Soil, Water Cycle, Carbon Cycle
1/40
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
41 Terms
soil
The loose, weathered material on Earth's surface in which plants can grow.
Humus
material formed from decaying leaves and other organic matter

Decomposition
the state or process of rotting; decay.
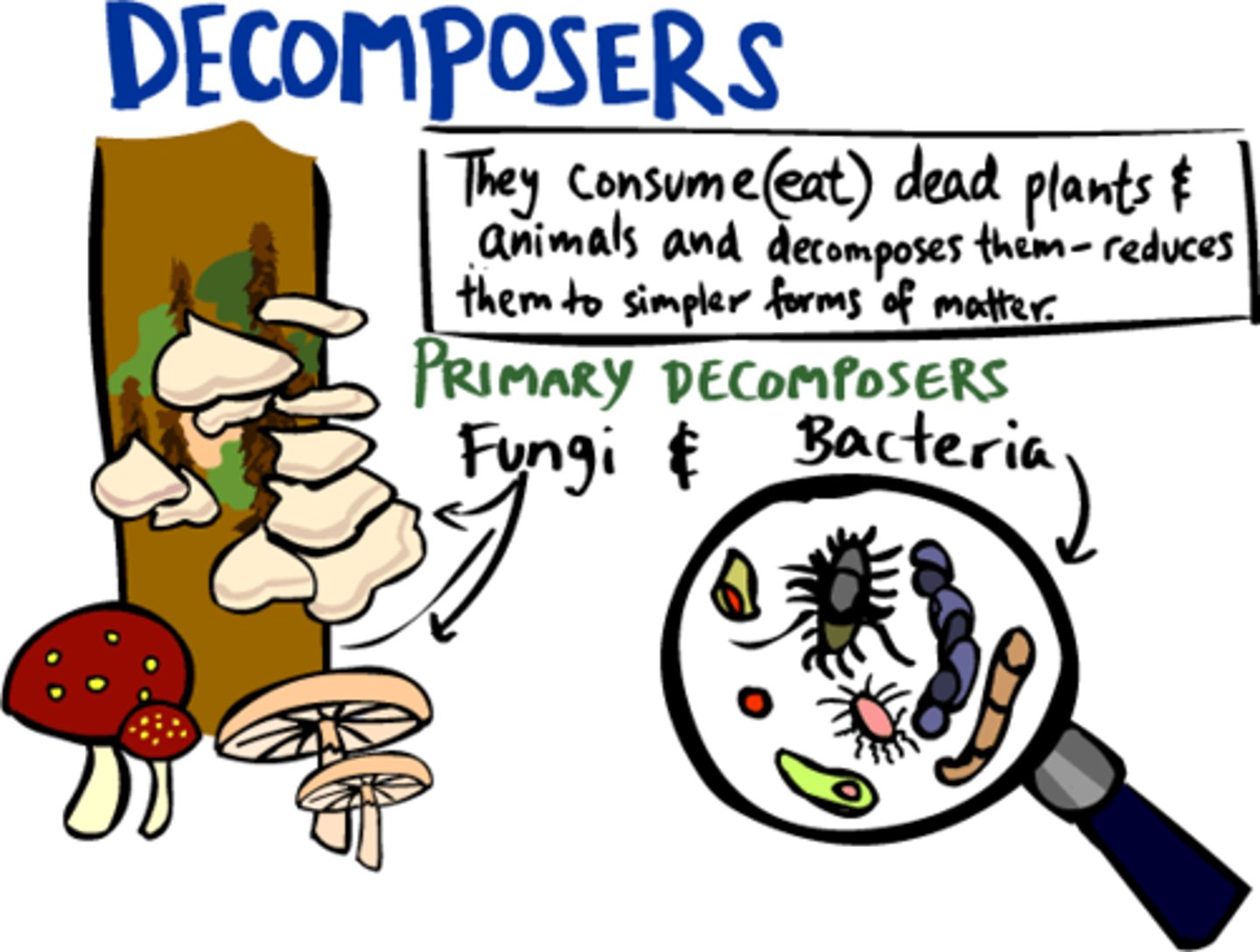
Decomposer
An organism that breaks down wastes and dead organisms
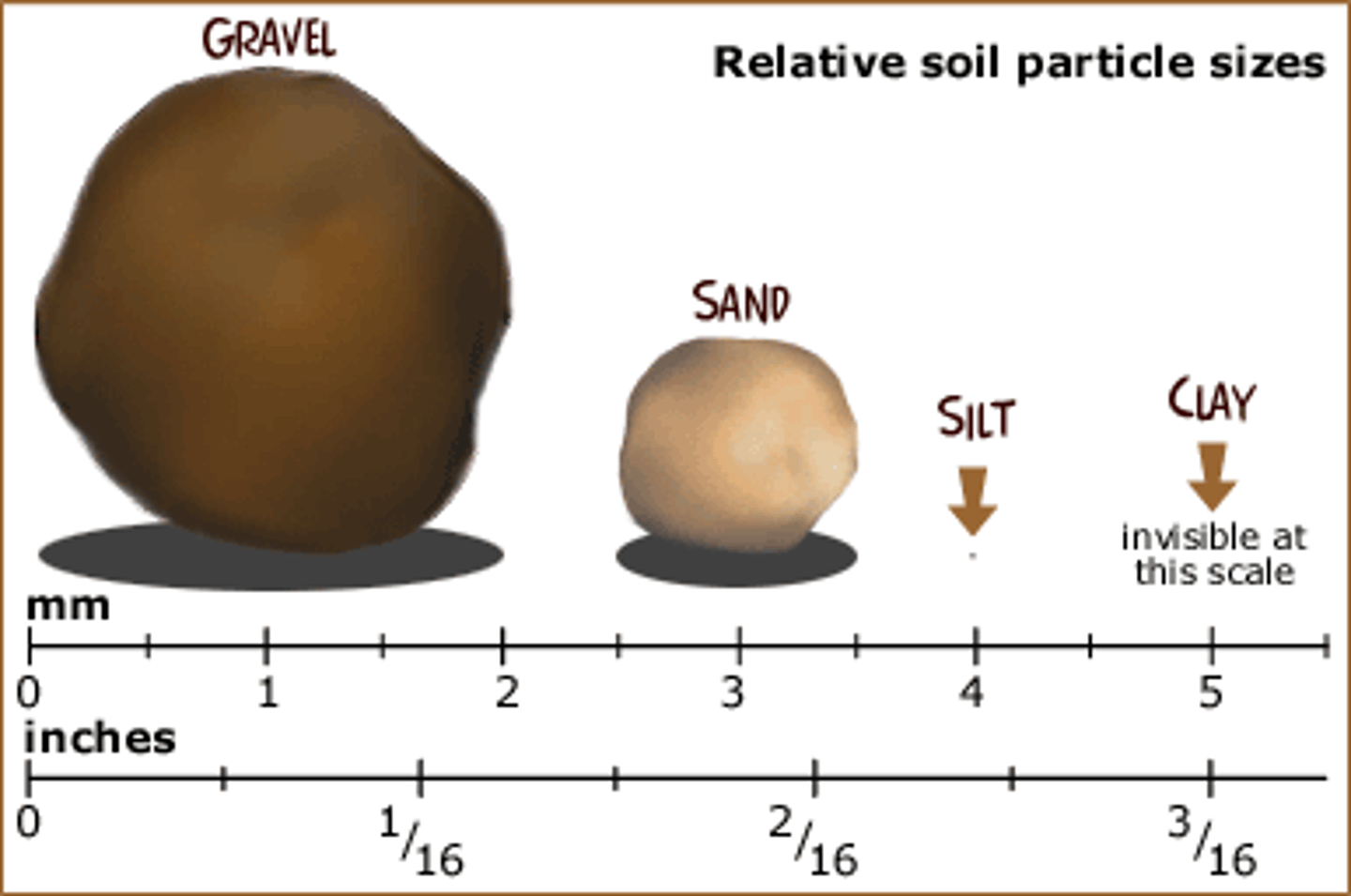
soil texture
the soil quality that is based on the proportions of soil particles: clay, silt, and sand
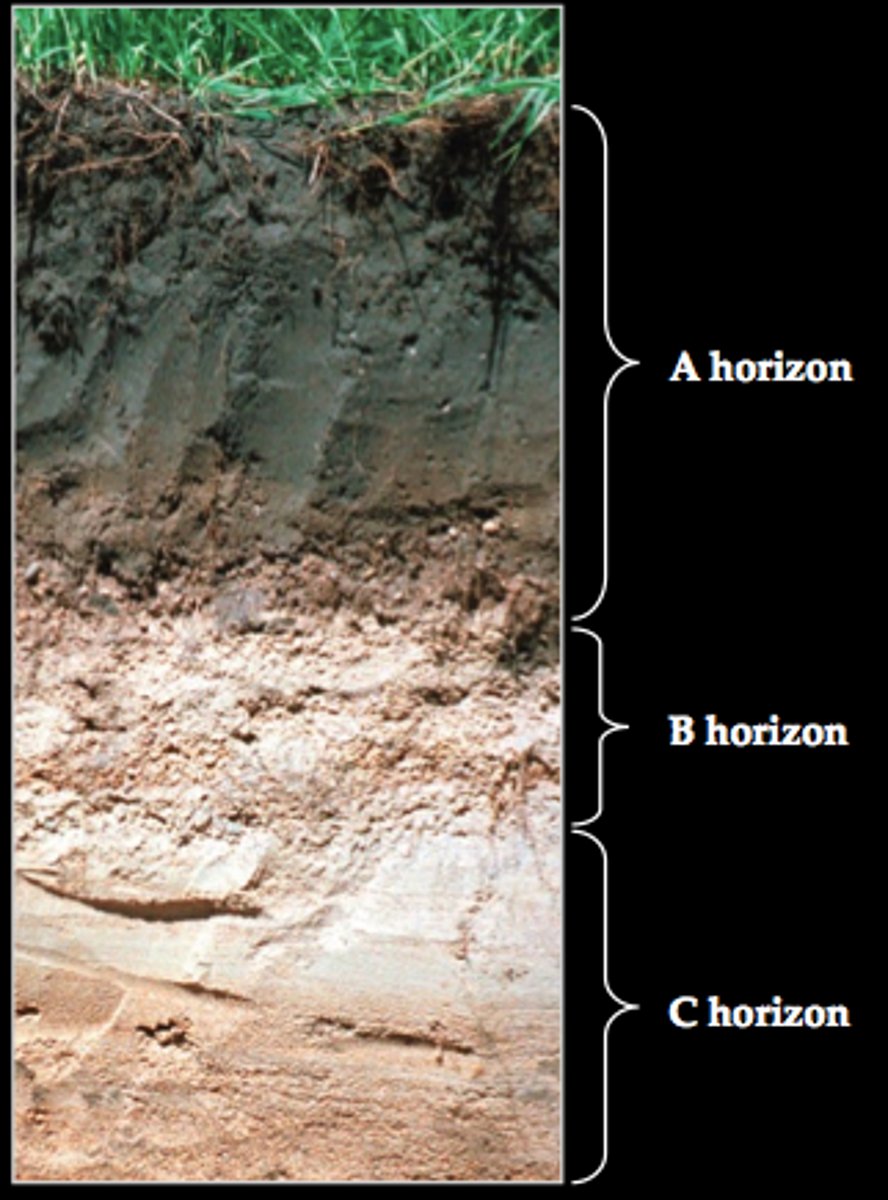
soil horizon
The layer of soil that differs in color and texture from the layers above or below it.
soil fertility
A measure of how well soil supports plant growth.

Loam
Rich, fertile soil that is made up of about equal parts of clay, sand, and silt.

topsoil
Mixture of humus, clay, and other minerals that forms the crumbly, topmost layer of soil.
subsoil
The layer of soil beneath the topsoil that contains mostly clay and other minerals.
How do living things Affect Soil?
Form Humus and Mix the Soil.
C Horizon
forms as bedrock begins to weather and rock breaks up into smaller particles.
A Horizon
Forms as plants add organic material to the soil, and plant roots weather pieces of rocks
B Horizon
forms as rainwater washes materials down from the A horizon.
Worms affect soil by
forming humus and mixing the soil
Mice affect soil by
mixing the soil
Mushrooms/Fungi affect soil by
forming humus
Soil pH
is how acidic or basic a the soil is. Most plants prefer soil with. pH between 6 and 7.5
Soil that is mostly clay
may hold too much water and not enough air
Soil that is mostly Sand
may lose water quickly
Soil that is about an equal mix of sand, silt, clay
allows for water and air spaces
natural resource
anything in the environment that humans use
Soil Conservation
the management of soil to limit its destruction
crop rotation
a farmer plants different crops in a field each year
contour plowing
farmers plow their fields along the curves of a slope instead of in straight rows to reduce runoff and soil erosion.
conservation plowing
dead weeds and stalks of previous year crop are plowed into the ground to help return nutrients, retain moisture, and hold soil in place.
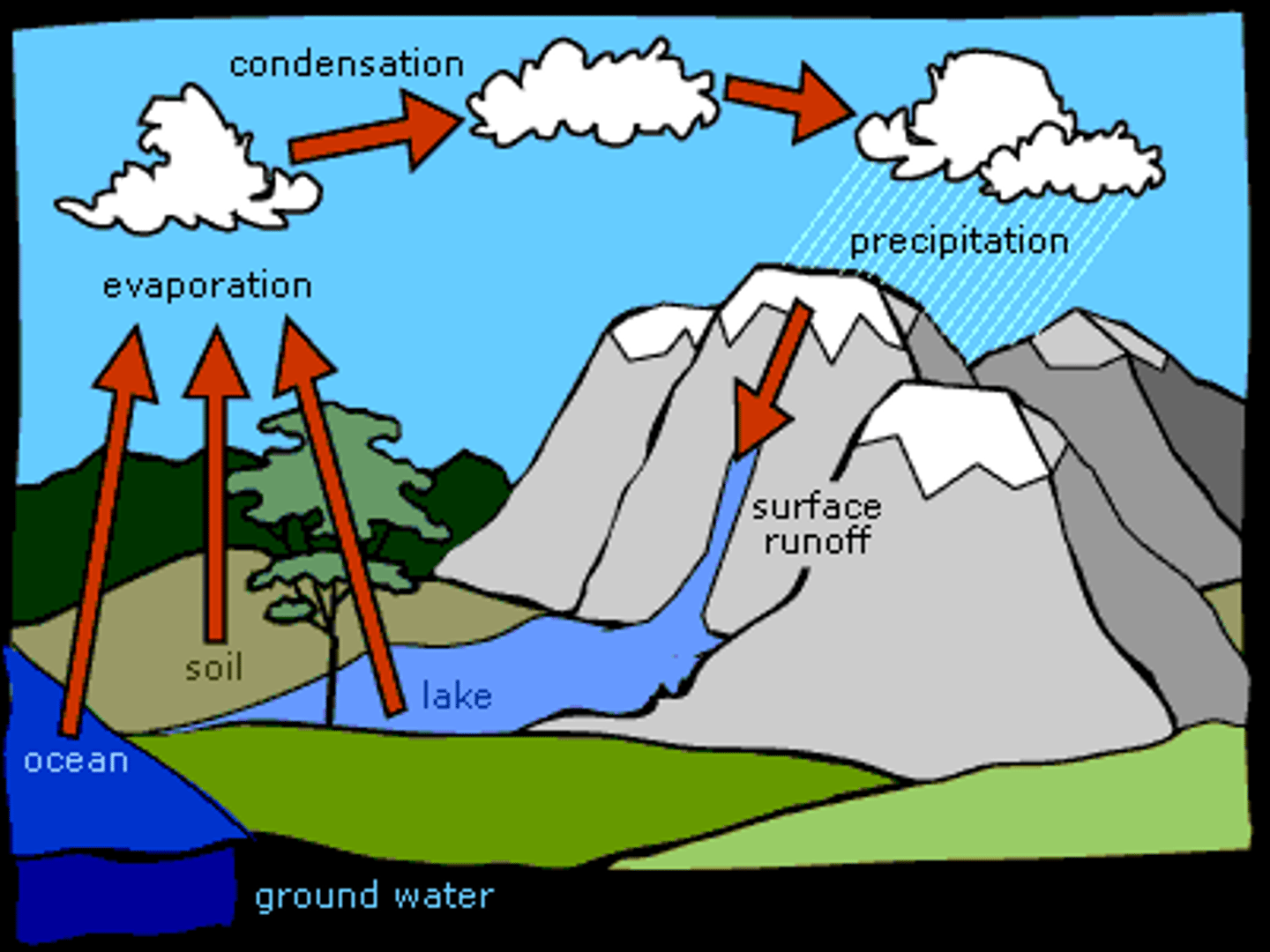
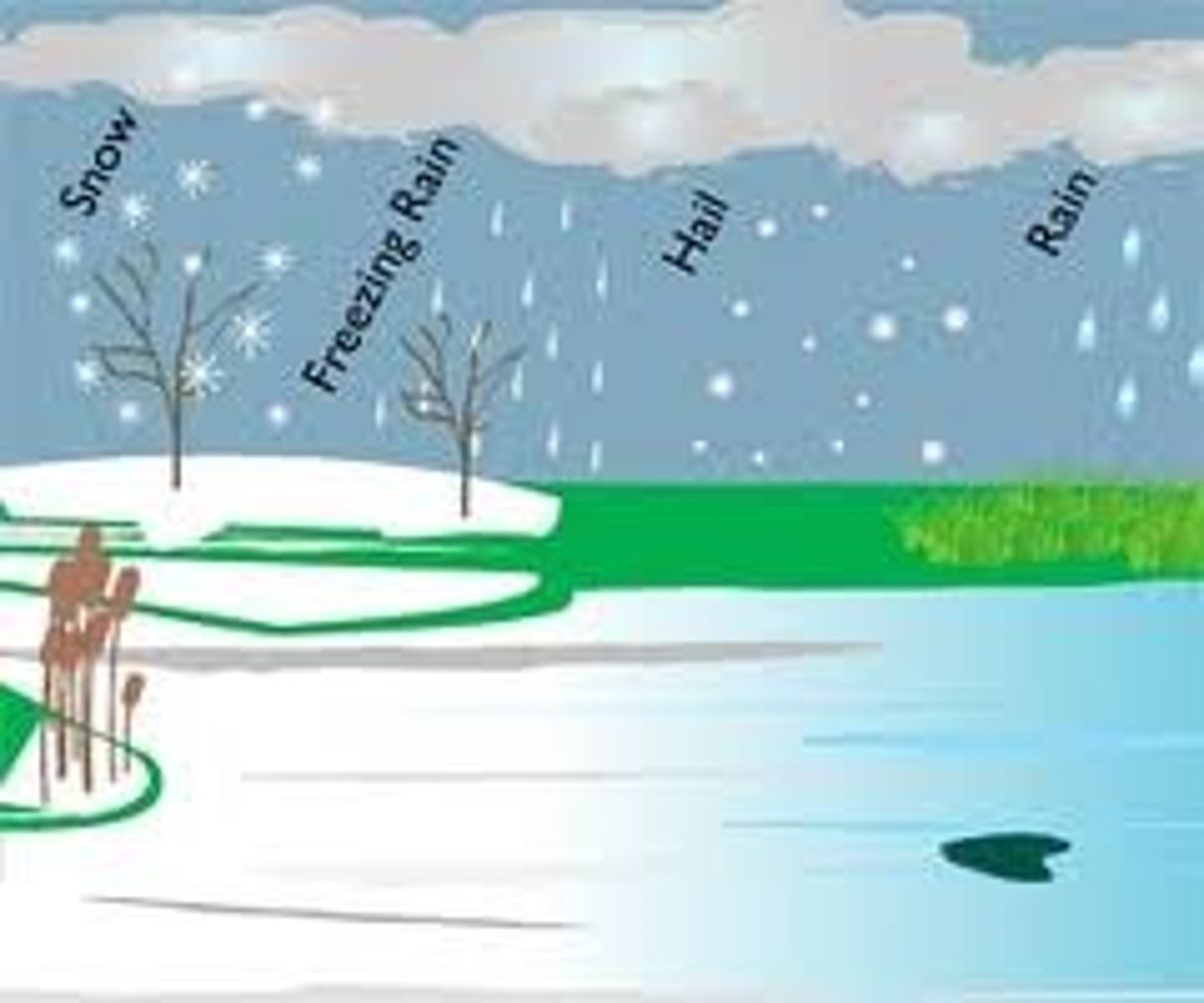
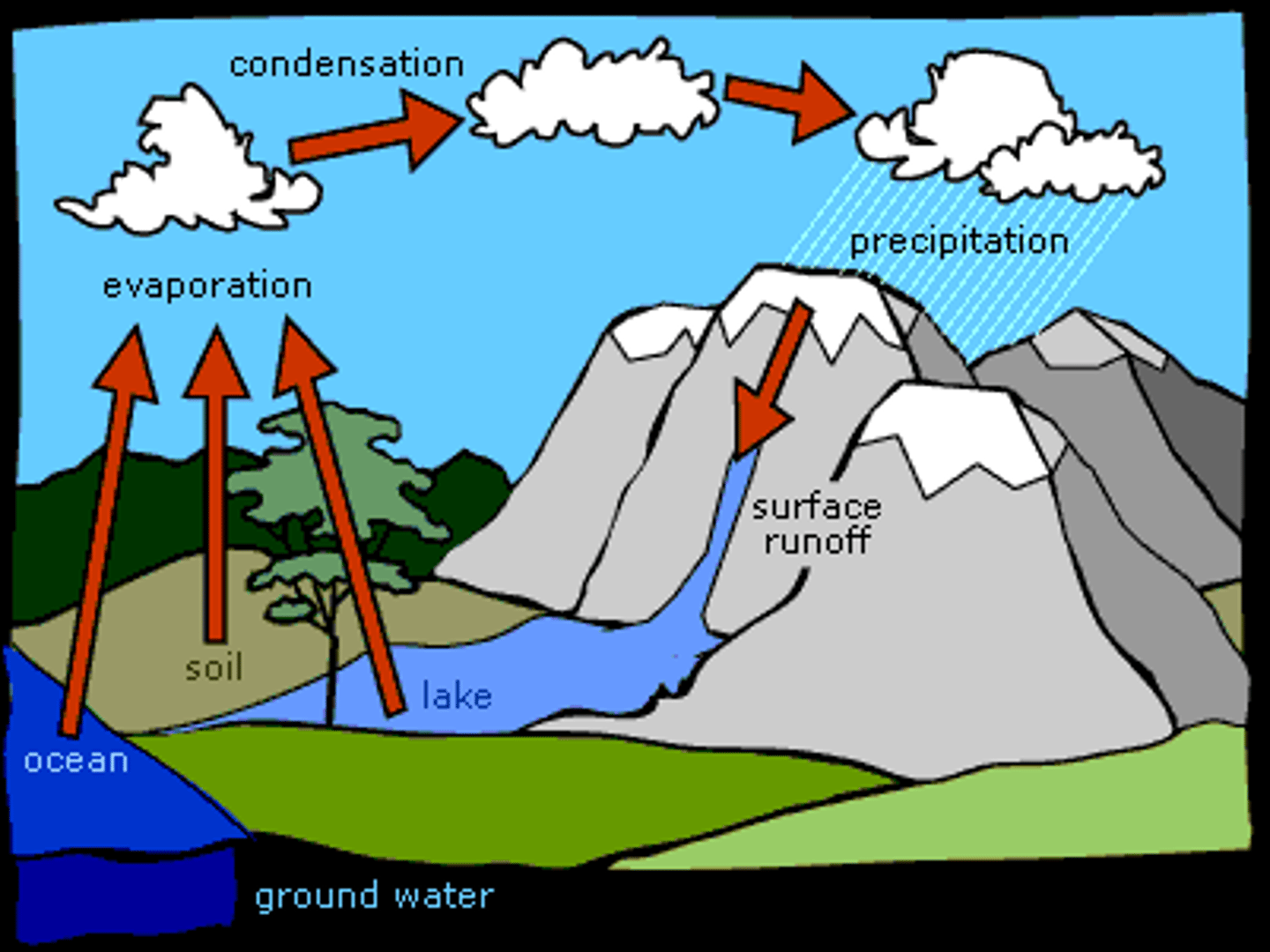
Precipitation
Any form of water that falls from clouds and reaches Earth's surface.
Condensation
The change of state from a gas to a liquid

Evaporation
The change of state from a liquid to a gas

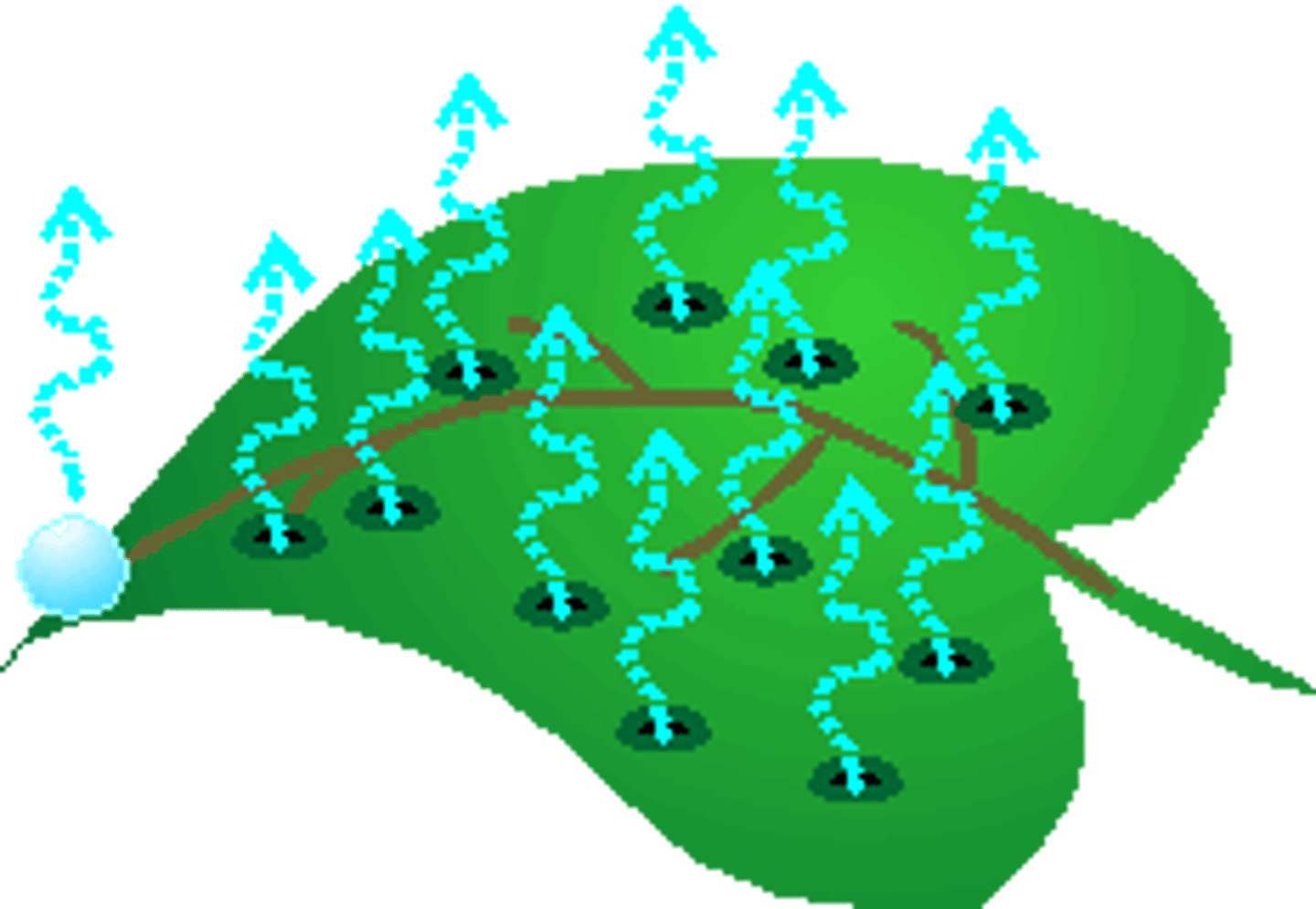
Transpiration
Evaporation of water from the leaves of a plant
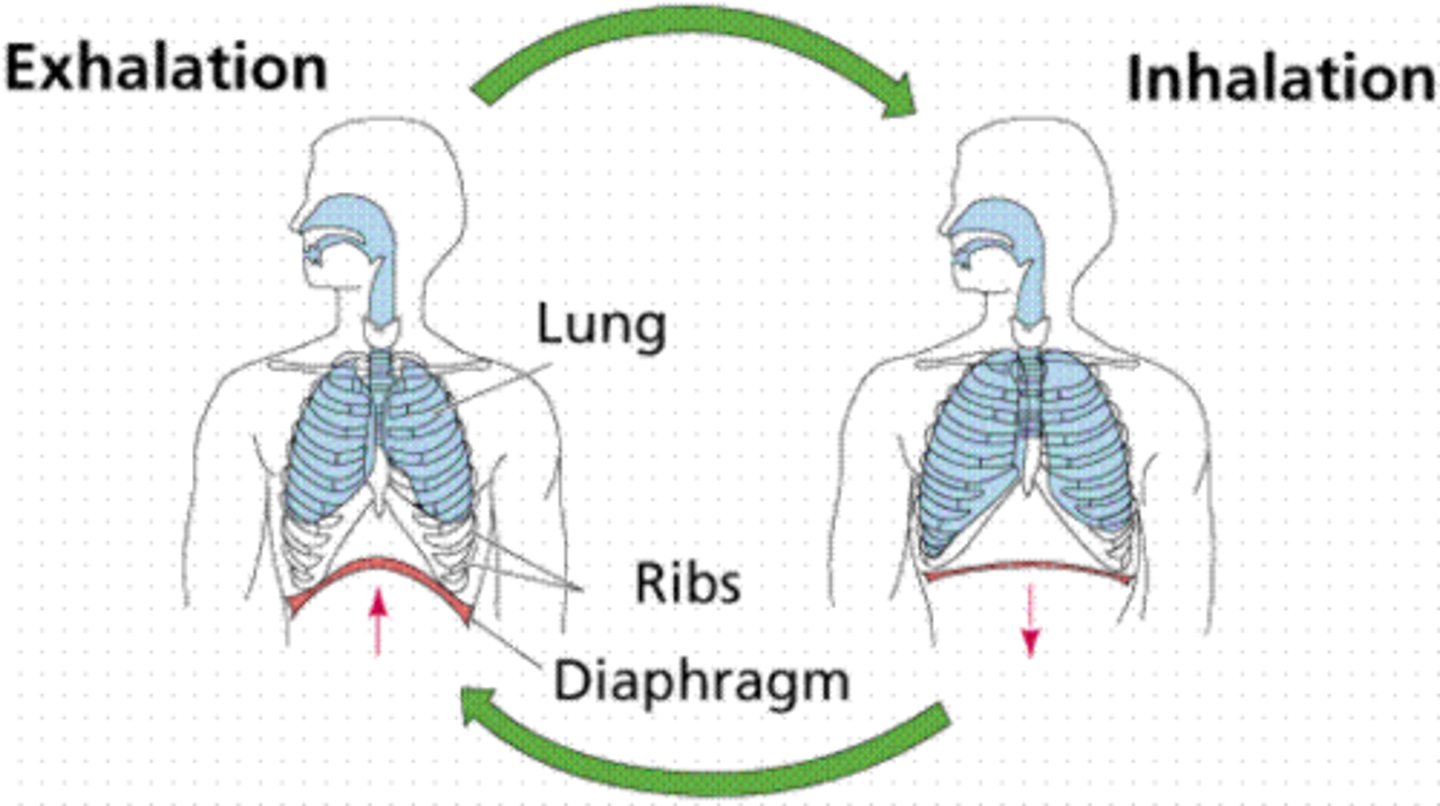
Respiration
breathing
Runoff
water that flows over the ground surface rather than soaking into the ground

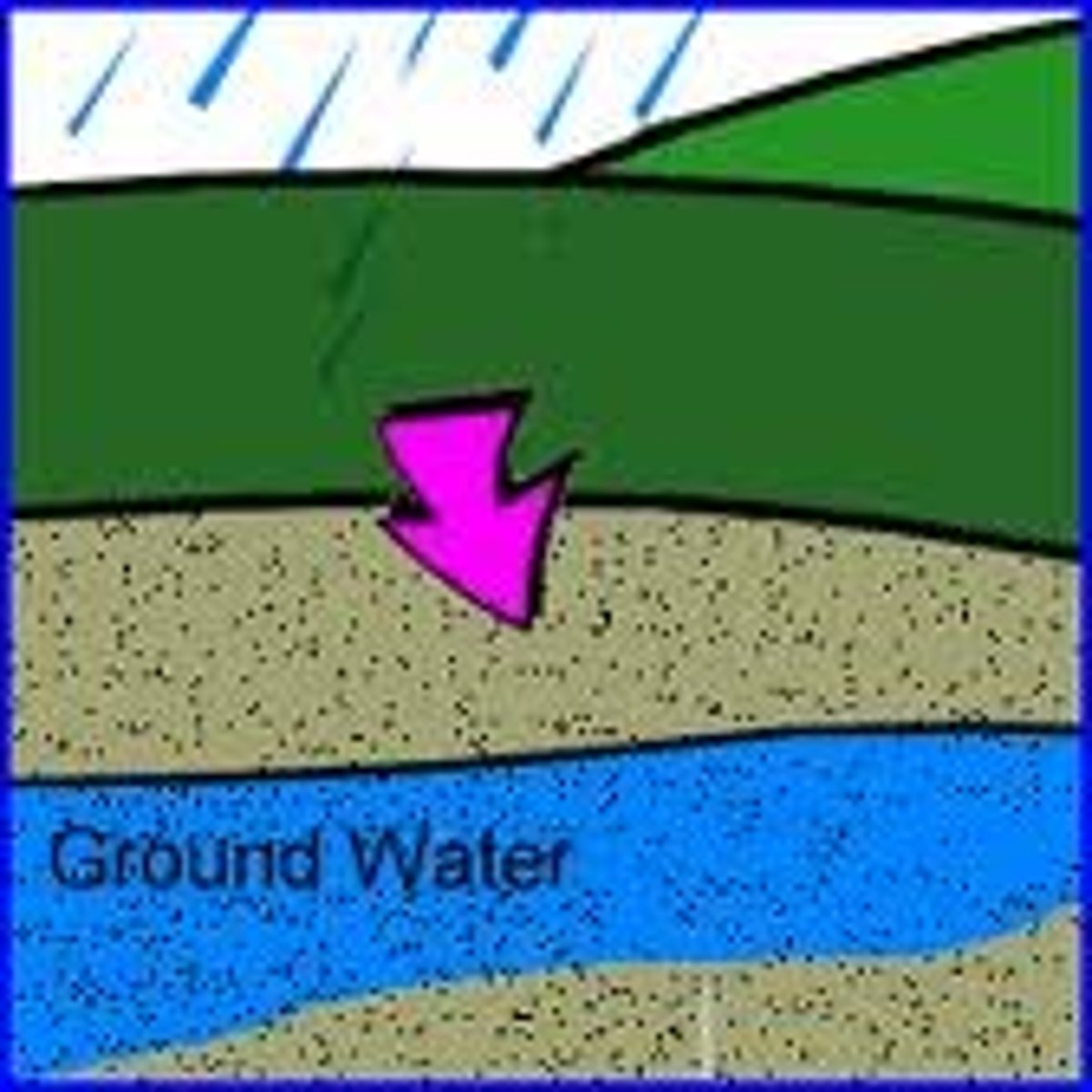
Groundwater
water that fills the cracks and spaces in underground soil and rock layers
water cycle
The continuous process by which water moves from Earth's surface to the atmosphere and back
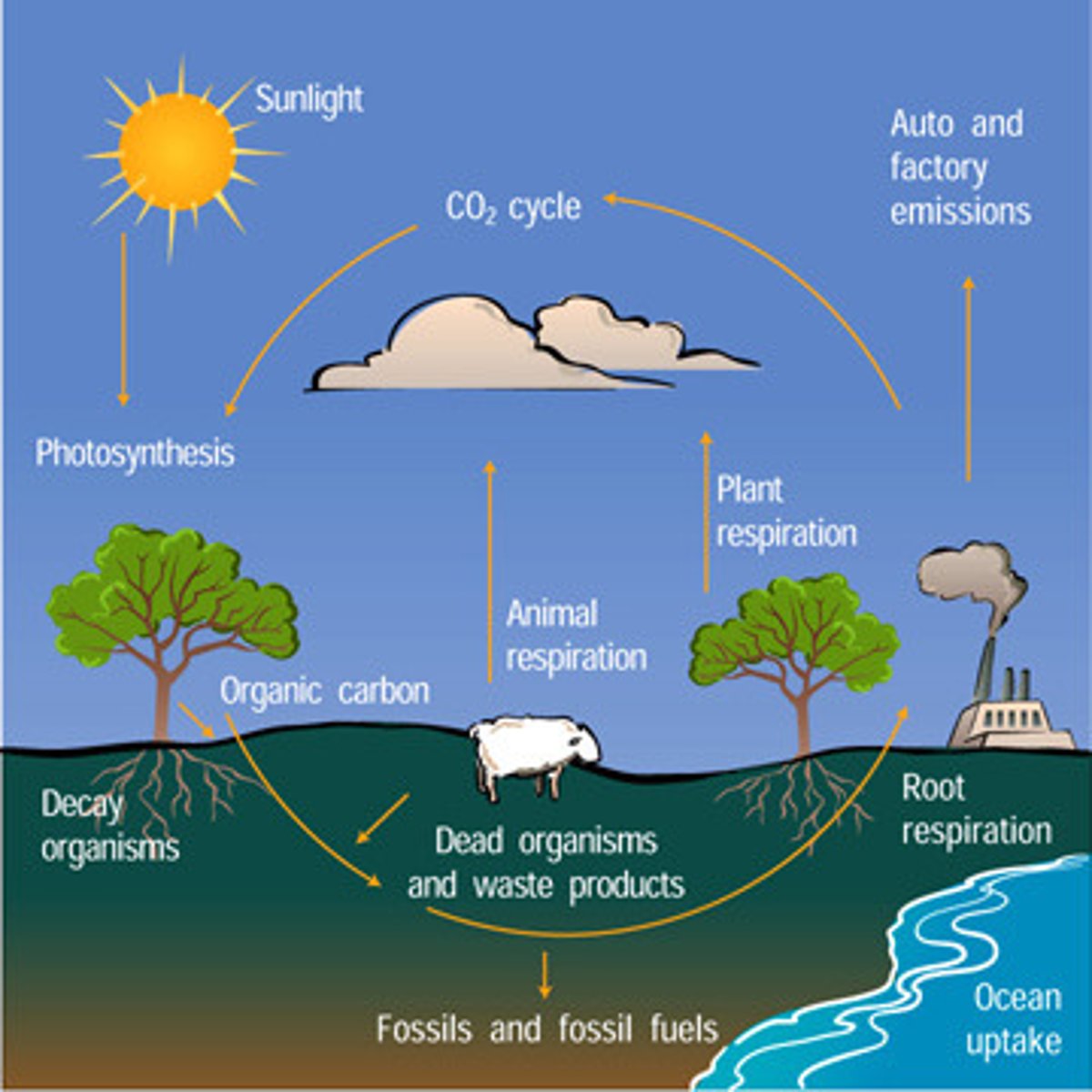
carbon emissions
Made from burning of fossil fuels, a major cause of global warming.

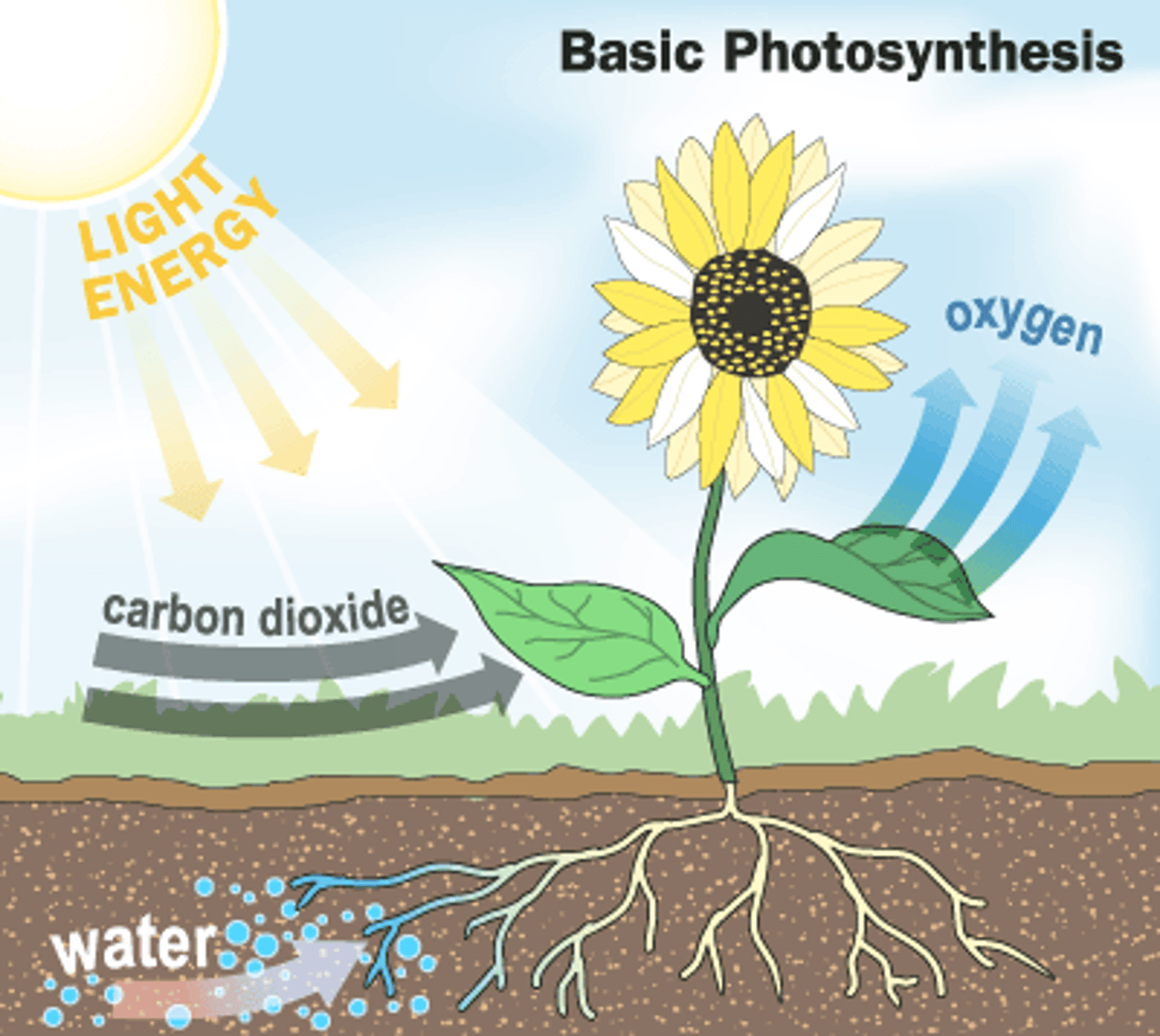
Photosynthesis
Plants use the sun's energy to convert water and carbon dioxide into sugars
Release Carbon
Animals, Factories
carbon sink
A natural environment that absorbs and stores more carbon dioxide from the atmosphere than it releases, which offsets greenhouse gas emissions.

Absorbs Carbon
Plants, Oceans,
carbon cycle
The organic circulation of carbon from the atmosphere into organisms and back again
water cycle
The continuous process by which water moves from Earth's surface to the atmosphere and back