18.2 Fiscal Policy and the Trade Balance
1/11
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
12 Terms
Why is the term twin deficits used when it refers to trade and the budget?
Select the correct answer below:
the economy only has a budget deficit
the economy has both a budget deficit and a trade deficit
the economy has a trade deficit with an inverse budget
the economy has a budget deficit with the opposite a trade surplus
the economy has both a budget deficit and a trade deficit
The term twin deficits means both trade and the budget have deficits. In the mid-1980s, it was common to hear economists and even newspaper articles refer to the twin deficits, as the budget deficit and trade deficit both grew substantially.
How does a budget deficit impact demand in market for domestic financial capital?
Select the correct answer below:
it does not affect the demand
it decreases the demand
it eliminates the demand
it increases the demand
it increases the demand
A budget deficit increases demand in markets for domestic financial capital, which raises the domestic interest rate. As a result, a higher interest rate will attract an inflow of foreign financial capital, and appreciate the exchange rate in response to the increase in demand for dollars by foreign investors and a decrease in supply of domestic dollars.
By adjusting the supply and demand curves, demonstrate what happens to the exchange rate between euros and U.S. dollars if there is a trade deficit.
A trade deficit results from an increase in imports and/or a decrease in exports. This means that more foreign currency is demanded (in exchange for dollars) - this is an increase in dollar supply. Additionally, fewer dollars are demanded due to the decrease in export demand - this is a decrease in dollar demand. Therefore, a trade deficit results in a cheaper dollar.
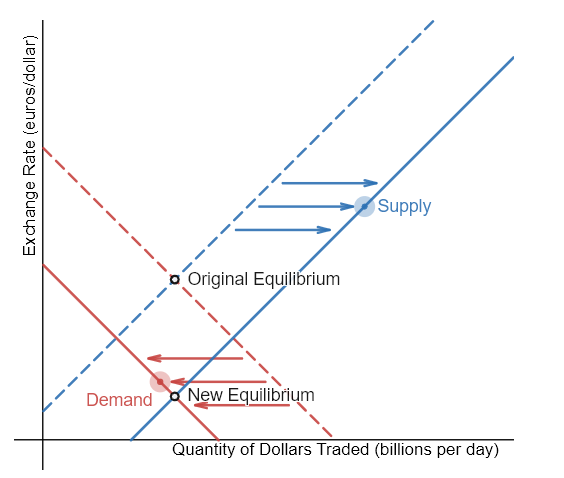
Imagine that the U.S. government increases its borrowing and the funds come from European financial investors. Illustrate what happens to this economy by moving both the supply and the demand for dollars.
To purchase U.S. government bonds, those European investors will need to demand more U.S. dollars on foreign exchange markets, causing the demand for U.S. dollars to shift to the right. European financial investors as a group will also be less likely to supply U.S. dollars to the foreign exchange markets, causing the supply of U.S. dollars to shift left. The equilibrium exchange rate strengthens
What is the main danger for governments with respect to sustained patterns of high budget deficits and high trade deficits?
Select the correct answer below:
When the inflow of foreign investment capital funds long-term physical investment capital by firms instead of short-term portfolio investment in government bonds.
When the inflow of foreign investment capital funds short-term portfolio investment in government bonds.
When the exchange rate increases to an unsustainable level.
When inflation steadily increases alongside the inflow of foreign investment capital.
When the inflow of foreign investment capital funds short-term portfolio investment in government bonds.
Governments should beware of a sustained pattern of high budget deficits and high trade deficits. The danger arises in particular when the inflow of foreign investment capital is not funding long-term physical capital investment by firms, but instead is short-term portfolio investment in government bonds. When inflows of foreign financial investment reach high levels, foreign financial investors will be on the alert for any reason to fear that the country’s exchange rate may decline or the government may be unable to repay what it has borrowed on time.
What happens when Americans find U.S. bonds more attractive than foreign bonds as a result of higher interest and exchange rates?
Select the correct answer below:
Americans supply fewer U.S. dollars.
Americans supply more U.S. dollars.
Americans cause the exchange rate to slowly decrease.
Americans increase the exchange rate even more.
Americans supply fewer U.S. dollars.
When Americans are buying fewer foreign bonds, they are supplying fewer U.S. dollars. U.S. dollar depreciation leads to a larger trade deficit (or reduced surplus).
Demonstrate what happens to demand for U.S. currency when there is an inflow of foreign financial capital.
demand increases
A budget deficit increases demand in markets for domestic financial capital, raising the domestic interest rate. A higher interest rate will attract an inflow of foreign financial capital, and appreciate the exchange rate in response to the increase in demand for U.S. dollars by foreign investors.
Express what happens to the demand for U.S. dollars when there is a U.S. government budget surplus.
demand decreases
A budget surplus implies that the government is borrowing less through the issuing of bonds, which increases the price of bonds in the bonds market. This will discourage international investors from wanting to purchase U.S. government bonds, thus reducing their demand for U.S. dollars. There is a decrease in the demand for U.S. dollars, shifting the demand curve down.
We shouldn't expect the budget deficit and trade deficit to move in lockstep because ________ will often change as well.
Select the correct answer below:
investment and consumption
investment and private savings
imports and exports
private and foreign savings
investment and private savings
Of course, no one should expect the budget deficit and trade deficit to move in lockstep, because the other parts of the national saving and investment identity—investment and private savings—will often change as well.
The combination of reduced foreign investment capital and __________ can sharply reduce aggregate demand, causing a deep recession.
Select the correct answer below:
inflation
increased U.S. investment abroad
banks that are bankrupt
decreased U.S. investment abroad
banks that are bankrupt
The combination of less foreign investment capital and banks that are bankrupt can sharply reduce aggregate demand, which causes a deep recession. Many countries around the world have experienced this kind of recession in recent years: along with Turkey in 2002, Mexico followed this general pattern in 1995, Thailand and countries across East Asia in 1997–1998, Russia in 1998, and Argentina in 2002.
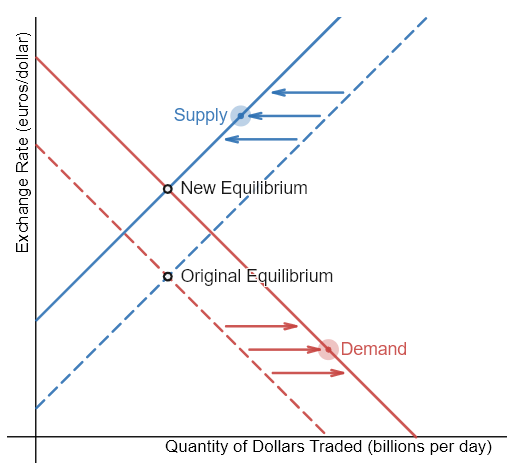
Demonstrate what happens to the exchange rate equilibrium if the U.S. decreases its budget deficit.
AD moves left, AS moves right.
A decrease in the budget deficit means that the U.S. government is making more than it spends. Because of this, there is a greater supply of U.S. dollars, and European nations are less likely to demand this currency; they have no desire to buy U.S. government bonds. As a result, the exchange rate weakens and the equilibrium point moves down.
Illustrate the impact on the demand and supply of U.S. dollars if there has been a trade surplus.
AD moves right, AS moves left.
A trade surplus means that exports have increased whereas imports have decreased. This means that the demand for US dollars has increased (due to the increase in exports) and the supply of US dollars has decreased (as fewer dollars are exchanged for foreign currency). The dollar value appreciates as a result of these changes.