Viruses
1/10
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
11 Terms
Central Dogma of Biology
describes the process which expresses genes into proteins.
Dictates that DNA can be converted into RNA and RNA into protein, or RNA into DNA, but proteins can never code for genetic information.
What makes up a virus
Core; genetic material DNA OR RNA (not both)
Capsid; Protective protein coat surrounding core, made up of many capsomeres, common shape is an icosahedron
Nucleocapsid: core + capsid
Envelope; some virus’s have a lipoprotein layer around capsid derived from the host cells membrane
Reproduction
obligate endoparasites → dont have ribosomes or enzymes to synthesize protein coats or DNA
highly specific → only attacks certain cells or affects a certain species
all viruses are agents of disease
Living or Non-living (TANTI)
No cell structure
require a host cell to replicate
dont respond to changes in the environment
non living organisms
Lytic Cycle
Absorption
adhesins bind to host receptors
Penetration
viral genome is transported through the sheath to enter the hosts cytoplasm
Biosynthesis
viral DNA is replicated using DNA replication enzymes of host cell
Viral DNA takes over protein-synthesizing machinery
Assembly or Maturation
replicated genome and new capsids assemble forming new virions
Lysis or Release
Host cell ruptures - viral DNA instructs production of enzyme
(eg T4 bacteriophage)
Lysogenic Cycle
steps of lytic
However before biosynthesis there is a period of integration
where the virus is latent and each time the host cell divides the virus’s genome is copied
Dormant stage is called the provirus
induction event - activates virus (eg changes in temp)
Phage Lambda
Retroviruses
genome comprises RNA
reverse transcriptase - turns RNA into DNA
integrase - integrates DNA into host' cells DNA
Human Immunodeficiency Virus
virus approaches a T-helper lymphocyte
undergoes the lysogenic cycle
after a latency period virus activates
rna and viral proteins are then assembled to continue to produce new viruses
How do mutations occur
In retroviruses reverse transcriptase makes many mistakes leading to incorrect copying of RNA to DNA
this leads to mutations
Life Cycle of a Retrovirus
virus approaches a helper t-lymphocyte
viral glycoproteins attach to the cell surface membrane
enter via a endocytosis
RNA + reverse transcriptase are released into host cell
RNA is synthesized into DNA
DNA moves into the nucleus and integrates with the hosts DNA
every time the cell divides, the viral dna divides with it, increasing the number of host cells infected
after a latency period (5yrs) the virus becomes active again
using the hosts protein synthesizing material creating RNA and viral proteins assembling new viral particles
through exocytosis the viruses are released

label.
a. glycoprotein - targeting and binding with the host cell.
b. envelope
c. viral genome
d. nucleocapsid/capsid/protein coat
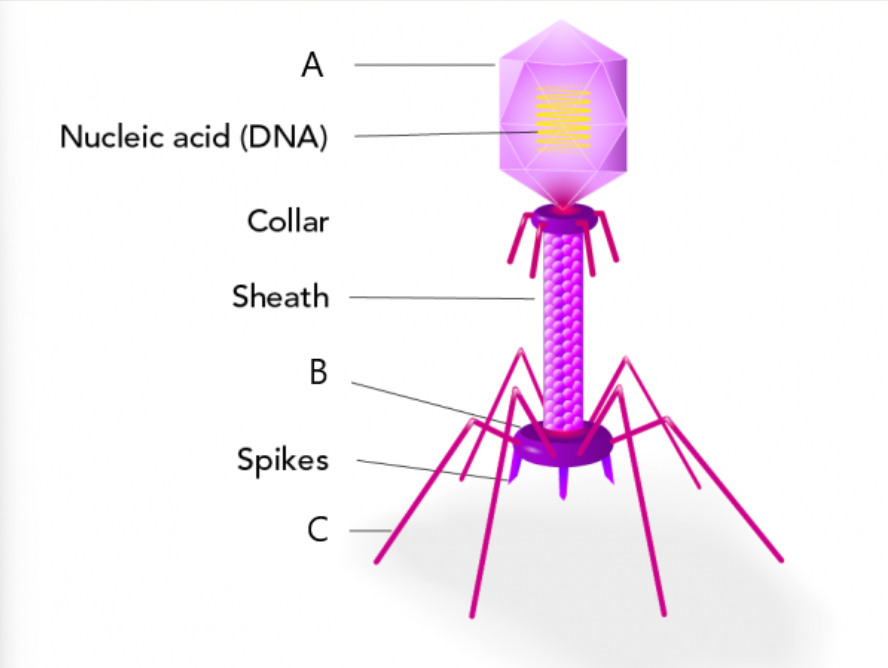
label + name virus
A. Polyhedral Head/Capsid
B. Base Plate
C. Tail Fiber
→ this is a bacteriophage