Pre AP Biology Final Exam Outline 2024
1/64
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
65 Terms
Experimental Design
The process of planning a scientific experiment, including identifying variables, groups, constants, hypothesis, and title.
Independent Variable
The variable that is changed or manipulated in an experiment.
Dependent Variable
The variable that is measured or observed in response to the independent variable.
Control Group
The group in an experiment that does not receive the treatment and is used as a baseline for comparison.
Constants
Factors in an experiment that are kept the same to ensure a fair test.
Hypothesis
A testable prediction, usually written as an If...then... statement.
Data Organization
The process of arranging data in a structured manner for analysis.
Data Interpretation
The analysis and understanding of data, often through graphs and tables.
Macromolecules
Large molecules essential for life, including carbohydrates, lipids, proteins, and nucleic acids.
Monomer
The basic unit that makes up a polymer.
Polymer
A large molecule made up of repeating units of monomers.
Mitosis
The process of cell division resulting in two identical daughter cells.
Diffusion
The movement of molecules from an area of high concentration to low concentration.
Active Transport
The movement of molecules against the concentration gradient requiring energy.
Enzymes
Biological catalysts that speed up chemical reactions in living organisms.
ATP (Adenosine Triphosphate)
The energy currency of the cell.
Cellular Respiration
The process of converting glucose into ATP in the presence of oxygen.
Photosynthesis
The process by which plants convert sunlight into energy in the form of glucose.
Homeostasis
The maintenance of stable internal conditions in living organisms.
DNA Replication
The process of copying DNA to produce two identical DNA molecules.
Transcription
The process of creating mRNA from DNA.
Translation
The process of protein synthesis where mRNA is decoded to produce a specific protein.
Mutation
A change in the DNA sequence that can result in genetic variation.
Punnett Square
A diagram used to predict the outcome of a particular cross or breeding experiment.
Abiotic factor
Non-living components of an ecosystem, such as sunlight, temperature, water, and soil.
Biotic factor
Living components of an ecosystem, including plants, animals, fungi, and bacteria.
Food Webs
A system of interlocking and interdependent food chains in an ecosystem.
Decomposer
Organisms that break down dead or decaying organisms.
Consumer
Organisms that obtain energy by consuming other organisms.
Producer
Organisms that produce their own food through photosynthesis or chemosynthesis.
Carnivore
Animals that primarily eat meat.
Herbivore
Animals that primarily eat plants.
Autotroph
Organisms that can produce their own food.
Heterotroph
Organisms that obtain energy by consuming other organisms.
Omnivore
Animals that eat both plants and animals.
Energy Transfer
The movement of energy through an ecosystem, often depicted in energy pyramids.
Carrying Capacity
The maximum population size of a species that an ecosystem can sustain indefinitely.
Limiting Factors
Factors that restrict the growth of a population, such as availability of food, water, or habitat.
Natality
The birth rate of a population.
Mortality
The death rate of a population.
Emigration
The movement of individuals out of a population.
Immigration
The movement of individuals into a population.
Density-dependent factors
Factors that influence population growth based on the population's density.
Density-independent factors
Factors that affect population growth regardless of the population's density.
Symbiotic Relationships
Close and long-term interactions between different species.
Ecological Succession
The process of change in the species structure of an ecological community over time.
Nutrient Cycles
The movement and exchange of nutrients in an ecosystem.
Keystone Species
A species that has a disproportionately large effect on its environment relative to its abundance.
Evolution
The process of change in the heritable characteristics of biological populations over successive generations.
Homologous Structures
Structures that are similar in different species because of common ancestry.
Vestigial Organs
Organs that have lost their original function through evolution.
Embryonic Development
The process by which an embryo develops.
Fossils
The preserved remains or traces of ancient organisms.
Charles Darwin
English naturalist who proposed the theory of evolution by natural selection.
Gradualism
The theory that evolution occurs slowly and steadily.
Punctuated Equilibrium
The theory that evolution occurs in rapid bursts separated by periods of little change.
Geographic Isolation
The separation of populations by physical barriers.
Reproductive Isolations
Mechanisms that prevent different species from interbreeding.
Experimental Design
The process of planning and conducting a scientific experiment to ensure valid results and draw accurate conclusions."
Properties of Water
High specific heat: resists temperature changes
Universal solvent: dissolves many substances
Cohesion & adhesion: water molecules stick together & to other substances
Surface tension: forms a "skin" on the surface
structure of a water molecule
Consists of two hydrogen atoms and one oxygen atom
Oxygen atom is slightly negatively charged, while hydrogen atoms are slightly positively charged
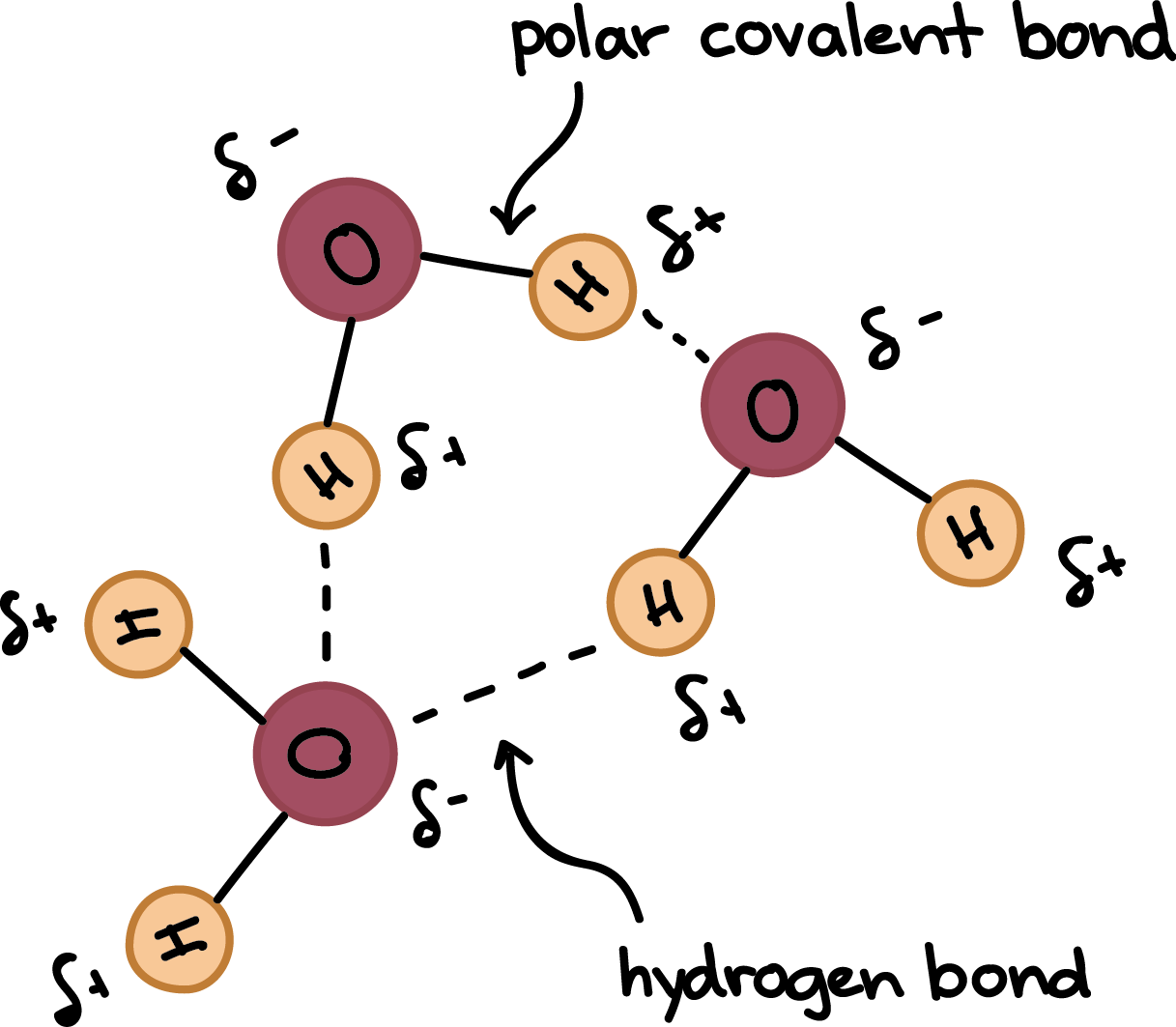
CHNOPS
Carbon, Hydrogen, Nitrogen, Oxygen, Phosphorus, Sulfur. Key building blocks in biological molecules.
types of macromolecules and the elements that compose each and their monomers
Carbohydrates: composed of C, H, O; monomer is monosaccharide.
Lipids: composed of C, H, O; no true monomer.
Proteins: composed of C, H, O, N; monomer is amino acid.
Nucleic Acids: composed of C, H, O, N, P; monomer is nucleotide.