BMM Module 11: Molecular Interaction Fields
1/10
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
11 Terms
Cause of interaction of 2 molecules
electrostatic effects: + and - attract
Hydrophobic effects
Van der Waals
Entropy driven clustering to minimize unfavorable surface contacts with water
Goal MIP
Molecular Interaction Potential
Help us understand how molecules interact with their environment
2 types of MIPs
Molecular Electrostatic Potential (MEP)
based on true electrostatic fields around a molecule
shows where molecule are electron rich and electron poor
Molecular Interaction Fields (MIF)
theoretical tool used to analyze how a molecule is likely to interact with another molecule
This done by placing a theoretical probe (Hydrophobic, Hb acc or don,…) around a molecule and computing it’s non bonded interaction energies using a force field
creates a map where probe would experience favorable and unfavorable interactions
displayed in 3D iso-energy contours
Both methods result in potential fields (energies)
MIP Calculations
Interaction energies of MIP’s are calculated using a grid surrounding the molecule, on each point on the grid a probe is place and the E is calculated
MEP:
Probe = H+
Use Coulomb and Poisson Boltzmann equation
MIF
Use molecular probe
and non bonded interaction terms from the forcefield
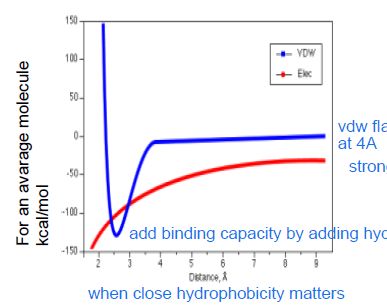
At larger distances:
electrostatics dominate: important for molecular recognition
At shorter distances (shorter than 3A)
VDW dominates: to lokck the binder in place
Partial charges of MEP
Describe how electrons are distributed in a molecule and are essential of molecular recognition
Can be estimated by
Topologica methods
define atomtype (EN and structural information of the binding type) and determine values from table
Only connectivity required, no 3D geometry
Quantum chemical methods
compute true electorn distributions
more accurate but takes longer
MEP defination
= map that shows a positively charged probe (H+) would interact with a molecule at different positions in space, describing electrostatic features around the molecule
the countours only show regions where interaction energy is above or below a predefined value
Formula represents:
interaction energy between the probe and particle 2 at gridpoint 1
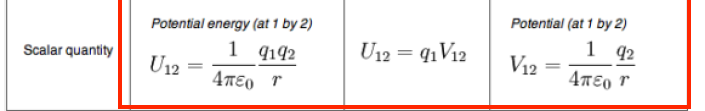
\epsilon
\epsilon = permitivity
how strongly a medium screens electrostatic interactions compared to vacuum
higher = charger are screened more strongly
\epsilon r = dielectric constant = relative permitivity
dimensionless quantity that compares the permitivity to vacuum
2~4 in a protein meaning strong electrostatic interactions
Poisson Boltzmann Electrostatics
Coulomb does not account for the continuous changing of solvent properties and electrostatics —> Poisson Boltzmann does: it tells us how the electrostatic potential due to distribution of charges varies in space
\epsilon r\left(r\right) = dielectric constant
\phi\left(r\right) = electrostatic potential
\rho\left(r\right) = charge density
r = position vector
They can all vary with position
Coulomb is just a version of PB where \epsilon is constant (independent of position)
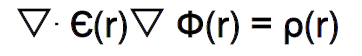
MIFs for molecular recognition
Allow us to see functionalities and properties on a receptor where a ligand can bind using probes
where non bonded terms determine the interection energy (summution of all VDW, electrostatic (and HB) terms)
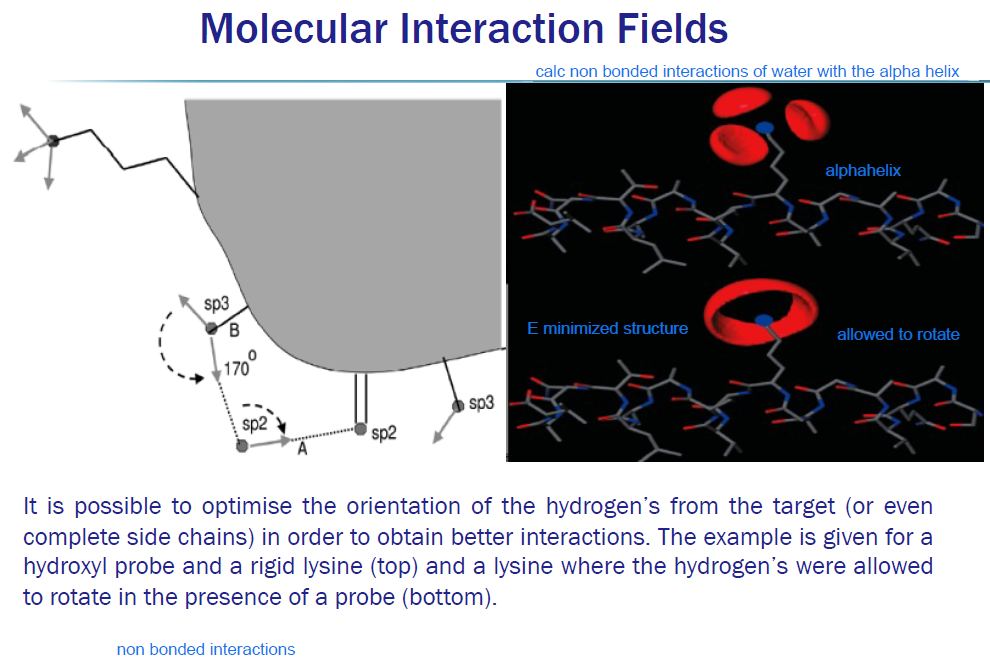
MIFs: Hydrogen orientation
In the top panel:
Lysine side chain is rigid
Hydrogen positions are fixed
Probe orientation is fixed
So only three discrete geometries satisfy:
correct distance
correct angle
no steric clash
Hence → three isolated lobes.
When hydrogens are allowed to rotate:
Lysine can reorient its H donors
The system can relax energetically
More geometries become viable
Result:
lobes merge or expand
interaction field becomes smoother and stronger
This is why the bottom panel looks “richer”.
Hydorphobic MIFs
originate from entropy driven clustering of hydrophobic molecules to minimize unfavorable contacts with water
Hydrophobic fields are visualised by using electrostic field to locate the neutral region. At this region, a hydrophibic methyl probe is used to highlight favorable dispersion contacts