5.1 The Animal Body
1/32
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
33 Terms
Types of Animal Tissue
epithelial: lines cavities, open spaces
connective: connects tissue
muscle: movement
nervous: sends electrical signals
Epithelial Tissue
tightly packed cells atop basement membrane
classified by cell shape and numbers of layers of cells
simple (one layer of cells) vs stratified (multiple layers of cells)
Squamous Epithelia
irregular shaped cells
simple: facilitate diffusion
stratified: protection
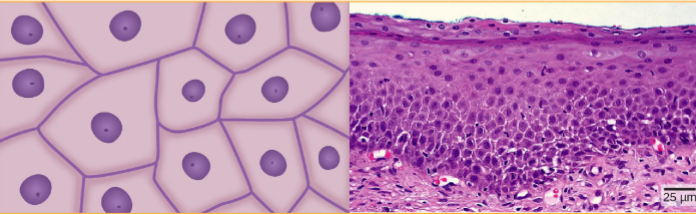
Cuboidal Epithelia
cube shaped
simple or stratified
clandular tissues, walls and ducts of tubules
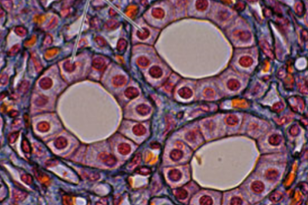
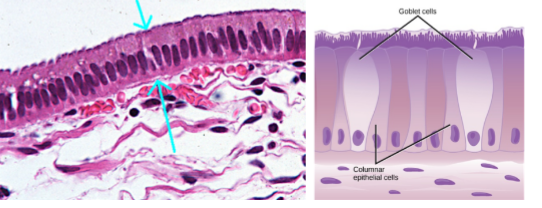
Columnar epithelia
taller
simple vs. pseudostratified
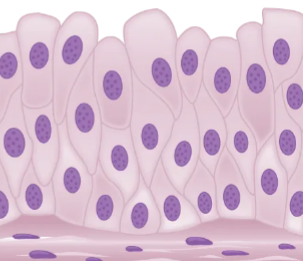
Transitional Epithelia
only in urinary system
stratified, unfolds for expansion
Connective Tissue
connect tissues/support body structure
fibroblasts: primary cell of connective tissue- produces the ECM
Loose Connective Tissue
fibroblast cells in loose matrix
surrounds blood vessels and body organs
Dense Connective Tissue
connects muscle to bone and bone to bone
Cartilage- connective tissue
in matrix of collagen fibers
provides flexible support
Bone- connective tissue
bone cells in matrix of collagen and minerals
provides firm support
Adipose Tissue
lacks fibroblasts and a matrix, few fibers
insulation and cushoining organs
store triglycerides
Blood
plasma: fluid matrix
red: deliver oxygen to tissue
white: immune response
platelets: clotting
Muscle Tissues
skeletal: voluntary, multinucleated
Cardiac (heart) /smooth (digestive system): involuntary
nervous tissue
neurons generate electrical impulses
Homeostasis
process of maintaining a constant internal state despite changes in external environment
temp
blood pressure
fluid comp
Homeostatic pathways
steps that reestablish homeostasis if any changes from set point through feedback loops
Acclimatization
adjustments of the set point for new environment
Negative Feedback Loop
counteracts change from the set point
pushes against stimulus
Positive Feedback Loop
maintains the direction of the stimulus
Endotherm
constant body temp with narrow range of internal temp
more energy
ectotherm
body temp based on environment with wide range of internal temp
less energy
Heat conservation: insulation
layer of protection
fat, fur feather
Heat conservation- shivering
increasing muscle activity
Vasodilation
increase in blood flow to body surface
heat lost
Vasoconstriction
reduction in blood flow to body surface
heat retained
Bioenergetics
heterotrophic
converted to ATP for anabolic reactions
metabolism produces heat
Energy storage- short term
glycogen in muscles and liver
energy storage long term
adipose in fat cells
Metabolic rate - BMR
basal metabolic rate- amount of energy used in non active state
SMR
standard metabolic rate
ectotherms, require less energy
Body Size energy effects
smaller animals lose heat faster= smaller animals require more energy per body mass to maintain a constant internal temp
Need to finish the rest of flashcards