Biology movement of substances across cell membranes and nutrient in humans
1/40
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
41 Terms
Independent and dependent variable
Factors under investigation what you changes
Factors that changes according to independent variable
Eukaryotic cells and prokaryotic cells
True nucleus and membrane bound organelle( mitochondria )
No nucleus and no membrane bound organelle
Process of scientific investigation
Make observation
Ask relevant questions
Propose a hypothesis and make prediction
Design and conduct experiments
Analyse data and draw conclusion
Cells in hypotonic solution (solution with higher water potential than cytoplasm)
Water enters cell by osmosis
Animals cells swell and burst
Plant cell become turgid
Cells in hypertonic solution ( solution with lower water potential than cytoplasm)
Water leaves cells by osmosis
Annals cells shrink and become wrinkled
Plants cells become flaccid or plasmolyed
Cells in isotonic solutions (solution with same water potential as cytoplasm)
no net movement of water in plant and animal cell
Cell membrane nucleus mitochondria
Control movement of substances in and out
Contains genetic material
Produce atp to carry out aerobic respiration
Chloroplast vacuole cell wall
Site of photosynthesis convert light energy to chemical energy
Transport food in animal cell keep plant cell in turgid state
Give shape to plant cell
Rough and smooth endoplasmic reticulum
Transport protein produces at ribsomes
Syntheses and transport lipids within cytoplasm
Plant cell and animal cell difference in structure
Has cell wall large vacuole has chloroplast while animals cells don’t
Osmosis
Net movement of water molecules from a region of higher water potential to a region of lower water potential through a differentially permeable membranes(only certain substances can enter)
Diffusion
Movement of particles from a region of high concentration to a region of lower concentration gradient , when particles are evenly distributed no net movement of of particles atp not required
Active transport
Need carrier protein movement of substances (moved from a region of low concentration to a region of high concentration) food absorption of small intestine , transcription of glucose and amino acid
In mineral in root of plant
And glucose in gut for humans
Phagocytosis
Engulf and digest large particles (second line defense)require energy and involve cell membrane (wbc engulf pathogens by phagocytosis)
differentially permeable
Only certain substances can pass through
Small non polar (oxygen CO2 and lipid soluble )and water can be dissolve while glucose amino acid can’t pass through
Autotrophs heterotrophs
Make own food (plants) by light or chemical energy
Depend on others for food
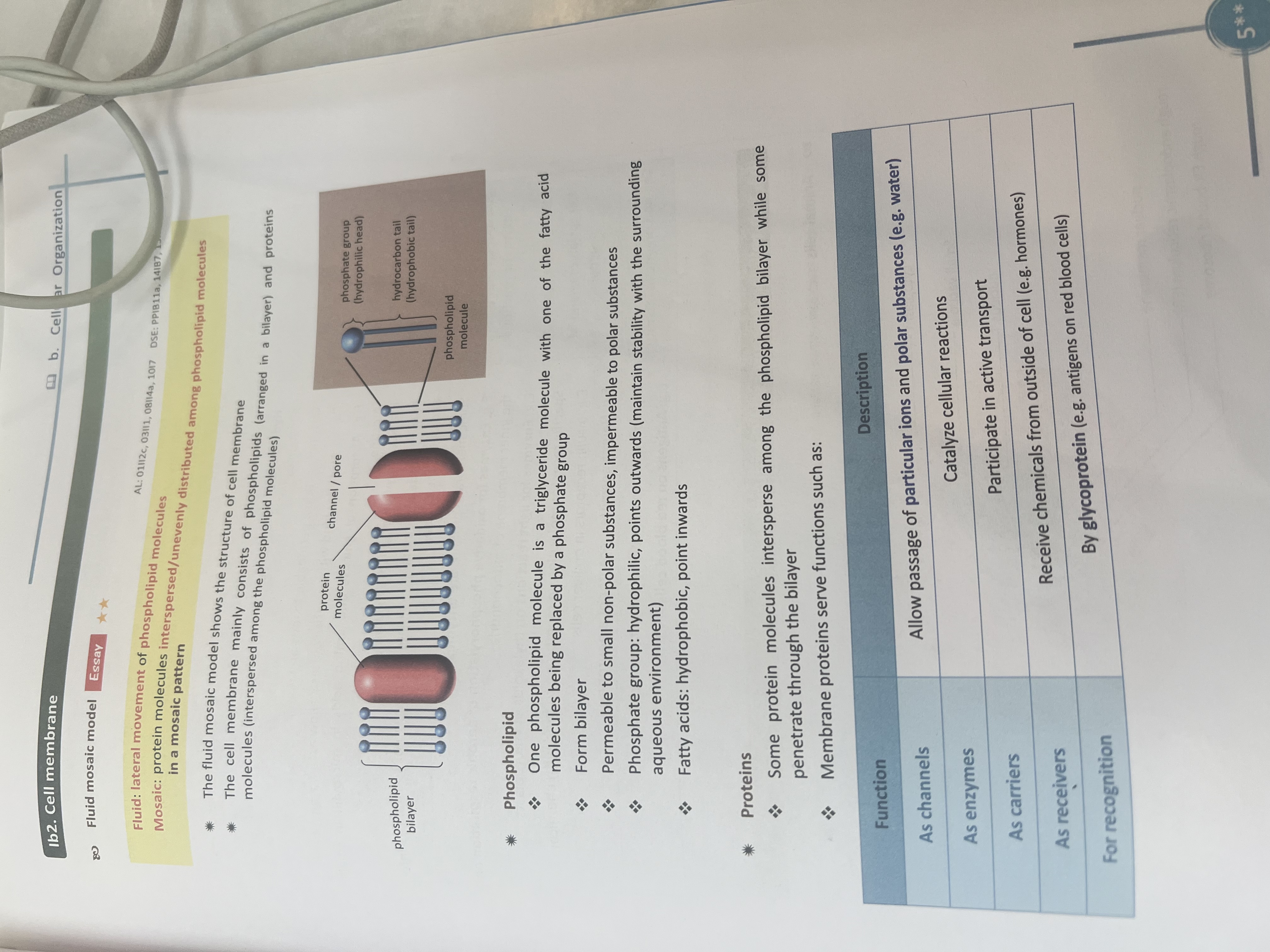
Fluid mosaic model
Fluid:lateral movement of phospholipid molecules
Mosaic:protein molecules uneven distributed among phospholipid molecules in mosaic pattern
Phospholipid bilayer:permeable to (small non polar substance) not polar
Carrier protein:active transport
Channel protein allow passage of ions and polar substance water
Types of teeth
Incisor canine premolar and molar
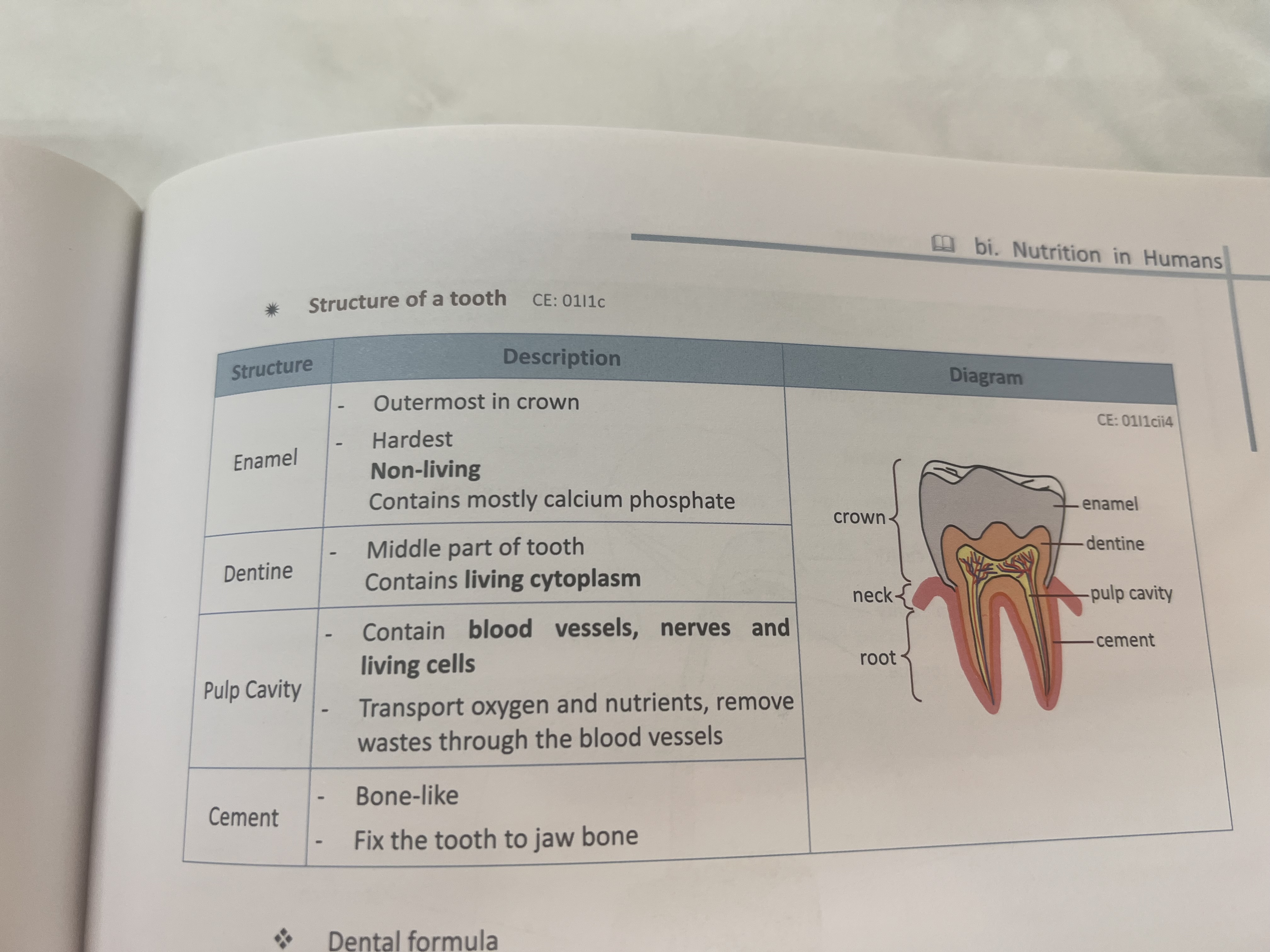
Enamel dentine pulp cavity and cement function
Hardest non living contain calcium phosphate
Living
Contain blood vessel nerve transport oxygen and nutrients remove waste
Bone like -fix tooth to jaw bone
Main purpose of digestion
Breakdown food into smaller moelcues for absorption
Two types of digestion
Physical and chemical
Where does physical digestion occur
Mouth and stomach
What is mastication
Process of chewing food to break it down
What enzyme involved in chemical digestion
Amylase protease lipase
Where does Most of absorption take place
Small intestine
Role of liver
Regulate blood glucose level
Store glycogen iron and vitamins
Deamination
Form bike vitamin a
Detoxification
What are faces
Waste produced from digestive system
How Does water absorption occur in intestines
Through osmosis into blood capillaries
Function of stomach in digestion
Churn food and mix it with gastric juice for digestion
Role of enzyme in digestion
To break down compelx molecules into simple forms
Peristalsis
To prevent constipation
Function of bile
To emulsify fats for easier digestion and absorption
What are villi
Small finger like projection in small intestine that can increase surface area for absorption
What nutrients are absorbed in small intestine
Carbs protein fats vitamini minerals
Siginifnace of detoxification in liver
Remove harmful substances from blood stream