A&P Exam 2: The Heart
1/85
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
86 Terms
Where is the heart located?
Located in the mediastinum in the pericardial sac
Directional term of base of the heart
Superior
Directional term of apex of the heart
Inferior/lateral
Layers of the Heart
Epicardium, myocardium, and endocardium
Epicardium
Outer later of the heart (visceral pericardium)
Myocardium
Thick cardiac muscle layer
Endocardium
Inner layer that is continuous with blood vessels
Types of Blood Flow
Systemic and pulmonary
Systemic Blood Flow
Blood flow to the body
Pulmonary Blood Flow
Blood flow to the lungs
Veins carry blood ___ the heart
Towards
Arteries carry blood ___ the heart
Away from
What are the upper chambers of the heart called?
Atria
What are the lower chambers of the heart called?
Ventricles
The right ventricle sends blood to the ___
Lungs
Oxygenated blood from the lungs returns to the heart through the ___
Left atrium
What is the function of valves have in the heart?
Act as a one-way entry to prevent blood from flowing backwards
Where does the inferior vena cava get its blood from?
Trunk, visceral organs, and lower body
Where does the superior vena cava get its blood from?
Head and upper body
What do the superior and inferior vena cava do?
Bring deoxygenated blood from the body back to the heart through the right atrium
Pulmonary artery
Carries deoxygenated blood away from the heart and to the lungs to be oxygenated
Pulmonary veins
Carry oxygenated blood back to the heart and empty blood into the left atrium
Aorta
Carries oxygenated blood to the rest of the body
Where do the coronary arteries branch off/arise from?
The aorta/aortic valves
What connects cardiac muscle cells to each other?
Intercalated discs
What are the components of intercalated discs?
Desmosomes and gap junctions
What do desmosomes in intercalated discs do?
Physically link adjacent cells together and allow them to contract as one unit
What do gap junctions in intercalated discs do?
Link cell cytoplasms
What is a functional syncytium?
A fused mass of cells that function as one; Linked mechanically, electrically, and chemically
Sarcomeres
Basic functional unit of cardiac muscles; Bundles of protein filaments that contract together
Sarcoplasmic Reticulum
Stores Ca++ when muscle fibers are at rest and release Ca++ when contraction is going to happen
Transverse Tubules (T-Tubules)
Allow the transmission of action potentials across the cell
T-Tubule Structure
Filled with interstitial fluid and walls are continuous with plasma membrane of cells
Action Potential
Short lived wave of depolarization on the plasma membrane of an excitable cell
What is the net charge of the inside of a cell?
Negative
What do action potentials do in muscle fibers?
Trigger contraction
Depolarization
Plasma membrane becomes more positive due to ion movement across the membrane (action potential)
What ion/molecule must be present for contraction to occur?
Calcium ions/Ca++
What type of metabolism does cardiac muscle rely on?
Aerobic
Why is the elastic recoil of the aorta useful?
Helps push blood forward in the aorta and back into the coronary arteries
Resting potential
-90 mV
Threshold for action potential
-75 mV
Voltage gated ____ channels open and cause depolarization at threshold
Na+ channels
Voltage gated Na+ channels close and Ca++ channels open at ____ mV
+30 mV
What happens in the plateau phase of action potential?
Na+ is being pumped out via active transport and Ca++ is flowing in
What channels open when Ca++ channels close?
K+ channels
What happens during the rapid repolarization stage?
K+ is flowing out of the cell and Ca++ is being pumped out and taken up by the sarcoplasmic reticulum
Sinoatrial (SA) Node
Group of cells that depolarize the fastest (leakiest cells); Called pacemaker cells
Atrioventricular (AV) Node
Group of cells that are slow at action potential conduction (delay AP)
SA node and AV node are connected by _____
Internodal pathways
Where does the electrical signal for contraction begin?
SA node
Systole
Contraction
Diastole
Relaxation
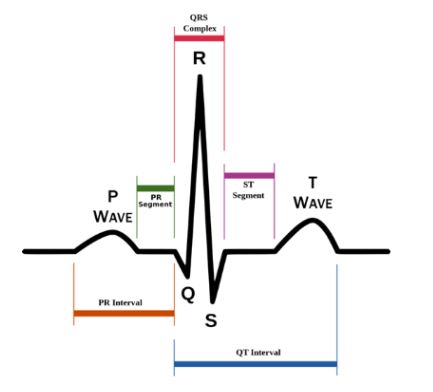
P-Wave
Depolarization of the atria
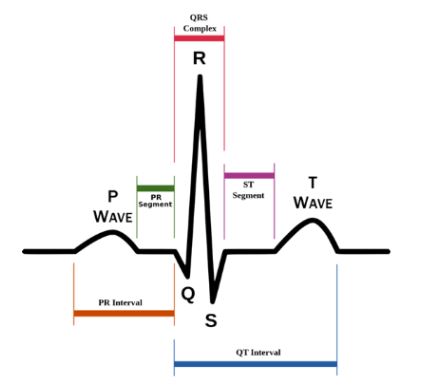
QRS Complex
Depolarization of the ventricles
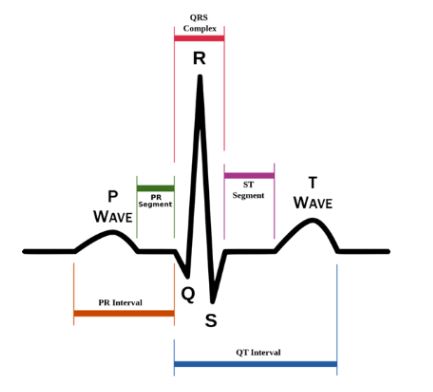
T-Wave
Repolarization of the ventricles
Arrythmia
Abnormal heart rhythm
Cardiac Cycle definition
Period between the start of one heartbeat to the beginning of the next heartbeat
Absolute Refractory Period
Another action potential cannot occur; Na+ channels are already open or inactive
Relative Refractory Period
Another action potential is possible, but Na+ channels will only respond to a larger stimulus
What is the purpose of the long action potential and long refractory period of cardiac muscle cells?
Prevent tetanus (sustained max. contraction) and limit the heart rate
Cardiac muscle cells do/do not require a nerve/neuron impulse to cause contraction
Do not
Why do cardiac muscles repolarize on their own?
They are leaky to Na+ and Ca++
Heart Beat Steps
SA node depolarizes
Conducting cells take action potential to AV node while the atria depolarizes (delay at the AV node)
Atrial contraction begins
Stimulus travels through AV node, AV bundle, AV branches, and Purkinje fibers
Atrial contraction ends, ventricles depolarize, and contract from apex to base
Electrocardiogram (ECG/EKG)
Graph of the heart’s electrical activity
Step 1 Cardiac Cycle
Atrial systole: Ventricles fill and the end quantity of blood = diastolic volume
Step 2 Cardiac Cycle
Atrial diastole
Step 3 Cardiac Cycle
Ventricular systole - Phase 1: AV valves close and pressure increases/no blood movement
Step 4 Cardiac Cycle
Ventricular systole - Phase 2: As ventricular pressure becomes greater than arterial pressure, ventricular ejection occurs. Amount ejected = Stroke volume
Step 5 Cardiac Cycle
Ventricular diastole: Ventricular pressure falls and semilunar valves close. When ventricular pressure falls below atrial pressure, AV valves open and ventricles fill passively. Both atria and ventricles are in diastole.
Cardiac Output
Amount of blood pumped out of the left ventricle in one minute
Controls of Cardiac Output
Nervous innervation (autonomic nervous system), blood volume reflexes, and hormones
Nervous Innervation
Both sympathetic and parasympathetic divisions of the ANS innervate the SA and AV node and atrial fibers
Mechanisms of Nervous Innervation
Neurons monitor blood pressure, O2, and CO2
Release of neurotransmitters which open K+ channels to slow depolarization
Release of neurotransmitters which open Na+ or Ca++ channels to increase depolarization
Blood Volume Reflexes
Atrial Reflex (Bainbridge): When venous return increases, stretching of the right atrium stimulates sympathetic activity and increases heart rate
Frank-Starling Principle: When more blood flows into the ventricles (higher end diastolic vol.) ventricles contract more forcefully and pump more blood out (SV) because sarcomeres are in a more optimal position
Hormones
Epinephrine, norepinephrine, thyroid hormone, and glucagon increase contractility
Length Tension Relationship
Tension generated depends on the length of muscle sarcomeres
Heart Sound “Lub Dub”
Lub = Slamming of AV valves
Dub = Slamming of semilunar valves
Murmur
Abnormal heart sounds (i.e. “Lub dush” or “lush dub”)
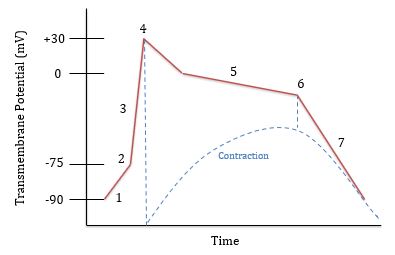
What is happening at 1?
Leaking of Na+ and Ca++ ions
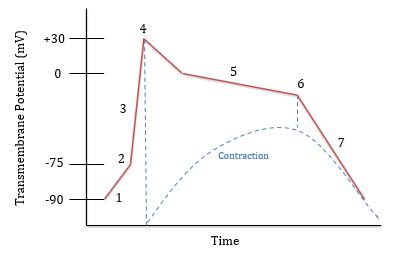
What is happening at 2?
Threshold is reached (-75 mV) and voltage gated Na+ channels open
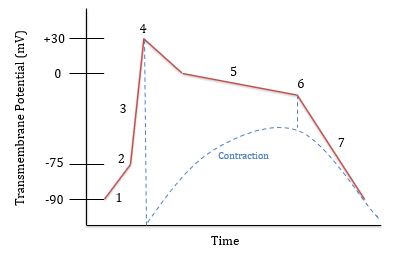
What is happening at 3?
Rapid depolarization; Na+ is flowing in
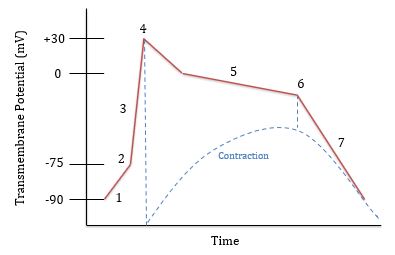
What is happening at 4?
Voltage gated Na+ channels close and Na+ is being pumped out. Voltage gated Ca++ channels open around 0 mV
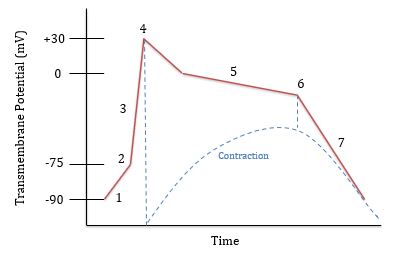
What is happening at 5?
Plateau phase; Na+ is pumped out and Ca++ flows in
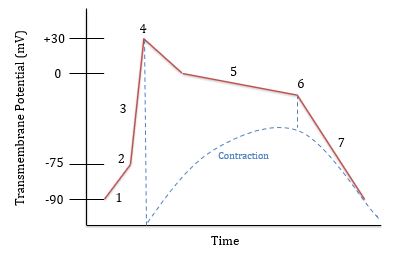
What is happening at 6?
Ca++ channels close and K+ channels open. K+ flows out
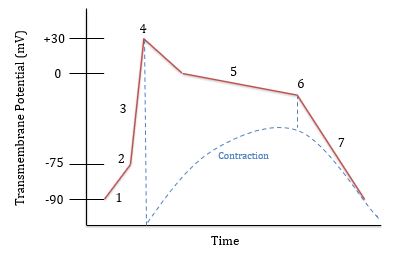
What is happening at 7?
Rapid repolarization