organic chemistry
1/100
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
101 Terms
what is a hydrocarbon
a compound made of hydrogen and carbon atoms only
what is an alkane
A saturated (single bonds only) hydrocarbon
what is an alkene
An unsaturated (double bonds) hydrocarbon
The shorter the carbon chain the …
the more runny a hydrocarbon is (less viscous) - If the number of carbon atoms increases, the attraction between the hydrocarbon molecules also increases which results in the liquid becoming more viscous with the increasing length of the hydrocarbon chain
The liquid flows less easily with increasing molecular mass
shorter hydrocarbons (at top of tower) are
more volatile (lower boiling points) + more flammable bcs Volatility refers to the tendency of a substance to vaporise
With increasing molecular size hydrocarbon liquids become less volatile
This is because the attraction between the molecules increases with increasing molecular size
properties of hydrocarbons affect
how they are used for fuels
what is complete combustion
it happens in the presence of oxygen + produces the waste products of carbon dioxide and water vapour
during combustion …
Both carbon and hydrogen from the hydrocarbon are oxidised
why are hydrocarbons used as fuels
due to the amount of energy released when they combust completely
what is crude oil
a fossil fuel formed by the remains of plankton that died and were buried in mud
what is crude oil made up of
A mixture of different hydrocarbons
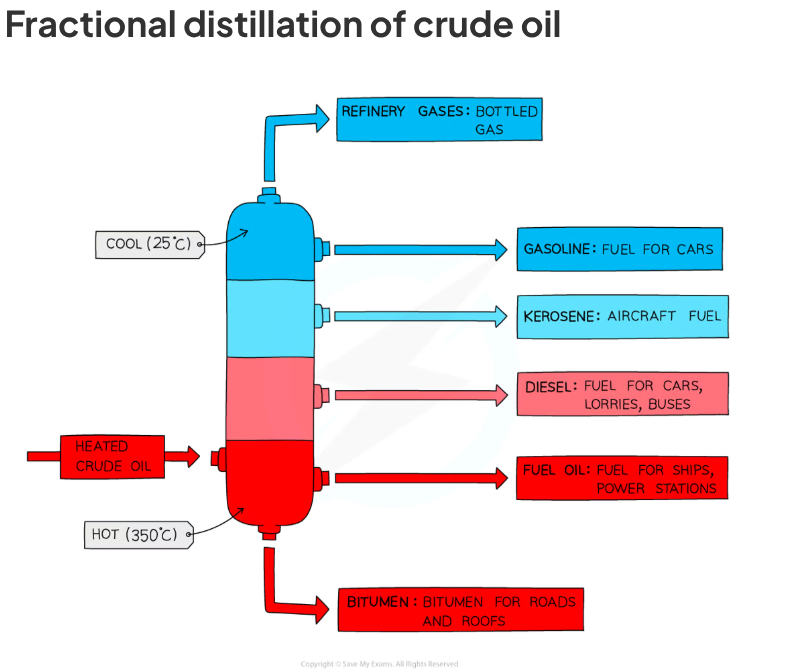
how are compounds in crude oil separated in fractional distillation
oil is heated until most of it has turned into gas and enters the fractioning column
there's a temperature gradient in the column
longer hydrocarbons have high boiling point so condense back into liquids and drain out of the column early on however the shorter hydrocarbons have lower boiling points so rise to the top of column and then condense
this leaves crude oil separated into different fractions
these fractions all have a mixture of hydrocarbons which have a similar amount of carbon atoms = similar boiling points
What are the fractions of crude oil? (top to bottom) + a use for each
refinery gases - bottled gas,gasoline - fuel for cars,kerosene - aircraft fuel,diesel - fuel for cars/lorries/buses, fuel oil - fuel for ships/power stations, bitumen - roads/rooftops
what is cracking
Splitting up long chain hydrocarbons
why do we use cracking
short chain hydrocarbons are flammable = good fuels = high demand
what is also produced in cracking
alkenes
what can alkenes make
other compounds and polymers
what type of reaction is cracking
thermal decomposition + endothermic
what is thermal decomposition
breaking down molecules by heating them
what happens in catalyctic cracking + conditions needed for it
Catalytic cracking involves heating the hydrocarbon molecules to around 600 – 700 °C to vaporise them
The vapours then pass over a hot powdered catalyst of aluminium oxide (alumina)
This process breaks covalent bonds in the molecules as they come into contact with the surface of the catalyst, causing thermal decomposition reactions
what happens in steam cracking
Long-chain hydrocarbons are vaporized.
The vaporized hydrocarbons are mixed with steam.
The mixture is heated to very high temperatures (over 850°C) and maintained under pressure.
This high temperature and pressure cause the long hydrocarbon chains to break down into smaller molecules, primarily alkanes and alkenes.
The products are then separated by fractional distillation.
what does a carbon carbon double bond mean
that alkenes have two fewer hydrogens compared with alkanes containing the same number of carbon atoms = unsaturated
straight-chain alkenes have..
twice as many hydrogen atoms as carbon
if there isn't enough oxygen in the air …
incomplete combustion occurs
why is carbon monoxide dangerous
it is a toxic and odourless gas which can cause dizziness, loss of consciousness and eventually death bcs the CO binds to haemoglobin so cannot bind to oxygen
fuels are burned in engines = high temperatures = what reacts and what does it produce?
nitrogen and oxygen from the air react to produce nitrogen oxides
These compounds (NO and NO2) are formed when nitrogen and oxygen react in the high pressure and temperature conditions of internal combustion engines and blast furnaces
Exhaust gases also contain unburned hydrocarbons and carbon monoxide
Cars are fitted with catalytic converters which form a part of their exhaust systems
Their function is to render these exhaust gases harmless
The adverse effects of nitrogen oxides include acid rain as well as producing photochemical smog and breathing difficulties, in particular for people suffering from asthma.
after nitrogen oxides have been produced, what can they combine with to produce
combine with water to produce nitric acid
what is the alkene functional group
-C=C-
what is the alcohol functional group
-O-H
what is the carboxylic acids functional group
-C=O-OH
what is the esters functional group
-C=O-O-
what are isomers
compounds with the same molecular formula but different structural formulas
how is acid rain caused
when gases such as sulphur dioxide and nitrogen dioxide dissolve in water in the atmosphere
sulphur dioxide = dissolves into rainwater droplets
nitrogen dioxide = this gas reacts with rainwater and more oxygen to form nitric acid & then when the clouds rise, the temps decrease and the droplets get larger so the droplets containing these acids are heavy enough and fall as acid rain
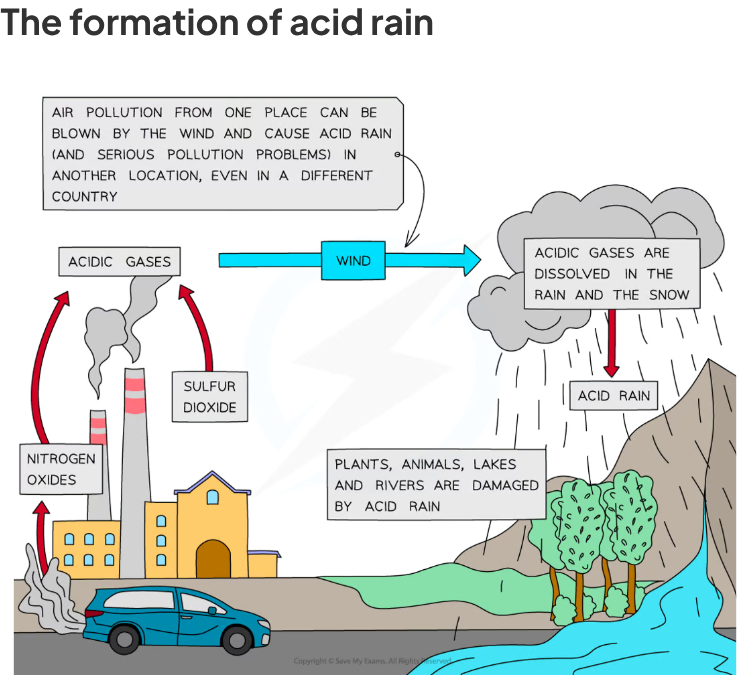
what can also trigger the formation of nitrogen monoxide & dioxides in air
lightning strikes
How is sulphur dioxide produced from burning fuels.
it comes from sulfur impurities in the hydrocarbon fuels
Fossil fuels are often contaminated with small amounts of sulfur impurities
When these contaminated fossil fuels are combusted, the sulfur in the fuels get oxidised to sulfur dioxide
S (s) + O2 (g) → SO2 (g)
The adverse effects of sulfur dioxide include acid rain:
Acid rain causes corrosion to metal structures, buildings and statues made of carbonate rocks, damage to aquatic organisms
It pollutes crops and water supplies, irritates lungs, throats and eyes
halogens react with alkanes to produce + type of reaction
haloalkanes - this is a substitution reaction
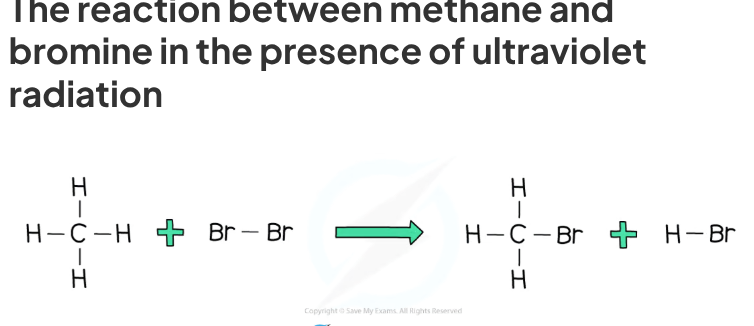
chlorine and bromine react with alkanes in the presence of
ultra violet light
Example of UV light + what exactly happens in the substitution reaction between alkanes & bromine
E.g sunlight, a hydrogen atom in the alkane is replaced by a bromine atom
what type of reaction is chlorine and bromine with alkanes and what happens
a hydrogen atom from the alkane is substituted with chlorine or bromine = substitution reaction
What is the alkane general formula?
CnH2n+2
what is the alkene general formula?
CnH2n
Describe the reactions of Alkenes with bromine to produce dibromoalkanes
alkenes react with bromine water (UV light is not required)
The double bond is broke and the bromine atoms are added - this is an addition reaction
During this reaction there is a colour change from orange to colourless
This is how we can test for the presence of an alkene or another type of unsaturated molecule
How to remember the colour change for alkenes in bromine water?
alkEne - colourlEss - brominE water
3 ways ethanol can be oxidised
burning in air or oxygen (complete combustion)
Reaction with oxygen in the air to form ethanoic acid (microbial oxidation)
Heating with potassium dichromate (VI) in dilute sulfuric acid to form ethanoic acid
2 ways ethanol can be oxidised
reacting Etheve with steam in the presence of phosphoric acid catalyst at a temp of about 300 degrees and a pressure of about 60-70 atm
The fermentation of glucose, in the absence of air, at an optimum temp of about 30degrees C and using the enzymes in yeast
Why does fermentation happen in the absence of air At optimum temp
Fermentation is carried out at temps of 30-40 degrees C because otherwise the enzymes would permanently denature and lose their structure, at temps lower than 30 degrees the process would be too slow
happens in absence of air bcs the yeast needs to respire anaerobically to produce ethanol (in air the yeast ferments aerobically and produces CO2 and H20 and the ethanol can oxidise to ethanoic acid)
2 pos and negs of hydration of ethene to produce ethanol
Pos
fast and continuous process
Produces pure ethanol
Cons
uses non-renewable crude oil
High energy costs
2 pos and negs of using fermentation to produce ethanol
Pos
uses renewable resources
Low energy process
Cons
slow and batch process
Produce impure ethanol
What is vinegar
An aqueous solution containing ethanoic acid
Describe the reactions of aqueous solutions of carboxylic acids with metals and metal carbonates
metals = dilute carboxylic acids react with metals the same way as other dilute acids e.g hydrochloric but more slowly e.g dilute ethanoic acid reacts with magnesium with a lot of fizzing to produce a salt and hydrogen, leaving a colourless solution of magnesium Ethanoate
Metal carbonates = dilute carboxylic acids react with metals the same carbonates as they do with other acids, to give a salt, carbon dioxide and water e.g dilute ethanoic acid reacts with sodium carbonate with a lot of fizzing to produce a salt, carbon dioxide and water, leaving a colourless solution of sodium ethanoate
What is ethyl ethanoate + type of reaction
The ester produced when ethanol and ethanoic acid react in the presence of an acid catalyst
this is a condensation reaction because water ( and ethyl ethanoate) is made when two molecules join together
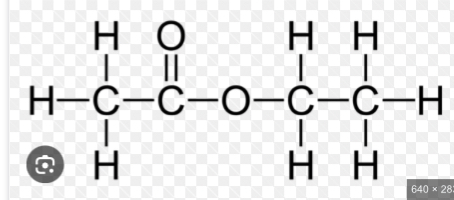
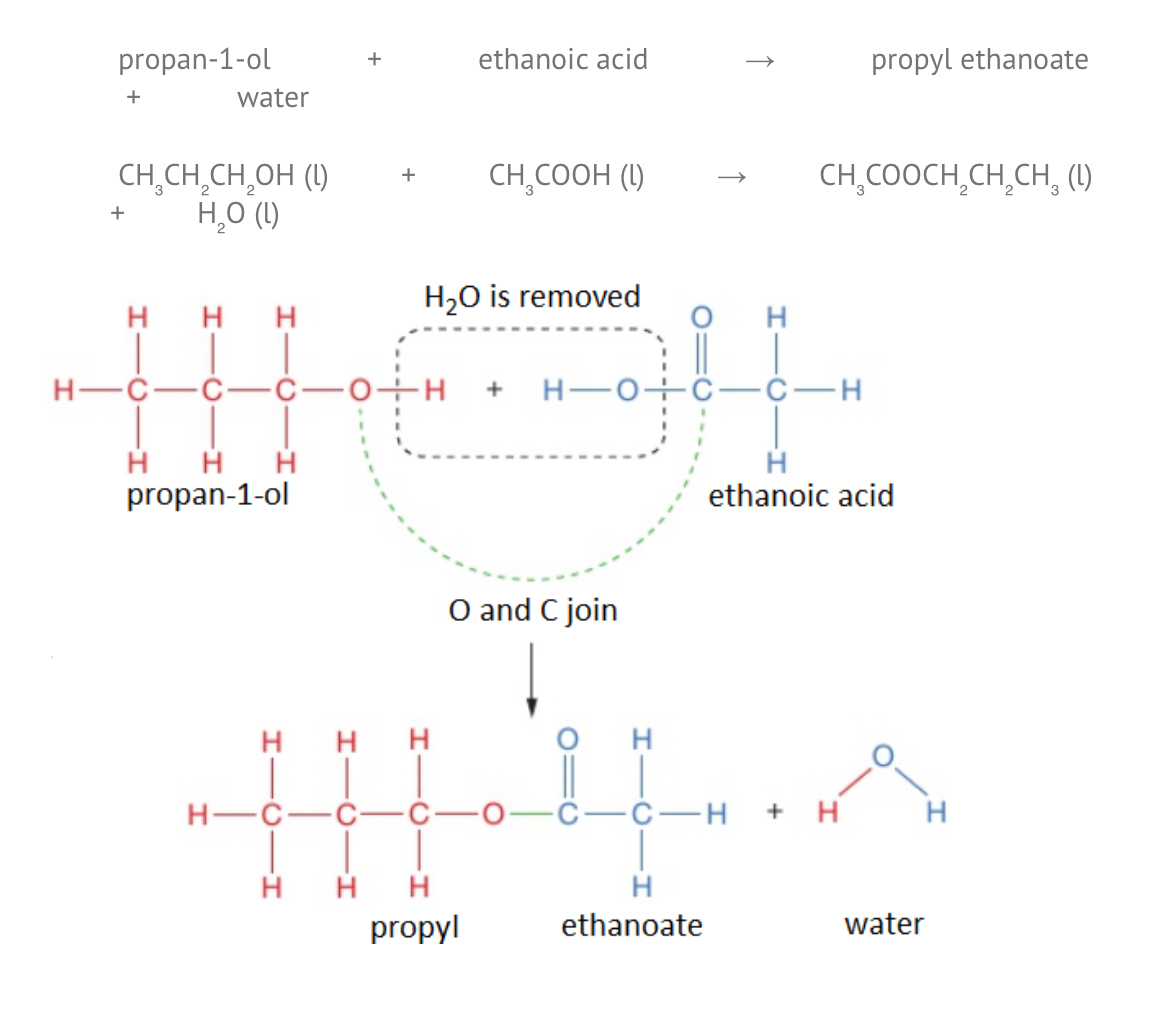
How to find structure/name of an ester
To work out the structure of the ester formed when an alcohol reacts with a carboxylic acid, it is easiest to first draw the structures of alcohol and acid and then remove the H₂O to see what is left when the molecules join.
This is still called propyl ethanoate: the alcohol bit of the name (propyl) comes first and then the carboxylic acid bit (ethanoate), even though the displayed formula is typically written the other way around. Notice that the structural formulae for esters is also typically written with the carboxylic acid bit first, so propyl ethanoate is CH₃COOCH₂CH₂CH₃.
what is a polymer
lots of the same molecules of monomers joined together in one long chain
what does polymerisation require
High pressure and a catalyst
the monomers that make up addition polymers have
a double covalent bond
addition polymerisation is
when unsaturated monomer molecules open up their double bonds to join together to form addition polymer chains.
an addition polymer contains exactly…
the same type and number of atoms as as monomers that formed it
general formula for alcohol
CnH2n+OH
alcohols are flammable and undergo complete combustion in air to form
carbon dioxide + water
alcohols can be oxidised to produce
a carboxylic acid
dif alcohols form
dif carboxylic acids e.g methanol = methanoic acid
why are methanol and ethanol used as solvents
they can dissolve same things as water but also ones water can't
how is ethanol produced
by fermentation which uses an enzyme in yeast to convert sugars to alcohol
what do carboxylic acids react with to produce
react with carbonates to produce salt, water and carbon dioxide
what happens when carboxylic acids dissolve
They ionise and release H+ ions, resulting in an acidic solution.
what is a condensation polymer
A polymer formed when monomers join together and eliminate a small molecule such as water (or hydrogen chloride)
Problems with disposal of addition polymers
they are inert and cannot biodegrade
They produce toxic gases when they are burned
what does an amino acid contain
a basic amino group and an acidic carboxyl group
amino acids can form .. via condensation polymerisation
polymers known as polypeptides
sugars can react together through polymerisation to form
larger carbohydrate polymers e.g starch
a carboxylic acid and an alcohol react to form
ester + water
What is produced in condensation polymerisation
Dicarboxylic acid + diol —> polyester + water
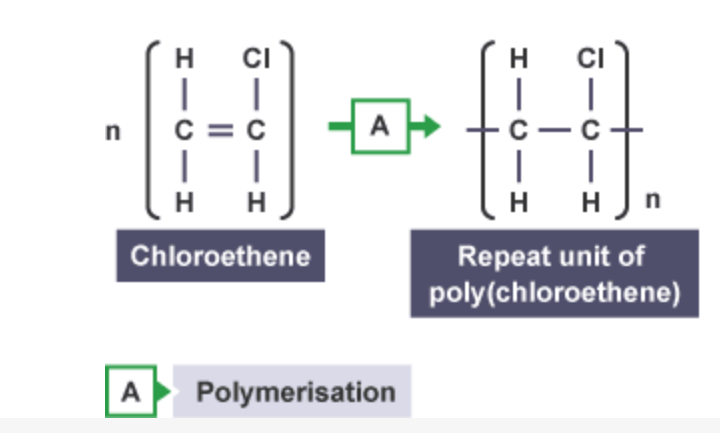
Structural display of poly(chloroethene)
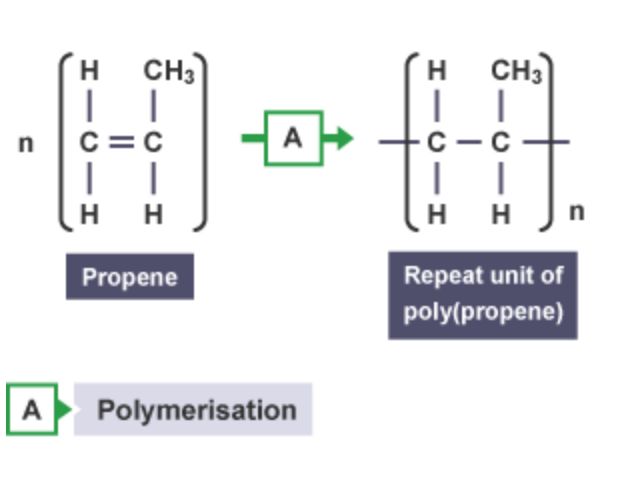
Structural display of poly(propène)
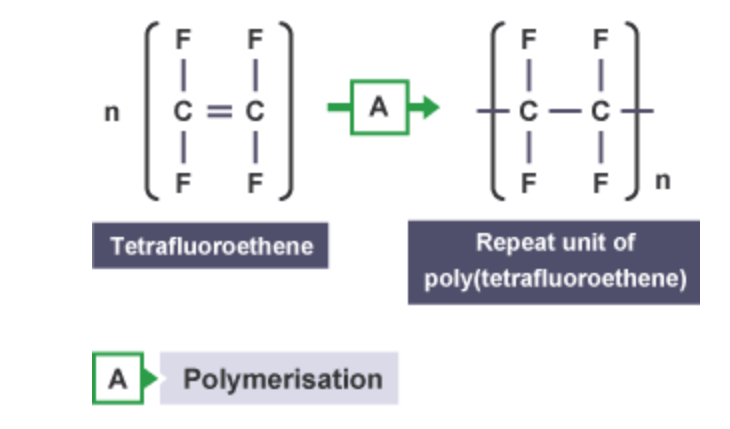
Structural display of poly(tetrafluoroethene)
what catalyst is used in esterification
an acid catalyst
esters are :
sweet smelling and volatile
ester functional group
C=O C-O same carbon
naming an ester
(length of carbon chain in alcohol)-yl (length of carbon chain in carboxylic acid)-oate
what is a homologous series
This is a series or family of organic compounds that have similar features and chemical properties due to them having the same functional group
All members of a homologous series have:
The same general formula
Same functional group
Similar chemical properties
Gradation in their physical properties
The difference in the molecular formula between one member and the next is CH2
Empirical formulae
The empirical formula shows the simplest possible ratio of the atoms in a molecule
Molecular formulae
The molecular formula shows the actual number of atoms in a molecule
General formula
The general formula shows a ratio of atoms in a family of compounds in terms of 'n' where n is a varying whole number
displayed formula
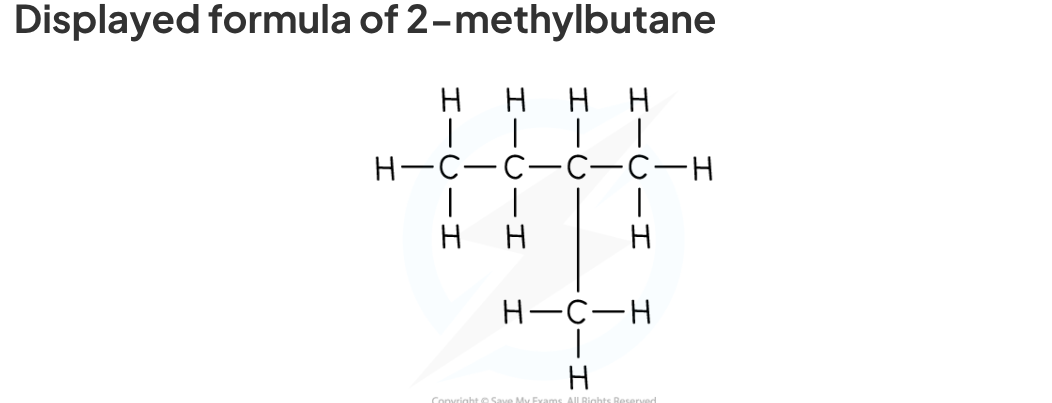
The displayed formulae shows the spatial arrangement of all the atoms and bonds in a molecule
structural formula
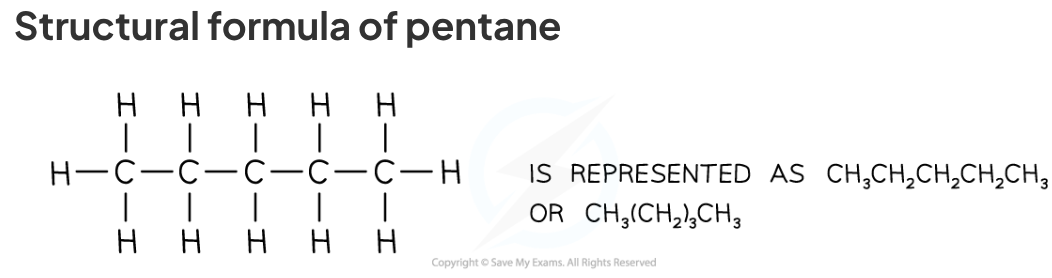
In a structural formulae enough information is shown to make the structure clear, but most of the actual covalent bonds are omitted
functional group
Functional group: A group of atoms bonded in a specific arrangement that influences the properties of the homologous series e.g alkene, alkane, alcohol
naming compounds
When there is more than one carbon atom where a functional group can be located it is important to distinguish exactly which carbon the functional group is on
Each carbon is numbered and these numbers are used to describe where the functional group is
When 2 functional groups are present di- is used as a prefix to the second part of the name
Substitution
A substitution reaction takes place when one functional group is replaced by another
Example: Methane reacts with bromine under ultraviolet light
CH4 + Br2 → CH3Br + HBr
methane + bromine → bromomethane + hydrogen bromide
addition
An addition reaction takes place when two or more molecules combine to form a larger molecule with no other products
Example: Bromine will react with ethene and the bromine molecule will react and add across the double bond of the ethene
C2H4 + Br2 → C2H4Br2
ethene + bromine → dibromoethane
combustion
This is the scientific term for burning. In a combustion reaction, an organic substance reacts with oxygen to form carbon dioxide (or carbon monoxide if incomplete combustion) and water.
Example: Alkenes burn when heated in air of oxygen
If there is an unlimited supply of air / oxygen, the products are carbon dioxide and water
This is termed complete combustion
CH4 + 2O2 → CO2 + 2H2O
C3H8 + 5O2 → 3CO2 + 4H2O
If there is a limited supply of air / oxygen, the products are carbon monoxide and water
This is termed incomplete combustion
CH4 + 2O2 → CO2 + 2H2O
C3H8 + 5O2 → 3CO2 + 4H2O
colour trend in fractional distillation of crude oil
As carbon chain length increases the colour of the liquid gets darker as it gets thicker and more viscous
melting/boiling point trend in crude oil distillation
As the molecules get larger, the intermolecular attraction becomes greater
So more heat is needed to separate the molecules
With increasing molecular size there is an increase in boiling point
What are the products when a hydrocarbon burns completely in oxygen?
As all hydrocarbons only contain the elements carbon and hydrogen, the only products will be oxides of these elements. So as long as enough oxygen is present for complete combustion, the two products formed will be carbon dioxide (CO2) and water (H2O)
What are the possible products of incomplete combustion of hydrocarbons with oxygen in the air?
happens when the supply of air or oxygen is poor. Water is still produced, but carbon monoxide. and carbon (soot) are produced. Less energy is released than during complete combustion.
what happens when te