CH 14: duplex scanning and color flow imaging of the abdominal vessels
1/218
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
219 Terms
Duplex and color flow imaging at the aortoiliac vessels can determine the presence/absence of what pathology?
Significant stenosis
Duplex and color flow imaging at the aortoiliac vessels can follow up/evaluate what 2 structures/pathologies?
Bypass grafts
Aneurysms
Which structure can duplex and color flow imaging be used to determine the presence/absence of significant stenosis?
Aortoiliac vessels
Which structure can duplex and color flow imaging be used to follow up on bypass grafts and evaluate aneurysms?
Aortoiliac vessels
Duplex and color flow imaging at the renal arteries determine if what sonographic finding is seen?
Significant stenosis greater than or equal to 60% diameter reduction
Which structure can duplex and color flow imaging be used to determine if a significant stenosis of greater than or equal to 60% diameter reduction is present?
Renal arteries
Duplex and color flow imaging at the kidneys can determine the presence/absence of what pathologies/procedures? (2)
Disease
Transplants
Which structure can duplex and color flow imaging be used to determine the presence/absence of disease and evaluates transplants?
Kidneys
Duplex and color flow imaging at the mesenteric arteries can determine the presence/absence of what pathology?
Significant stenosis
Which structure can duplex and color flow imaging be used to determine the presence/absence of a significant stenosis?
Mesenteric arteries
Stenosis of the mesenteric arteries can account for or cause what pathology?
Chronic mesenteric bowel ischemia
The stenosis of which structure can account for or cause chronic mesenteric bowel ischemia?
Mesenteric arteries
Duplex and color flow imaging at the liver can evaluate the presence/absence of what pathology/procedure? (2)
Portal hypertension
Pre/post liver transplants
Which structure can duplex and color flow imaging be used to evaluate for suspected portal hypertension and evaluate pre/post liver transplants?
Liver
List the 6 limitations of abdominal duplex and color doppler imaging.
Patient body habitus
Bowel gas
Scar tissue from previous abdominal surgeries
Rapid respirations
Patient can’t hold their breath
Non-fasting patient
With duplex and color flow imaging, the appropriate transducer should be selected according to patient ______.
For example, adults will have what kind of transducer and what frequency?
Size
Curvilinear, 5 MHz
In both the sagittal and transverse, doppler and color flow imaging can be used to evaluate _____________ and _______________ patterns.
The sonographer will observe for what 2 pathologies?
Grayscale, Color-flow
Aneurysm
Plaque
In the sagittal plane and with duplex/color flow imaging, what should the doppler angle be set at for accurate PSVs?
Less than or equal to 60 degrees
What doppler angle is the standard/best for duplex imaging?
@ 60 degrees
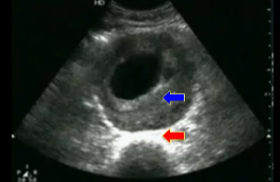
Disregarding the arrows, what pathology is seen here?
Aneurysm (thrombus)
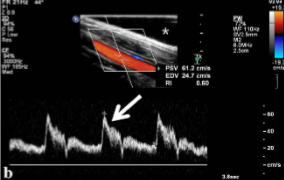
What doppler angle should be used for duplex imaging?
Less than or equal to 60 degrees
What structures can be evaluated for an aortoiliac study? (8)
Prox aorta
Mid aorta
Distal aorta
Bifurcation
Bilateral iliac arteries
Celiac artery
SMA
Renal artery
What 2 things are kept in mind when measuring the aorta?
Measured outer to outer
Measured at maximum diameter
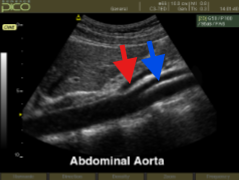
What structure is seen at the red arrow?
What structure is seen at the blue arrow?
Celiac artery
SMA
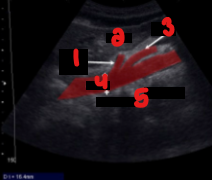
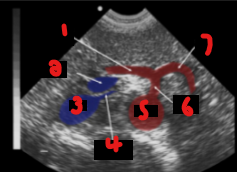
Label the crossed-out structures on this image.
Celiac artery
Liver
SMA
Aorta
Vertebra
Label the crossed-out structures on this image.
Hepatic artery
Venous confluence
IVC
Left renal vein
Aorta
Celiac artery
Splenic artery
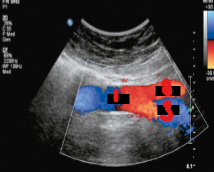
Label the crossed-out structures on this image.
Aorta
RT CIA
LT CIA
What velocity criteria is used for a stenosis at the aorta? (2)
2:1
4:1
What dilatation measurement qualifies as an aneurysm?
Greater than 3 cm
An increase in diameter of __% or more from the adjacent normal portion qualifies an artery as aneurysmal.
50%
List the 2 qualifications that label an artery aneurysmal.
Dilatation greater than 3 cm
Diameter greater than 50%
List the 2 qualities of a majority of AAAs.
Atherosclerotic
Infrarenal
A majority of AAAs are located where?
Infrarenal
When an aneurysm is found, what 2 factors should be noted?
Type of aneurysm
Presence of thrombus
When examining an aneurysm, the sonographer should take note of what kind of aneurysms is here? (3)
True (fusiform/saccular)
False/Pseudo
Dissecting
What is the most frequent complication of an AAA?
Rupture
What are the 2 complications of an AAA?
Rupture
Embolization
What are the 2 primary complications of peripheral arterial aneurysms?
Thrombosis
Embolization
What is the most frequent complication of peripheral arterial aneurysms?
Embolization
It is not uncommon for both abdominal and peripheral aneurysms to contain varying amounts of what?
Thrombus
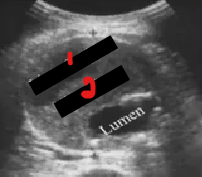
Label the crossed-out structures on the image.
What pathology is this?
Liquefaction
Thrombus
Thrombus within aneurysm
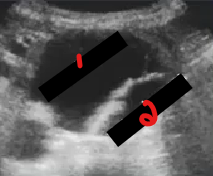
Label the structures crossed out on this image.
What pathology is this?
True lumen
False lumen
Dissecting aneurysm
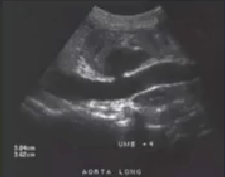
What pathology is seen here?
Pseudoaneurysm
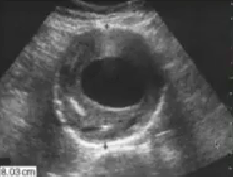
What pathology is seen here?
Aneurysm with thrombus
Many patients having a renal doppler study present with what clinical symptom?
Systemic hypertension
Define ‘systemic hypertension.’
Sustained elevated arterial blood pressure
Systemic hypertension can occasionally be caused by what other pathology?
Renal artery stenosis
Renal artery stenosis can be secondary to what 2 pathologies?
Atherosclerosis
Fibromuscular dysplasia
Fibromuscular dysplasia is __________.
Hereditary
Fibromuscular dysplasia could be related to…
Hormones
Fibromuscular dysplasia is seen mainly in which gender?
Women
Which structure is fibromuscular dysplasia commonly seen in?
Renal arteries
Renal artery stenosis _______ blood flow to the kidney
In return, the kidney produces the enzyme ______
Which will promote the conversion of ______________ to __________
This will result in ___________
Which will cause _____________ of the blood vessels
The result of this process is called _____________________
Reduces
Renin
Angiotensinogen
Angiotensin
Hypertension
Vasoconstriction
Renovascular hypertension
The narrowing of the renal arteries (renal artery stenosis) reduces blood flow to the kidneys.
What does the kidney do in response to this?
Produce the enzyme, renin
When the kidneys produce renin, what will it promote?
Conversion from angiotensinogen to angiotensin
The conversion of angiotensinogen to angiotensin will result in what pathology?
What does this pathology cause?
Hypertension
Vasoconstriction of the blood vessels
What is renovascular hypertension? (5)
Renal artery stenosis →
Renin production →
Angiotensinogen becomes angiotensin →
Hypertension →
Vasoconstricted blood vessels
Name the pathology:
“The narrowing of the renal artery reduces blood flow to the kidney and in response, the kidney produces the enzyme renin, which promotes conversion of angiotensinogen to angiotensin, which results in hypertension which causes vasoconstriction of the blood vessels.”
Renovascular hypertension
What is the function of ‘angiotensinogen’?
Regulates BP
What is the function of ‘angiotensin’?
Increases BP
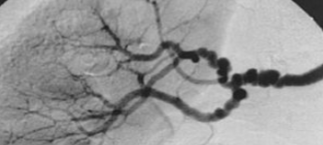
The appearance of these vessels are similar to what?
What is the name of this pathology if renal artery stenosis is secondary to it?
Beads
Fibromuscular dysplasia
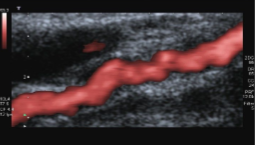
The appearance of these vessels are similar to what?
What pathology is secondary to this pathology?
What is the name of this pathology?
Beads
Renal artery stenosis
Fibromuscular dysplasia
With varying renal doppler protocols, some can require velocity data from which 2 vessels at their proximal segments?
Celiac artery
SMA
Where is PSV typically obtained?
Distal to the SMA
Which 2 imaging planes can be used to locate the renal arteries?
Transverse
Coronal
What is the landmark for finding the left renal artery in transverse?
Left renal vein
Where is the right renal artery found off of the aorta?
Anterolateral
When performing a renal doppler exam, what structure should still be evaluated bilaterally for their size and overall appearance?
Kidneys
List the 6 arteries that can be dopplered for PSVs and EDVs for a renal doppler.
Proximal renal arteries bilaterally
Mid renal arteries bilaterally
Distal renal arteries bilaterally
Segmental arteries (upper/lower pole)
Interlobar arteries (upper/lower pole)
Accessory renal arteries
Where are the segmental arteries located on the kidneys?
Pelvis of the kidney
Where are the interlobar arteries located on the kidneys? (2)
More distal and outward beyond the pelvis
Not yet to the edge
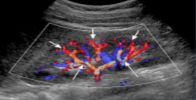
What vessels represented by the short white arrows?
What vessels are represented by the long white arrows?
Interlobar arteries
Segmental arteries
Which 2 vessels are typically dopplered in the kidneys for a renal doppler?
Segmental arteries
Interlobar arteries
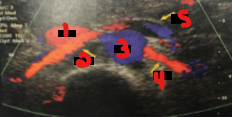
Label the crossed-out structures seen on this image.
IVC
RRA
Aorta
LRA
LRV
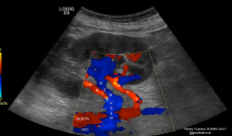
What is seen in this image?
How will the sonographer doppler this image?
Accessory renal arteries
Doppler each one
What waveform is seen in the renal arteries?
Low resistance flow
What waveform is seen in the kidney arteries?
Low resistance flow
What waveform is seen in the aorta?
High resistive flow
What waveform is seen with vessels that are constantly feeding organs?
Low resistance flow
What does ‘RAR’ stand for?
Renal to aortic ratio
What is the formula for the RAR?
Renal Artery PSV / Aortic PSV

This formula is used to calculate the…
RAR
What is a normal RAR?
Less than 3.5
What is an abnormal RAR?
Greater than or equal to 3.5
A RAR greater than or equal to 3.5 indicates a __% or greater diameter reduction.
60%
An RAR greater than or equal to 3.5 indicates what diameter reduction?
60% or greater
A PSV with post stenotic turbulence greater than 180-200 is suggestive of what diameter reduction?
Greater than or equal to 60%
What PSV with post stenotic turbulence is suggestive of a greater than or equal to 60% diameter reduction?
180-200
A PSV of greater than 180-200 with __________________ is suggestive of a greater than or equal to 60% diameter reduction
Post stenotic turbulence
Post stenotic turbulence should be…
Documented
List the 3 ways RAR may not be accurate.
When AAA is present
PSV of aorta is less than 40 cm/s
PSV of aorta is greater than 90 cm/s
Kidneys are examined for abnormalities.
List 2 examples.
Cysts
Cortical thinning
What is the typical length measurement for the kidneys?
10 - 12cm
List the 2 other terms for end diastolic ratio (EDR).
Parenchymal resistance ratio (PRR)
Diastolic/systolic ratio (DSR)
Parenchymal resistance ratio is another term for what?
End diastolic ratio
Diastolic/systolic ratio is another term for what?
End diastolic ratio
What does ‘EDR’ stand for?
End diastolic ratio
What does ‘PRR’ stand for?
Parenchymal resistance ratio
What does ‘DSR’ stand for?
Diastolic/systolic ratio
What is used to characterize the vascular resistance in the kidney?
End diastolic ratio/Parenchymal resistance ratio/Diastolic-systolic ratio