Unit 4: Medieval & Renaissance Astronomy
1/221
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
222 Terms
What was the Dark Ages’ time period?
400 C.E. ↔ 700 C.E.
What was the Roman Empire & Christian world’s capital?
Constantinople
What time period was Constantine the Roman Empire & Christian world’s capital?
326 C.E. ↔ 1450 C.E.
What are the word origins of “Constantinople?”
Constantine the Great
1st Istanbul emperor
What did Constantine the Great do to the Roman Empire?
Christianizing east Roman Empire
What date did Christianity become the Roman Empire’s official religion?
380 C.E.
What is the name of Constantine the Great’s mother?
St. Helen
What is the Hagia Sophia?
Church of Holy Wisdom
became mosque when it fell to Turkish Empire
8th Wonder of the World
What was the Hagia Sophia’s construction date?
537 C.E.
True or False: Constantine the Great’s son built the Hagia Sophia.
True.
What were some changes in scientific discovery’s pace?
Church was involved in education
rejected Greek & Roman science / religion
interpreted Bible to be all God wanted one to know about astronomy
Church language = Latin
What is 1 example showing the lack of interest in astronomy during the Dark Ages?
lunar eclipse in 755 B.C.E.
Moon also passes in front of Jupiter
Simeon of Durham quotes monk writing ‘Moon passed bright star’
‘bright star’ = Jupiter
What was Boethius’ identity, & what did he try to do with Greek & Roman texts?
6th century Roman philosopher
translated to Latin
charged with treason & executed
What was the time period of Islam’s early spread?
632 C.E. ↔ 750 C.E.
What are some regions affected by Islam’s early spread?
Asia
North Africa
Spain
Portugal
What is Islamic astronomy’s time period?
800 C.E. ↔ 1300 C.E.
What text encouraged knowledge of the sky in Islamic astronomy?
Qur’an
What is a lunar year’s time length?
354 days / 12 lunations
What starts a lunar month?
waxing crescent
What is the House of Wisdom’s location?
Baghdad
What did Islamic leaders do with their scholars in response to the fleeing Greek refugees?
encouraged to collaborate & translate into Arabic
What were Abd al-Rahman al-Sufi’s birth & death dates?
903 C.E. ↔ 986 C.E.
What did Abd al-Rahman al-Sufi do in 964 C.E?
published “The Book of Fixed Stars”
What was “The Book of Fixed Stars?”
star catalogue
What method did Ptolemy use to name stars?
Greek alphabet
ranked in constellation by brightness
What was Betelgeuse’s Ptolemaic name?
Alpha Orionus
What was Rigel’s Ptolemaic name?
Beta Orionus
What was the translation of Rigel’s Islamic name?
The Foot of the Great One
What was Rigel’s Islamic name?
Rijl Jauzah al Yusrā
What was the translation of Betelgeuse’s Islamic name?
The Giant’s Shoulder
What was Betelgeuse’s Islamic name?
Bat al-jawzā
What is The Southern Fish’s Latin translation?
Piscis Austrinus
What did Al-Sufi assign the Mouth of the Whale?
brightest Piscis Austrinus star
What is the Mouth of the Whale’s modern name?
Fomalhaut
What divisions happened in the 13th century?
west Roman Empire dissolved
Spain
France
Germany
east Roman empire became Byzantine Empire
What were some reasons encouraging scientific progress in the 13th century?
Black Plague
contact between Christian & Islamic scholars in Muslim Spain → Latin translations of Arabic versions of Greek texts
What are the word origins for “renaissance?”
rebirth
French
True or False: The Dark Ages were not occurring by the 1200s.
False: The Dark Ages were still occurring frequently along west Europe.
What was the Latin translation date of The Almagest?
1150 C.E.
What was the time period of Latin scholars processing Greek knowledge?
1200 C.E. ↔ 1400 C.E.
What was the identity of the person that made the 1st notable astronomy achievement in between the 14th & 15th centuries?
Regiomontanus
What did Regiomontanus do in 1460?
published “Epitome of the Almagest”
annotated
True or False: Regiomontanus was one of the 1st Latin scholars who could read Greek.
True.
What was the identity of the person that made the last notable astronomy achievement in the mid-1300s?
Buridan
Parisian
What were some of the weaknesses in Aristotle’s theories?
natural motion
projectile motion
What did Aristotle believe about projectile motion?
can go in different direction if continually pushed by something else
2 motion sources
1. gradual air
2. fall
What did Buridan propose about projected objects?
impetus
in addition to natural motion
What did Buridan believe about projectile motion?
thrower gives impetus to projectile
weakened because it has to resist motion
What did Buridan do with Aristotle’s thought experiment?
if Earth spun, Earth has impetus = everything in contact with Earth has impetus
so
arrow shot upwards has 3 motion components
1. upward motion from bow
2. downward motion from natural motion
3. impetus from Earth
arrow has curved motion
so
fixed Earth = moving Earth
What were Nicolaus Copernicus’ birth & death dates?
1473 C.E. & 1543 C.E.
What was Copernicus’ former life like?
devout Polish Christian
clergyman
What did Copernicus believe about simplifying the universe?
simpler universe if heliocentric
What were the identities of the people whom Copernicus referred to in his writings?
Aristarchus
Herakleides
What were some weaknesses in the Ptolemaic model?
equant point
Sun governance
What did Copernicus do in 1514 C.E?
circulates “Commentariolus”
What is “Commentariolus’” translation?
Little Commentary
What was the Commentariolus?
6-leaf-long cosmos hypothesis list
True or False: Commentariolus was published work.
False: Commentariolus was not published, titled, or given authorship.
What beliefs comprised Commentariolus?
3 motion components
spin
orbit
wobble
What did Copernicus believe about Earth’s mobility?
daily spin about axis
What did Copernicus believe about planetary orbit?
planets orbit Sun; Earth annually orbits Sun
What did Copernicus believe about the precession of the equinoxes?
2600 year wobble
What did Copernicus believe about apparent planetary motion?
Earth moves & passes planet in orbit
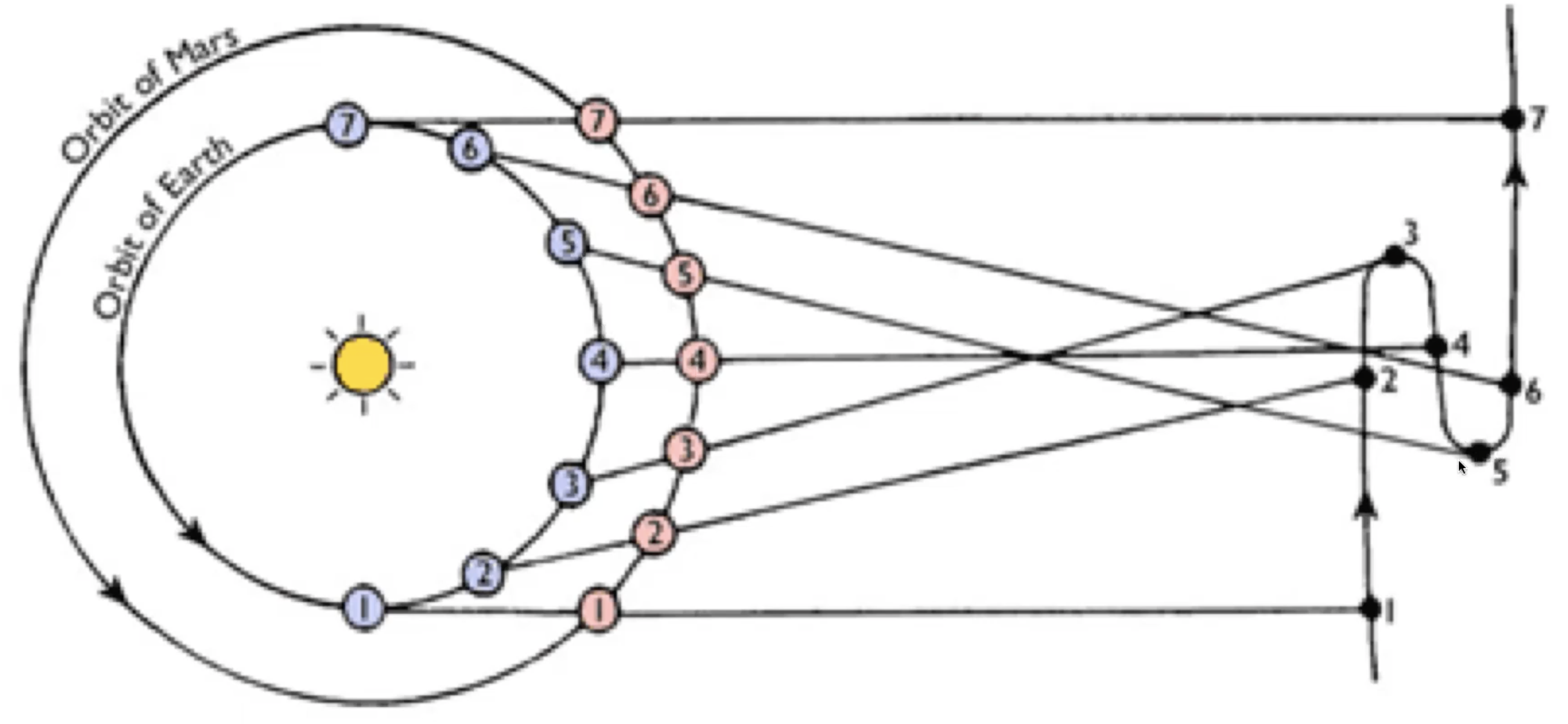
What did Copernicus believe about changing brightness?
varying distance from Earth
What did Copernicus believe about changing speed?
angle that Planet traverses decreases as Earth passes
What was Copernicus’ response to common controversy?
Earth’s mobility is because of appearance
What was Jupiter’s deferent-epicycle ratio, according to Ptolemy?
5:1
What was Saturn’s deferent-epicycle ratio, according to Ptolemy?
10:1
What did Copernicus interpret from Jupiter’s deferent-epicycle ratio?
Jupiter’s orbit is 5x larger than Earth’s orbit
5 REarth
What did Copernicus interpret from Saturn’s deferent-epicycle ratio?
Saturn’s orbit is 10x larger than Earth’s orbit
10 REarth
What unit of measure is R?
orbital radius
What is Mercury’s REarth?
0.4 REarth
What is Venus’ REarth?
0.7 REarth
What did Copernicus believe about Mercury & Venus?
inner planets
What did Copernicus realize about P & R?
follow same planetary rank
What unit of measure is P?
orbital period
What is Mercury’s P?
88 days
What is Venus’ P?
225 days
What is Jupiter’s P?
12 years
What is Saturn’s P?
30 years
What is 1 example of a church scholar that didn’t feel a heliocentric universe conflicted with Scripture?
Nikolaus von Schönberg
1536 Archbishop of Capua
What were Copernicus’ reasons for not publishing Commentariolus?
felt he was amateur
controversial idea
What is 1 example of a church scholar that felt a heliocentric universe conflicted with Scripture?
Martin Luther
1539 C.E.
What did Copernicus do in 1543 C.E?
published “De Revolutionibus orbium coelestium”
What was the translation of Copernicus’ text?
“On the Revolutions of the Celestial Spheres”
What was the identity of the person that Copernicus’ text was dedicated to?
Pope Paul III
What was inserted at the beginning of Copernicus’ book?
anonymous preface
model doesn’t have to be true to work
What were Tycho Brahe’s birth & death dates?
1546 C.E. & 1601 C.E.
What was Tycho’s background?
Danish noble
kidnapped by uncle
parents allowed kidnap
What was the reason for Tycho’s gold nose?
argued at party over math & duelled but nose was sliced off so created gold bridge
What was the story behind Tycho’s spouse?
8 children but wasn’t allowed to legally marry
What was Tycho’s most famouse story?
pet mouse that got drunk on beer & died of broken leg
What did Tycho do in 1563 C.E?
discover planetary conjunction
Jupiter
Saturn
Venus
What does “planetary conjunction” mean?
planet overtakes other planet in orbit causing planets to appear close
What did Tycho believe about Ptolemaic & Copernican models?
incorrect planetary conjunction in 2 ways
incorrect in predicting planets’ closeness
incorrect dates
Ptolemaic: 1 month
Copernican: 2 days
What did Tycho notice in his late 20s?
1572 supernova
What was the elapsed time of the 1572 supernova?
16 months
What did Tycho believe about supernovas?
remained fixed relative to stars
What did Tycho realize from supernovas?
celestial realm isn’t unchanging
What were the reasons for Tycho’s rocket to fame?
best observational astronomer
few people were ready