ASAM EXAM 2
1/48
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
49 Terms
4 cultural themes of AAPI values
collectivism, relational orientation, familism, family obligation
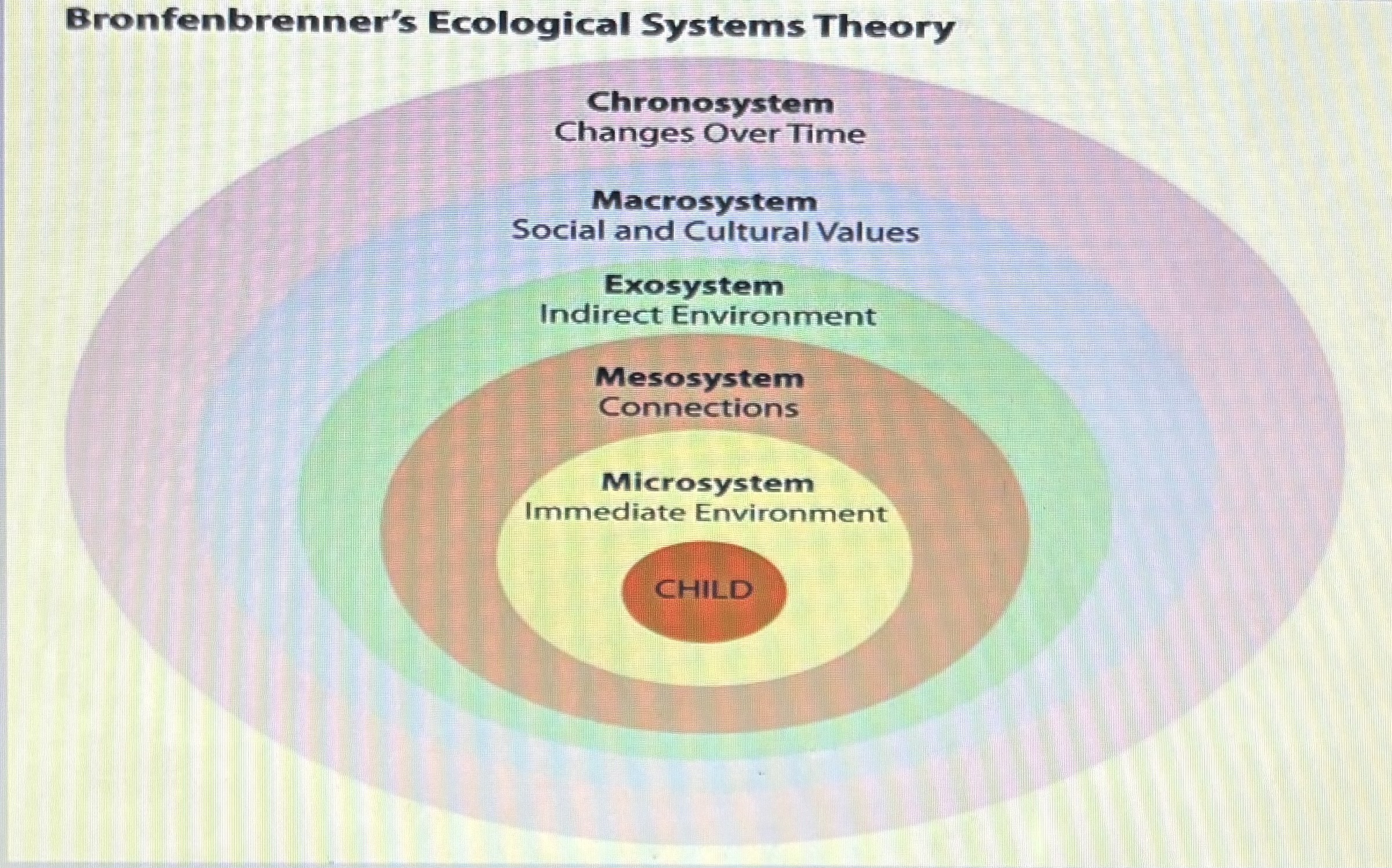
Ecological Systems Theory
Bronfenbremmer
Microsystems: individual interactions with immediate family/environment
Mesosystems: linkages between immediate family and outside settings and people (e.g parent teacher conference)
Ecosystems; factors that don’t directly include the child but indirectly influences (e.g traveling father/mother)
Macrosystems: broader societal,cultural,economic, political environment
Chronosystems: transition and shifts in one’s lifespan
authoritative parenting style
parent gives child independence, collaborative, place boundaries, open communication, nurturing, loving (most beneficial)
authoritarian parenting style
strict, punishment based parenting (e.g helicopter parenting)
permissive parenting style
full range of freedom given to child, no punishment
neglectful parenting style
physically or emotionally uninvolved parent by choice or circumstance
how does culture influence parenting style?
the collectivism in A.A culture presents parental warmth and responsiveness through investment, devotion, and sacrifice for children
authoritarian style is associated with beneficial outcomes for AA families
adherence to this results in shame, guilt, poor mental health, and discipline
racial socialization experiences
parents need to teach their children about their own native culture and about the dominant culture and about racism and prejudice
REASONS FOR LACK OF SUPPORT:
parents may be struggling with their own adjustment issues
parents may be unaware of the potential racism their children will face
parents may not know how to talk about or handle racism/discrimmination
traditional AAPI families
adhere to clearly defined positions in the patriarchal hierarchy based on age gender and birth order
mainly speak native language
highly collectivistic
assimilated AAPI families
live according to mainstream values
adopt individualistic and egalitarian orientation
generally speak english
relinquish cultural identities, values, and traditions
bicultural AAPI families
rapid acculturation of children may lead to growing value differences and tensions
speak both native language and english
creates imbalance in hierarchy but can also serve as motivational change in family dynamic
1.5 generation dilemma
bicultural members
proficient in both english and native
children who grew up in america for majority of their life but still have strong ties to home
parachute children
minors immigrating alone to use countries
immigrate at a much younger age, sent by parents, and obtain primary and/or secondary education without parental supervision
reasons: education, uncertain politics, status, planned immigration process, english proficiency, and job success
face issues like behavioral problems, financial burdens, school, chores. identity formation, maintaining parental relations, abandonment
older families and caretaking
might be easier for caregivers to admit ailments rather than emotional difficulties in caring for elderly family members
approach to AA family therapy
resolution of problems through negotiation and medication while remaining non confrontational
meet with individuals first
understand the hierarchy
address members with equal respect
understand harmony & peace etc.
intermarriage patterns
majority of AA marry intraethnically (same ethnicity)
acculturation is directly related to interethnic relationships (different ethnicities, out marrying) + third generation out married the second and the second out married the first
AA are out marrying at higher rates
AA women out marry at higher rates than AA men
stronger ethnic identity = less likely to interracially date/marry
influencing factors on interracial relationships
antimiscegenation laws: prohibited interracial relationships and marriage
repealed in 1967 in violation of fourteenth amendment of equal protection
arranged marriage stressors
conflicts with extended family and in-laws
societal expectations
strong gendered roles
therapy approaches: do not make assumptions about each others racial backgrounds
media stereotypes for AA men
invisible man
not having the central role
having a strong accent
perpetual foreigner
masculinity myth
dominant form of masculinity
carries contradictory and inconsistent expectations for men and consequences for men who either live or don’t live up to that
men should be aggressive daring or visibly strong
men should not have any feminine presenting traits or interests
elements of gender role conflict
success, power, and competition (SPC)
restrictive emotionally (RE)
restrictive affectionate behavior between men (RABBM)
conflict between work and family (CWF)
minority identity development model
conformity
dissonance
resistance immersion
introspection
integrative awareness
conformity
relate to dominant group
adopt hegemonic attitudes (legitimizes a man’s dominant position in society)
ashamed of being asian
unaware of overt/covert racism
dissonance
realization to that he isn’t fully accepted by society
awareness of racism and oppression of ethnic minorities
aware of own prejudices and stereotypical attitudes toward other Asians
might establishes first close relationship with a fellow AA
might become aware of overcompensation of masculine notions
left in an ambiguous state
resistance immersion
individual’s reference group shifts
becomes completely immersed in AA culture (although superficially)
adhering to more traditional roles
bitterness towards the majority group
introspection
reflection and understanding what it means to be Asian
reassess his feelings towards people of the majority group
attempting to balance, negotiate, and become more flexible regarding notion of masculinity
integrative awareness
positive notion of what it means to be AA
feels comfortable with new identity
negative feelings subside towards majority group
still exploring issues of racism and masculinity faced by AA men
redefining and developing new progressive form of nonhegemonic masculinity
asianized attribution
the process when certain attributes or characteristics of AA adhere to an evaluators schema or stereotypical notions
(negatively evaluated)
(e.g AA male attributes: polite modest agreeable grateful but the evaluator has preconceived notions and perceives them as negative/“too this , too that”)
transgressive attribution
process in which attribution of AA individual are incongruent/do not match with the evaluators stereotypic notions
(negatively interpreted)
doesn’t match the evaluators preconceived notions so it gets negatively interpreted
therapeutic approach w/ AA men
culturally appropriate approaches of assessment and treatment that allow for saving face in personal and professional life
understand how AA males express and cope with distress
ask self reflection questions about masculinity and saving face
understand AA cultural conflicts that exist
“A Different Outlook”
AA men are thriving and voices are stronger
they are developing psychologically healthy and flexible identities
not adhering to gender roles and masculinity norms
developing nonhegemonic masculinities
important to construct an ambiguous model of masculinity in order to counter the hegemonic model
the women’s role
role is to serve and honor men in patriarchal hierarchy
3 obediences
3 obediences
honor father
submit to husband
indulgence to the son
dual standard
important to display wisdom and genes
be successful but not as much as the man
career cannot trump family
women cannot be TOO educated (reduce her feminine attributes, lower marriage opportunities, fear of career trumping family)
racial and feminist identity development downing & roush 1985
passive acceptance
revelation
embeddedness-emanation
synthesis
active commitment
passive acceptance
denial of sexism
acceptance of transitional roles
no awareness
revelation
instances of discrimination get difficult to ignore
realizes she has to recognize and/or trust her observation
embeddedness-emanation
“discovery of sisterhood”
development of gender curiousness
acknowledges loss of self due to transitional roles
synthesis
recognize positive aspects of being female
positive self concept
independent decision making overlooking traditional gender role expectation
autonomy
active commitment
using well integrated identity to bring societal change
domestic violence
pattens of repeated abuse
physical
emotional
sexual
financial
digital
thrives on power dynamic
cycle of abuse
tension → abusive incident → honey moon phase
acute/crisis phase: when the incident actually takes place
cultural contributing factors
patriarchy
women must allocate housecleaning/chores
collectivism
divorce stigma
societal contributing factors
immigration/acculturation stressors
language barriers
limited economic resources
social isolation
individual/familial contributing factors
immigration history and trauma
child abuse
witnessing abuse/normalizing it
marital dissatisfaction
in-law conflicts
risk & reporting
incidents go unreported due to:
fear of jeopardizing financial dependence
not making personal issues public
self blame
deciding factors of reporting
severity of violence
perceived sense of self efficacy
availability of socioeconomic resources
social support
therapy assistance
limited research results in difficulty examining dv in Asian communities (prevalence rates, attitudes, & cultural/social aspects
PCPs are the first line of care and support
beneficial to use specific culture focused questions during clinical assessments