8-Charge and Current, 9-Energy, power and resistance, 10-electrical circuits
1/28
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
29 Terms
define electric current?
what is the formula for the net charge on a particle
-electric current is the rate of flow of charge
-the net charge on a particle is given by Q = ne
What is conventional current?
what is different about the actual electron flow in a metal wire?
conventional current is the rate of flow of charge from the positive to the negative terminal
the actual electron flow in a metal wire is from the negative terminal to the positive terminal
what is kirchoff's first law?
Conservation of charge - the sum of currents into a junction equals the sum of current out of a junction
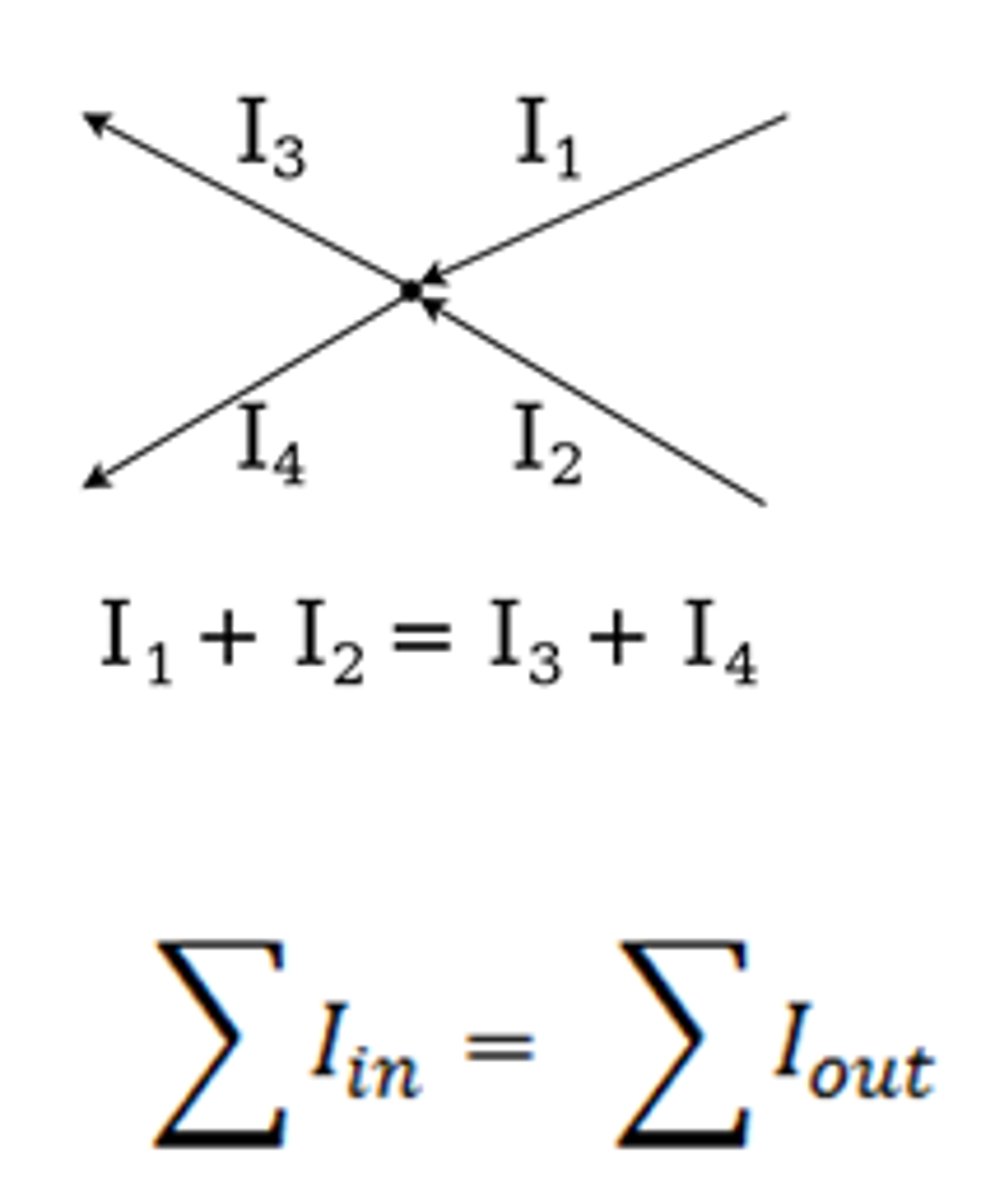
fundamentally, what is mean drift velocity
it is the average velocity of charge carriers (electrons in this case) as they travel down the wire, colliding with positive metal ions that are vibrating with an amplitude about their fixed position
what is meant by the number density, n , of a material ?
-the number density , n , of a material represents the number of free electrons per unit volume
What is one volt?
The potential difference across a component when you convert one joule of energy moving one coulomb of charge through the component.
1 J C^-1
define the electromotive force
define potential difference
electromotive force (E.M.F.) is when work is done on the charge carriers when they gain energy passing through a power supply
potential difference is when work is done by the charge carriers when they lose energy passing through a component
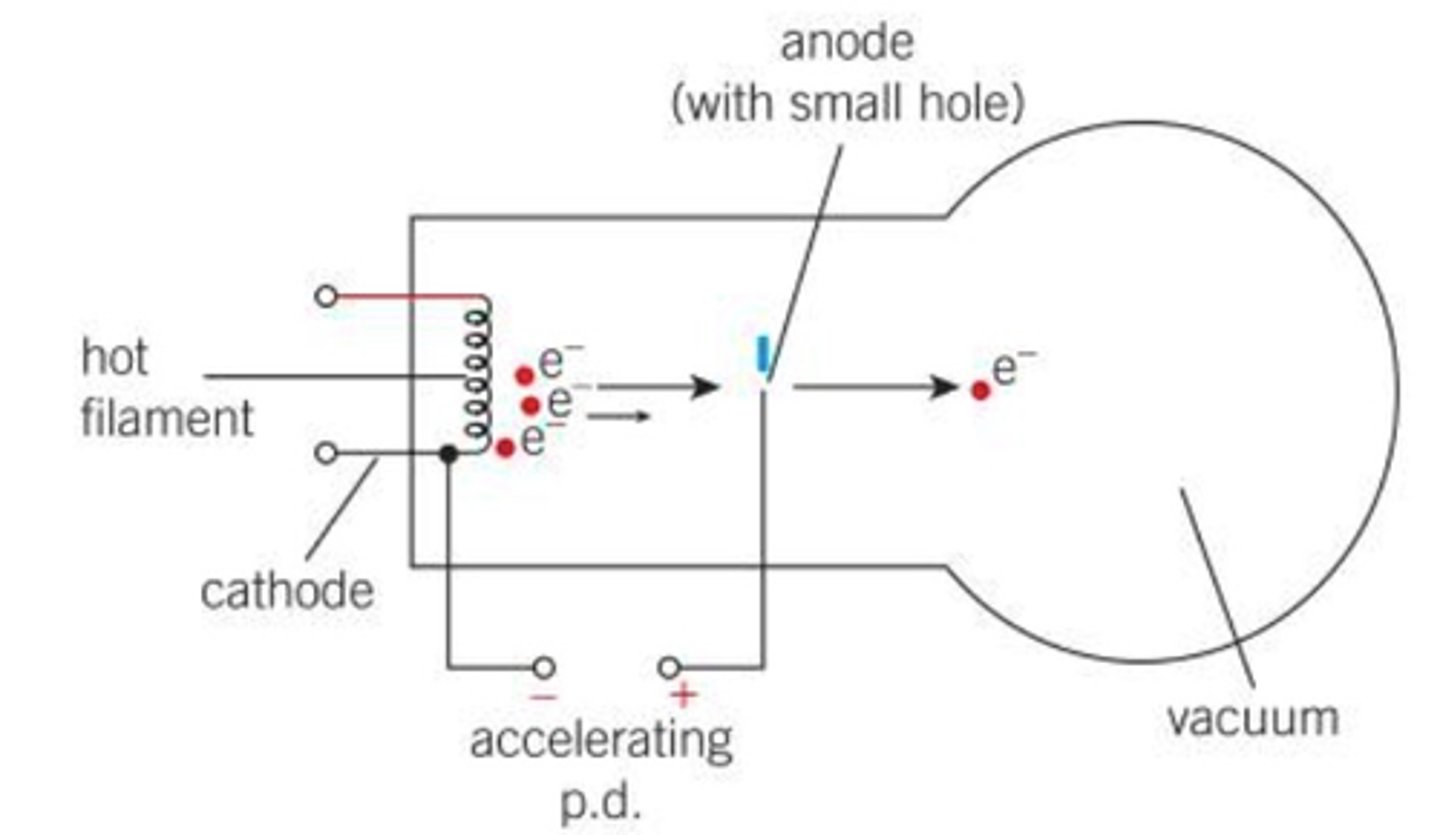
how does the electron gun work
- hot fillament heated by an electric current which gain enough kinetic energy to escape from the surface through thermionic emission
- when placed in a vacuum with an anode, the fillament acts as a cathode meaning there is a potential difference causing the freed electron to accelerate towards the anode
- if the anode has a hole in it, electrons can pass through it creating a beam of electrons with a specific kinetic energy
what formulas to equate to calculate velocity of one electron ?
to calculate the velocity of one electron;
eV=½mv²
what is meant by resistance
how much a component opposes the flow of charge carriers through it
What is Ohm's Law?
for a metallic conductor kept at a constant temperature, the current in the wire is directly proportional to the p.d. across its ends
V = IR
how does temperature affect resistance on a microscopic level?
when temperature of the wire increases, positive ions vibrate with a greater amplitude about their mean positions therefore the frequency of collisions between charge carriers and the positive ions increases so charge carriers transfer more energy as they travel through the wire
I-V graph for filament lamp
as temperature increases resistance increases
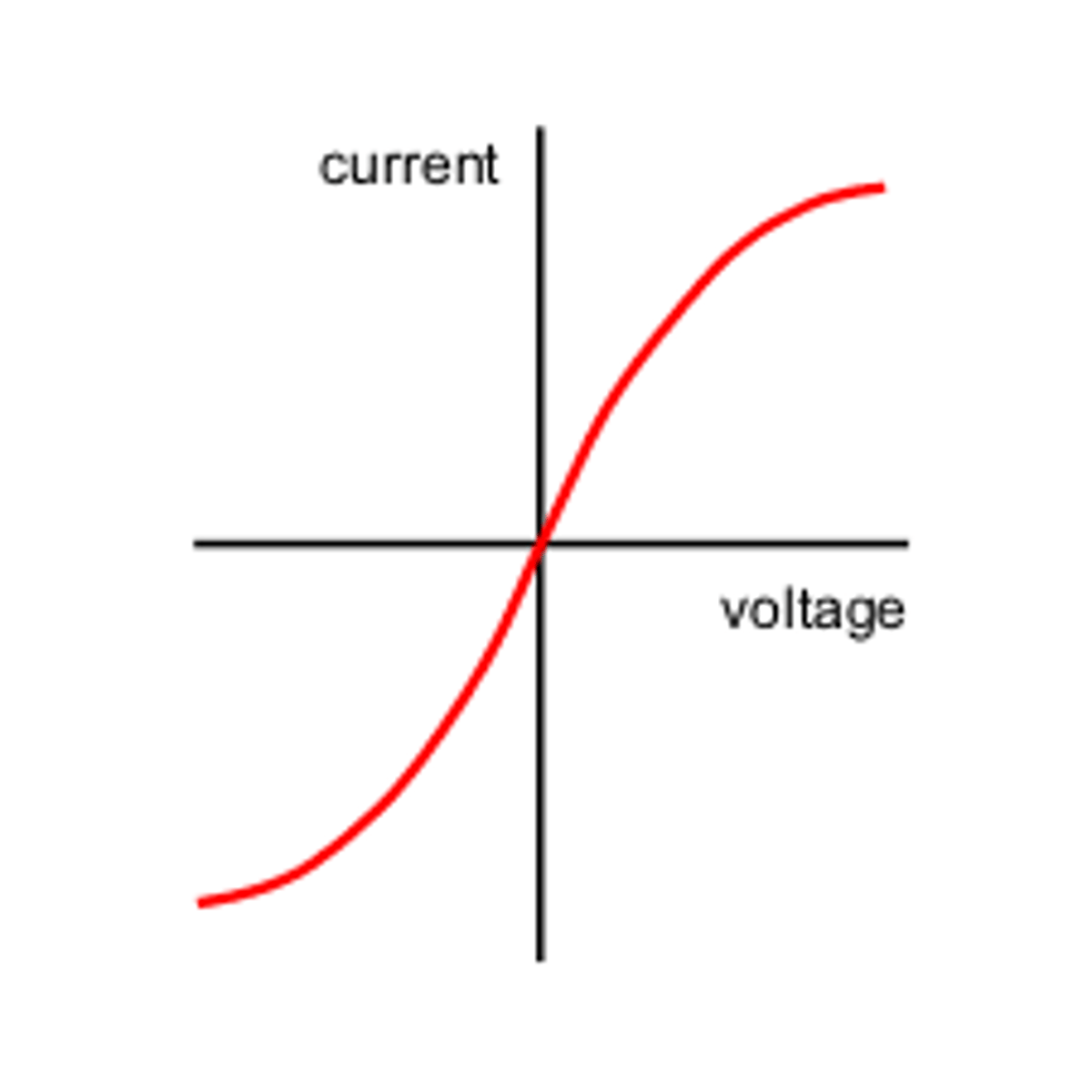
I-V graph for a fixed resistor
at constant temperature has a constant resistance.
It is an ohmic conductor
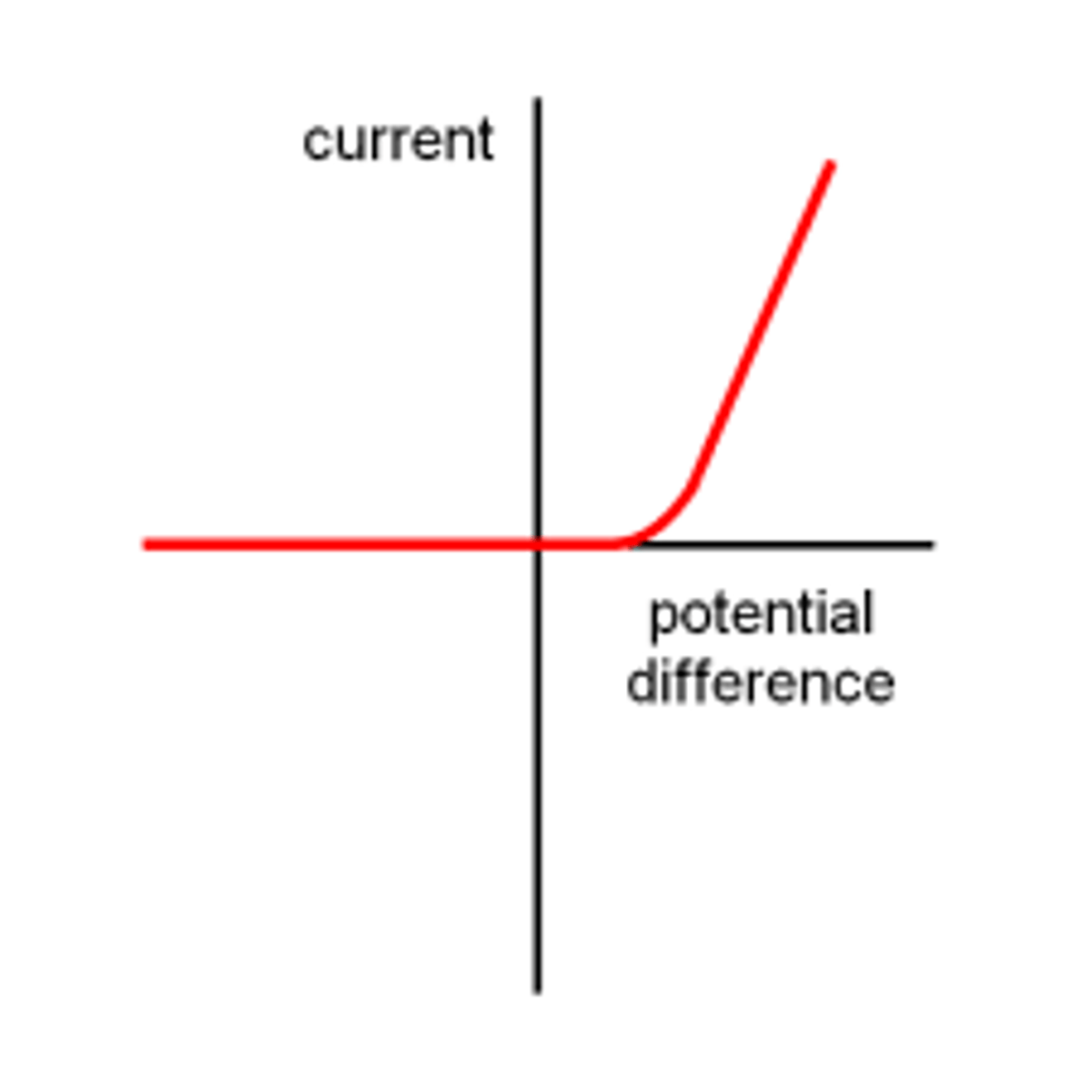
I-V graph for a diode
explain how resistance behaves in both polarities and why it behaves as such
-diode's are made from semiconductors which allow current to only flow in one direction
-when the diode is reversed, resistance is infinite
-the diode does not conduct until a threshold value for P.D.
-after the threshold value is reached, resistace rapidly decreases because the number density of charge carriers increases
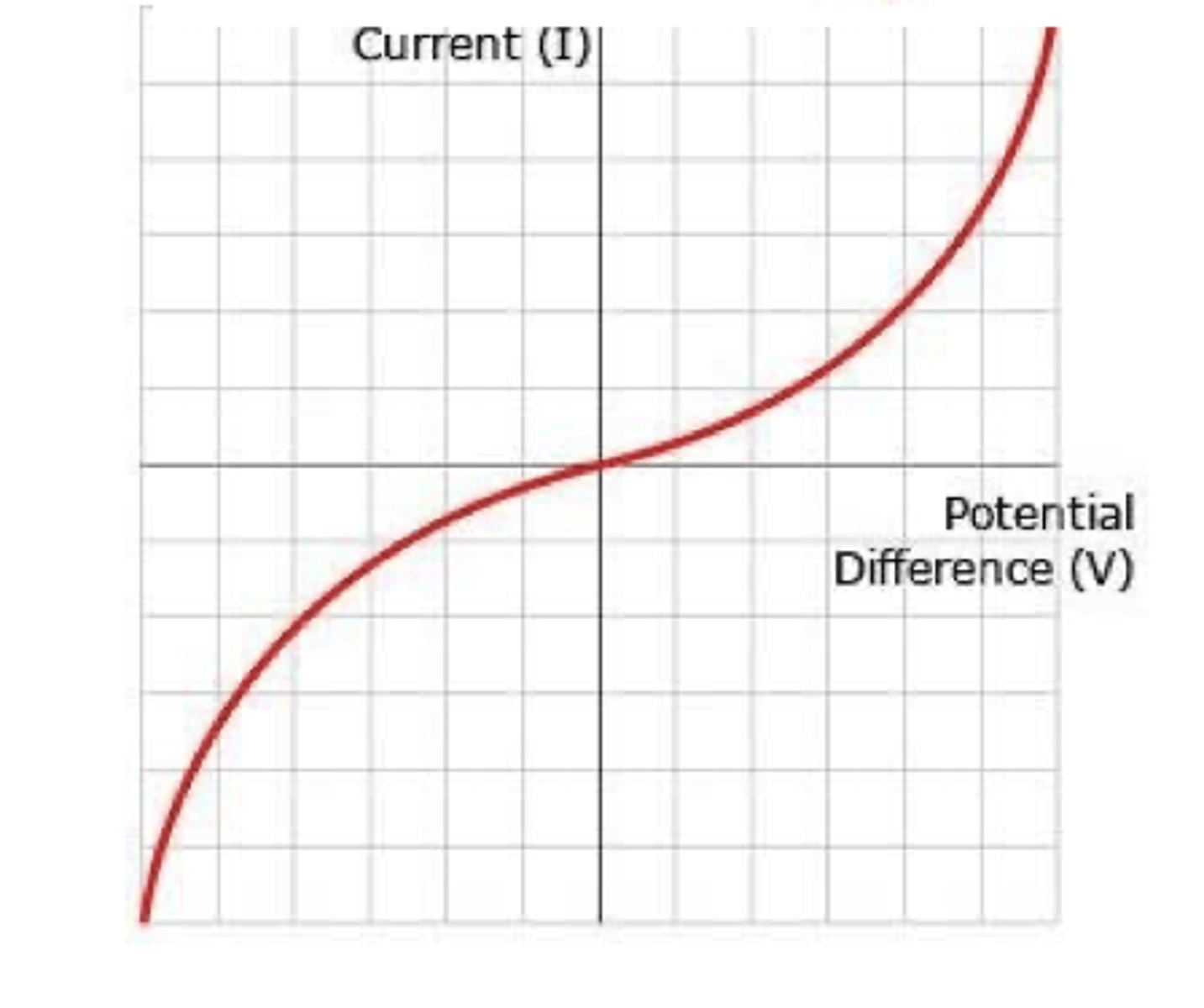
I-V graph for a thermisor
-non-ohmic component
-resistance decreases when temp increases
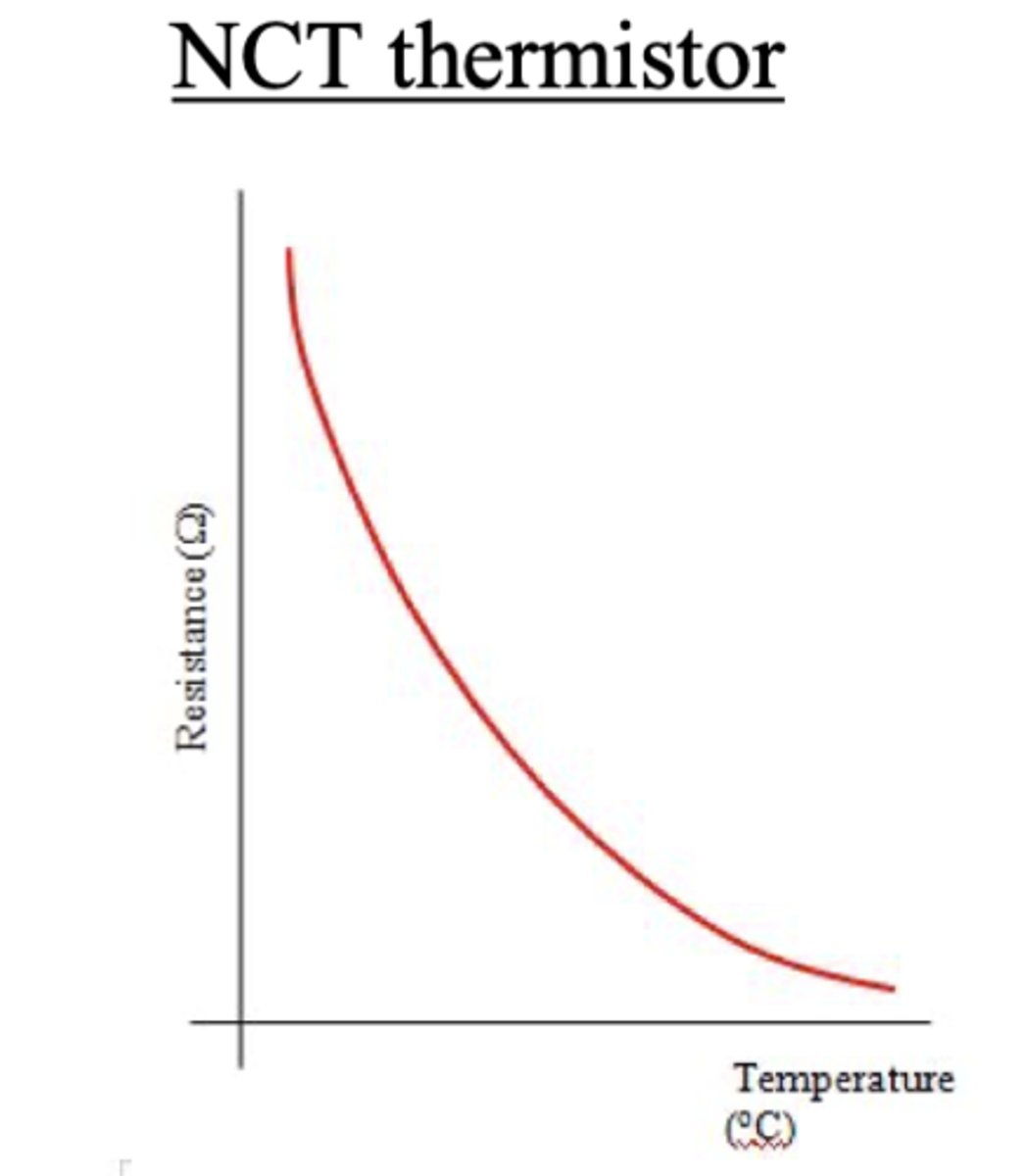
resistance temp graph for a NTC thermistor
explain the behavior
-thermistors have a negative temperature coefficient (NTC) meaning as the temp increases, resistance decreases
-it is made of an NTC semiconductor material so the number density of charge carries increase when temperature increases
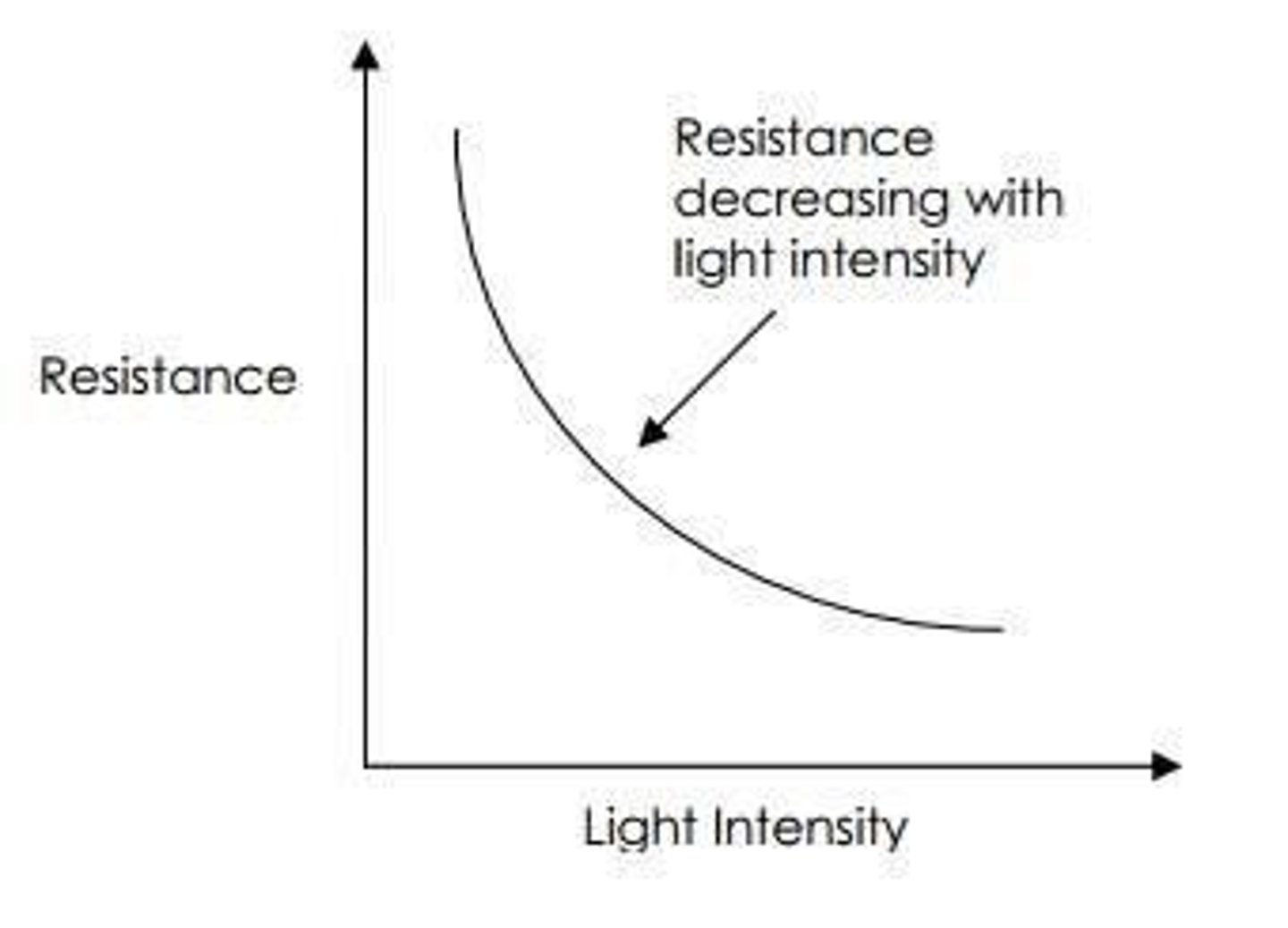
resistance light intensity graph for an LDR
-non-ohmic component made from semiconductors
what three factors affect resistance?
Three things determine resistance:
- length
- area
- resistivity of its material
What is a resistivity?
what is the formula?
R = 𝜌L/A
resistivity is an intrinsic property of a material. it describes how strongly a material opposes the flow of electric current independent of its shape or size.
𝜌 (Ωm)
how can you determine the resistivity of a wire?
what could invalidate the results?
Finding Cross-sectional Area:
- use a micrometre and measure the diametre of a wire in at at least 3 separate points & then take an average then divide by 2 for radius then get cross-sectional area
setting circuit:
- clamp wire to a ruler at the 0 mark
- connect to the circuit with power supply, ammeter, voltmetre
- use a crocodile clip to to connect wire at various lengths:
record lengths and record V&I for R
- plot graph of R against L, calculate gradient
- R/L = gradient = 𝜌/A
- multiply by A obtained at start
evaluation:
- control the temp as resistivity is affected by temp so not controlling could invalidate results
define power
what is the formula for power in ciruits
power is the rate of energy transfer
in circuits: P=IV
P=V²/R
P=I²R
define current
define potential difference
- rate of transfer of charge
- energy transferred per coulomb / work done per coulomb
what is 1kWh in joules?
1kWh = 3.6 million J
1000 W x 3600s = 3.6 million
what is Kirchoff's second law?
what law is it a result of?
Kirchoff's second law - in a circuit, the sum of electromotive force is equal to the sum of potential difference in a closed system as a result of the conservation of energy
why do all sources of e.m.f. have internal resistance?
explain why there is a difference between terminal p.d. and e.m.f. in terms of energy
what is this difference referred to as?
what si the relationship between e.m.f. and terminal p.d. and lost volts?
- sources of e.m.f. have internal resistance due to charge carriers colliding with atoms inside the power supply
- not all energy that is transferred to charge carriers is available for the circuit, as some are transferred to the internal resistance of the cell
- results in a difference between measured p.d. across terminals of power supply and actual e.m.f., referred to as lost volts.
∴ e.m.f. = terminal p.d. + lost volts
the formula for lost volts?
what is r?
lost volts (v) = Ir
where r = internal resistance
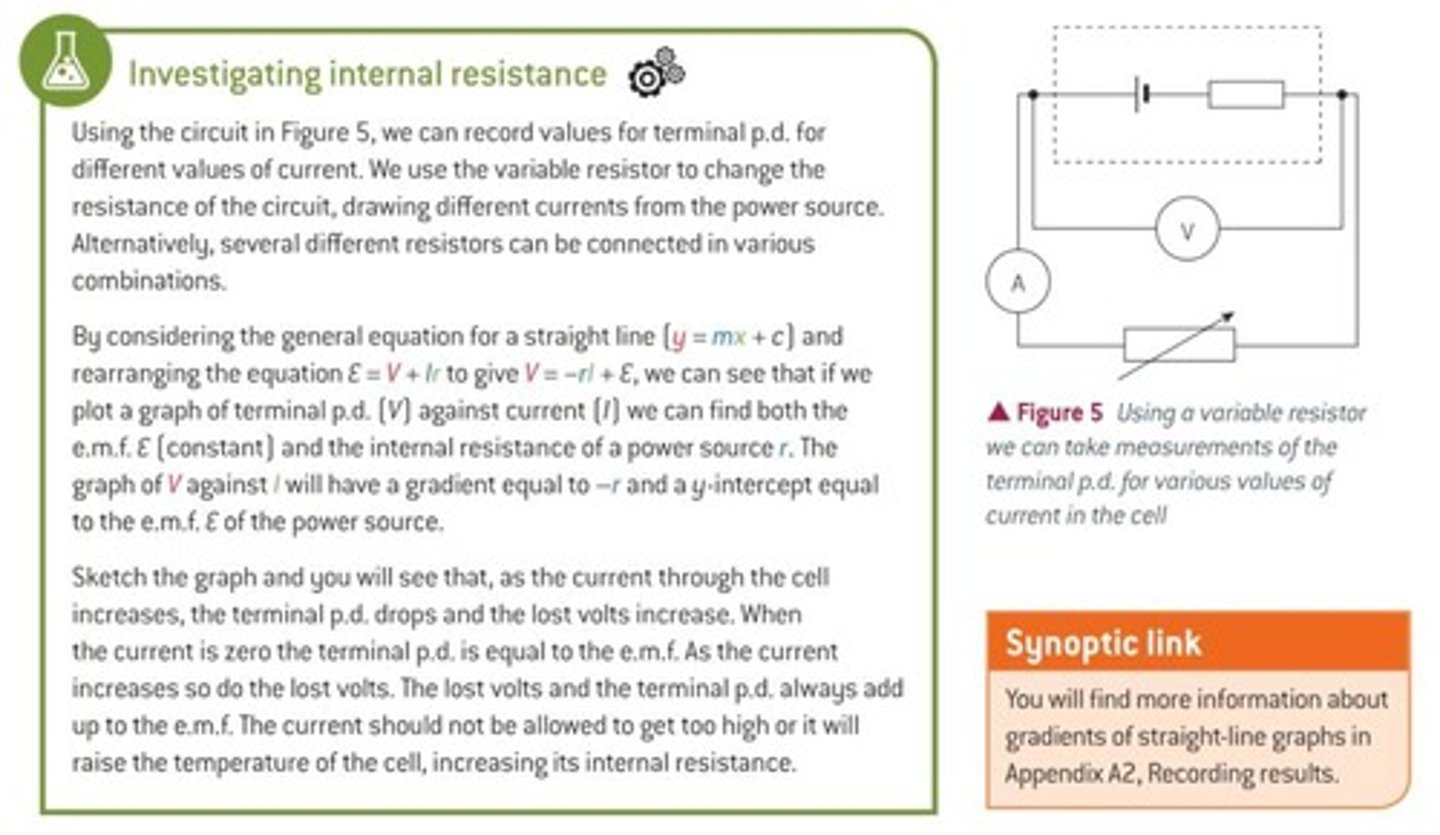
to investigate internal resistance, what circuit to set up?
what values to record?
how to obtain internal resistance?
investigating internal resistance:
- circuit with voltmetre parallel to power supply, ammeter and variable resistor
- vary current using a variable resistor and measure p.d. and I
- plot graph of V against I
- V = -rI + 𝜀
- y-intercept = e.m.f. &
(-ve) gradient = r
when explaining the variation of resistance across a component, what must always be mentioned about the resistance if the circuit is on?
the resistance is a non-zero value from when the circuit is on