APES Unit 3 - Populations Diagram | Quizlet
1/48
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
49 Terms
population density
number of individuals per unit of area
population dispersal
movement of individuals between populations
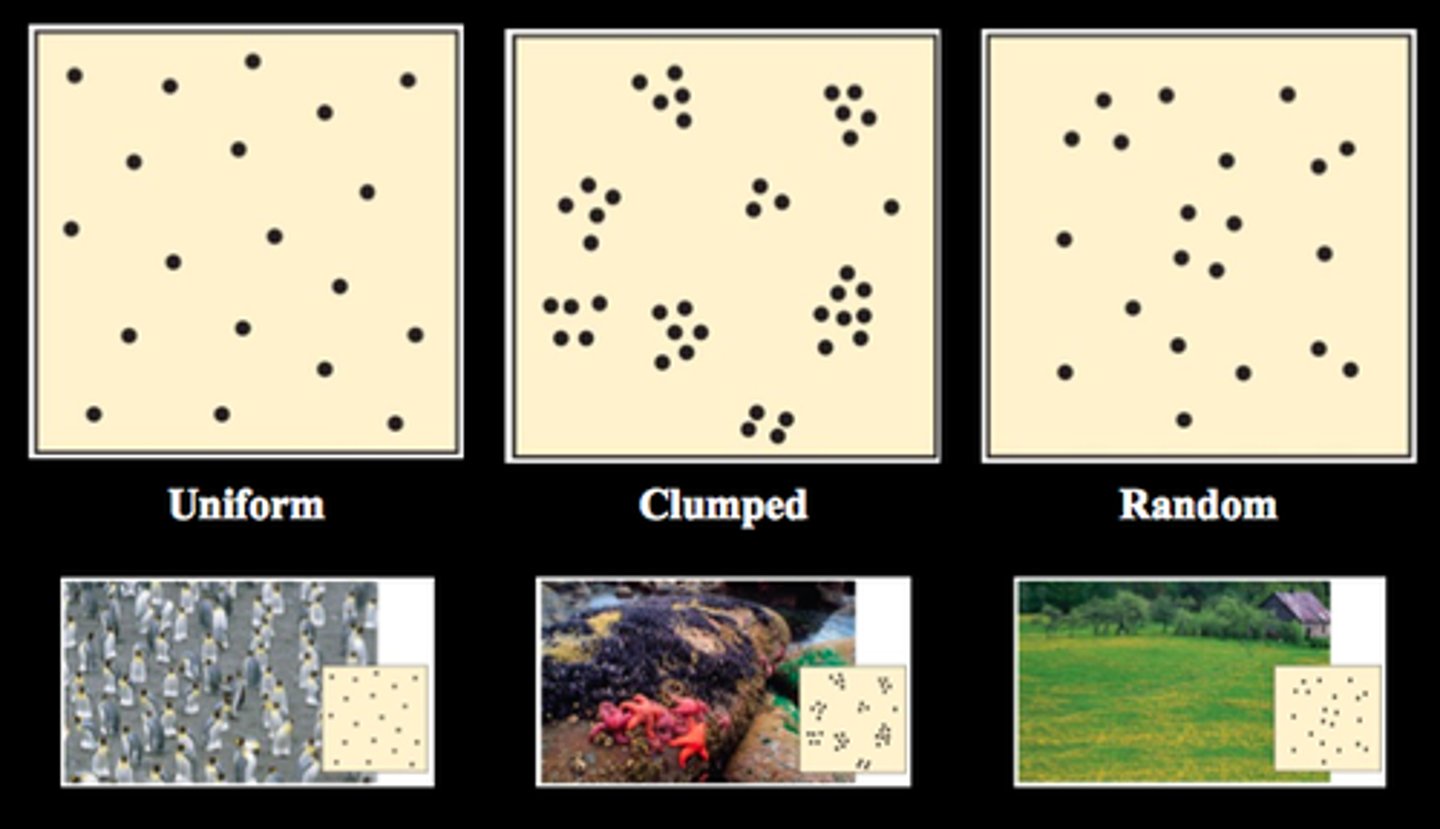

uniform dispersal
evenly distributed
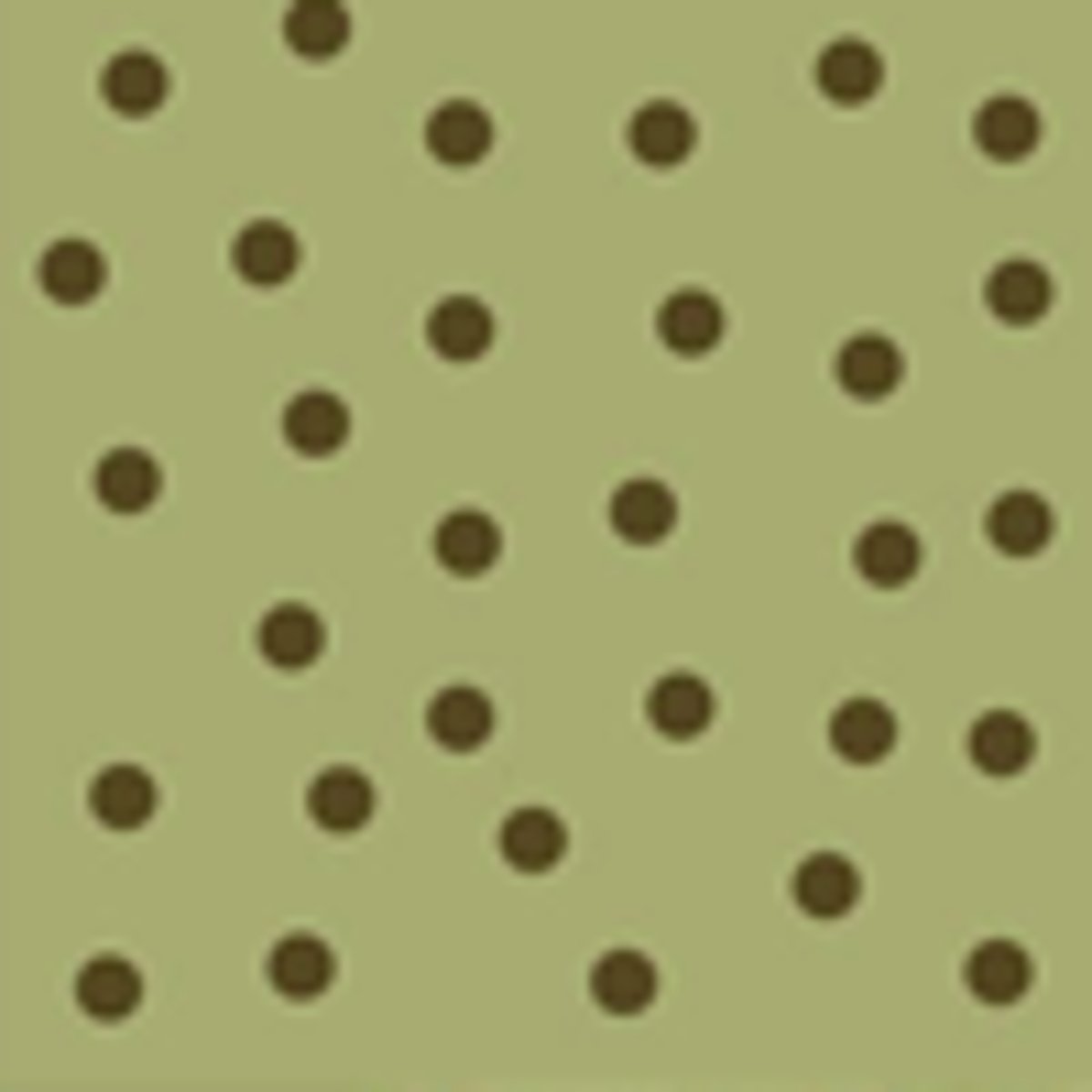

random dispersal
randomly arranged
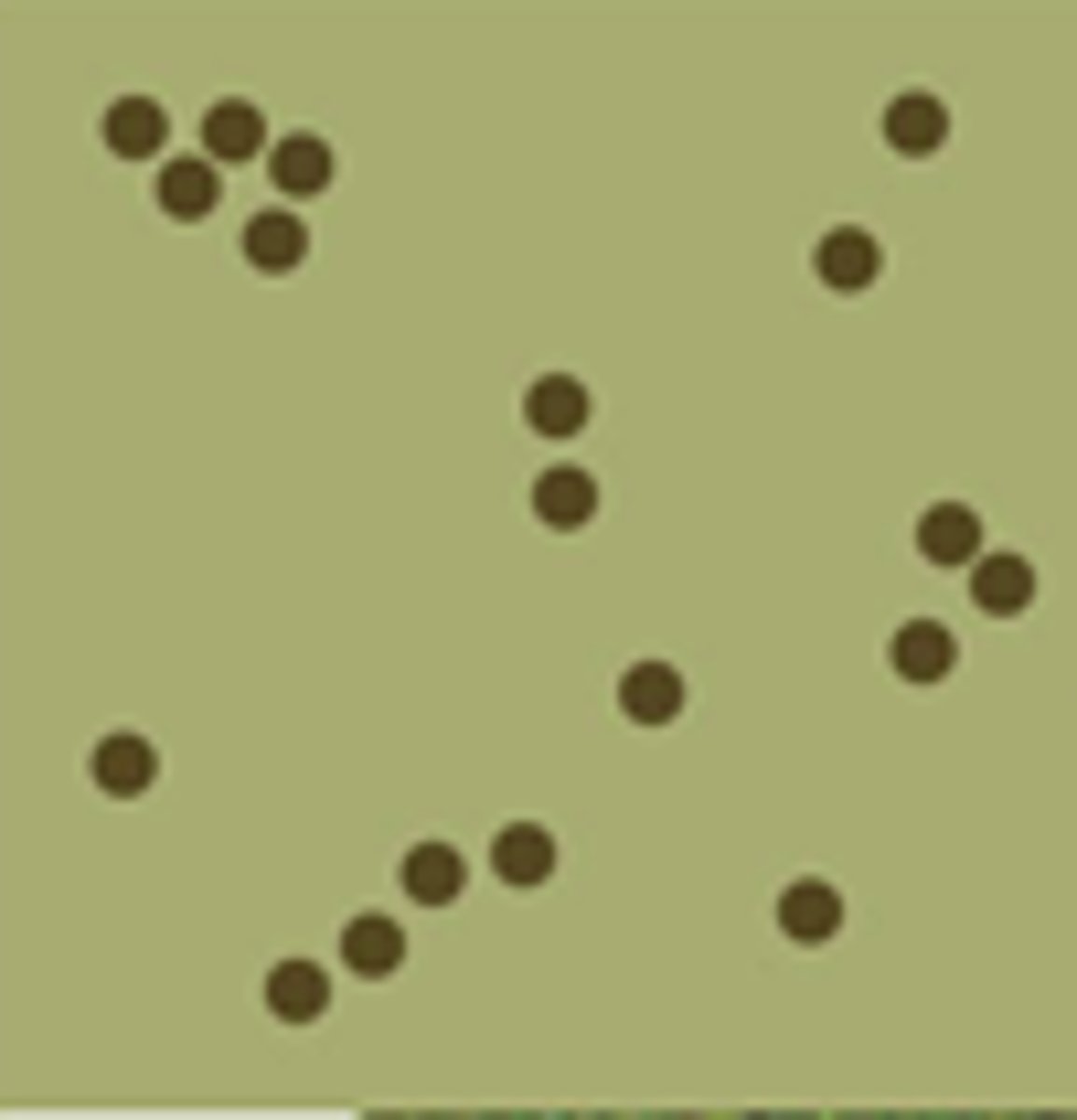

clumped dispersal
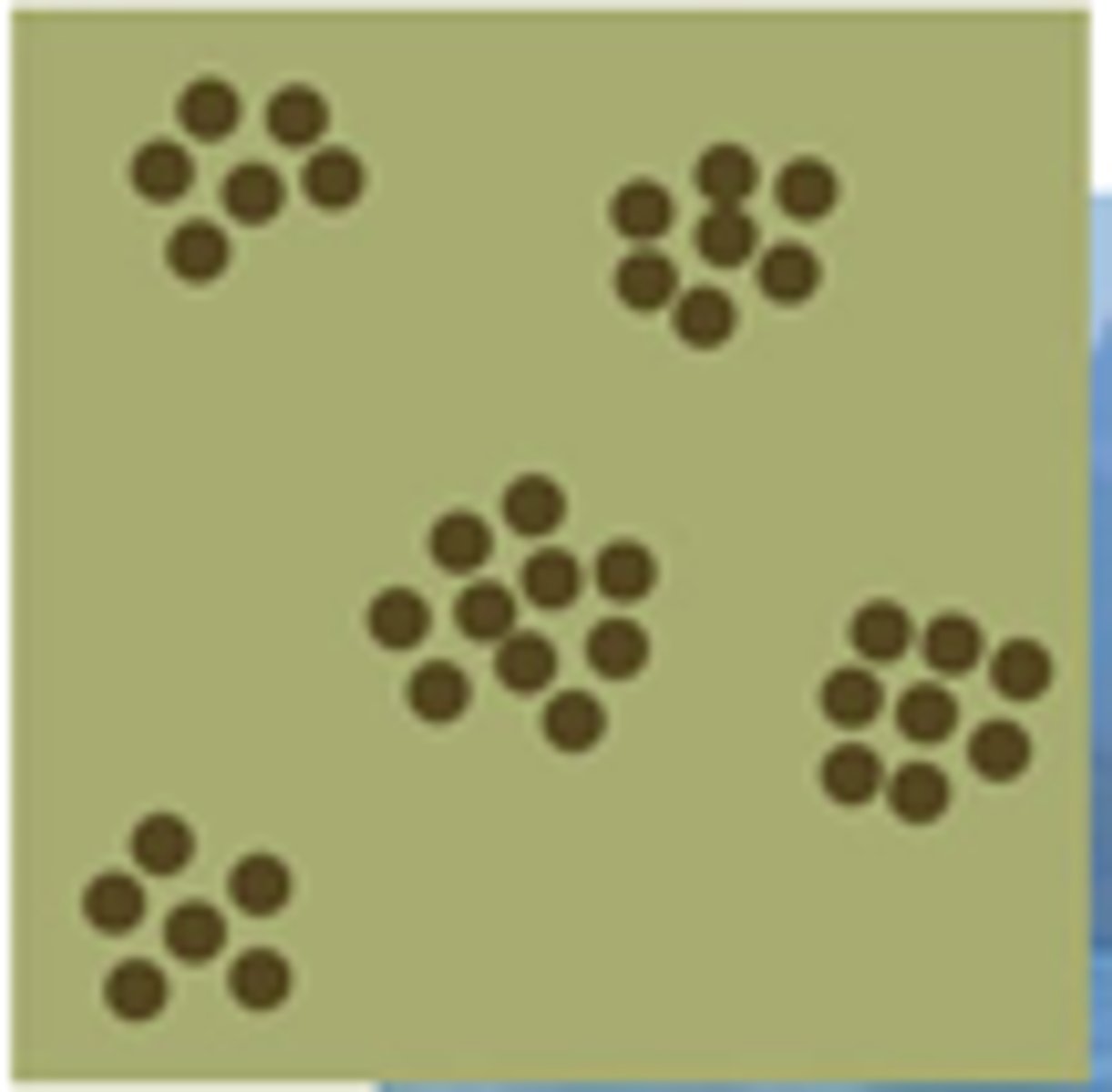

aggregation
clumping behavior of insects
TERM
Population Change
DEFINITION
(b + i) - (d + e)
biotic potential (intrinsic rate of increase)
maximum rate at which a population can increase under ideal conditions
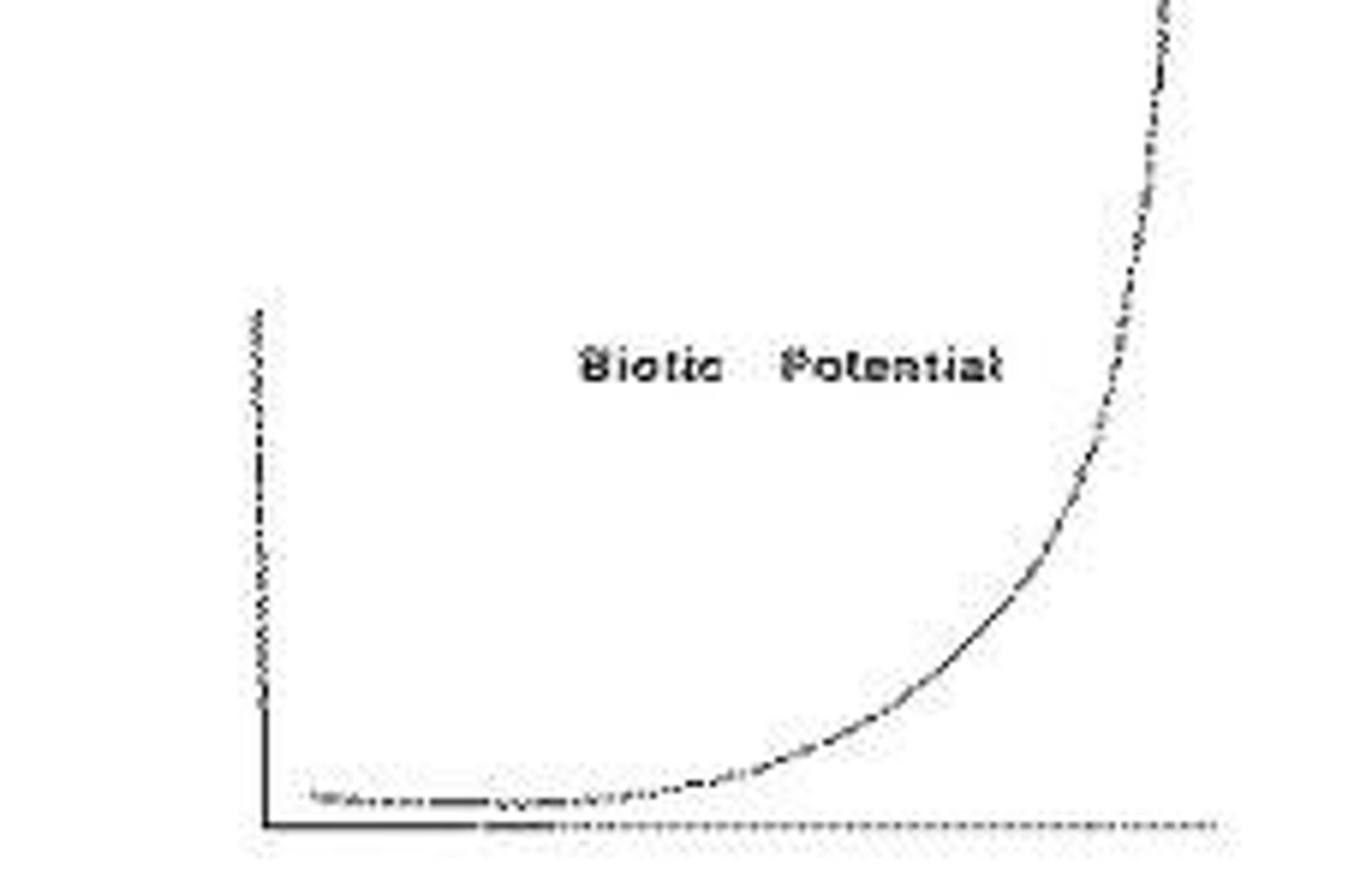
environmental resistance
combination of factors that prevent populations from reproducing at max rate
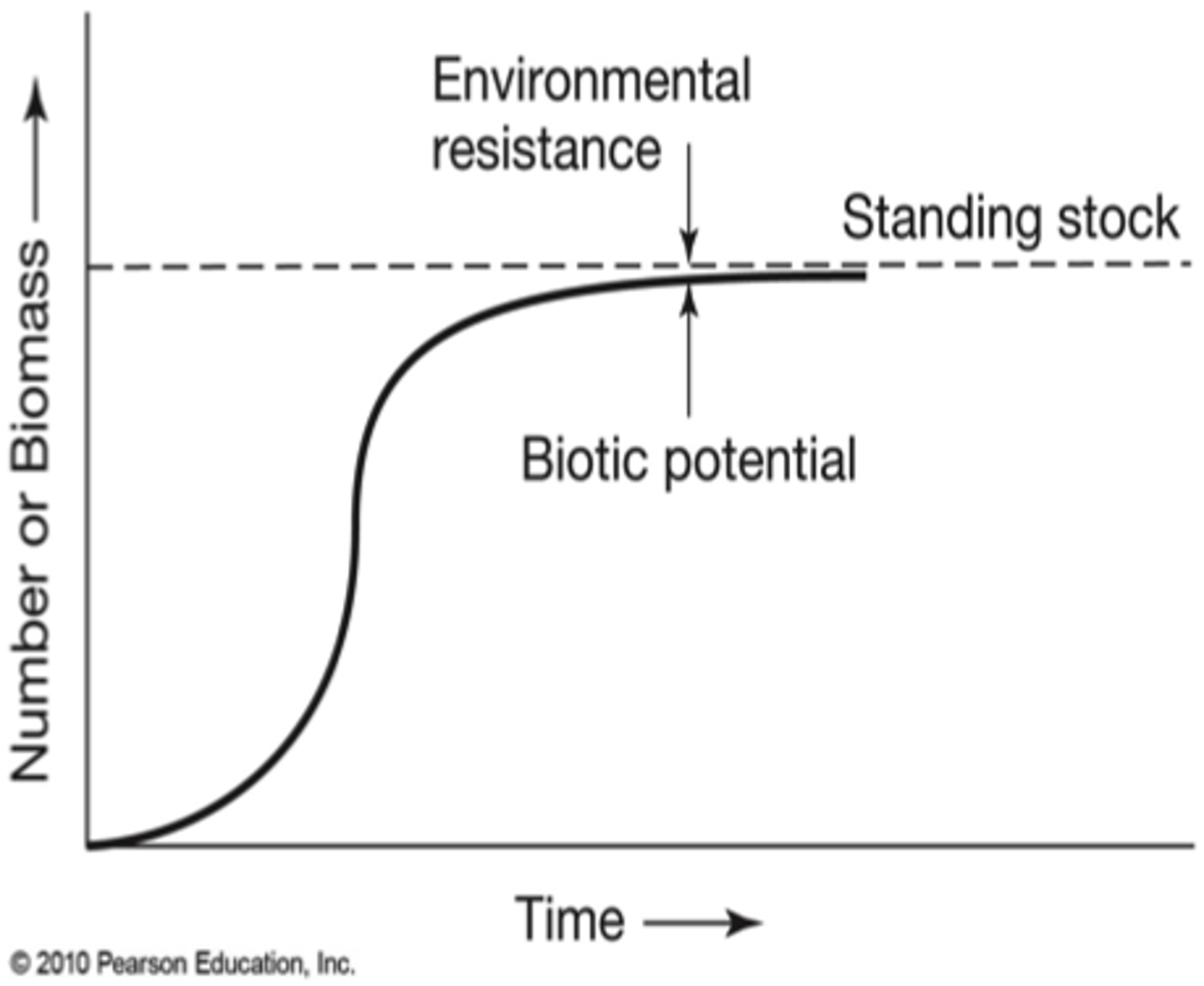
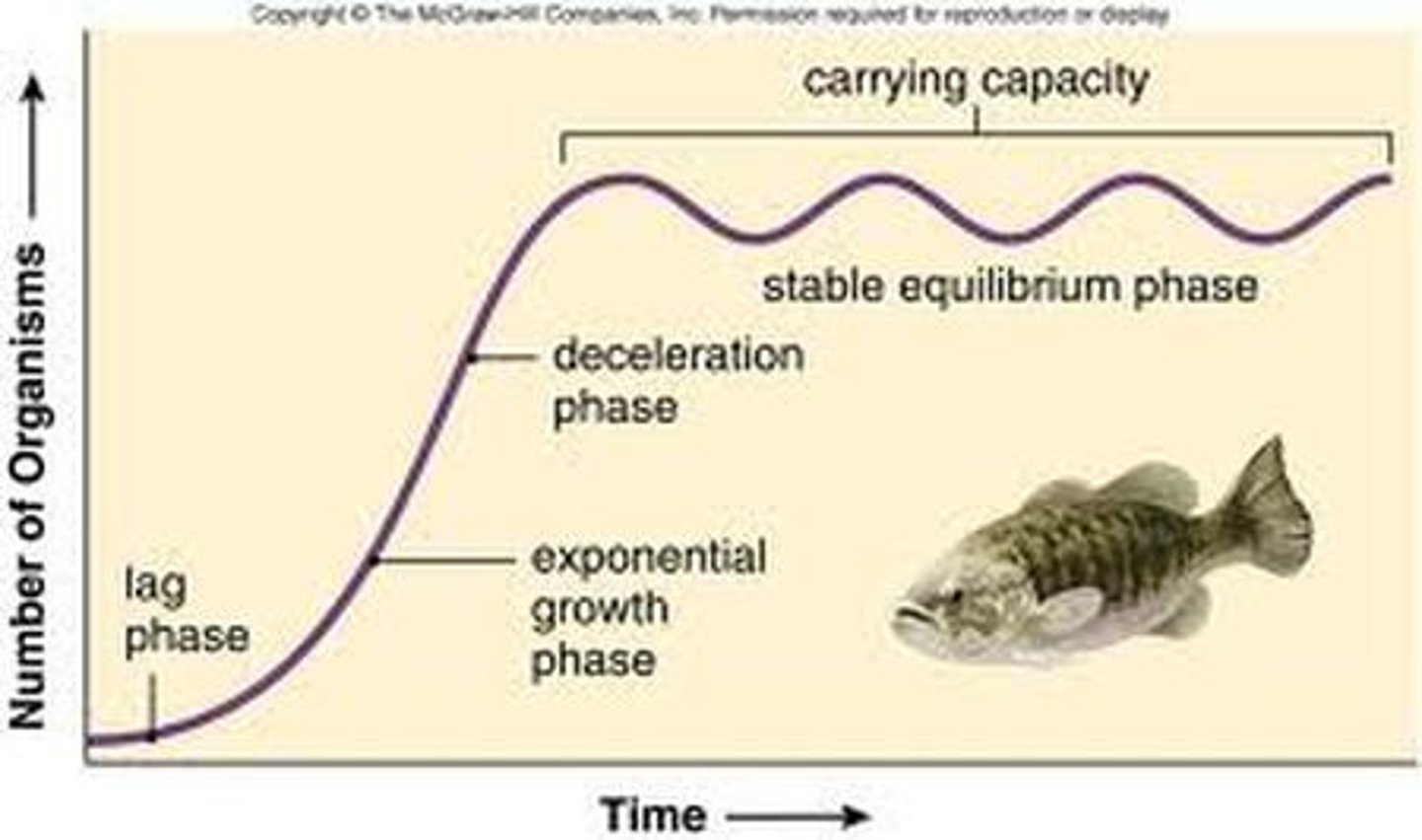
carrying capacity (K)
most limiting factor of a population
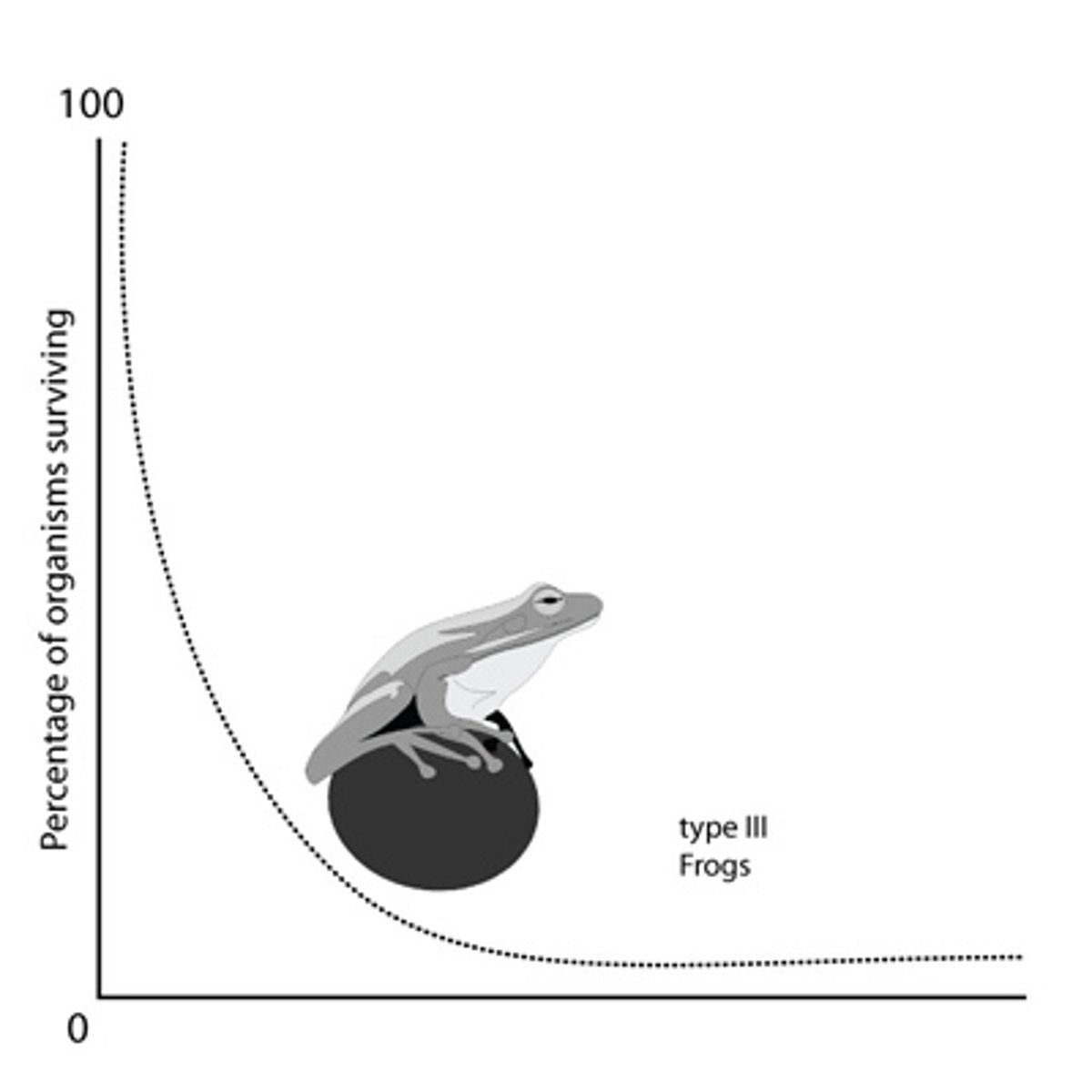
survivorship
probability that an individual survives at a certain age
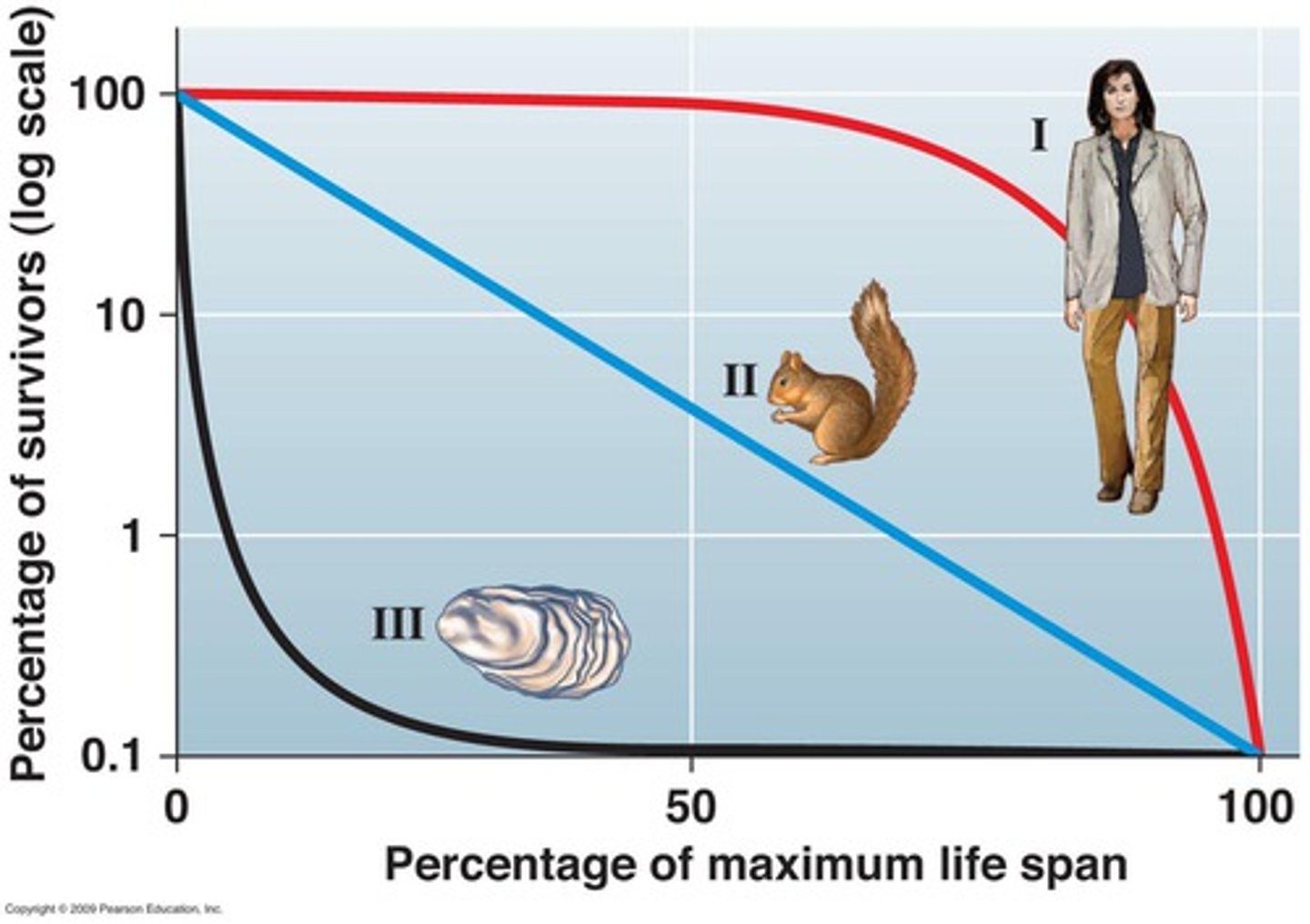
r-selected
type III reproductive strategy
- large number of offspring
- small body size
- fast maturation
- short lifespan
k-selected
type I reproductive strategy
- small number of offspring
- large body size
- slow maturation
- long lifespan

density-dependent factor
limiting factor that is affected by population size

density-independent factor
limiting factor that is not affected by population size

zero population growth
birth rate = death rate

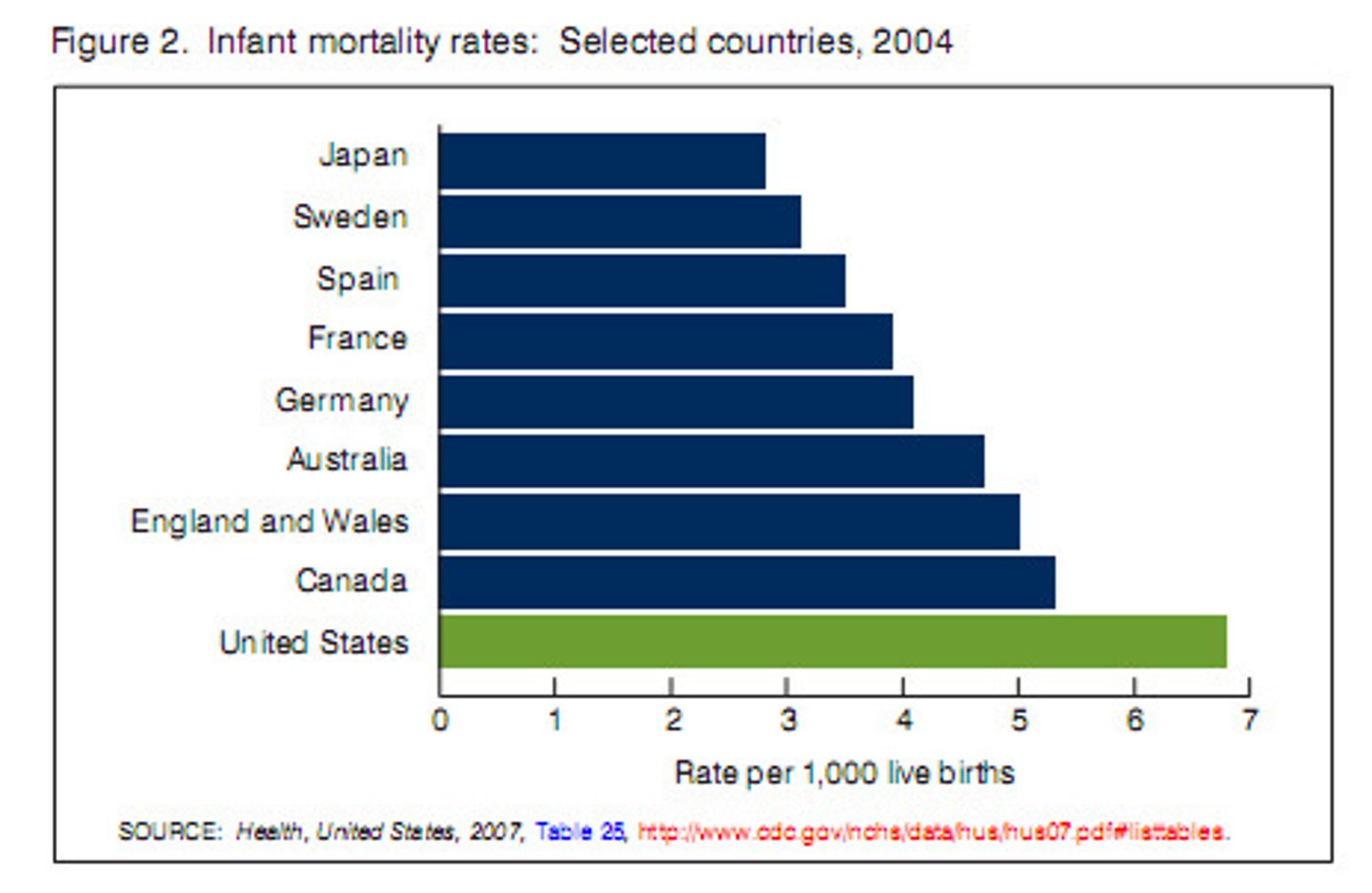
infant mortality rate (IMR)
number of infant deaths per 1000 births
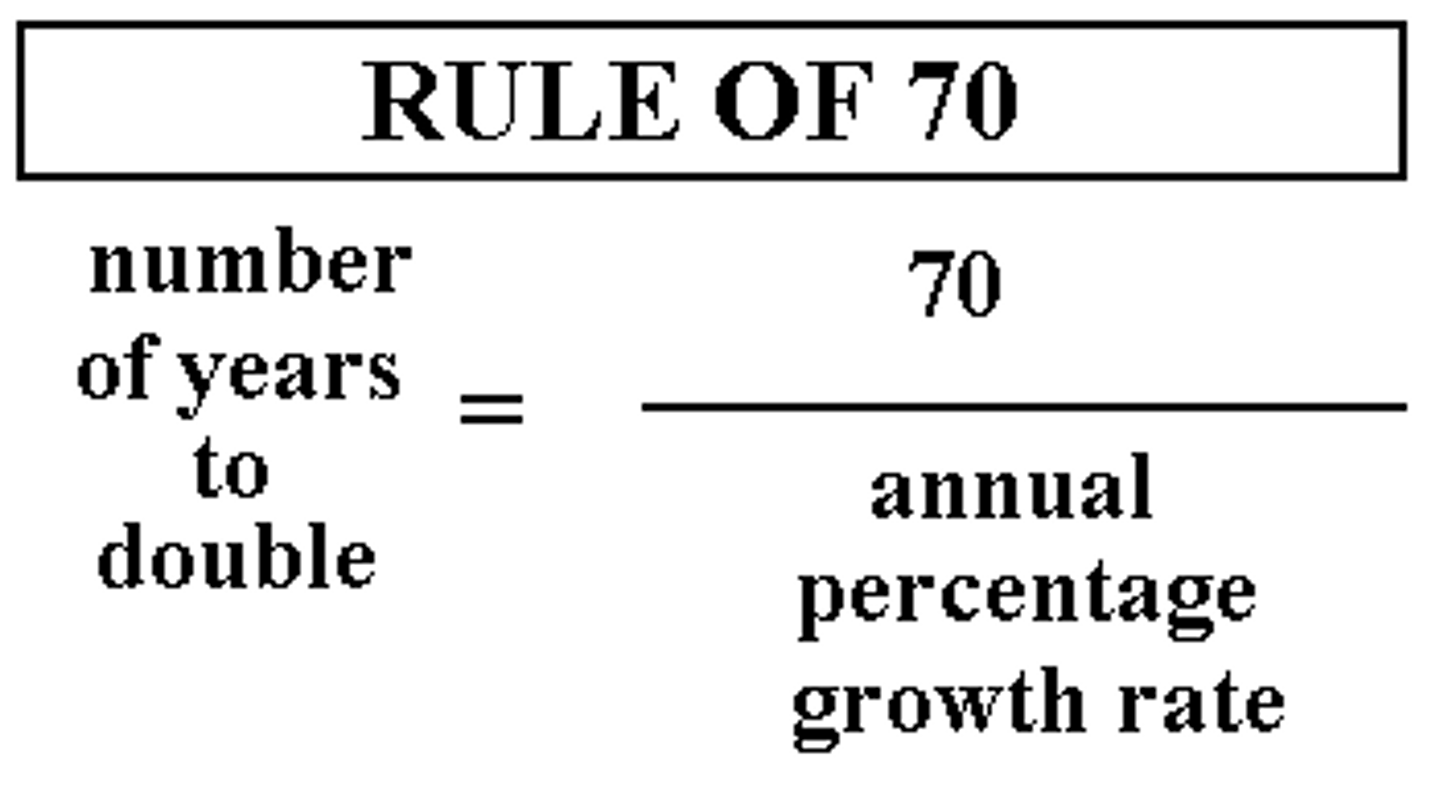
doubling time
number of years it will take for a population to double = 70%/population growth rate (%) - RULE OF 70
replacement level fertility
number of children a couple must have to replace themselves (2.1)

total fertility rate (TFR)
average number of children born to each woman
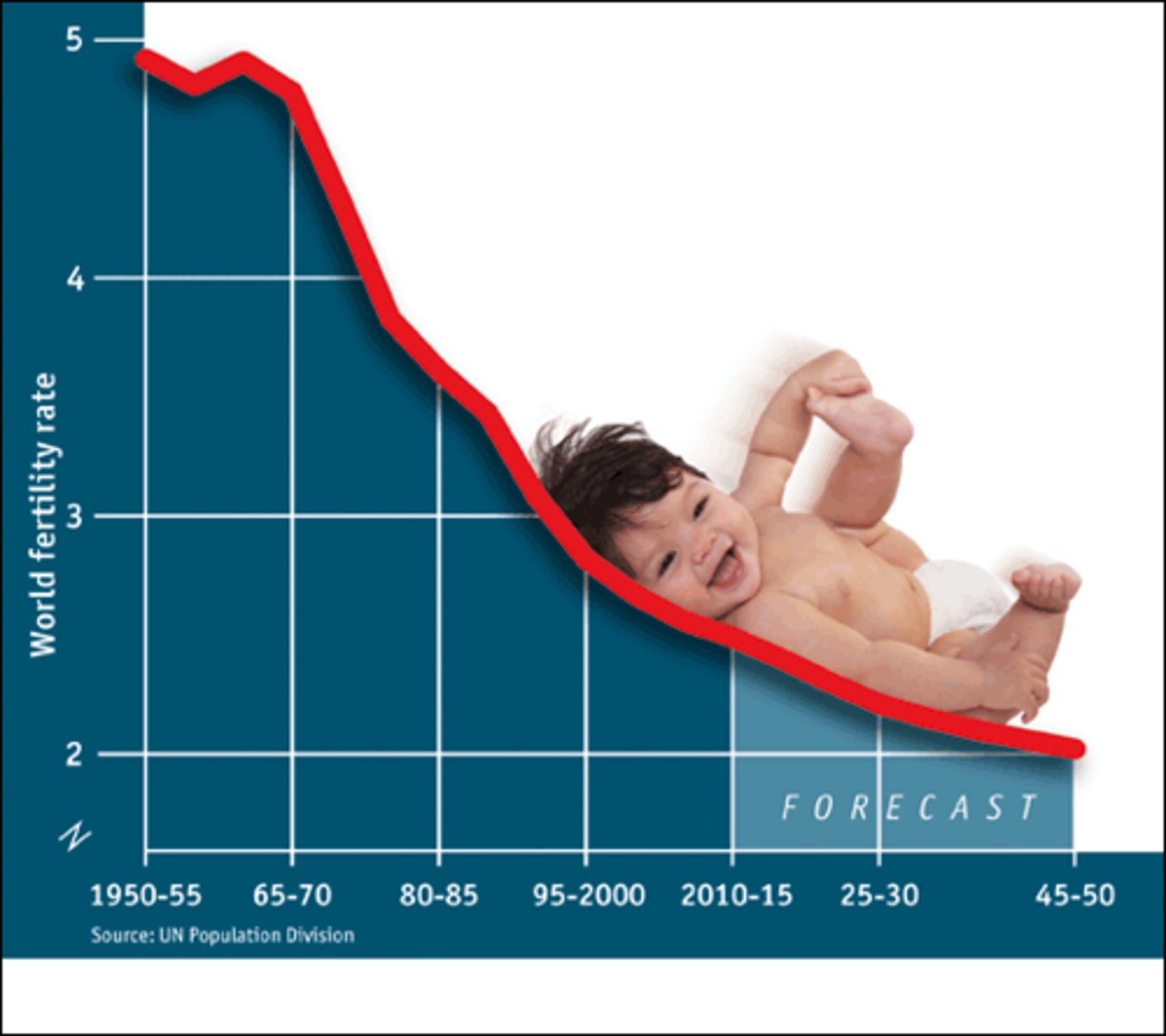
demographics
distribution of human population groups
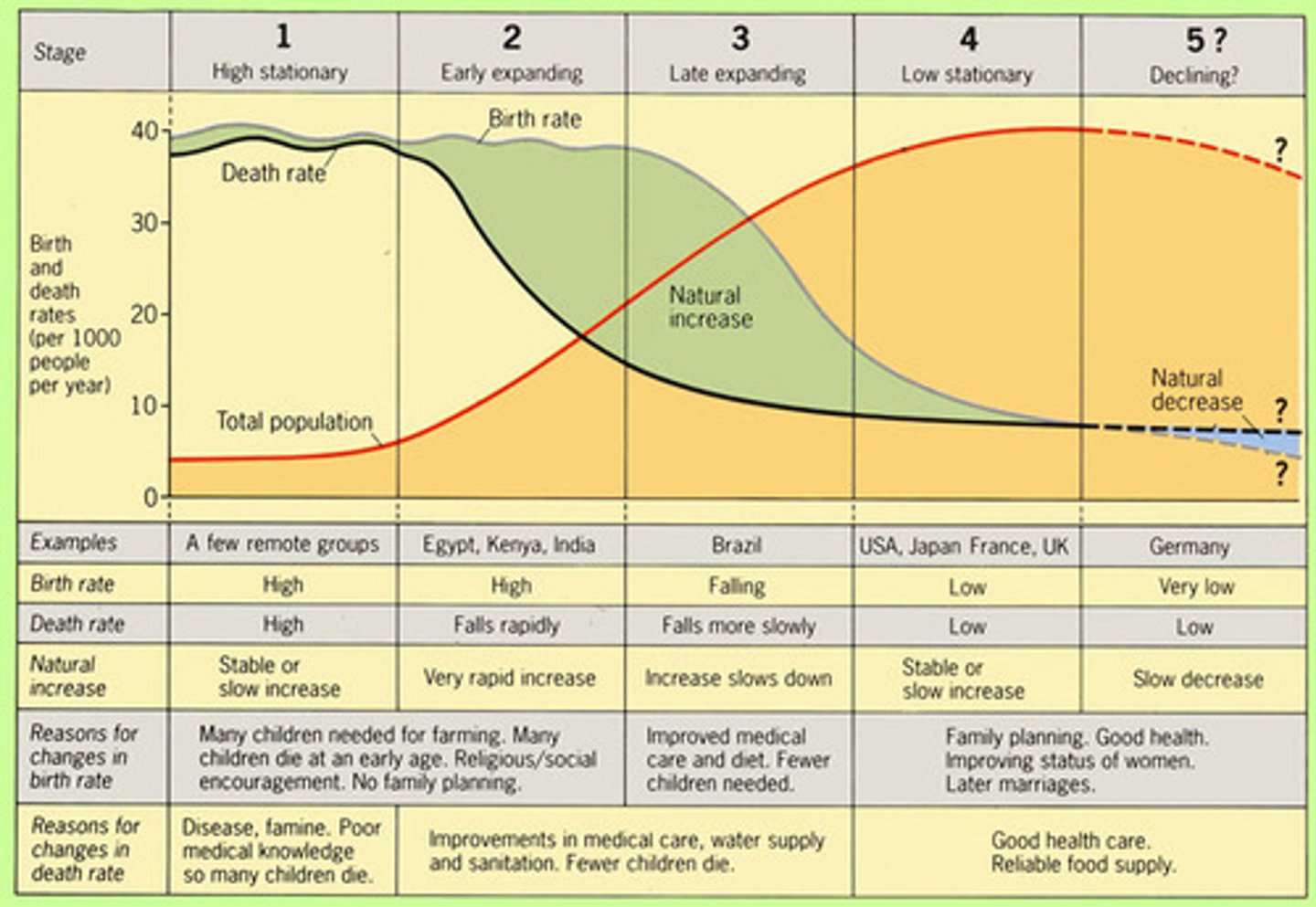
TERM
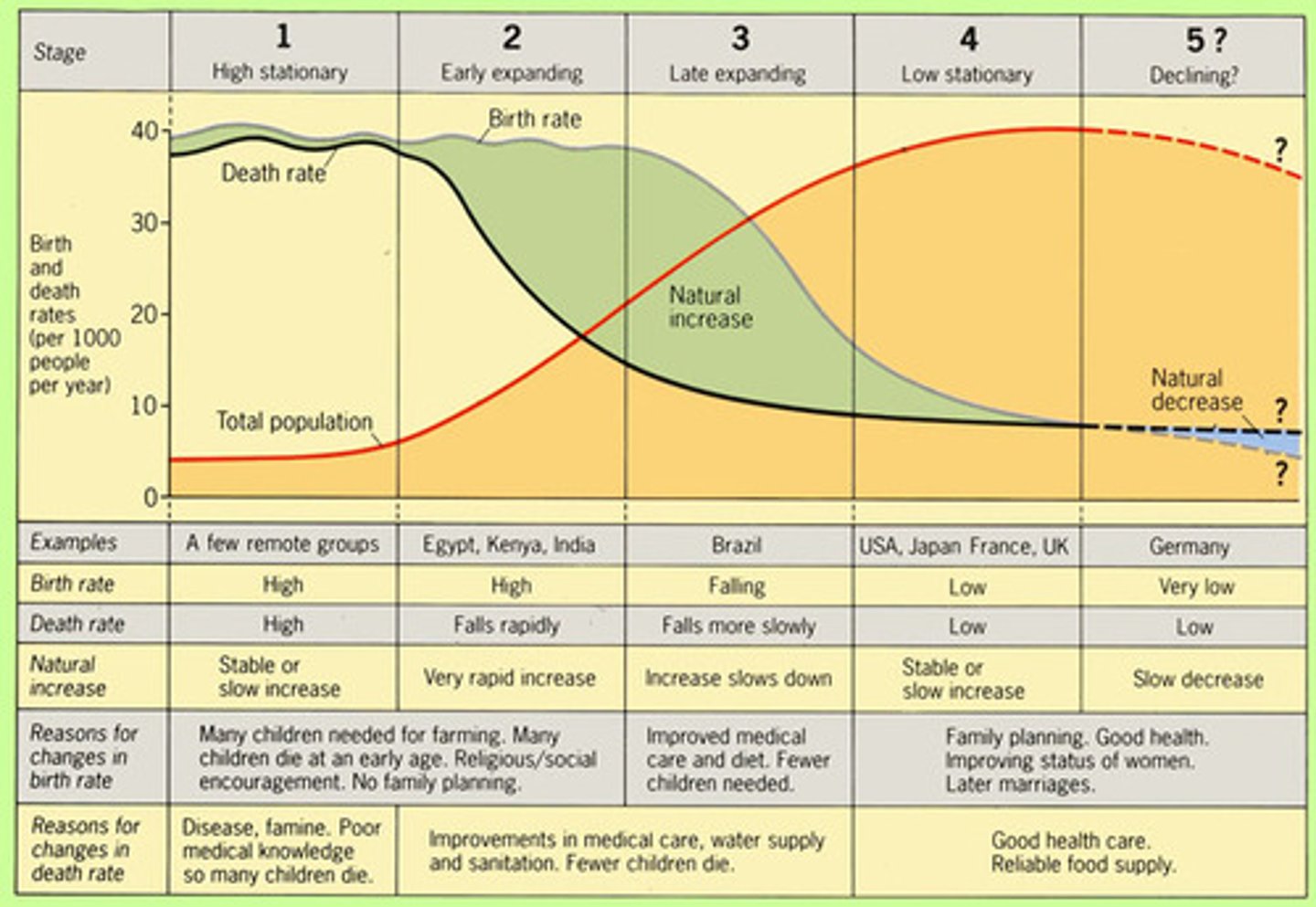
pre-industrial stage
DEFINITION
- b and d are very high, oscillate
- population grows at a modest rate
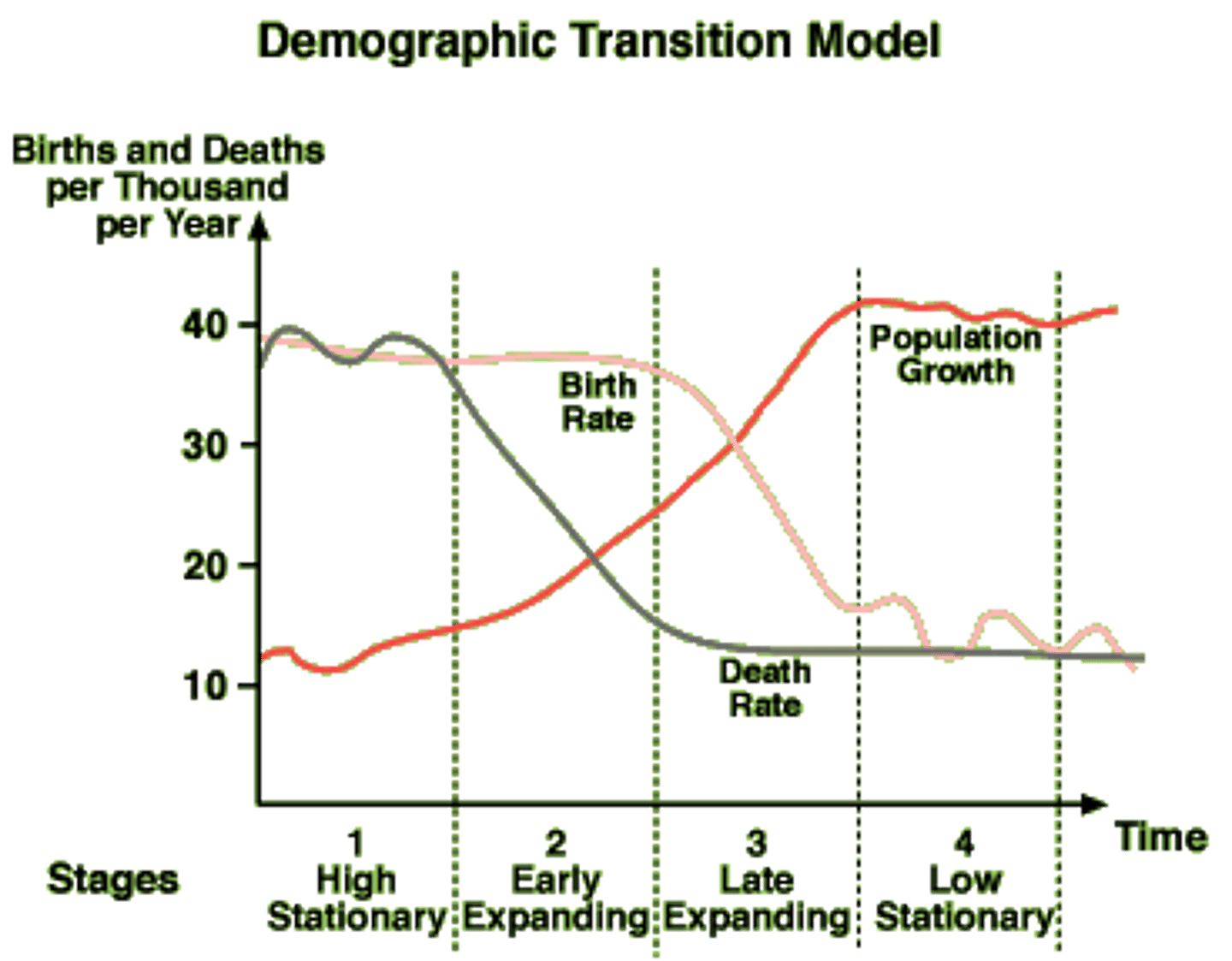
TERM
transitional stage
DEFINITION
- d decreases
- b still high
- causes a boom in population
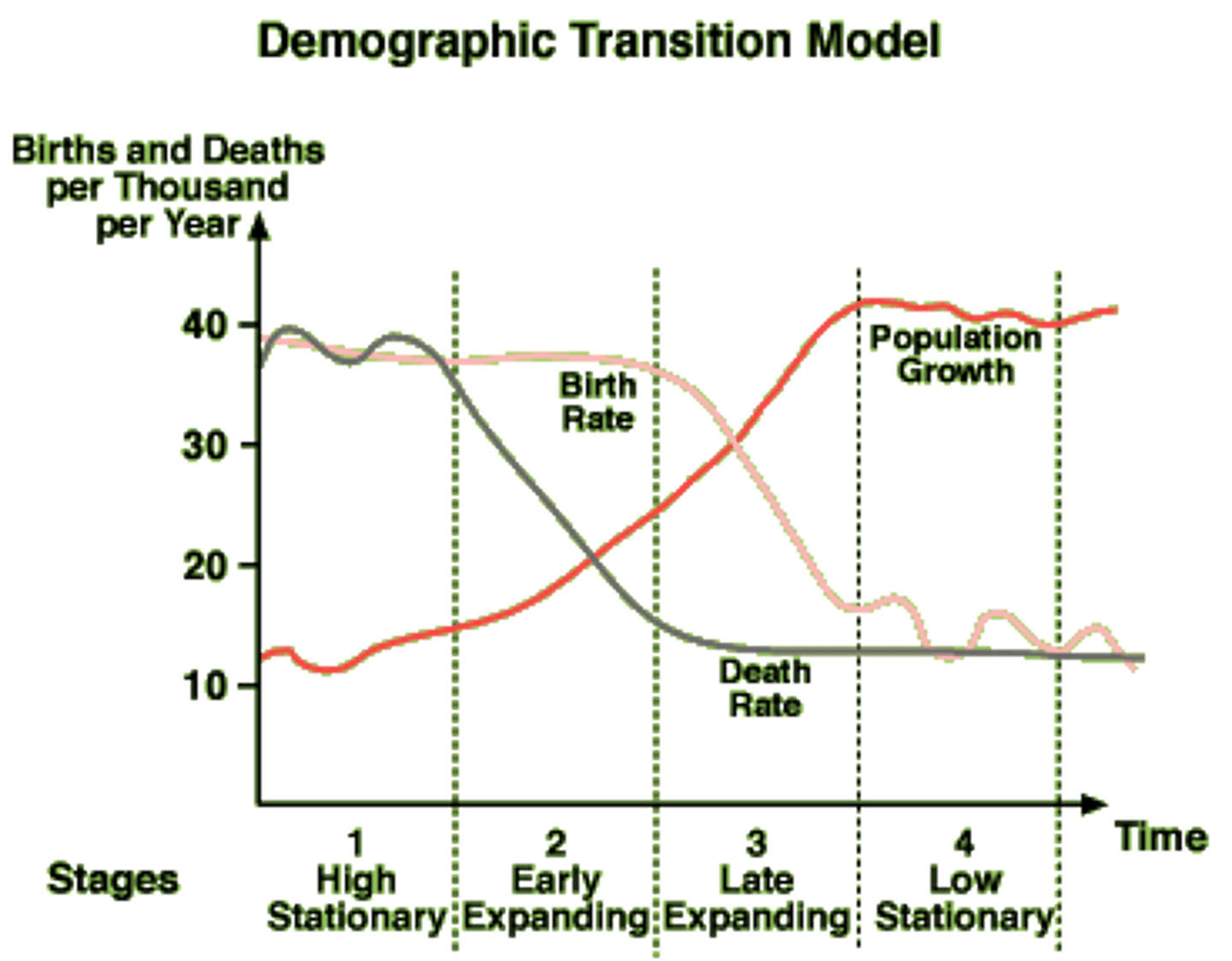
TERM
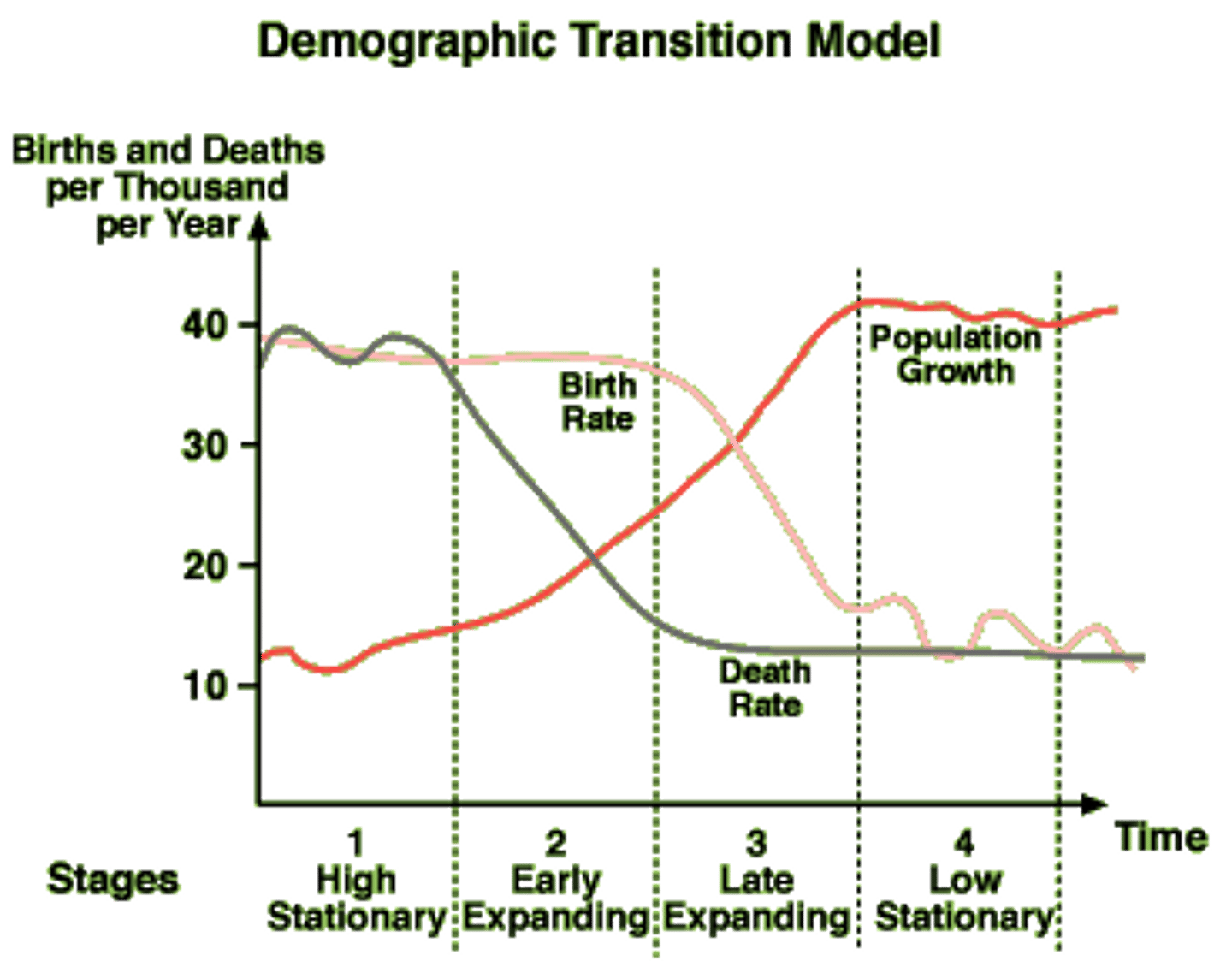
industrial stage
DEFINITION
- b starts decreasing
- d still decreases
TERM
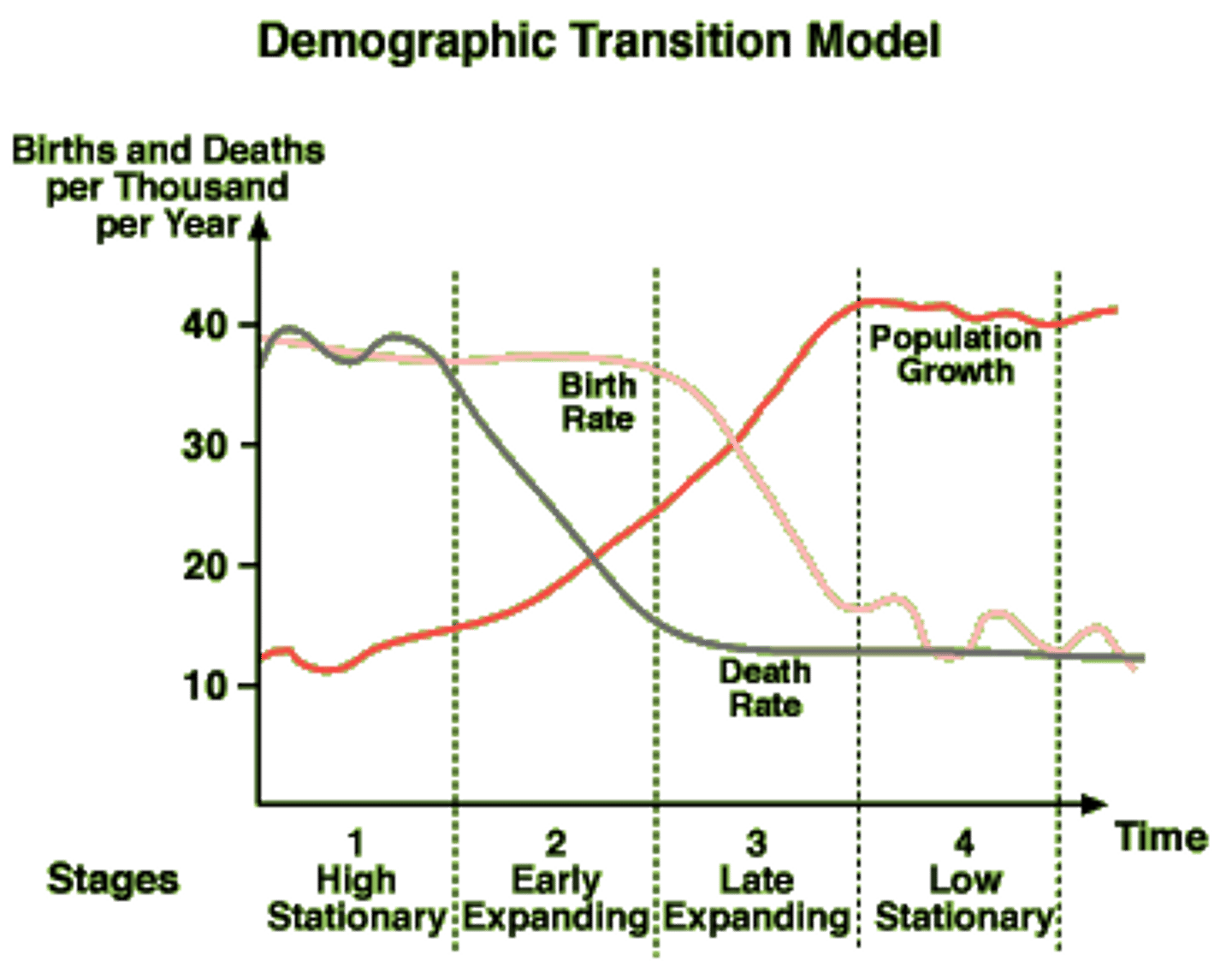
postindustrial stage
DEFINITION
- b decreases
- d levels off
- population oscillates and levels off
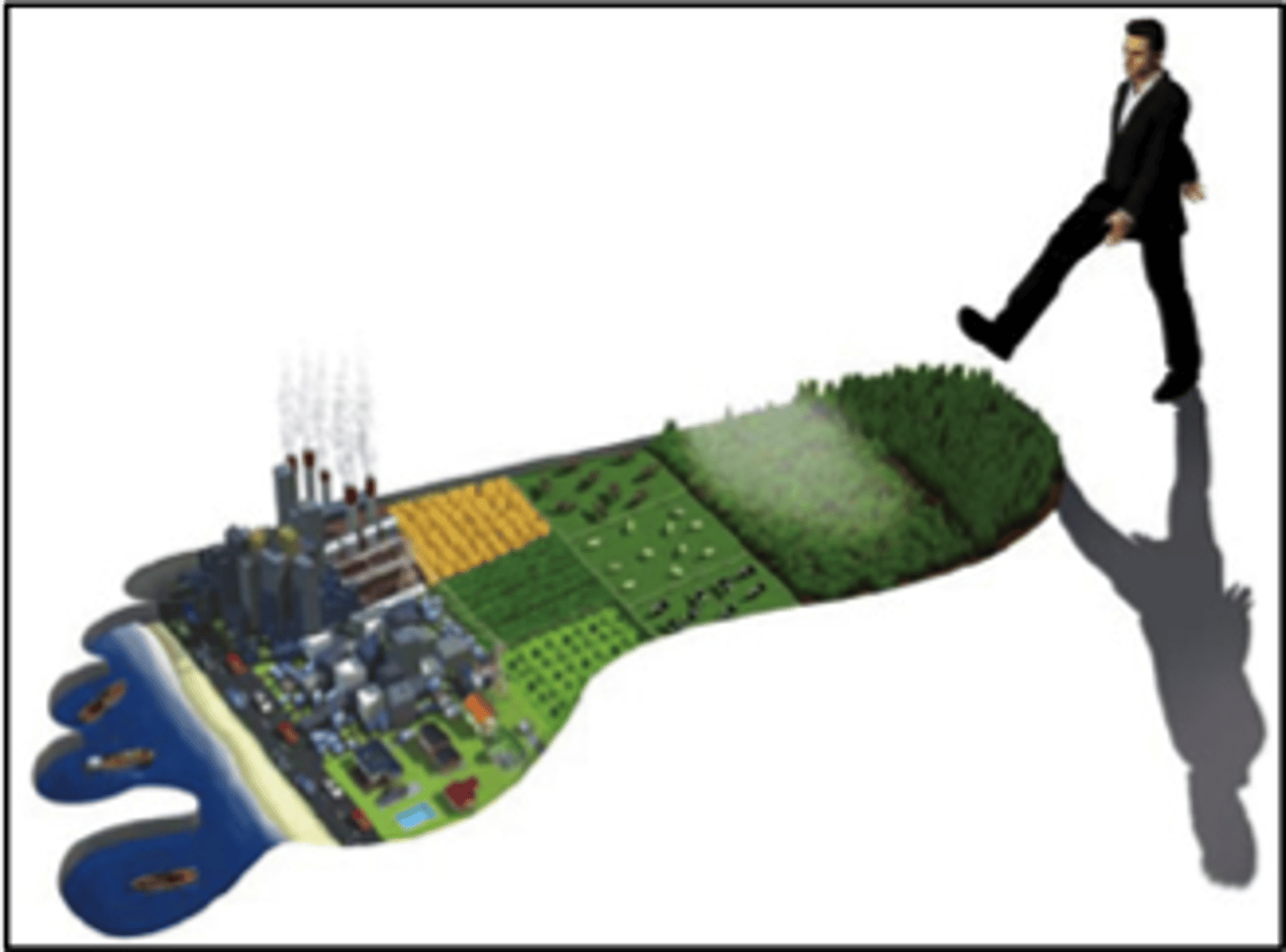
ecological footprint
measure of human impact, amount of land (hectares) required to sustain a person for a year

TERM
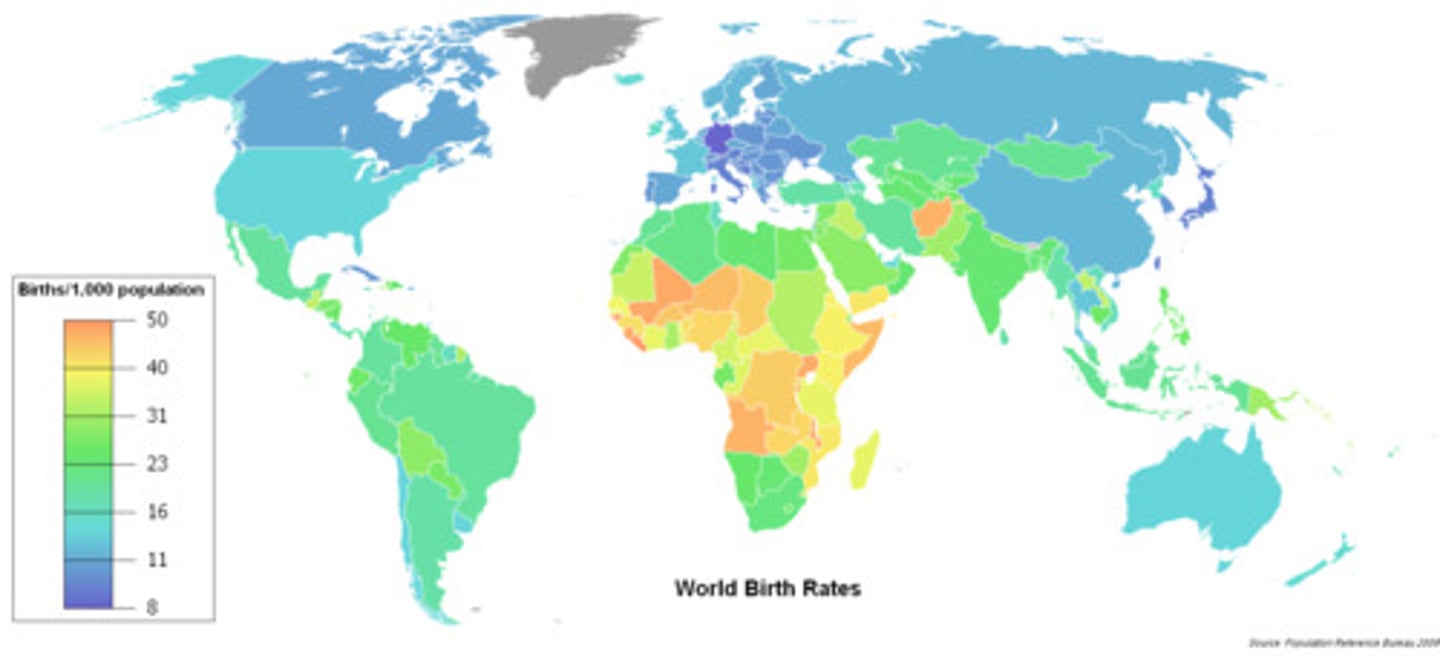
Crude Birth Rate (CBR)
DEFINITION
The total number of live births in a year for every 1,000 people alive in the society.
TERM
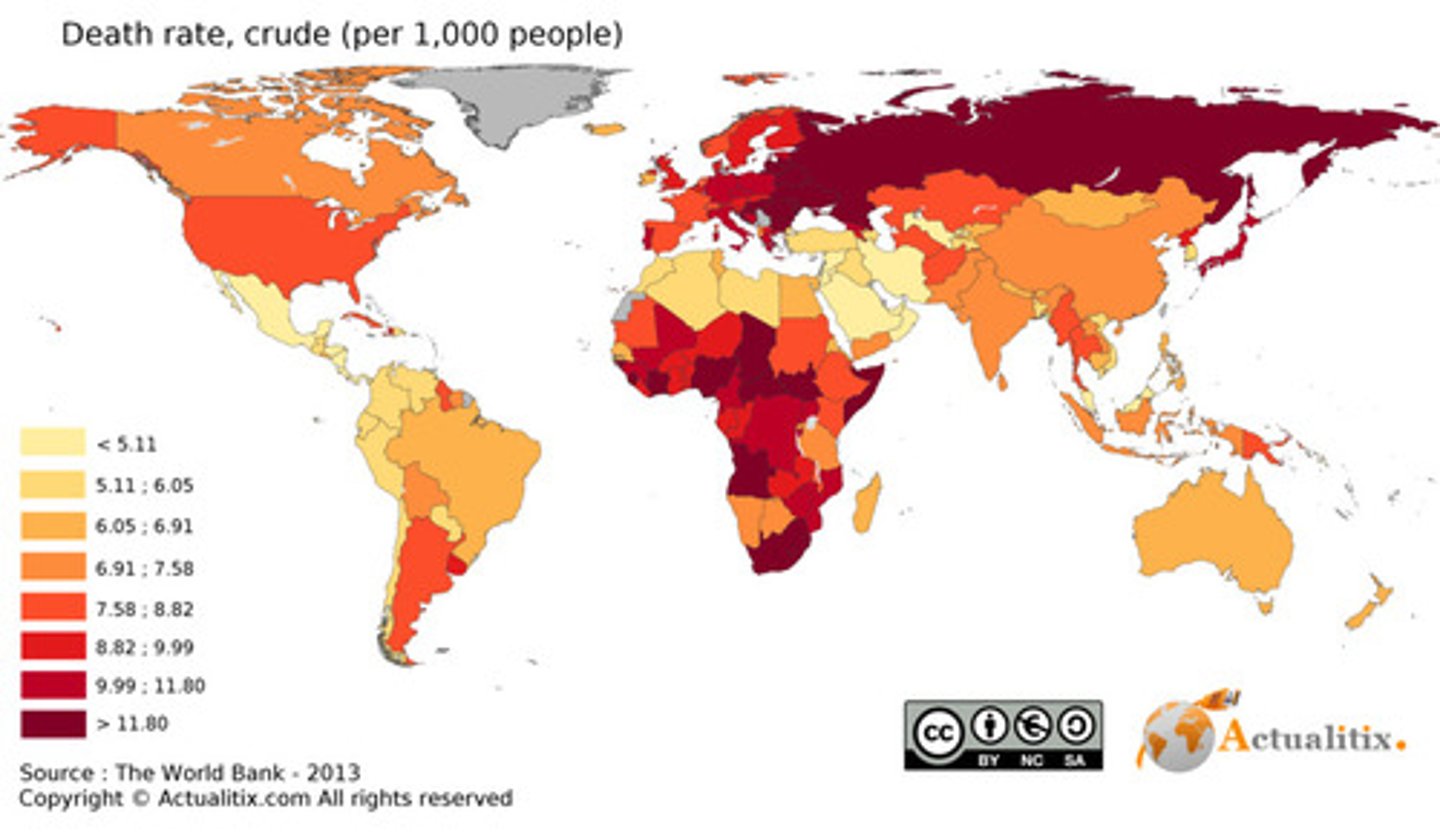
Crude Death Rate (CDR)
DEFINITION
The number of deaths per year per 1,000 people.
TERM
population momentum
DEFINITION
continued population growth after growth reduction measures have been implemented
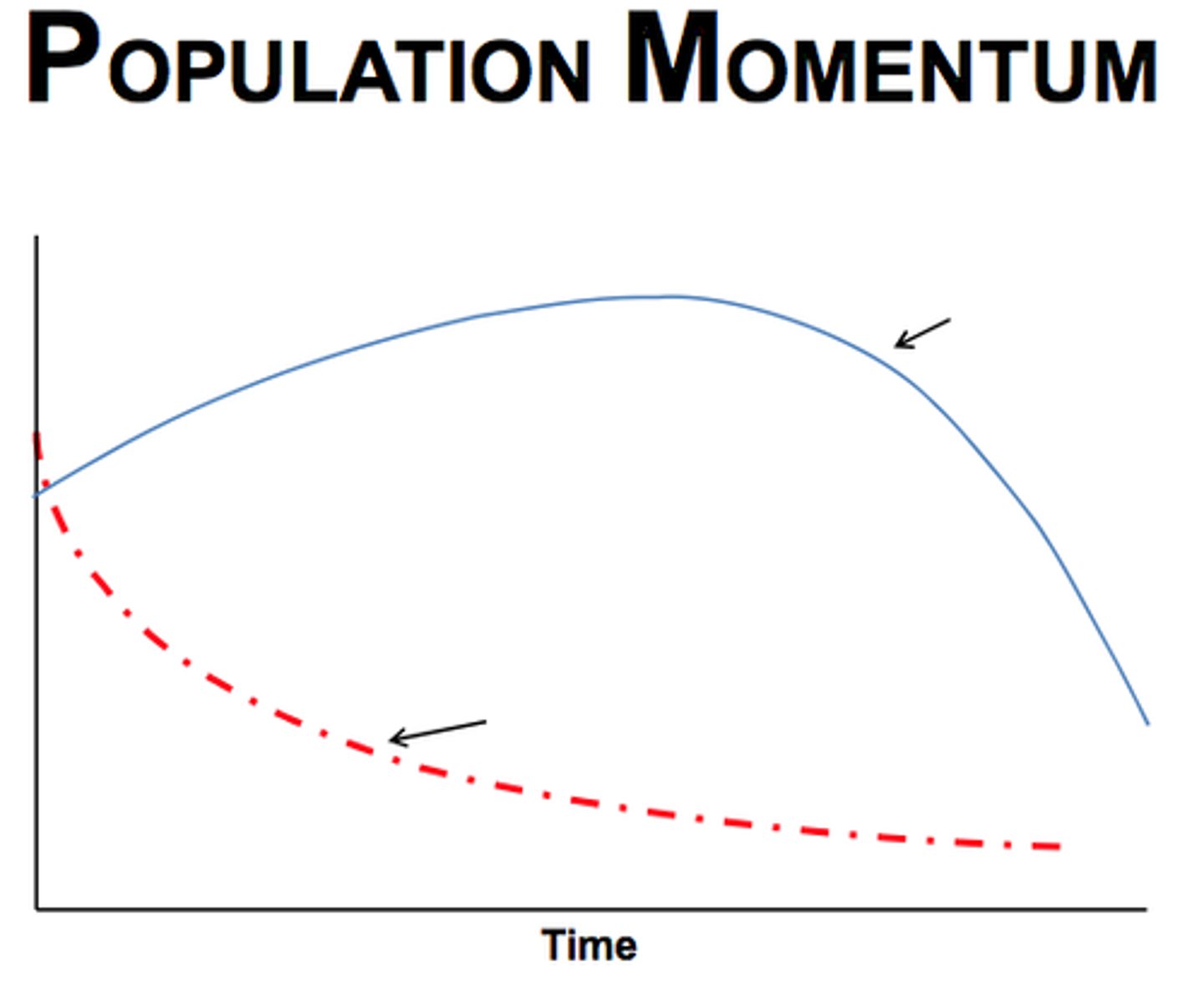
TERM
demographic transition model
DEFINITION
A sequence of demographic changes in which a country moves from high birth and death rates to low birth and death rates through time.
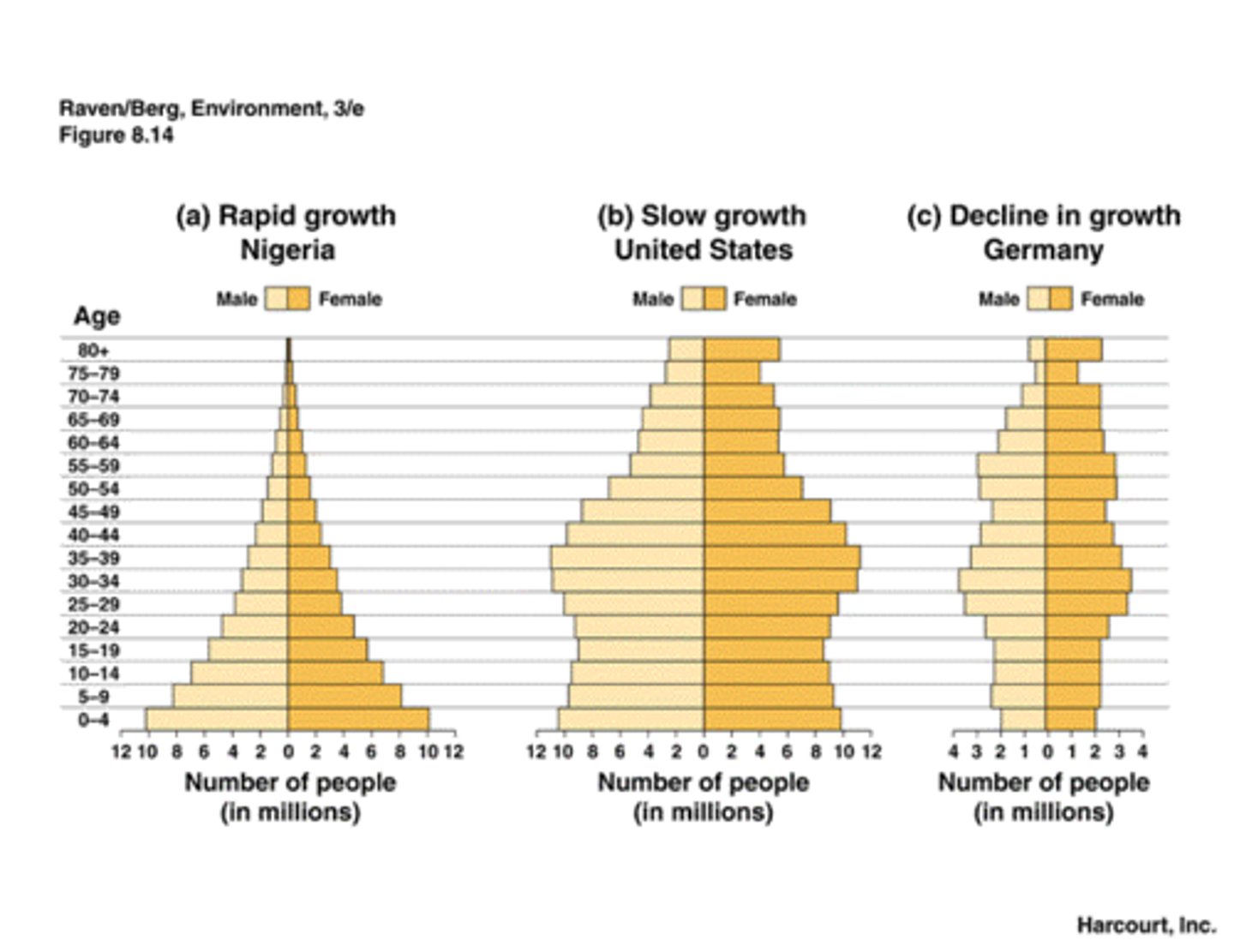
age structure diagram
graph of the numbers of males and females within different age groups of a population
Rule of 70
to find doubling time of pop, divide 70 by the percent of growth
limiting factor
An environmental factor that prevents a population from increasing

life expectancy
A figure indicating how long, on average, a person may be expected to live
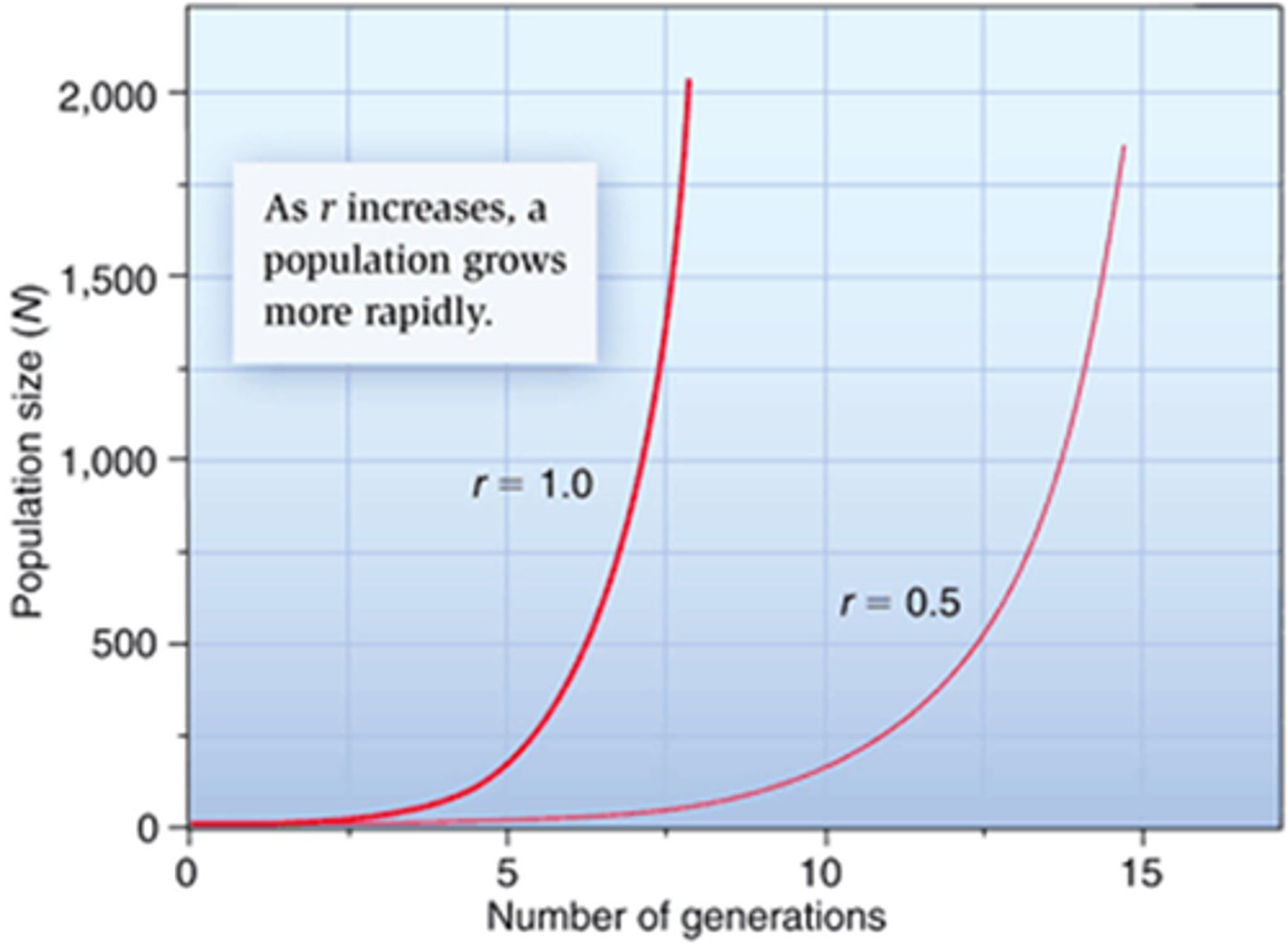
exponential growth
Growth pattern in which the individuals in a population reproduce at a constant rate
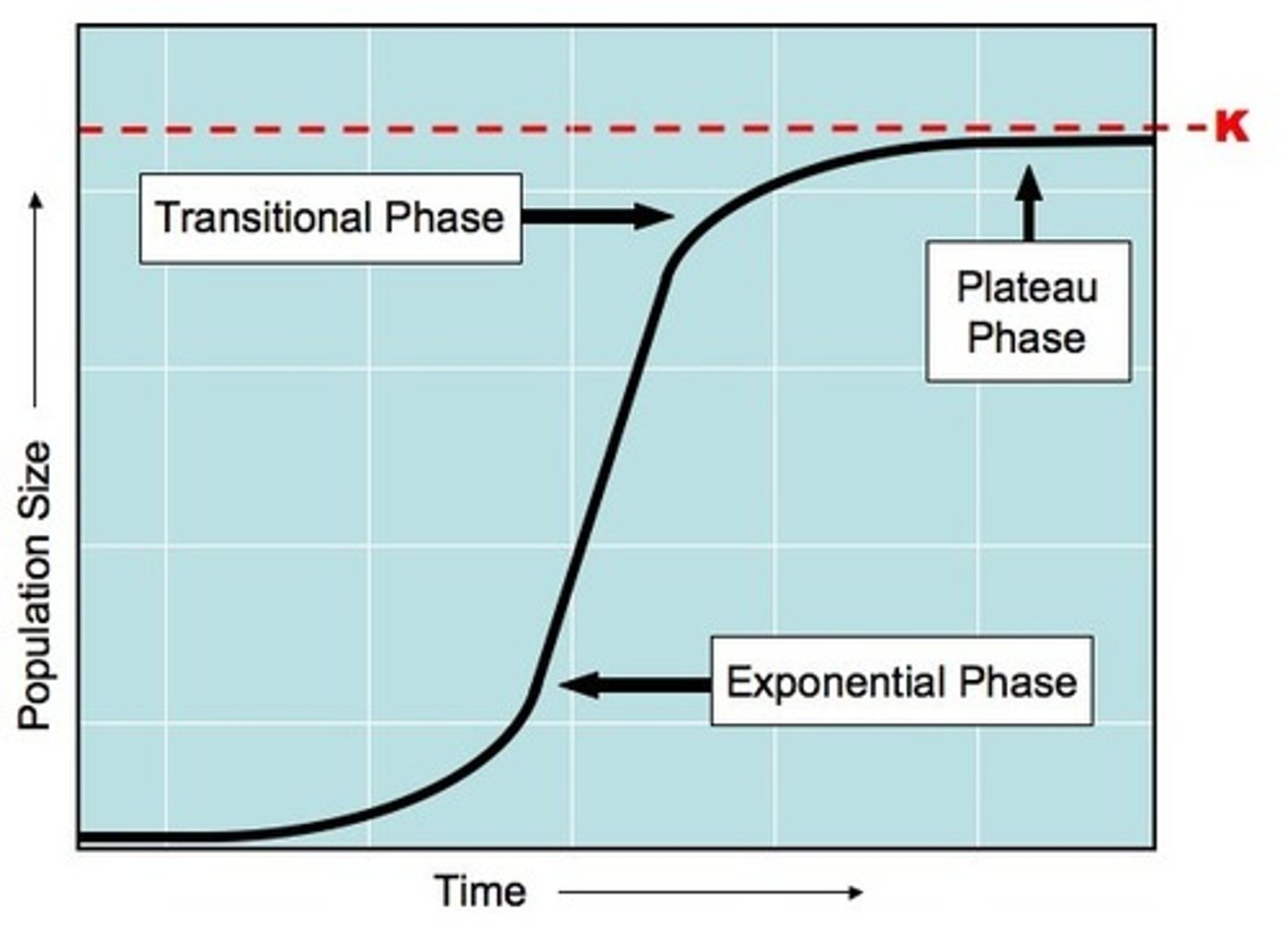
Logisitic growth
Growth of a population which may be rapid at first, but then levels off at carrying capacity due to limited resources (S-curve)
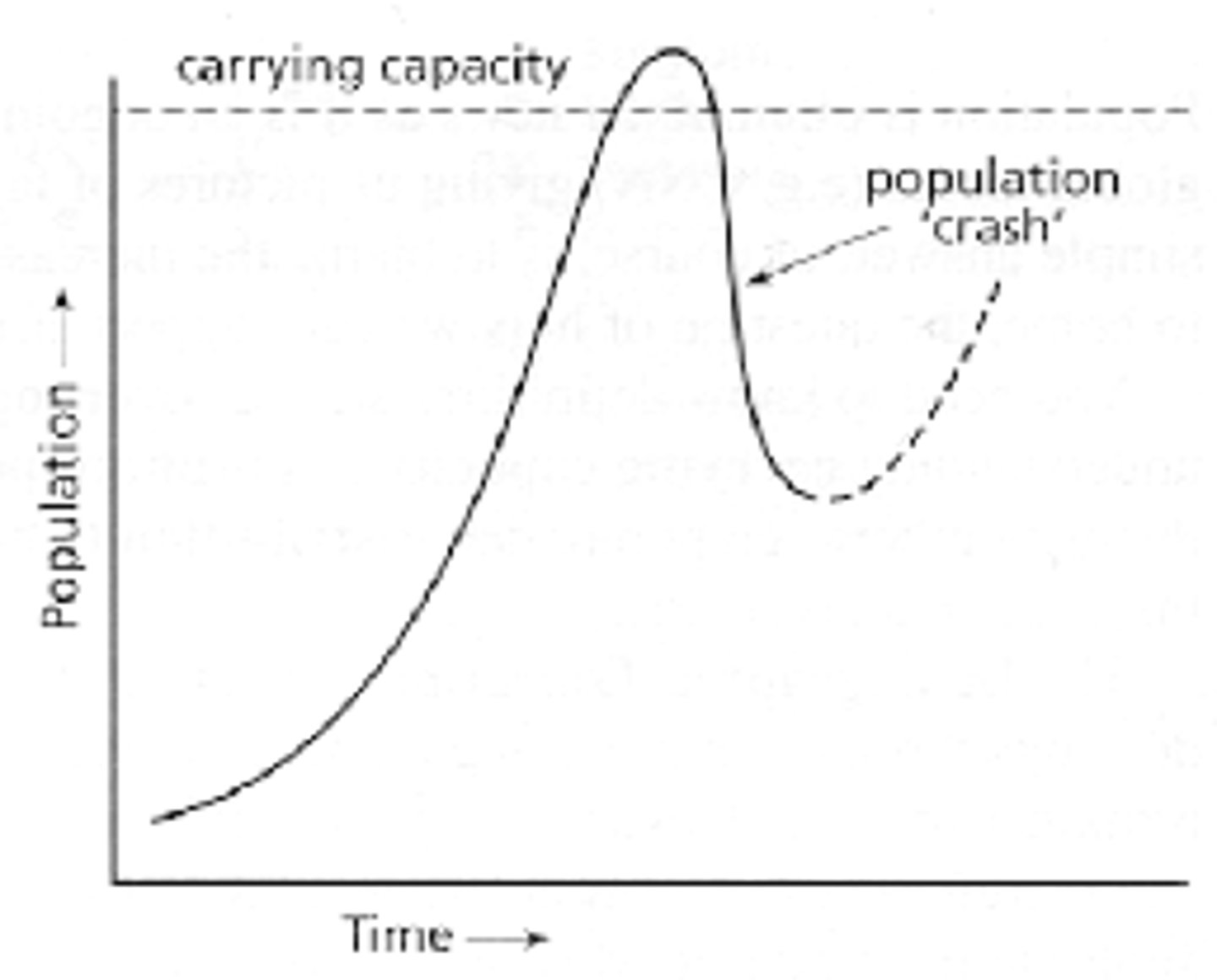
dieback or population crash
When population suffers a sharp decline, unless the excess individuals can switch to new resources or move to an area that has more resources.
Rate of Natural Increase (RNI)
The percentage of annual growth in a population excluding migration.
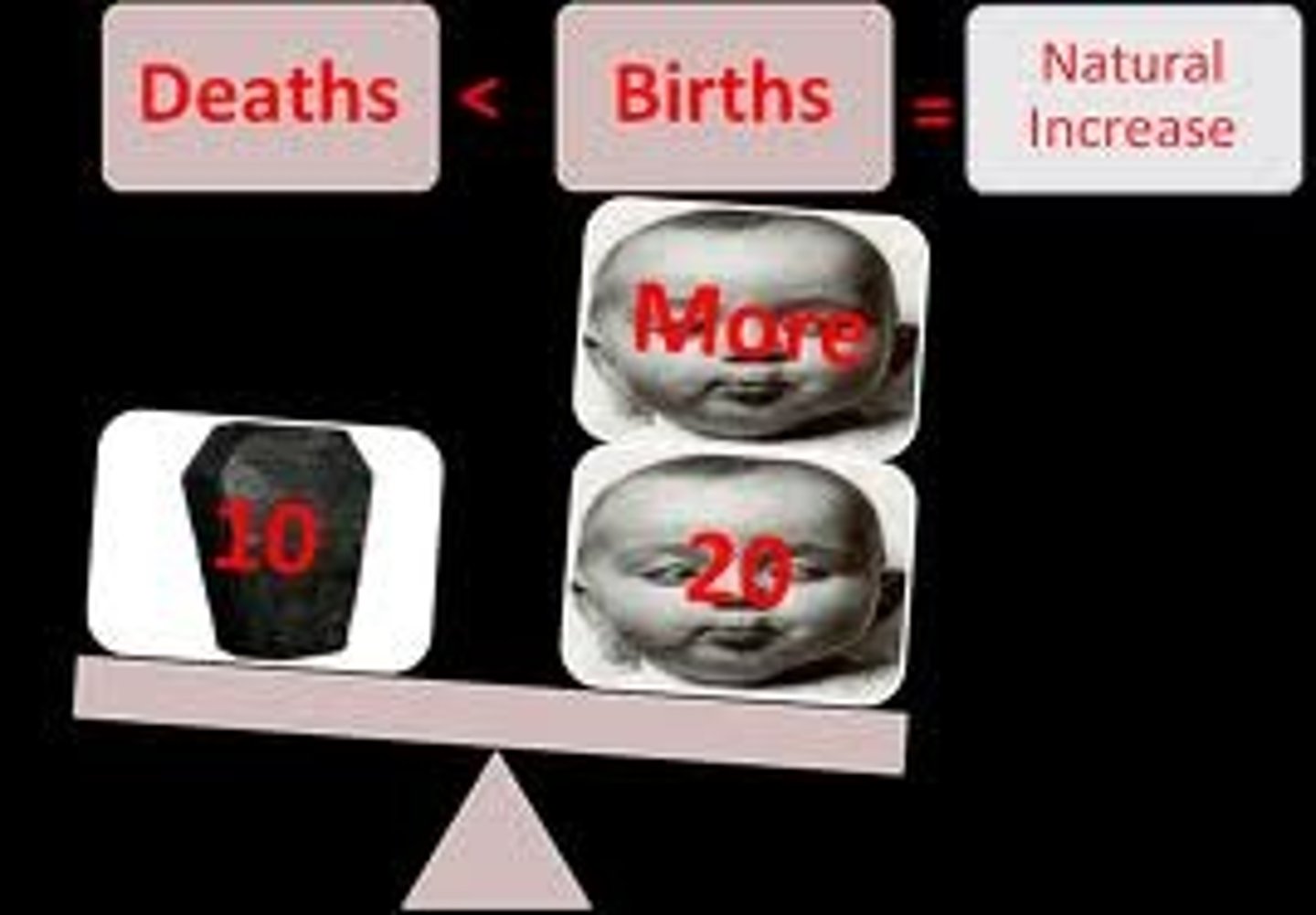
Immigration
Movement of individuals into a population

emigration
movement of individuals out of a population
economic development
improvement of human living standards by economic growth
Population sampling techniques
Visual survey (direct survey and indirect survey) quadrats, radio telemetry, Mark-recapture, probability sampling
mark-recapture method
A sampling technique used to estimate the size of animal populations.
GDP per capita
Gross domestic product divided by the number of people in the population.
Gross Domestic Product (GDP)
The total output of all economic activity in the nation, including goods and services.
generalist species
Species with a broad ecological niche. They can live in many different places, eat a variety of foods, and tolerate a wide range of environmental conditions. Examples are flies, cockroaches, mice, rats, and human beings. Compare specialist species.

specialist species
Species with a narrow ecological niche. They may be able to live in only one type of habitat, tolerate only a narrow range of climatic and other environmental conditions, or use only one type or a few types of food.

invasive species
species that enter new ecosystems and multiply, harming native species and their habitats

growth rate (r)
[(b+i) - (d+e)]/population X 100
OR
(CBR - CDR)/10