Chapter 16: Market Power and Monopoly Strategies in Economics
1/65
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
66 Terms
What is the firm demand curve?
The quantity a firm will sell if it changes its price.
How does the firm demand curve differ from the market demand curve?
The market demand curve represents the total quantity consumers will purchase across all firms at any given price.
What characterizes a perfectly competitive market?
Many buyers and sellers, identical goods, and no market power.
What does it mean for a firm to be a price taker?
It can sell as much as it wants at the prevailing market price but cannot set a price above that.
What is market power?
The ability to charge higher prices without losing many sales to competitors.
What defines a monopoly?
Only one seller exists, making the market demand curve equal to the firm demand curve.
What is an oligopoly?
A market structure with a few large sellers where products may be similar or somewhat different.
What is monopolistic competition?
A market structure with differentiated products, many sellers, and free entry.
How do firms compete in monopolistic competition?
They compete in terms of price and product attributes like quality, customer service, and reputation.
What factors determine a firm's market power?
The number of competitors and the degree of product differentiation.
What is the trade-off when setting prices to maximize profit?
Higher prices increase profit per item but decrease the quantity sold.
How can a firm discover its demand curve?
By experimenting with different prices and measuring the quantity sold.
What does MR stand for and how is it calculated?
Marginal Revenue; it is the addition to revenue from selling one more unit.
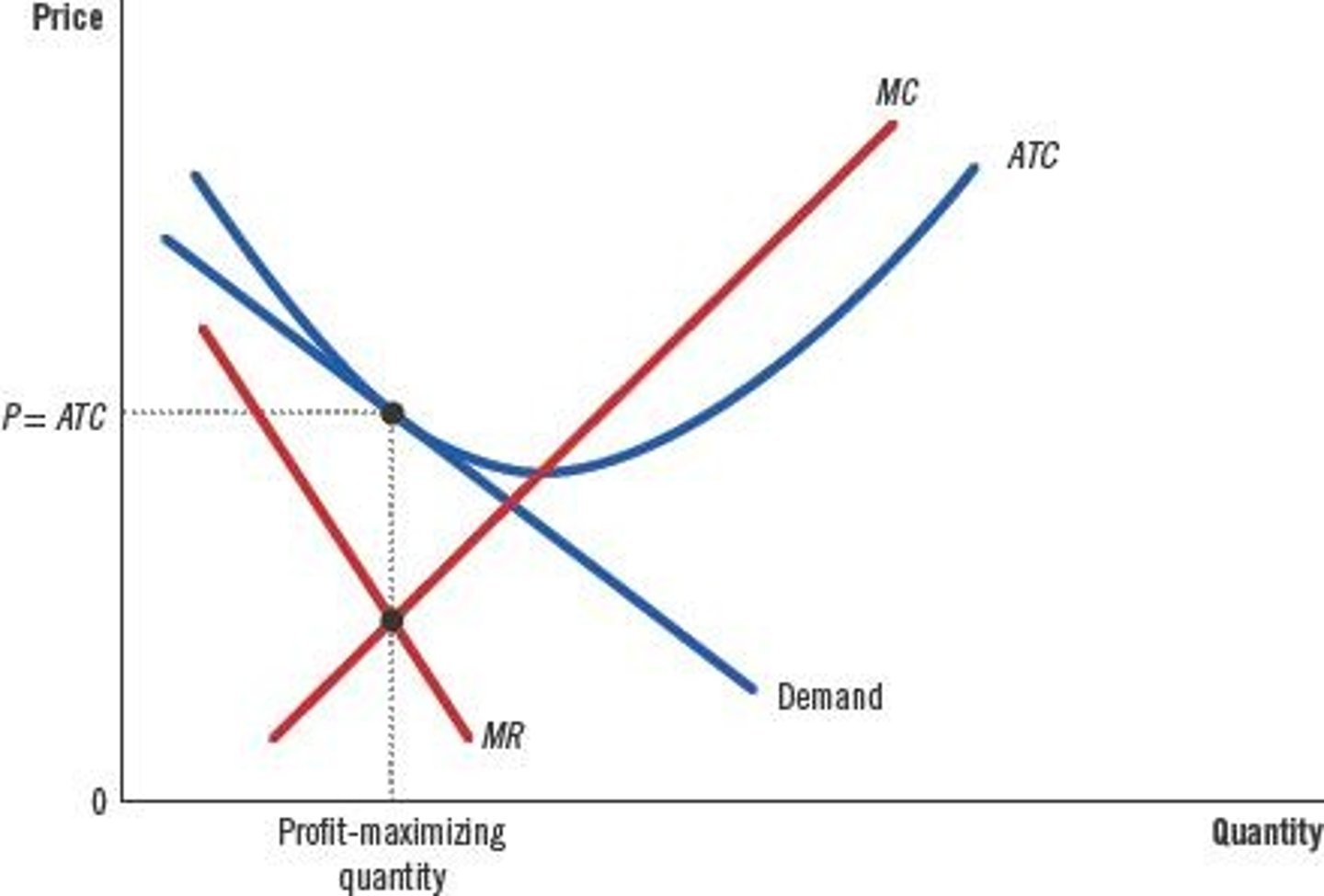
What is the relationship between MR and MC for profit maximization?
Increase quantity when MR > MC and decrease quantity when MR < MC.
What is unique about the MR for firms with market power?
MR is less than price (MR < P) unlike in perfect competition where MR equals price (MR = P).
What are the two steps for choosing price and quantity with market power?
Choose quantity where MR = MC, then set the highest price at which that quantity can be sold.
Why is there no supply curve for a monopoly?
A firm with market power is a price-maker, and quantity and price are determined by MC, MR, and the demand curve.
What is the welfare cost of market power?
Market power leads to a deadweight loss because the quantity produced is less than the socially optimal level.
How does competitive equilibrium differ from market power equilibrium?
In competitive equilibrium, price equals marginal cost (P = MC) and maximizes total surplus.
What is deadweight loss?
The loss of economic efficiency when the equilibrium outcome is not achievable or not achieved.
How do competitive prices compare to market power prices?
Competitive prices are lower and competitive quantities are greater than those under market power.
What is the condition for competitive market equilibrium?
At P = MC, which maximizes total surplus.
What occurs at market power equilibrium?
At P > MR = MC, leading to a lower quantity (QM) and deadweight loss.
What is deadweight loss in the context of market power?
It represents the loss of total surplus due to underproduction.
How does market power affect prices and quantity compared to perfect competition?
Market power results in higher prices and lower quantities than perfect competition.
What is the source of deadweight loss under market power?
The smaller quantity produced compared to the competitive equilibrium.
What is the discount effect in relation to market power?
Firms avoid lowering prices due to concerns over reduced profits, despite benefits to consumers.
What are the Sherman and Clayton Antitrust Acts designed to do?
They aim to increase competition by preventing monopolies and mergers.
What is a natural monopoly?
A market structure where a single firm can supply the entire market at a lower cost than multiple firms.
What is the relationship between average total cost (ATC) and marginal cost (MC) in a regulated monopoly?
If P is set at MC, it maximizes surplus, but can lead to losses if MC < ATC.
What is the effect of barriers to entry on market structures?
They protect monopolies and oligopolies from competition, allowing them to maintain profits.
What are monopoly resources?
Situations where a single firm owns a key resource necessary for production.
How do government regulations create monopolies?
By granting exclusive rights to produce goods, such as patents and copyright laws.
What is the significance of economies of scale in natural monopolies?
They allow a single firm to produce at a lower cost than multiple firms over the relevant output range.
What happens to market dynamics in the long run without barriers to entry?
New rivals can enter the market, driving down profits for existing firms.
When should a firm consider exiting the market?
If implicit opportunity costs exceed accounting profits, indicating negative economic profit.
What is the formula for a firm's profit?
Profit equals (P - ATC) x Q.
What happens to market power when new competitors enter?
Demand decreases for incumbents, reducing their market power and profitability.
What is the effect of existing firms exiting a market?
It increases demand for remaining firms, enhancing their market power.
What is the equilibrium outcome of free entry and exit in a market?
Economic profits tend to zero in the long run.
How can incumbent firms influence barriers to entry?
By strategically building barriers to protect their market position.
What is the inherent tension within markets regarding barriers to entry?
Entrepreneurs seek to build barriers while also facing competition from potential new entrants.
What is the primary goal of a firm seeking to maximize profits?
To enhance market power, which requires high barriers to entry.
What is the effect of increased market power on prices and quantity?
Higher prices and profits but lower quantity, exacerbating the underproduction problem.
What do policymakers aim to achieve regarding market competition?
To eliminate barriers to entry and maximize economic surplus by enhancing competition.
What are demand-side strategies for creating barriers to entry?
Creating customer lock-in through switching costs, reputation, goodwill, and network effects.
What is a switching cost?
Any impediment that makes it difficult or costly for customers to switch to another business.
How do reputation and goodwill contribute to market power?
They keep customers loyal, making it harder for competitors to attract them.
What are network effects?
A product becomes more useful as more people use it, benefiting incumbents and potentially leading to the success of inferior products.
What are supply-side strategies for creating barriers to entry?
Developing unique cost advantages, economies of scale, and access to key inputs.
How do economies of scale create a barrier to entry?
As production increases, costs decrease, allowing firms to charge lower prices and establish market leadership.
What role do patents play in market entry?
They prevent other companies from using an idea without permission, creating a monopoly.
What is price discrimination?
Selling the same good at different prices to different customers based on their willingness to pay.
What is perfect price discrimination?
Charging each customer the maximum price they are willing to pay, resulting in zero consumer surplus.
How does price discrimination affect economic welfare?
It can increase economic welfare by expanding the market and converting consumer surplus into producer surplus.
What is a common problem with implementing price discrimination?
Firms often cannot precisely target consumers' willingness to pay.
What is one solution to identify customers for discounts?
Offering group discounts based on verifiable characteristics indicating lower willingness to pay.
How do quantity discounts work?
Firms charge less per unit for larger quantities, as a buyer's willingness to pay often declines with additional units.
What is the hurdle method in price discrimination?
Offering lower prices only to buyers who are willing to overcome a specific hurdle, such as waiting for a product release.
How does the timing of product releases serve as a hurdle?
Customers must wait for a lower-priced version, allowing firms to charge higher prices to those who cannot wait.
What is an example of a hurdle method in practice?
Tesla restricting its vehicle range to differentiate between high and low willingness-to-pay consumers.
How do coupons function in price discrimination?
They identify consumers willing to spend time searching for bargains, allowing firms to charge higher prices to those who value their time more.
What is the relationship between price discrimination and economic surplus?
While it transfers consumer surplus to producer surplus, total economic surplus remains unchanged.
What is the impact of selective discounts on market expansion?
They can increase the quantity sold and help solve the underproduction problem.
What is the significance of high willingness-to-pay (WTP) consumers in price discrimination?
They are charged higher prices, which allows firms to maximize profit margins.
What are the implications of price discrimination for low WTP consumers?
They may gain some consumer surplus from increased market size but are generally offered lower prices.