Cell Structure and Microscopy
5.0(2)Studied by 106 people
Card Sorting
1/33
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Suitable for Cambridge International Examinations (CIE) Biology at A Level
Last updated 11:41 PM on 11/27/22
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
34 Terms
1
New cards
magnification
the number of times an image is larger than the original
2
New cards
magnification equation
magnification = image size/actual size; M = I/A
3
New cards
1 cm = ? micrometers (μm)
10,000
4
New cards
1 cm = ? nanometres (nm)
10,000,000
5
New cards
resolution
the smallest distance where two points can be distinguished as separate
6
New cards
scanning electron microscope
view images in 3D, scans surface of samples
7
New cards
transmission electron microscope
view images in 2D, can be used to view inside specimens as small as 5 nm
8
New cards
light microscope
uses natural/artificial light to view (living) specimens under a lens
9
New cards
difference(s) between electron and light microscopes
- light microscopes: use light rays; electron microscopes: use electron beams (with electromagnets)
- light microscopes: specimens can be alive; electron microscopes: specimens are dead (due to vacuum)
- light microscopes are cheaper and portable; electron microscopes are expensive and are not portable
- light microscopes have lower magnification and resolution; electron microscopes have higher magnification and higher resolution
- light microscopes: specimens can be alive; electron microscopes: specimens are dead (due to vacuum)
- light microscopes are cheaper and portable; electron microscopes are expensive and are not portable
- light microscopes have lower magnification and resolution; electron microscopes have higher magnification and higher resolution
10
New cards
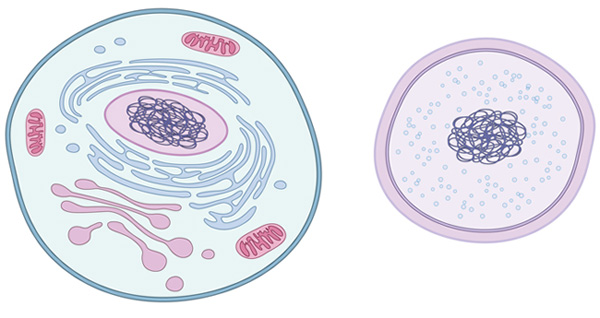
cell
basic unit of all living organisms, consists of organelles with specific functions
11
New cards
organelle
a part of the cell with specific functions and structures
12
New cards
eukaryote
a cell containing a nucleus and membrane-bound organelles, large (up to 40 μm in diameter), genetic material is linear and associated with proteins (histones), ribosomes can be 80S or 70S
13
New cards
prokaryote
a cell without any membrane-bound organelles, small (up to 5 μm in diameter), consists of a nucleoid region (where genetic material is found as circular DNA) and ribosomes (70S only)
14
New cards
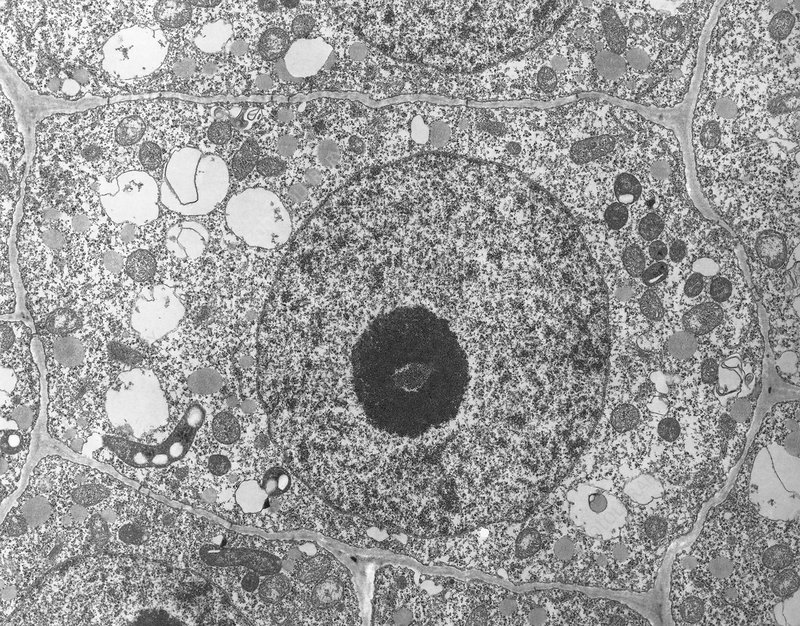
nucleus
largest cell structure, found in eukaryotic cells, holds DNA, consists of a nuclear envelope with pores and a nucleolus that is darkly stained; responsible for storing and replicating of genetic material, synthesis of ribosomes (in nucleolus), and production of RNA (specifically mRNA)
15
New cards
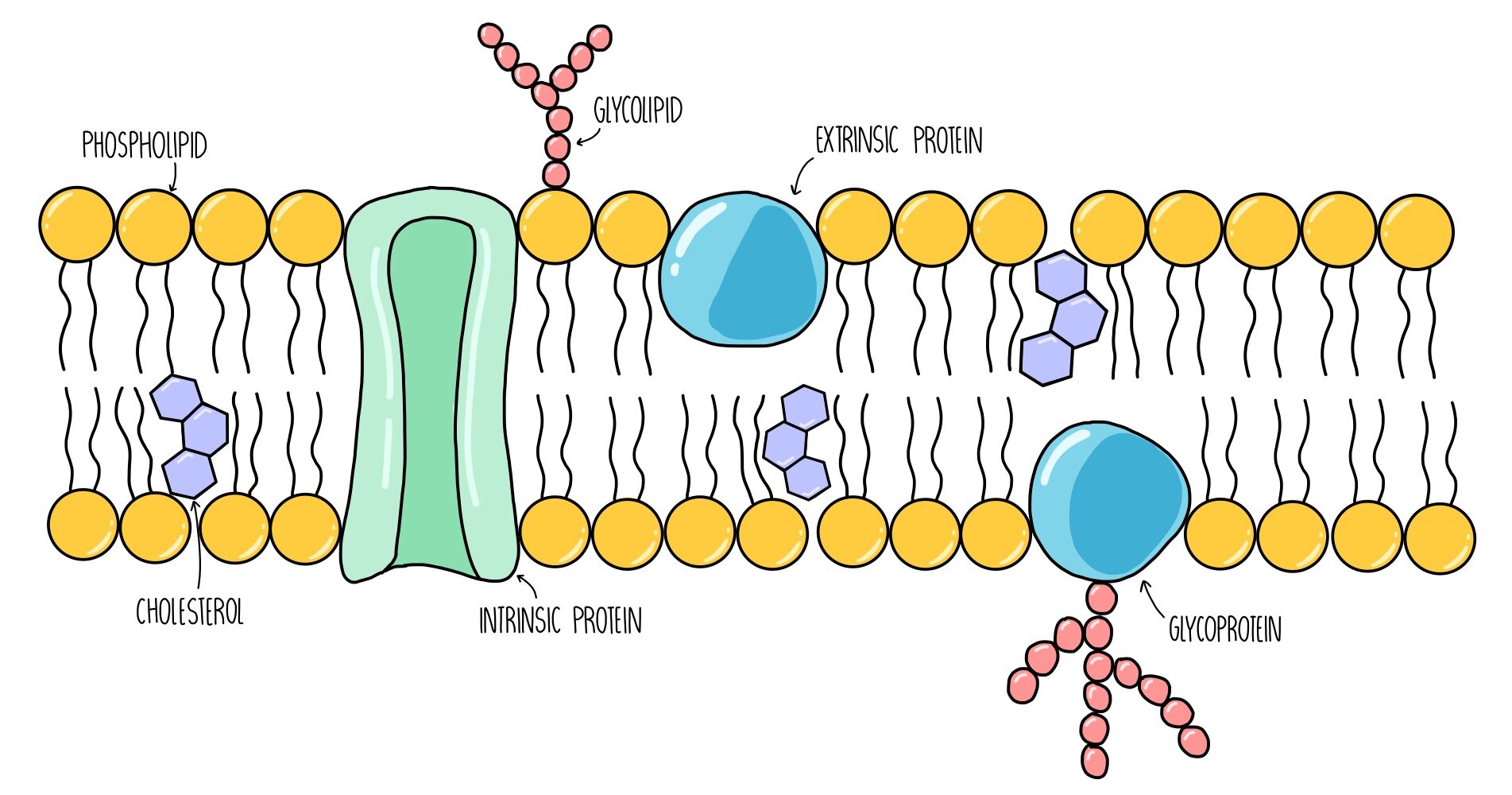
cell surface membrane
a thin membrane about 7 nm wide, partially permeable; responsible for controlling the exchange between the intracellular and extracellular environment via cell transport, cell signalling, and acts as a boundary between the intracellular and extracellular environment
16
New cards
cytoplasm
contents of the cell, excluding the nucleus
17
New cards
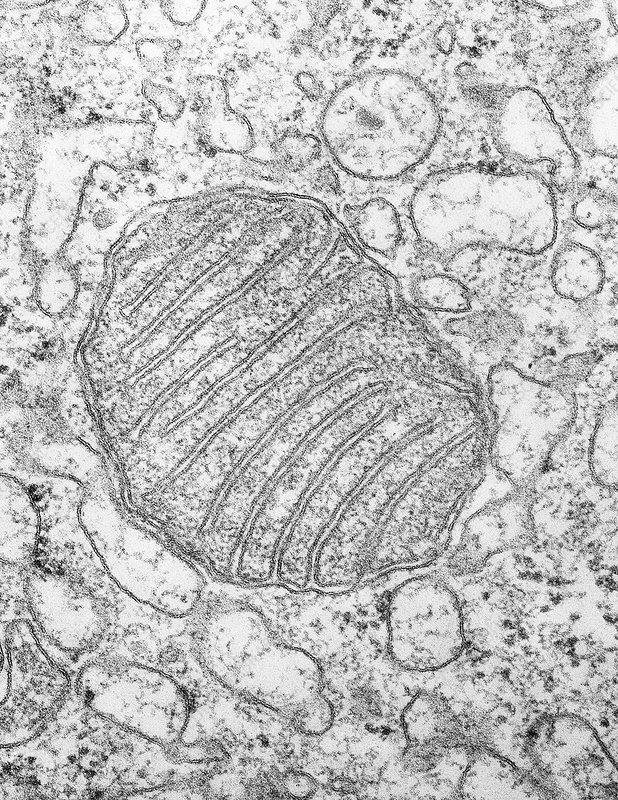
mitochondria
a double-membrane bound organelle with infoldings called cristae; responsible for aerobic respiration
18
New cards
cell wall
present in prokaryotes and plant cells, contains strengthening material such as peptidoglycan or lignin; responsible for preventing bursting by osmosis and keeping the cell's shape
19
New cards
plasmodesmata
pore-like structures found in plant cells connecting neighbouring plant cells; responsible for transporting materials from one plant cell to another
20
New cards
vacuole
usually found in plant cells, a large storage organelle; responsible for storing biochemicals, waste products, and temporary vacuoles such as phagocytic vacuoles
21
New cards
tonoplast
the partially permable membrane surrounding plant vacuoles
22
New cards
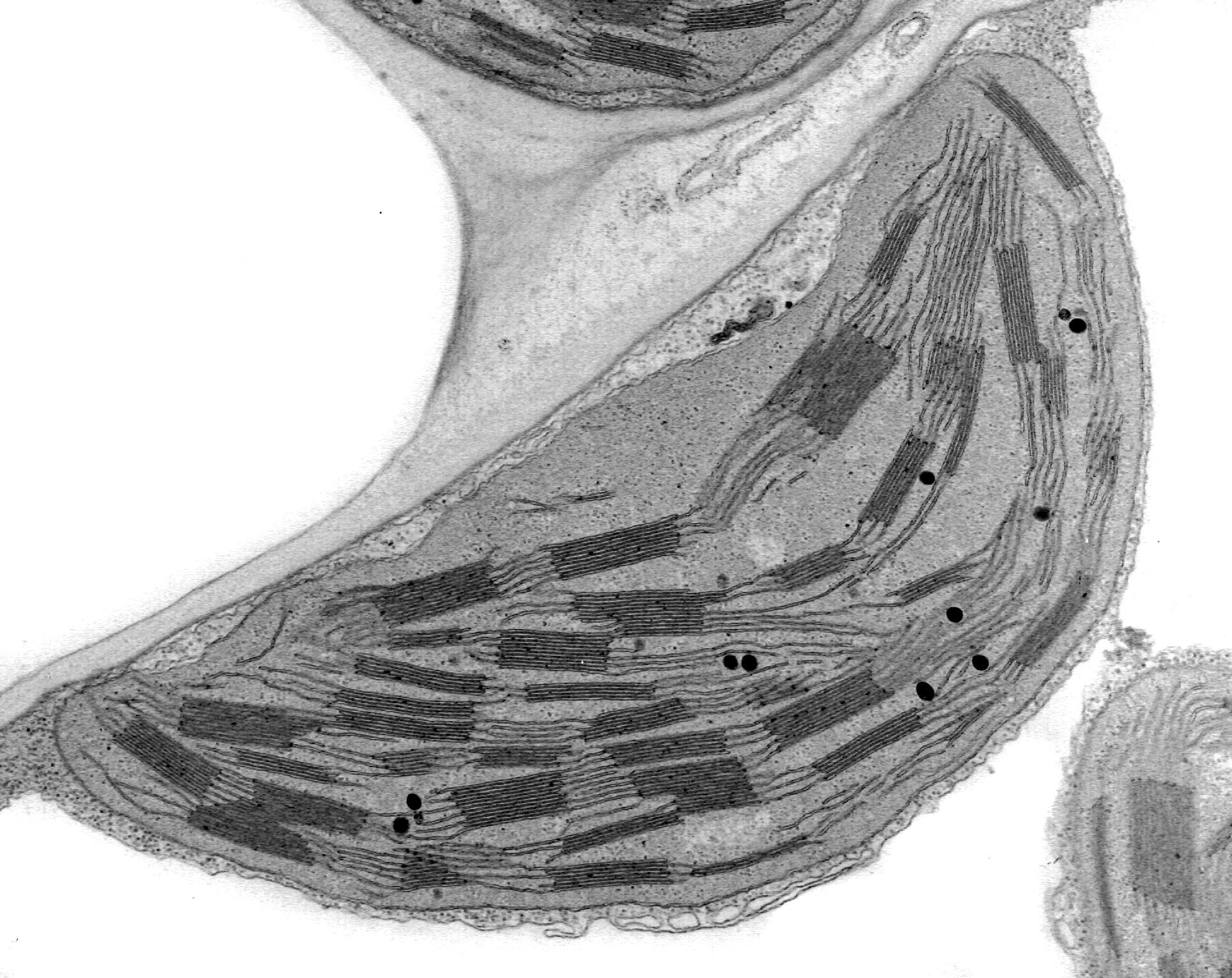
chloroplast
a double-membrane bound organelle containing ribosomes (70S), grana made up of thylakoids and connected by lamellae, lipid droplets/starch granules; responsible for carrying out photosynthesis
23
New cards
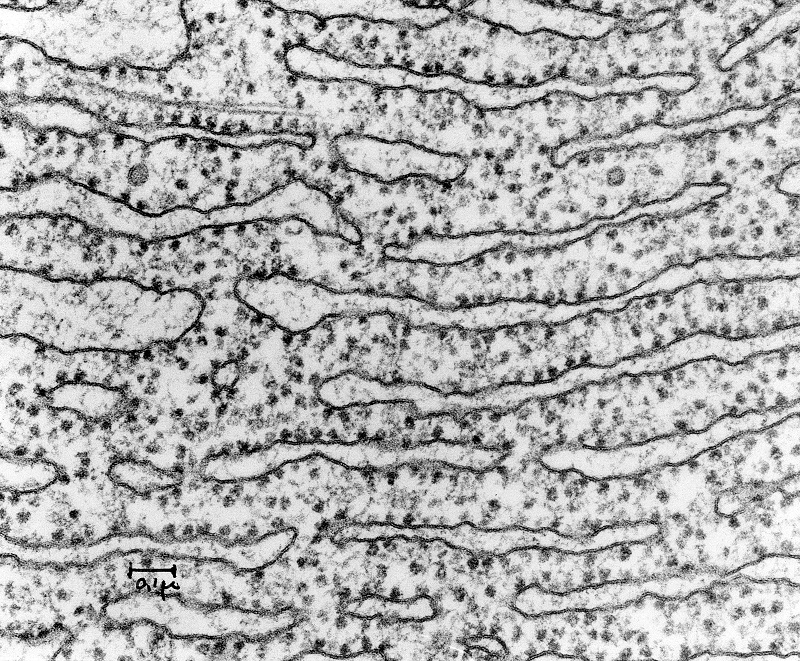
rough endoplasmic reticulum
contains ribosomes on its surface; responsible for transport and synthesis of proteins
24
New cards
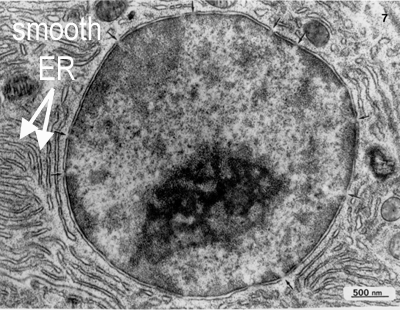
smooth endoplasmic reticulum
does not have ribosomes on its surface; responsible for transport and synthesis of lipids and steroids
25
New cards
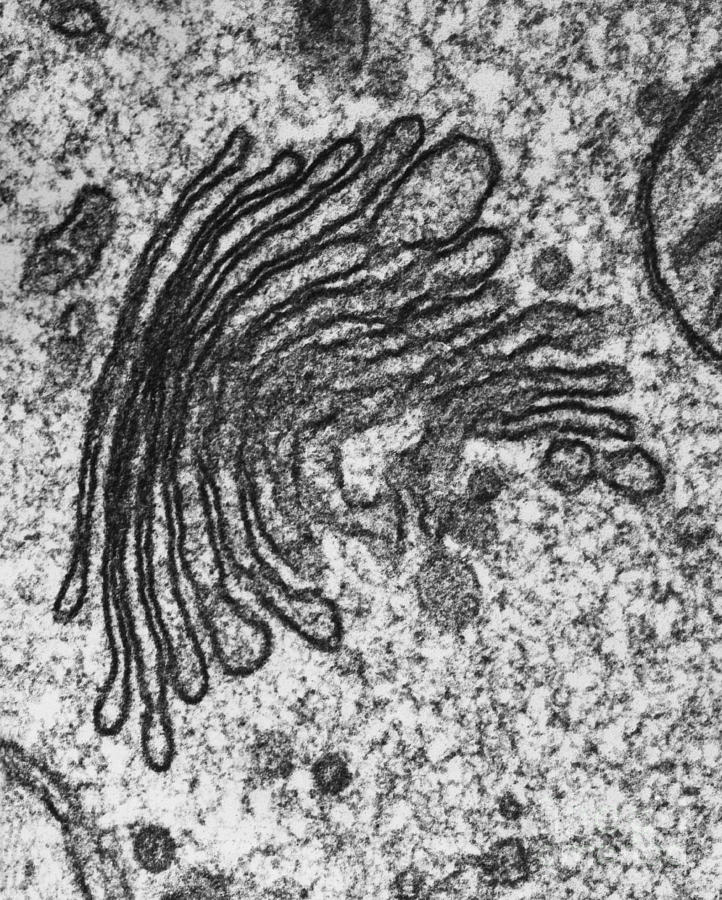
Golgi body
flattened discs made up of cisternae; responsible for modification and packaging materials such as proteins and lipids into vesicles, also produces lysosomes
26
New cards
lysosome
a vesicle containing hydrolytic enzymes (hydrolases); responsible for breaking down pathogens and/or old organelles, they also break down cells after cell death
27
New cards
ribosome
contains two subunits (depending on size), can be 80S (only in eukaryotes in cytoplasm) or 70S, made up of ribosomal RNA (rRNA) and protein; responsible for synthesis of proteins
28
New cards
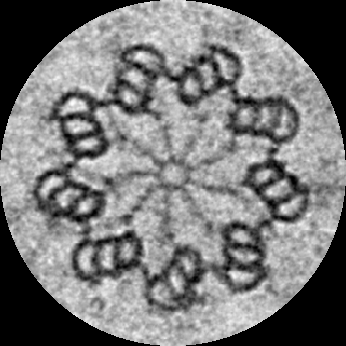
centrioles
a cylindrical structure formed by nine 'triplets' of microtubules; responsible in replication during interphase and organise microtubules during mitosis
29
New cards
microtubules
long, rigid, hollow tubes about 25 nm in diameter, made from the protein tubulin; responsible for forming the cytoskeleton and allow transport within the cell
30
New cards
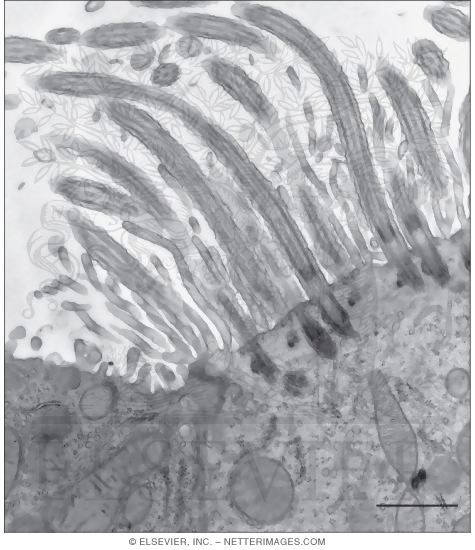
cilia
hair-like projection of a cell that may allow movement (motile) or not (non-motile), has a '9+2' arrangement of microtubules
31
New cards
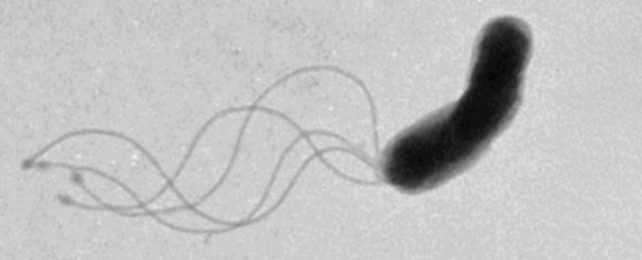
flagella
tail-like projection of a cell that allows movement of a cell
32
New cards
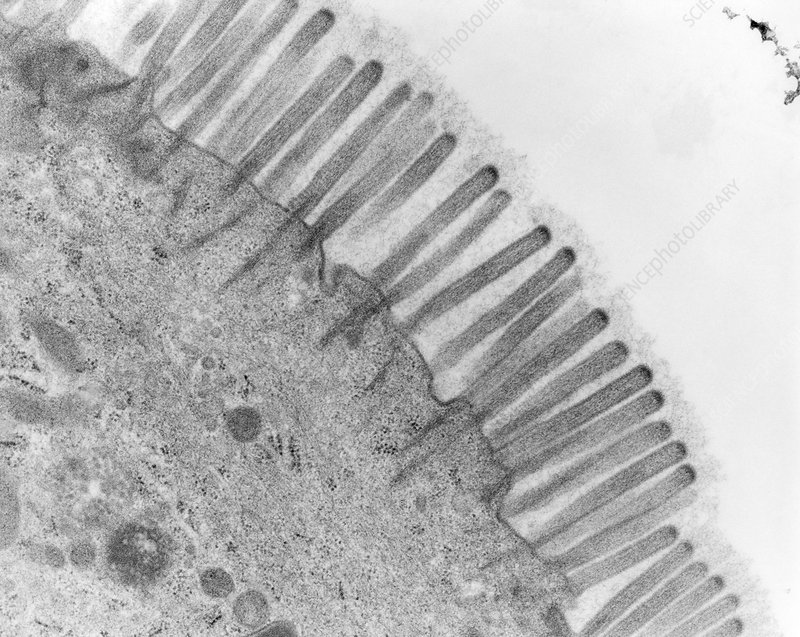
microvilli
projections of a cell membrane (can be caused by infolding); responsible for increasing the surface area to volume ratio to increase efficiency of cell transport
33
New cards
bacteria
unicellular prokaryotic microorganism, typically associated with disease, cell wall contains peptidoglycan and may also have a capsule layer among other structural features
34
New cards
virus
a very small (20-300 nm) infectious particle that only replicates in living cells; contains genetic material (DNA/RNA) and surrounded by a protein coat, viruses do not contain any other structures