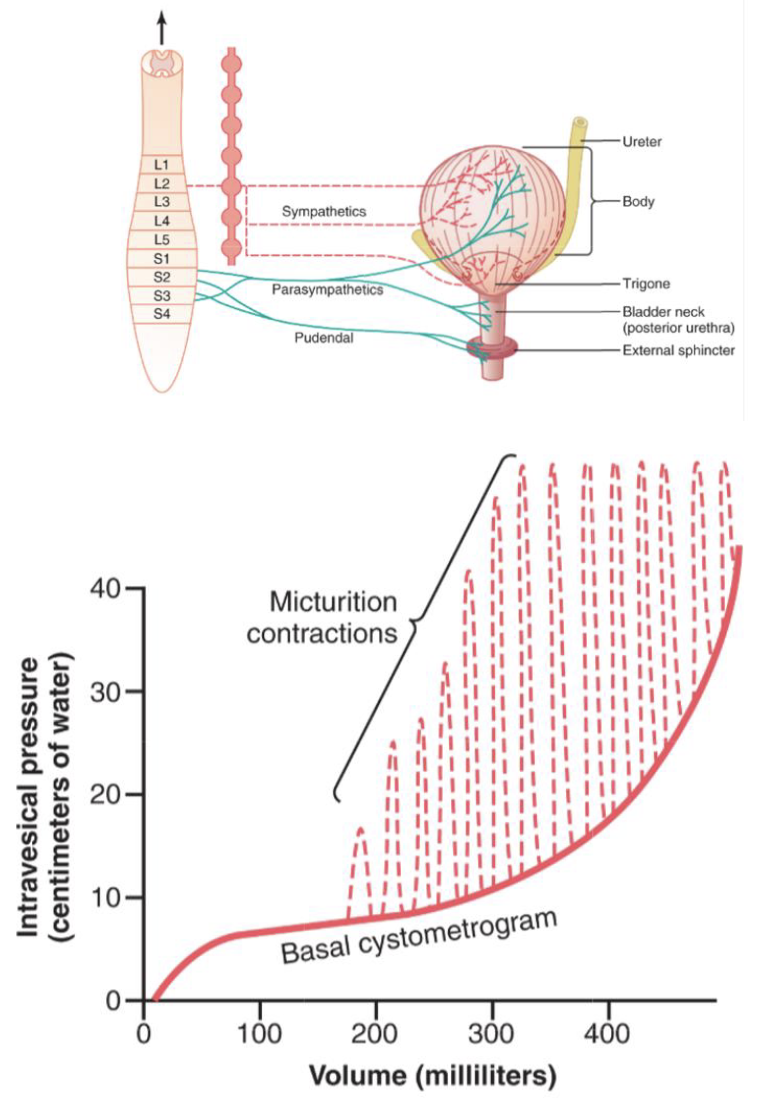
Na+ reabsorption in the proximal tubule
65% of reabsorption occurs here and is non regulated
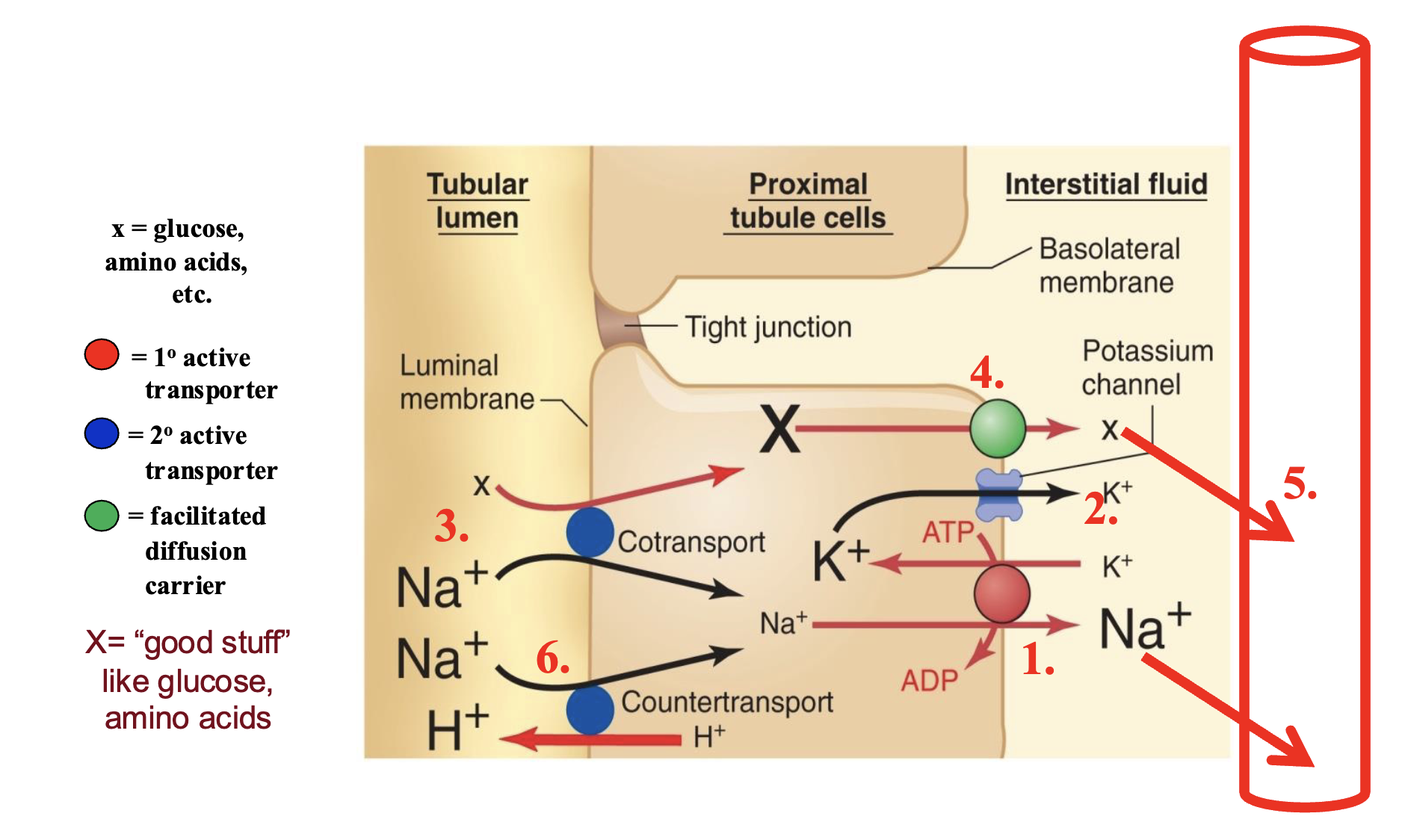
Na+ reabsorption in the distal tubule and cortical collecting duct (distal nephron)
Na+ reabsorption occurring here is regulated by hormones, no Tm
ex. aldosterone builds Na+ channels and Na+/K+ ATPases
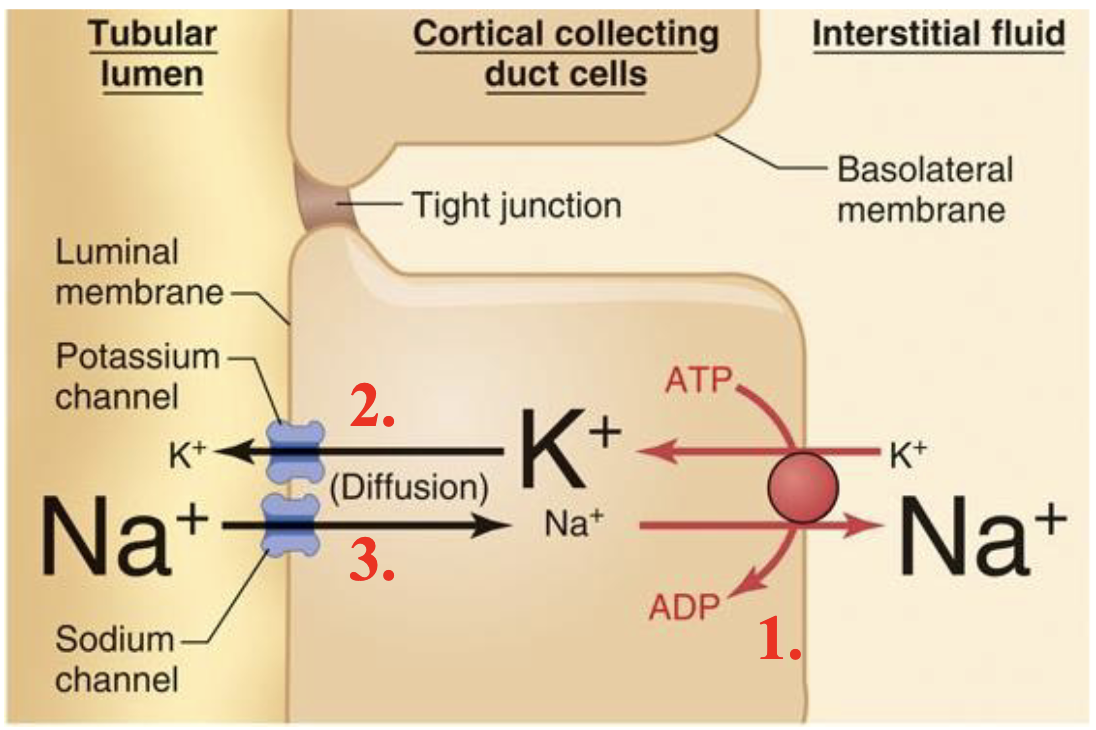
distal tubule/collecting duct
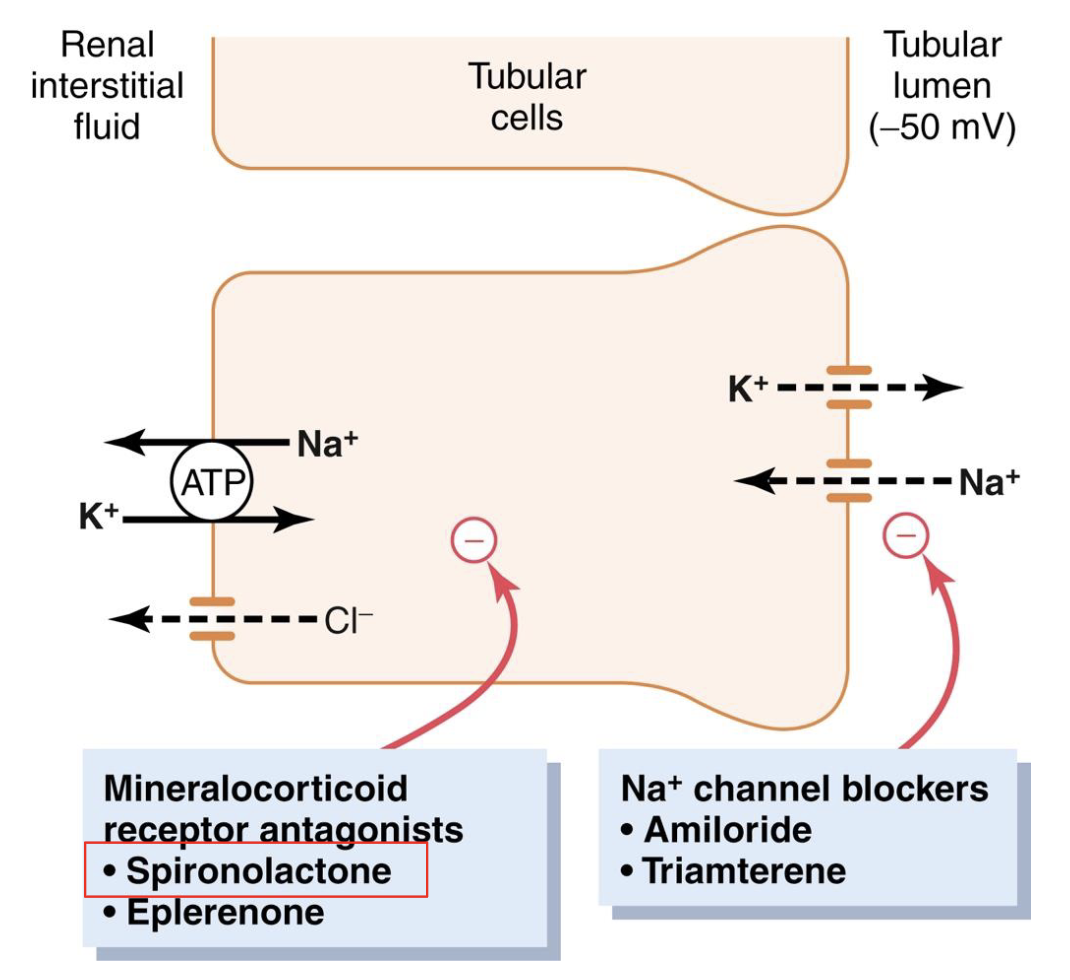
there are diuretics that block the actions of aldosterone, and thus inhibit the reabsorption of Na+ from the distal tubule/collecting duct
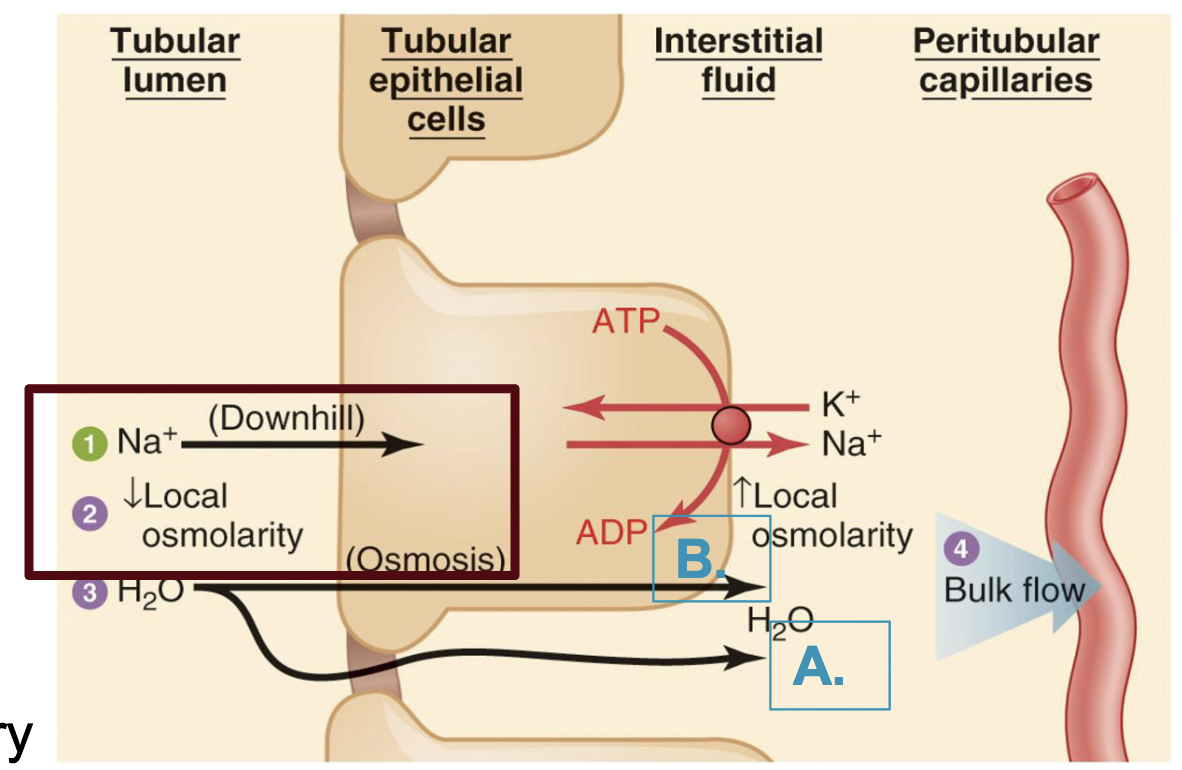
water follows Na+ passively by osmosis (2 routes)
paracellular
main water route in proximal tubule (leaky tight junctions)
non regulated
transcellular
main water route in the distal tubule and collecting ducts (very tight junctions)
requires the insertion of aquaphorins (regulated by ADH/vasopressin)
review: Na+ and H2O reabsorption (proximal tubule/loop of henle)
Na+ reabsorption is high and constant (not regulated)
H2O permeability is high and constant (not regulated)
reabsorption of Na+ and H2O are coupled
review: Na+ and H2O reabsorption (distal tubule/collecting duct)
Na+ reabsorption is variable, is regulated by aldosterone, and is NOT directly coupled to water reabsorption
water permeability is variable, regulated by ADH, and requires the renal medullary gradient
the renal medullary gradient
the countercurrent multiplier system
active transport of NaCl (reabsorption) from the ascending limb
ascending limb is impermeable to water
water reabsorption via osmosis from the descending limb
recycling of urea from the collecting duct
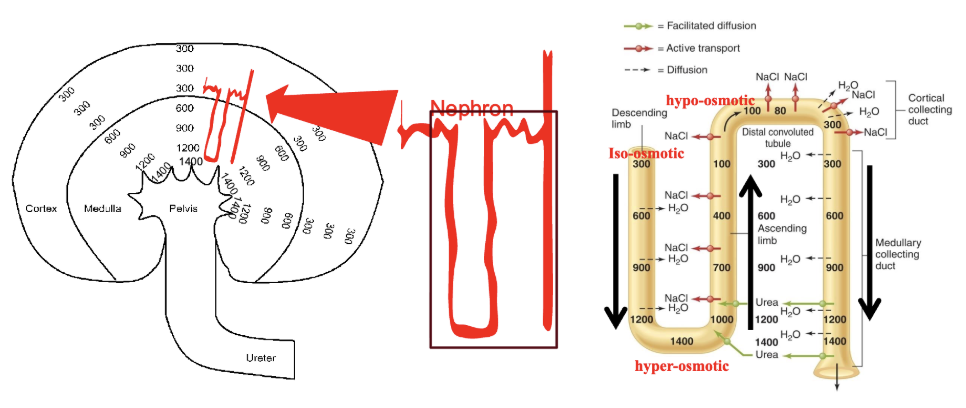
concentration of urine
because of the hyperosmotic medullar ISF, filtrate can become highly concentrated with a low volume in the presence of ADH
net result: excretion of a low volume of highly concentrated urine
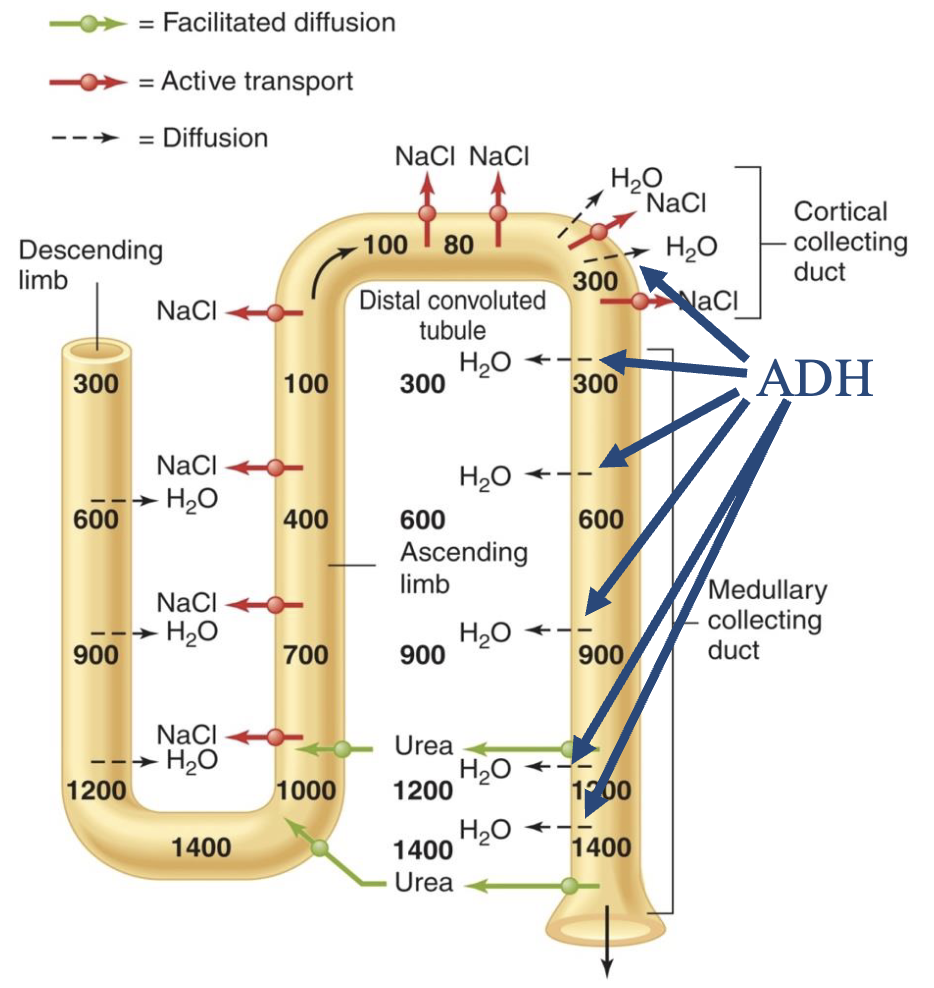
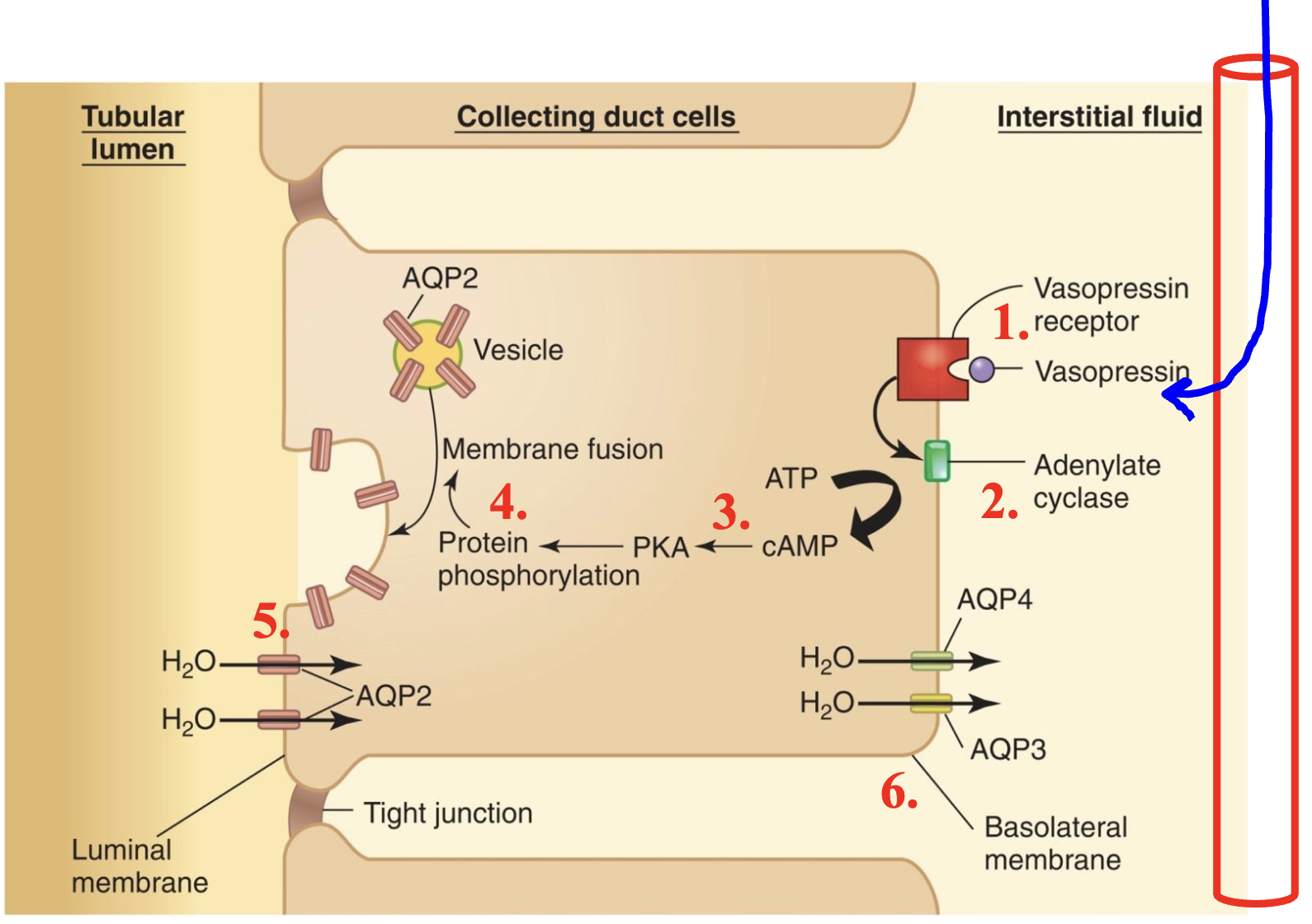
concentration of urine requires ADH
aquaporins 3 and 4 (AQP3, AQP4) are always present in the basolateral membrane. AQP2 is the only present on the luminal membrane if ADH is present
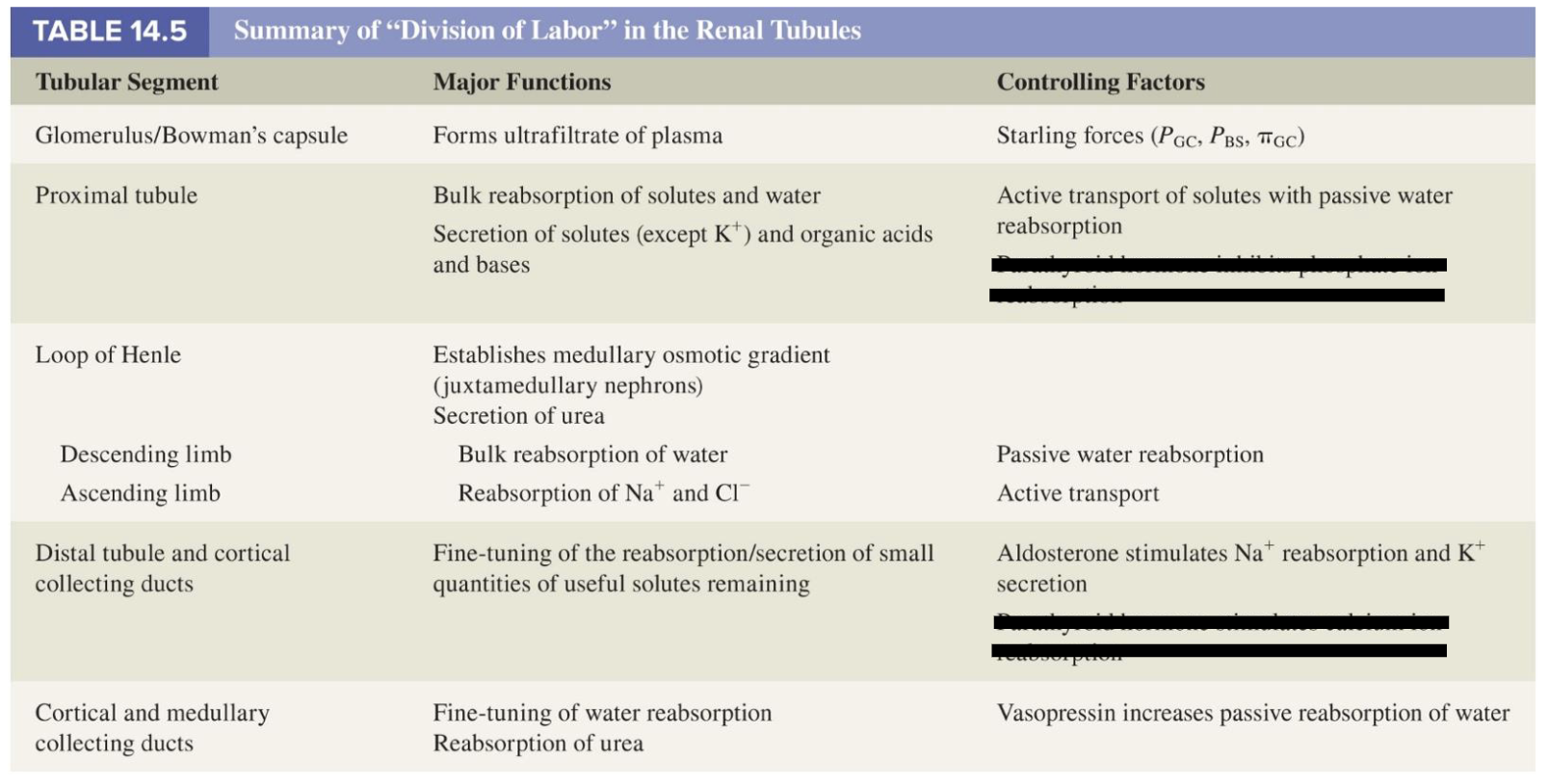
summary: importance of each nephron region
the response to sweating
sweat comes out of your ECF and contains both water and NaCl
both must be preserved after severe sweating in order to maintain blood volume and osmolarity
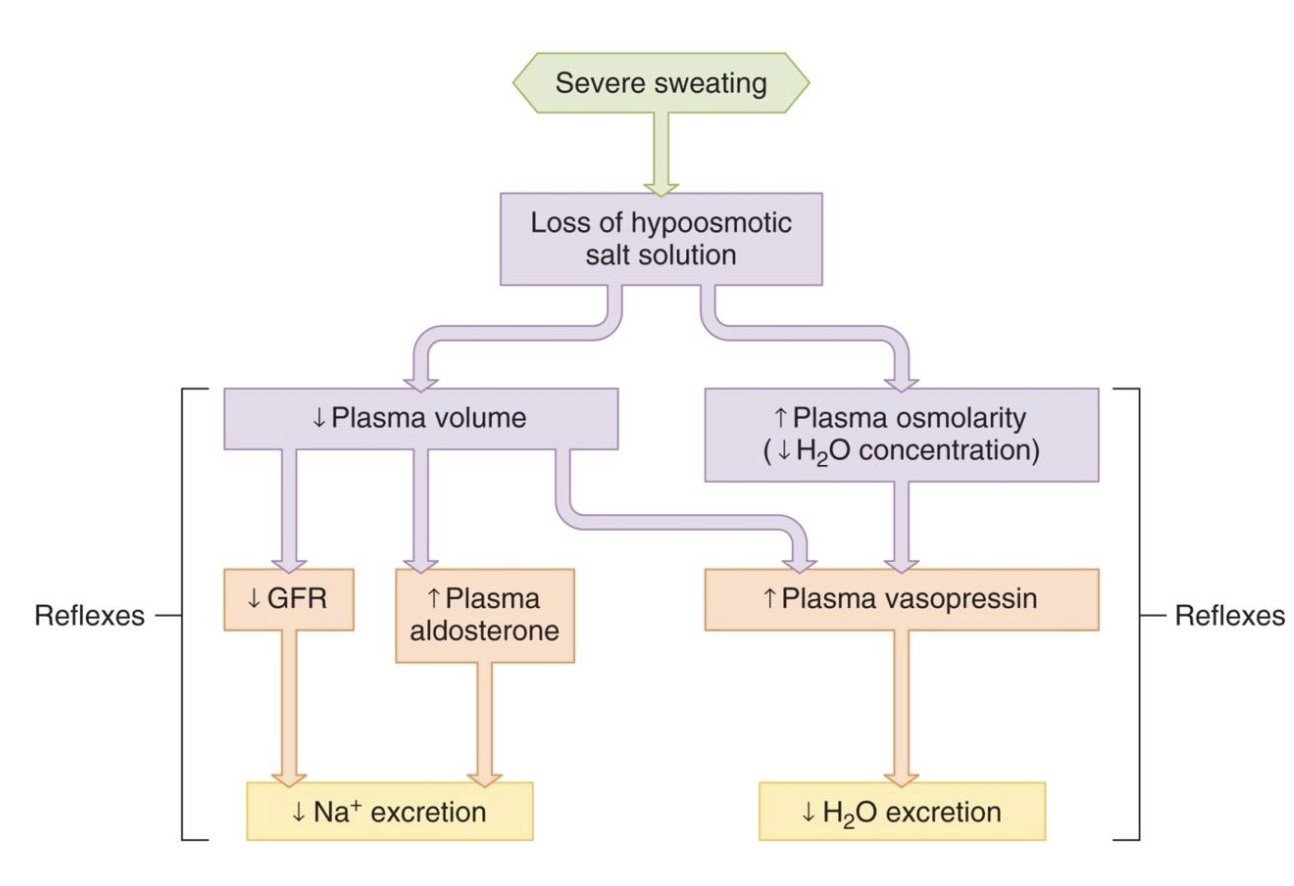
thirst and salt appetite
kidneys can excrete excess water and Na+ that you ingest but can only reduce the rate (cant completely stop excretion) at which you lose them in times when you dont eat/drink enough
you must urinate some volume, so there will be fluid loss even when you are dehydrated
you need regular intake to replace regular losses, and need to intake extra when excess fluid is lost through regular processes like sweating, vomiting, diarrhea, hemorrhage
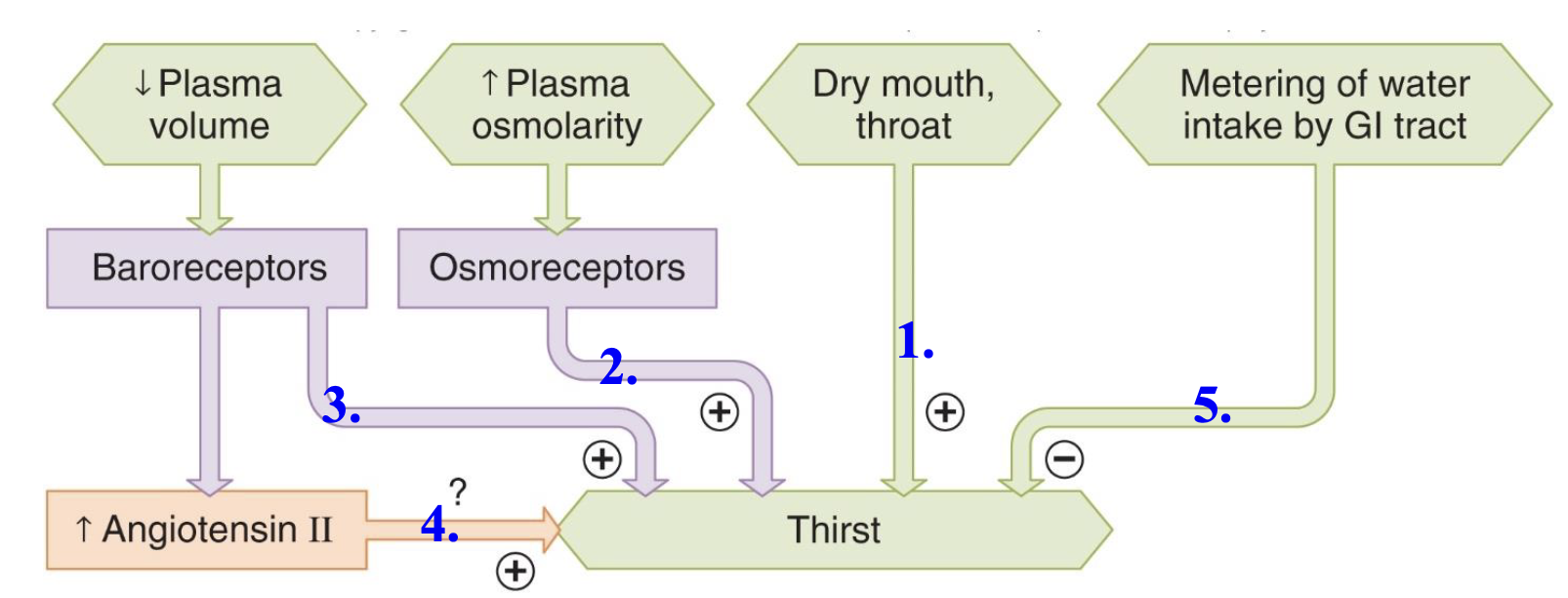
thist
thirst must be obeyed, but keep in mind…
caffeine dilates afferent arterioles
alchohol inhibits ADH secretion
respiratory vs metabolic acid base disorders