Industrial Microbiology and Health Products
1/74
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
75 Terms
Primary Metabolites
Essential compounds produced during microbial growth such as amino acids, nucleotides, and vitamins that are directly involved in growth and reproduction.
Secondary Metabolites
Compounds produced after microbial growth phase (exp phase) such as antibiotics, alkaloids, and pigments that are not directly involved in growth or reproduction.

what is biotransformation?
Biotransformation is the process by which microorganisms or enzymes convert substances into more biologically active, less toxic, or more easily excretable forms.
This is often used in the modification of pharmaceuticals and environmental contaminants.
Yeast Biomass Production
Cultivation of yeast for nutritional and industrial purposes.
Can all vitamins be synthesized chemically?
No, some are too complex and are produced by microbes.
What vitamin is associated with pernicious anemia?
Vitamin B12.
Where is vitamin B12 naturally produced in the human body?
In the gut by certain bacteria.
Which microbe is used industrially to synthesize vitamin B12?
Propionibacterium freudenreichii is the primary microbe used in the industrial production of vitamin B12, particularly through fermentation processes.
Which fungus is known for producing riboflavin (Vitamin B2)?
Ashbya gossypii.
Penicillin Discovery
First antibiotic discovered from Penicillium notatum.
What is the role of Brevibacterium flavum in amino acid production?
Brevibacterium flavum is used to produce lysine, which is an essential amino acid.
What controls lysine production in bacteria?
Lysine production is controlled by a negative feedback loop tightly controlled by gene regulation
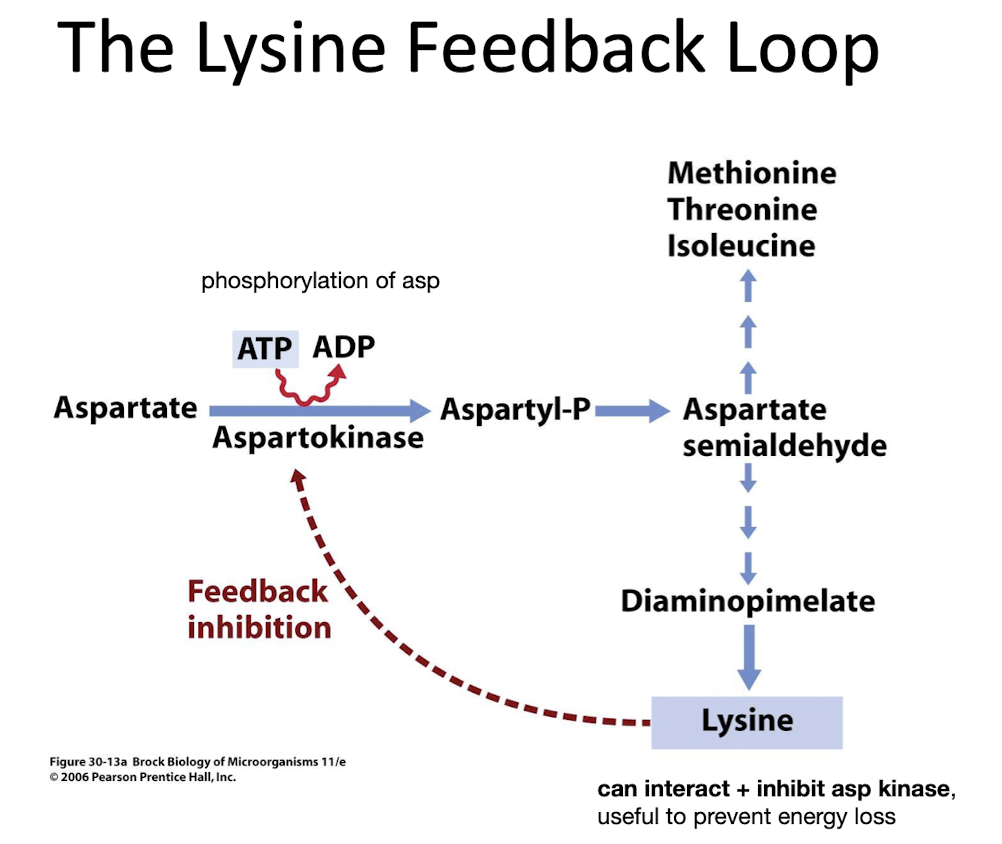
Evolutionary benefit of not overproducing Lys to conserve energy & outcompete competitors and resources in nutrient-limited environments.
What is the effect of using lysine analog (AEC) in lysine production?
AEC inhibits aspartokinase and thus lysine production.
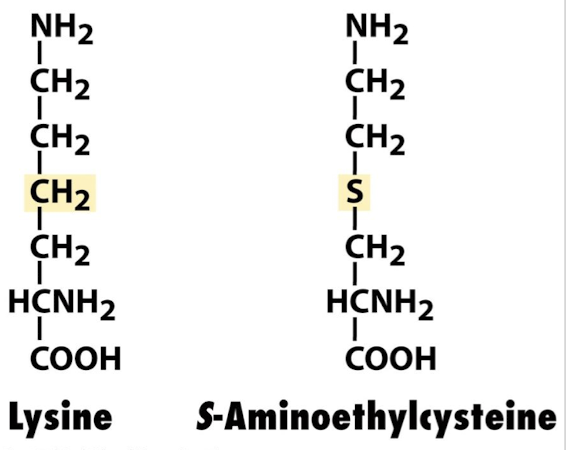
What must bacteria do to survive when aspartokinase is inhibited?
Bacteria must create a mutant aspartokinase that is not inhibited.
What is the result of having a mutant aspartokinase in lysine production?
The new strain produces higher amounts of lysine as aspartokinase is no longer inhibited by lysine or AEC, commerically viable
What is the lysine feedback loop?
It is a regulatory mechanism that controls the production of lysine, preventing overproduction and conserving resources.
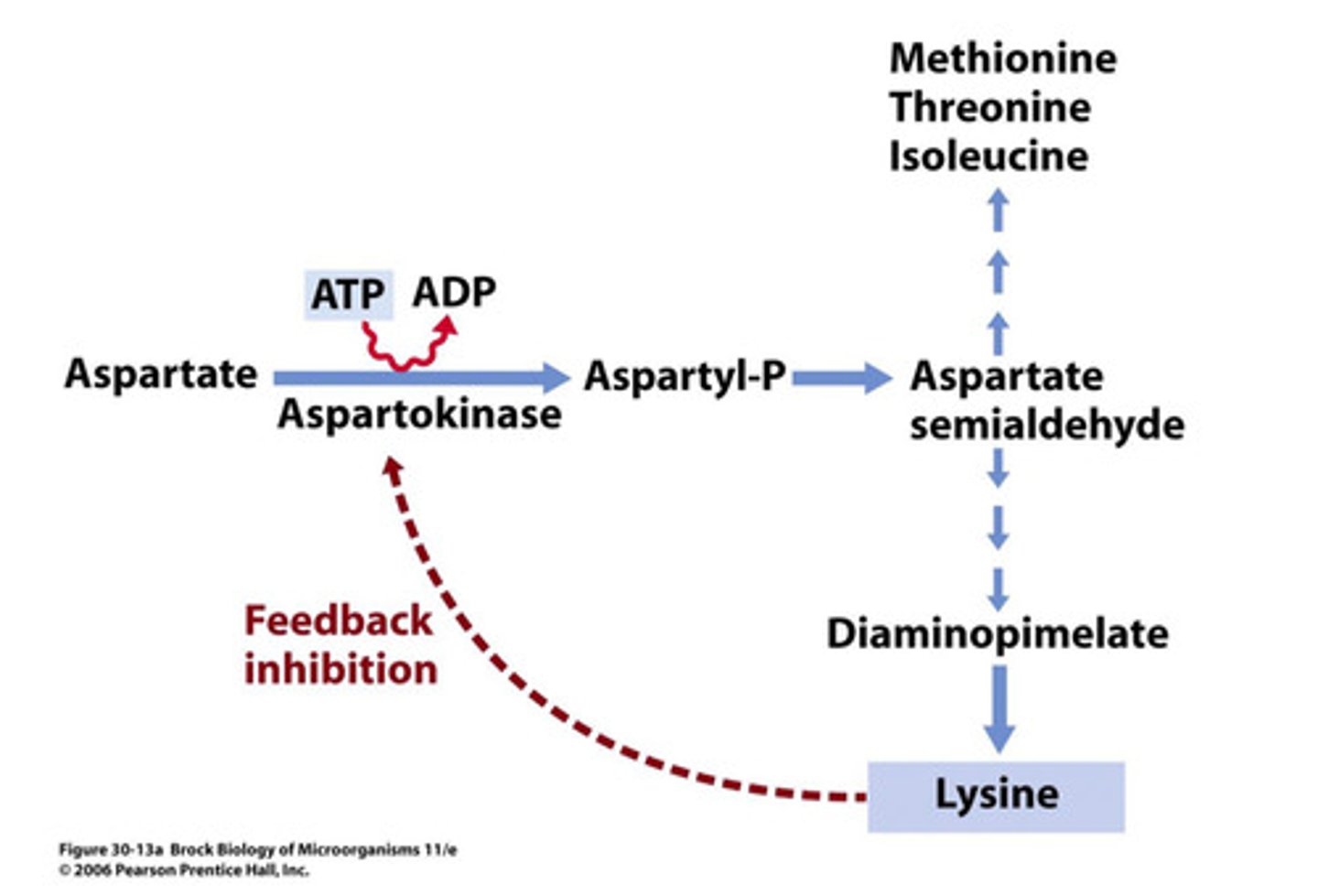
What is the role of aspartokinase in lysine biosynthesis?
Aspartokinase catalyzes the phosphorylation of aspartate, a precursor for lysine.
How does lysine inhibit aspartokinase?
Lysine binds to a regulatory site on aspartokinase, changing its shape and reducing its activity.
What happens to lysine biosynthesis when lysine levels are high?
The biosynthesis pathway slows down or halts to prevent excess lysine production.
What is a negative feedback loop?
A negative feedback loop is a regulatory mechanism in which a change in a system triggers a response that counteracts or reduces that change.
What is the purpose of a negative feedback loop in biological systems?
It helps to maintain stability or balance by keeping conditions like temperature, hormone levels, or metabolite concentrations within a narrow, healthy range.
What are corticosteroids used for?
Steroid - animal hormone used to reduce inflammation and suppress immune response.
What are androgenic steroids used for?
To support fertility and increase muscle mass.
What role do microorganisms play in biotransformation?
They carry out complex chemical reactions that are difficult to do synthetically.
Why is chemical synthesis of cortisone hard and expensive?
It requires adding specific functional groups, which is complex.
Which microbe is used to convert progesterone into cortisone?
Rhizopus nigricans
What are the advantages of microbial methods in cortisone production?
They are more efficient, specific, and cost-effective.
What is the starting molecule for cortisone production?
Progesterone (C21 steroid) undergoes biotransformation by Rhizopus nigricans producing 11⍺- hydroxyprogesterone, which is further converted to cortisone.
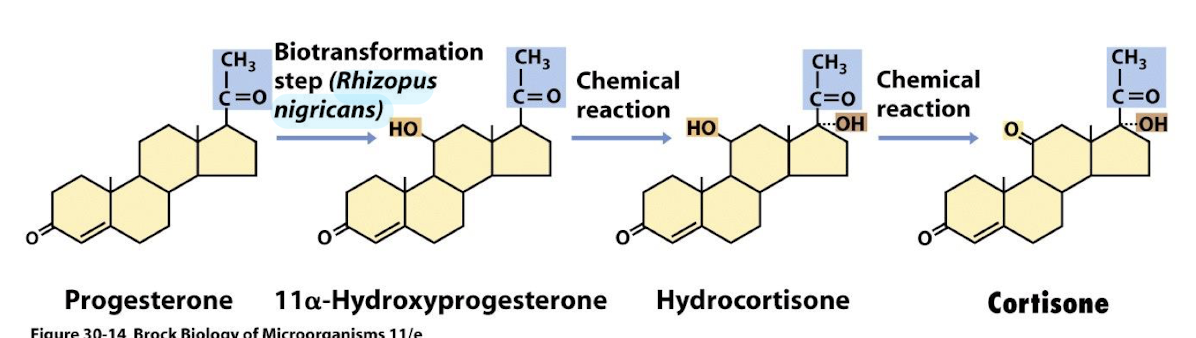
What modification does microbial hydroxylation add to progesterone?
Adds a hydroxyl group (-OH) at the 11α-position
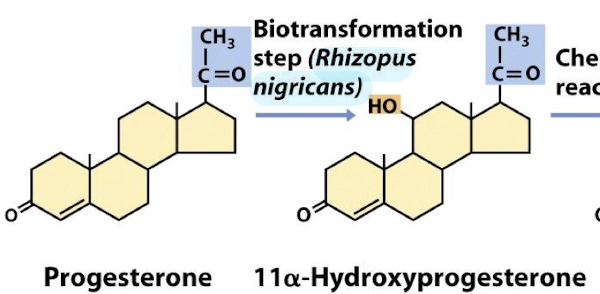
What is the simplified overall reaction for cortisone production?
Progesterone → (microbial hydroxylation) → 11α-hydroxyprogesterone → (oxidation and further steps) → Cortisone
Androgenic Steroids
Hormones that promote muscle growth and fertility.
Who first discovered Penicillin?
Alexander Fleming
What bacterium did Alexander Fleming observe in relation to the fungus Penicillin notatum?
Staphylococcus aureus
Who purified the Penicillin mold and initiated human trials?
Howard Florey and Ernst Chain
Which company achieved mass production of Penicillin in 1942?
Pfizer
What technique did Pfizer use for mass production of Penicillin?
Deep-tank fermentation
In what year was Penicillin made available orally to the public without prescription?
1950
Who were the recipients of the Nobel Prize for the discovery of Penicillin?
Fleming, Florey, and Chain
What are antibiotics?
Compounds produced by microorganisms that kill or inhibit the growth of other microorganisms.
Naturally occurring but are harnessed for biomedical uses
What percentage of antibiotics are produced by Streptomyces bacteria?
70%
what are some additional examples of antibiotic producing organisms?
Streptomycin by Streptomyces griseus,
Bacitracin by Bacilluslicheniformis (EFB)
Kanamycin by Streptomyces kanamyceticus.
What was the first antibiotic and which organism produced it?
Penicillin, produced by Penicillium notatum.
How much penicillin did the original Penicillium mould (notatum) produce per ml of broth in 1943?
Less than 10 units.
Which strain of Penicillium was found to produce 100 times more penicillin than notatum?
Penicillium chrysogenum.
how did scientists improve the amount of penicillin produced from penicillium strains?
By introducing mutations in the DNA i.e by UV-irradiation, chemical mutagenesis and selective breeding techniques to enhance antibiotic production.
What is the first step in preparing a bioreactor?
Steam sterilise the bioreactor
Load with sterilised growth medium
Inoculate with strongly growing hyphae
Tight control of temperature, pH and aeration
Penicillium
The name Penicillium comes from penicillus = brush, and this is based on
the brush-like appearance of the fruiting structures
What is added to the culture to initiate growth?
Inoculum of strongly growing Hyphae
Why must the pH be adjusted during penicillin production?
Ammonia is produced, which must be neutralized as too high a pH will affect growth & damage hyphae
NH3 levels must be appropriate so that the natural environment is not available to counteract it
What temperature condition is necessary for optimal growth?
Temperature must be set to maximize growth and maintained.
What are essential factors for the growth phase of penicillin production?
Aeration and continuous mixing.
When is the majority of penicillin produced?
After the microbes have grown and used the sugar substrates involved to grow.
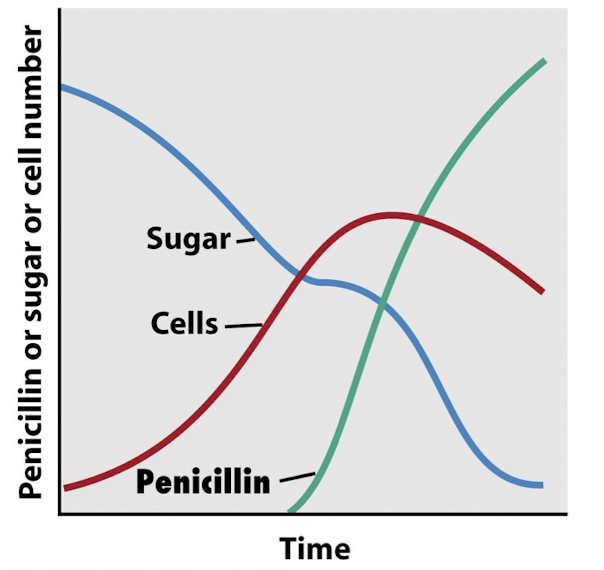
What is the first carbon source used in penicillin production?
Lactose
What additional feedings are used to keep the culture alive?
Feedings of glucose and nitrogen sourcei
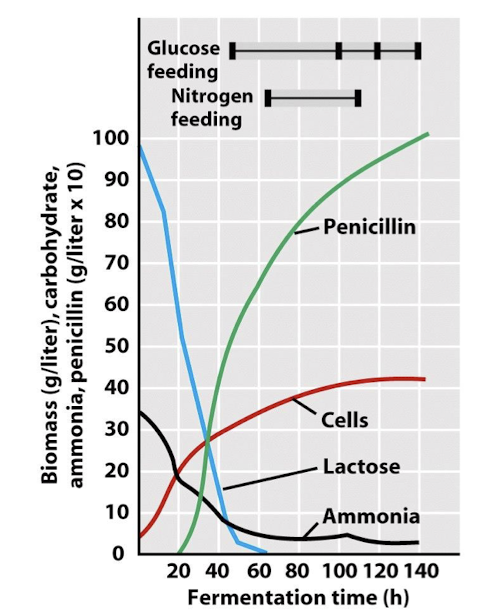
.e NH3, keeps culture alive and
producing lots of penicillin at just the right conc. to keep it at the stationary phase
What is an advantage of using hyphae in penicillin production?
Better oxygen transfer and nutrient uptake due to the increased surface area in the bioreactor for biochemical rxns to occur
What is a disadvantage of using hyphae in penicillin production?
Increased viscosity.
What is key to the mixing process during penicillin production?
Mixing is essential for maintaining uniform growth.
What considerations are there for improving the antibiotic?
Can it be taken orally, is stability an issue, and could structural alterations help?
Teixobactin
New class of antibiotic discovered from soil.
Botulinum Toxin
Potent toxin used in medical treatments and bioterrorism.
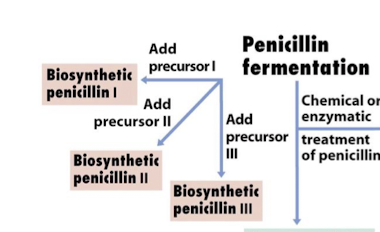
What can be created by adding different precursors to penicillin?
Different biosynthetic penicillins can be made by directly altering penicillin, semi-synthetic penicillin can be created to improve efficacy and spectrum of activity.
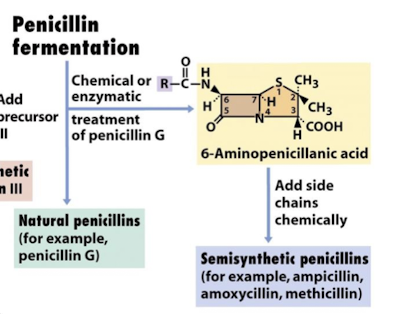
What is created by directly chemically altering penicillin?
Semisynthetic penicillin eg ampicillin or amoxycillin, methicillin
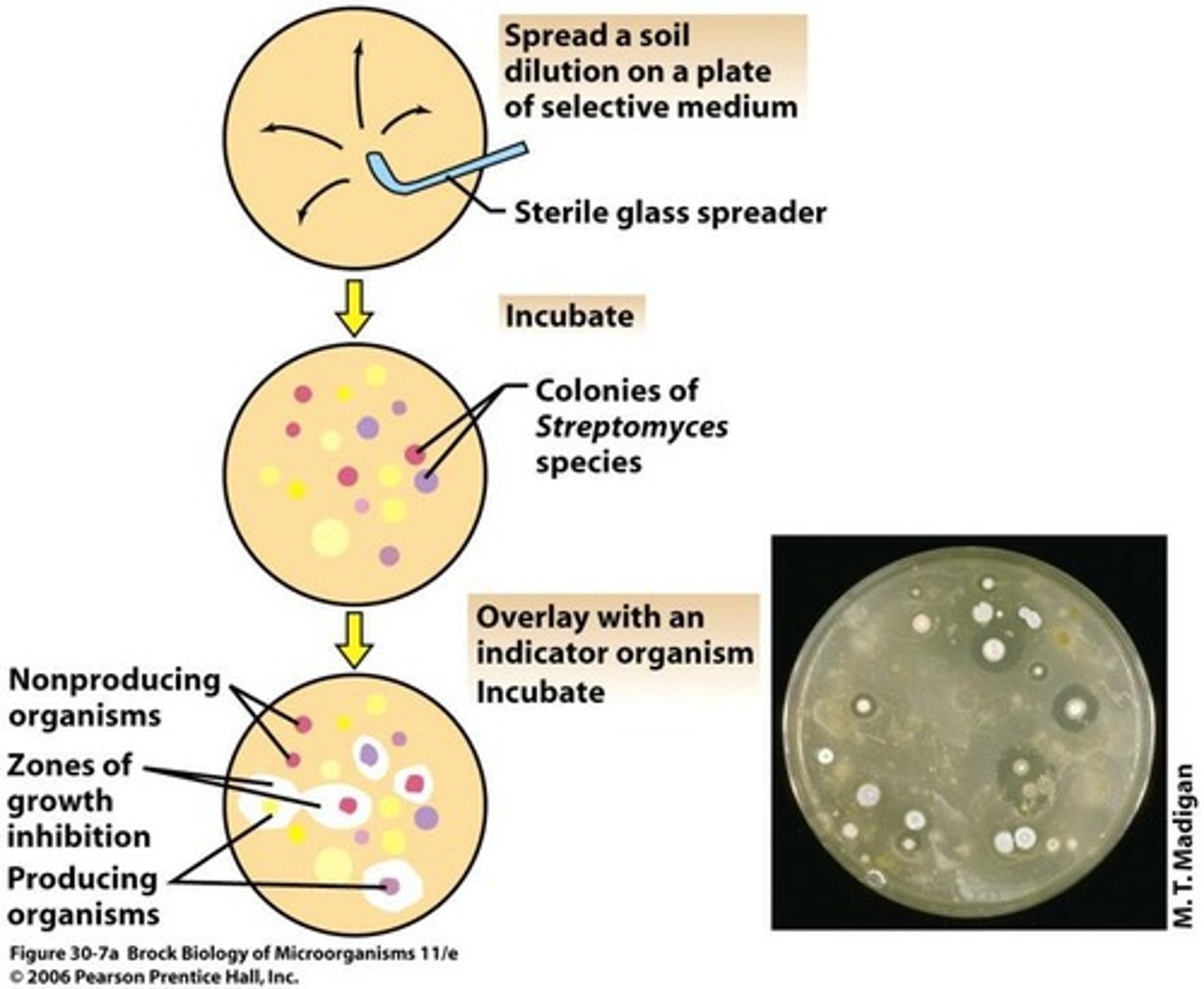
What is the primary method for discovering new antibiotics?
Computer modelling on known antibiotics
How can new antibiotics still be discovered?
By searching for new strains producing useful compounds
What type of bacteria is often used in antibiotic discovery?
Streptomyces species from soil
What is the initial screening process for antibiotic-producing strains?
Select for Streptomyces colonies and overlay with a test strain to assess antibacterial activity.
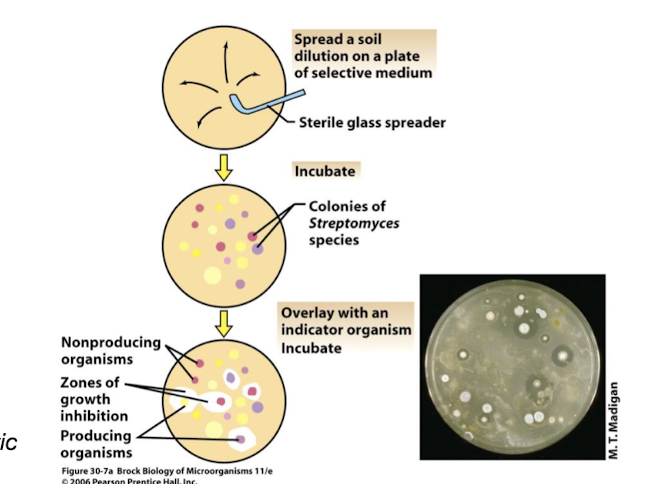
What do you check for in the initial screening of antibiotic strains?
Colonies with zones of inhibition
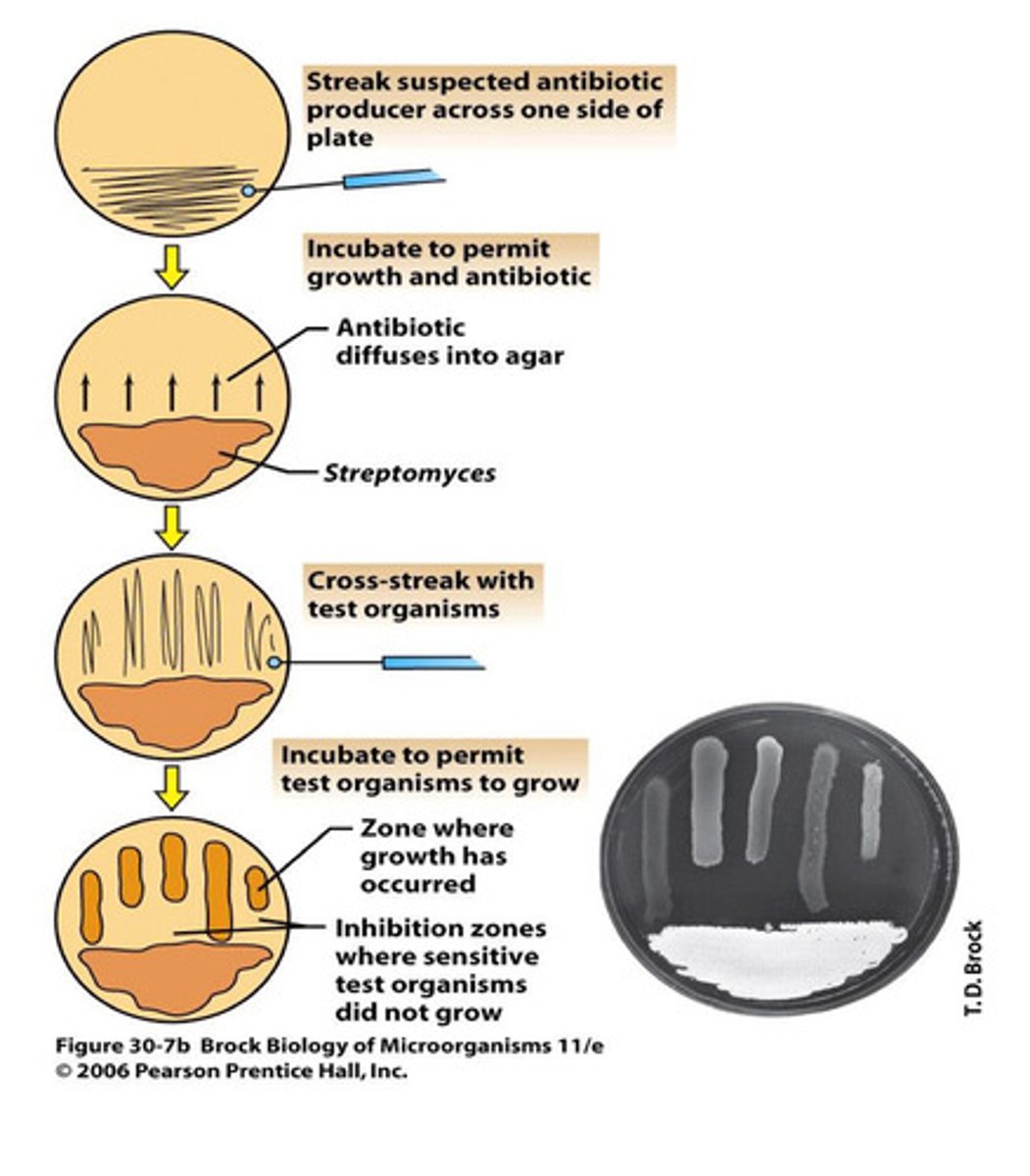
What is checked to determine the antibiotic spectrum?
Looking for inhibition zones against multiple organisms post, initial streak of a new m/o to evaluate effectiveness across different bacterial species.
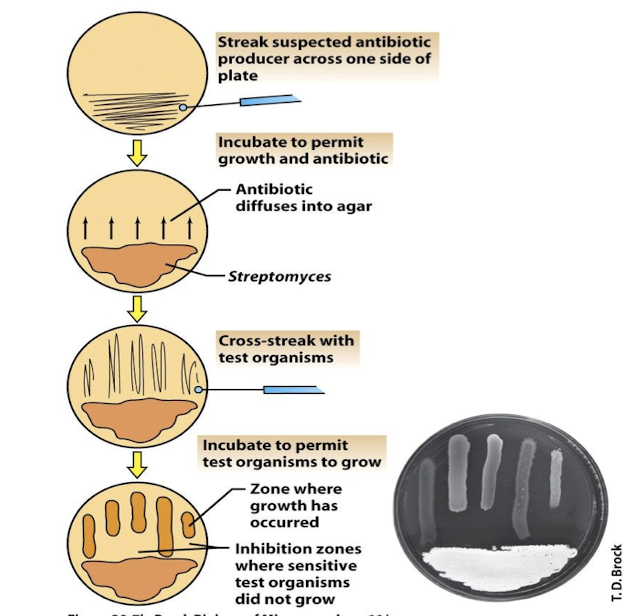
What are the steps in further development of antibiotics?
Check the structure, test for toxicity, test therapeutic activity in animals
How can large scale production of m/o occur?
Through fermentation and bioreactor systems.

What is the most potent toxin known that is an early candidate for bioterrorism?
Botulinum toxin due to its potency and potential for lethal effects, produced by the bacterium Clostridium botulinum.
What condition does botulinum toxin lead to?
Flaccid paralysis and death
What is the effect of local injections of botulinum toxin?
Localized paralysis
What can botulinum toxin be used to treat?
Various spasms
What is a common cosmetic use of botulinum toxin?
Botox