basal ganglia
1/38
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
39 Terms
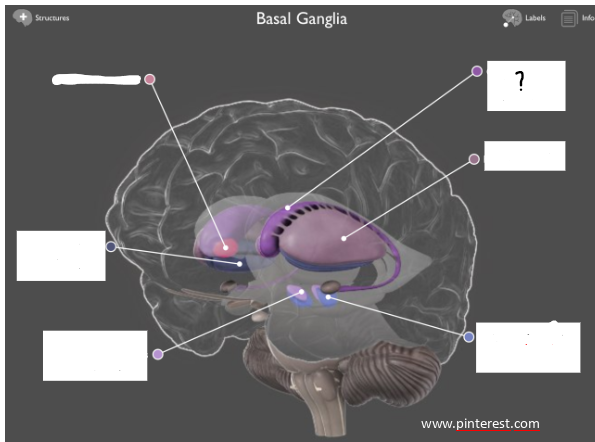
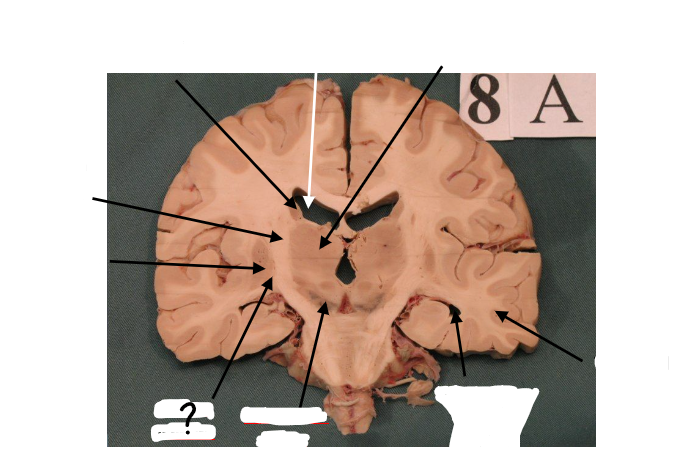
caudate nucleus
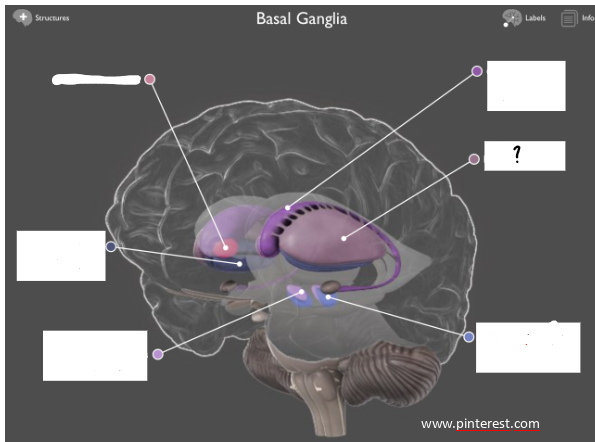
putamen
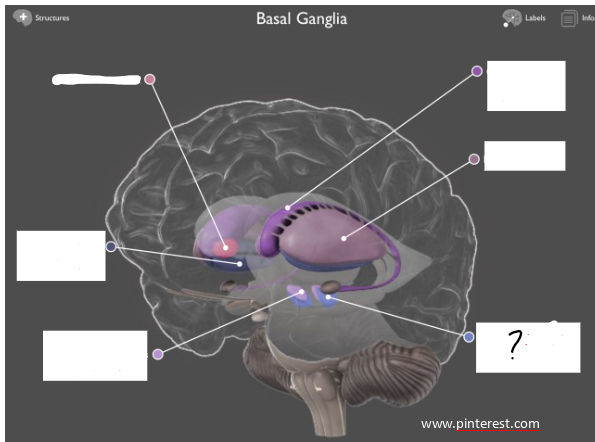
substantia nigra
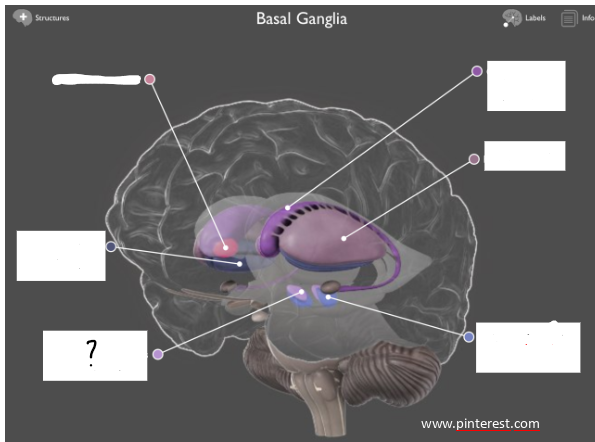
subthalamic nucleus
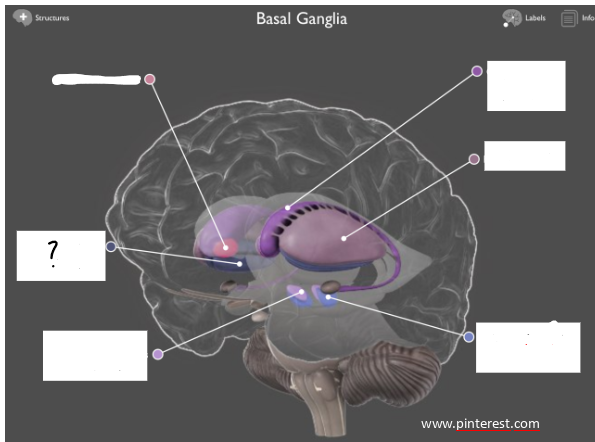
globus pallidus
nucleus accumbens
what are the 2 parts of the striatum?
putamen, caudate nucleus
what are the 2 parts of the globus pallidus?
internal and external segment
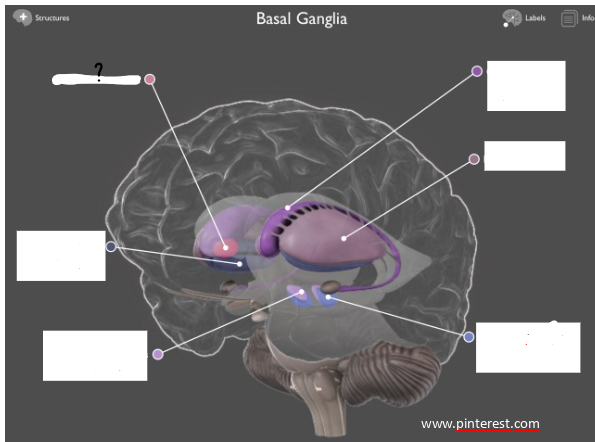
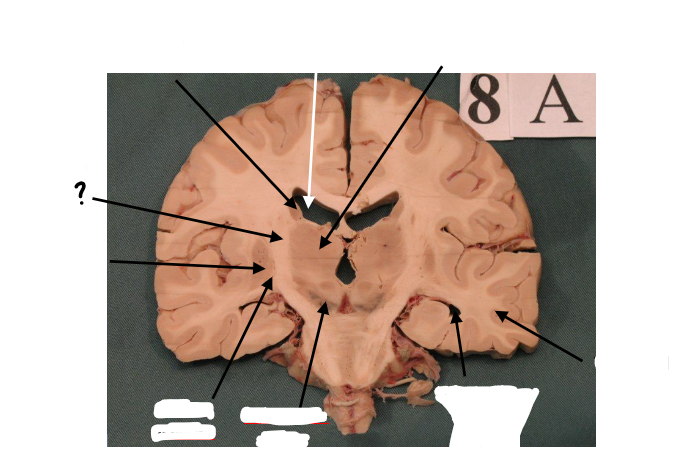
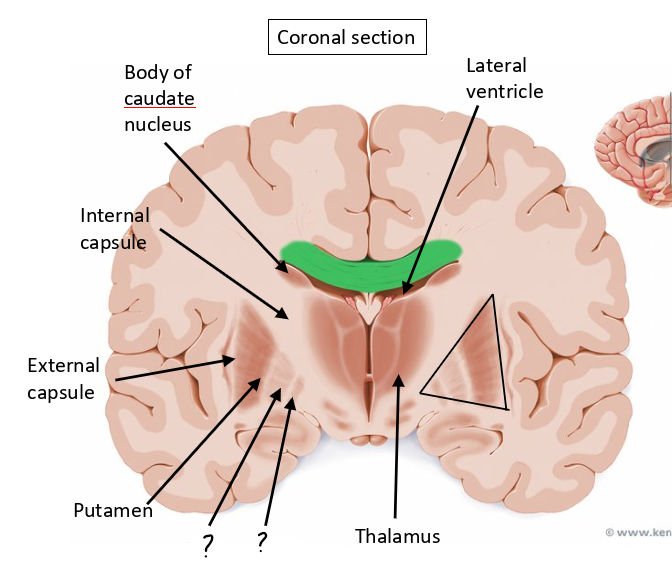
body of caudate nucleus
lateral ventricle
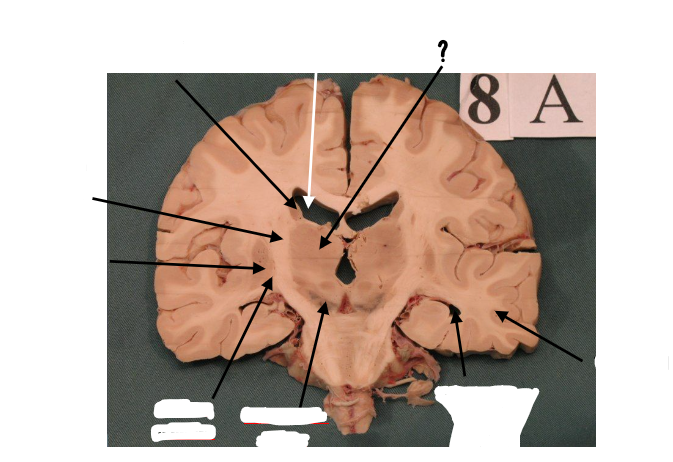
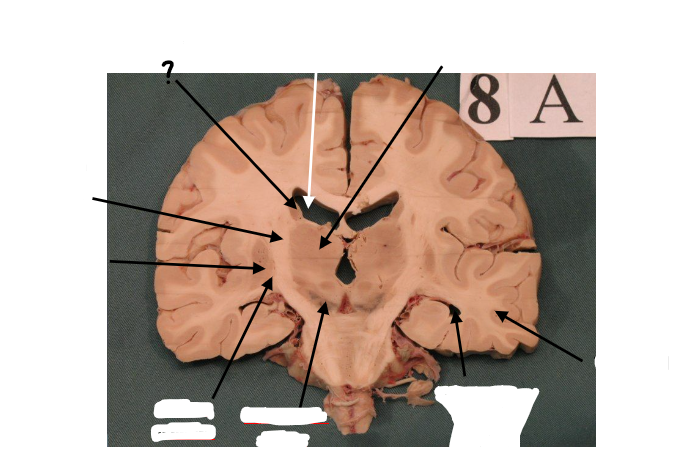
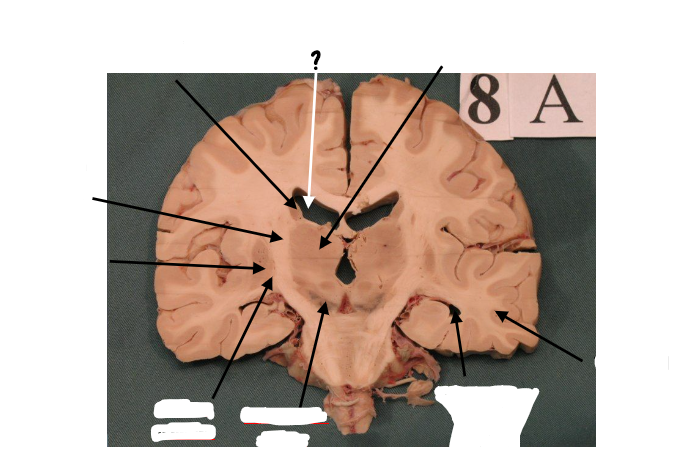
thalamus
internal capsule
putamen
globus pallidus
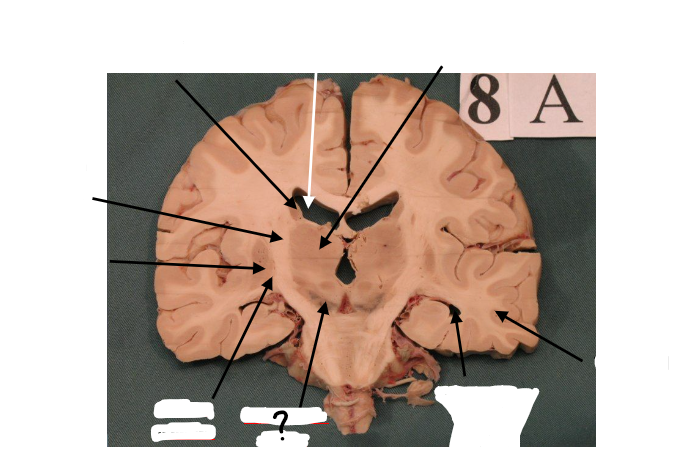
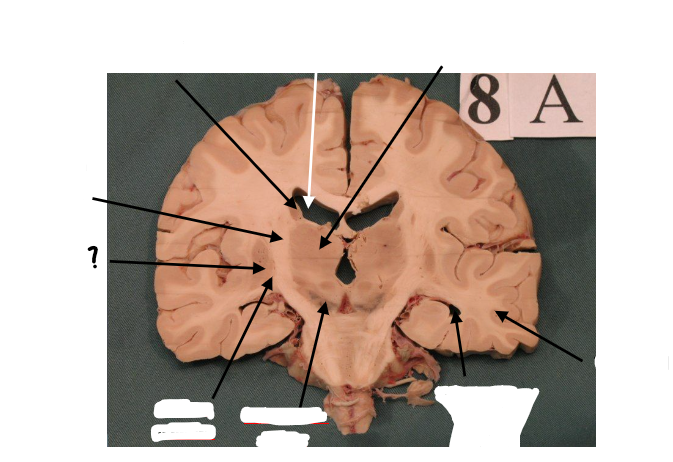
substantia nigra
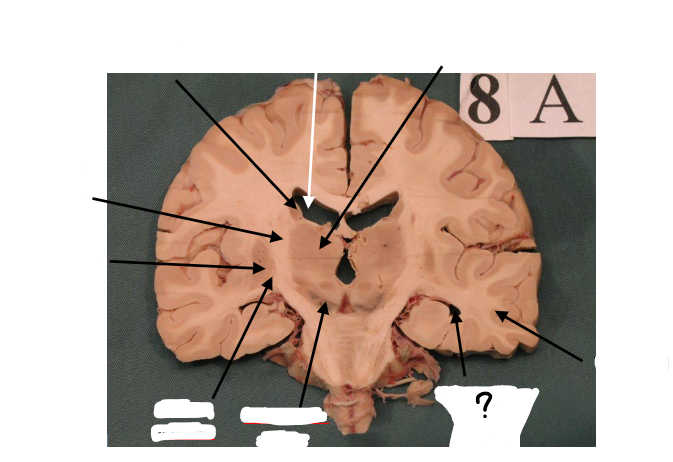
inferior horn of lateral ventricle
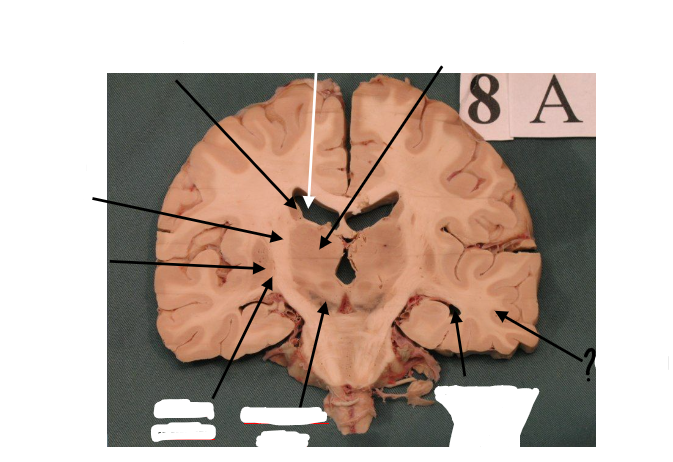
temporal lobe
gp external and gp internal
what are the inputs of the basal ganglia
cerebral cortex, thalamus, substantia nigra pars compacta → striatum
what are the main outputs of the basal ganglia? (2 paths)
GPi →thalamus →frontal cortex (motor cortex)
substantia nigra pars compacta →neurons in superior colliculus (midbrain)
what is the purpose of the direct pathway in the basal ganglia?
facilitates the initiation of purposeful movement
what is the purpose of the indirect pathway in the basal ganglia?
inhibits unwanted movement
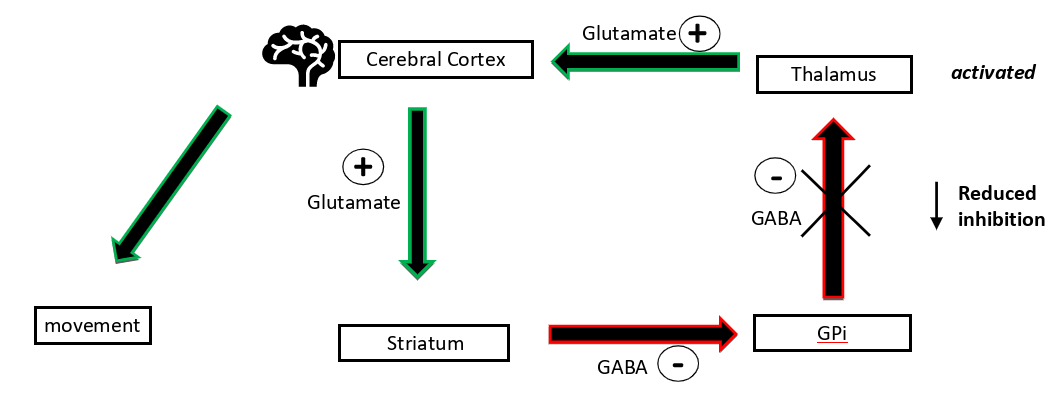
describe the glutamatergic/ GABAergic paths of the direct pathway
cerebral cortex excite striatum which inhibits GPi, reducing its inhibitory effect on the thalamus, so thalamus can excite cerebral cortex more → movement
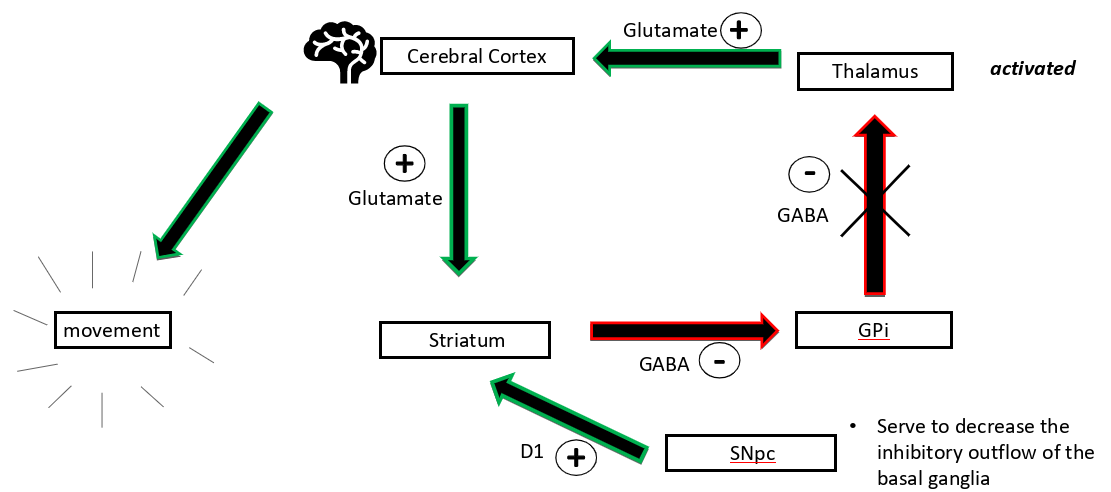
how does dopamine impact the direct pathway
the SNpc → D1 → excites striatum→ thalamus is less inhibited
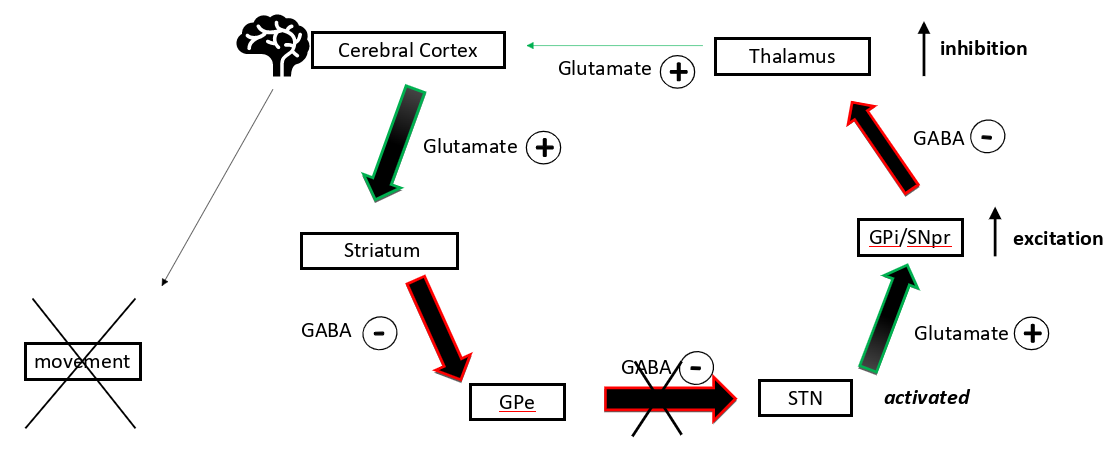
describe the indirect pathway
cerebral cortex excites striatum which inhibits GPe which stops it ihibiting subthalamic nucleus which excites GPi/ SNpr which inhibits the thalamus which excites the cerebral cortex less
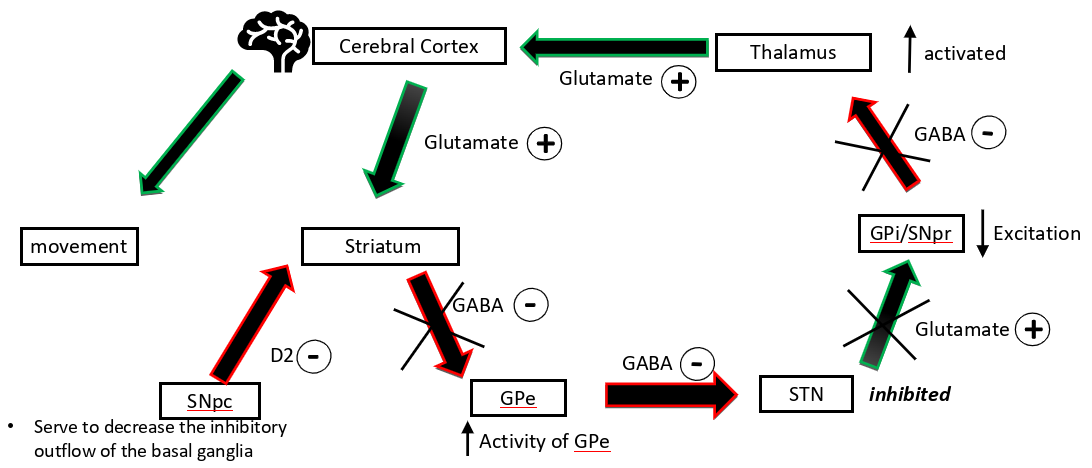
how does dopamine impact the indirect pathway
SNpc→ D2→ striatum so the GPe is less inhibited so the STNis more inhibited so the GPi/SNpris less excited so thalamus is less inhibits so excites the cerebral cortex more → more movement
in what disease is less pigmentation seen in the substantia nigra?
parkinsons (Degeneration of nigrostriatal dopaminergic neurones)
what are some of the motor symptoms of parkinsons?
bradykinesia
resting tremor
rigidity- cogwheel
postural disturbance
what are some non-motor symptoms of parkinsons?
impaired cognitive and behaviour functions, psychological and emotional changes
what are some treatment options for parkinsons
dopamine precuroes -levodopa, deep brain stimulation
what is the cause of huntingtons
selective loss of medium spiny neurons in the striatum that project to GPe (indirect path)
how is Huntingtons inherited?
autosomal dominant
Huntingtons and parkinsons, which is hyper and which is hypokinetic?
huntingtons- hyper, parkinsons- hypo
what are choreform movements (Huntingtons)?
quick, jerky movements, involuntary
what are the 2 loops the basal ganglia is involved with for non-motor functions?
pre-frontal loop and limbic loop
what does the pre-frontal loop do?
initiate/ terminate cognitive processes (planning)
short term memory
attention
what does the limbic loop do?
-emotion
-motivated behaviour
-transitions from one mood state to another
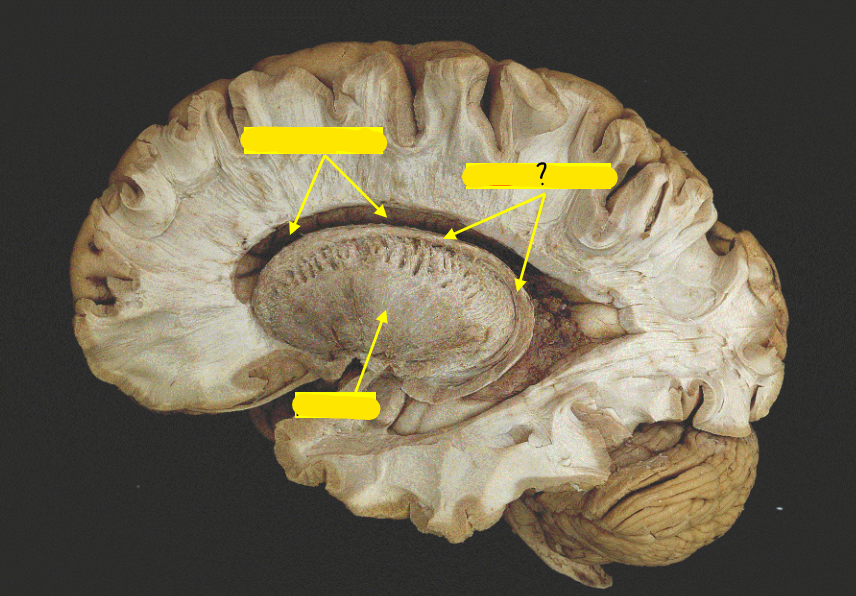
caudate nucleus
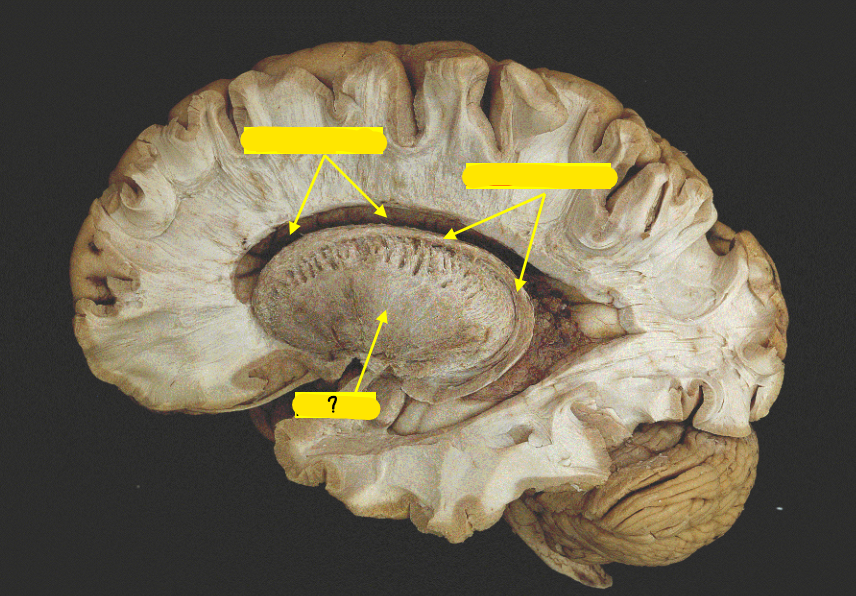
putamen