Hemoglobinpathies
1/46
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
47 Terms
Hemoglobinopathy
Genetic mutation in one or more genes that affect Hb synthesis
- globin or polypeptide chains
altered amino acid sequence
Structural defect and its function
- qualitative
- Point mutations, deletions, insertions, fusions
Reduced rate of synthesis
- No alteration to amino acid sequence
- quantitative
ζ2ε2
Gower I
α2ε3
Gower II
ζ2γ2
Portland
α2γ2
Hgb F
- 60-90% newborn
α2δ2
Hgb A2
α2β2
Hgb A
- 10-40% newborn
Zygosity
Association between the number of gene mutations and the level of severity
Four outcomes
1. Abnormal Hb= hemolytic anemia
2. Abnormal Hb= methemoglobin
3. Hbs different oxygen affinity
4. Abnormal Hbs= benign
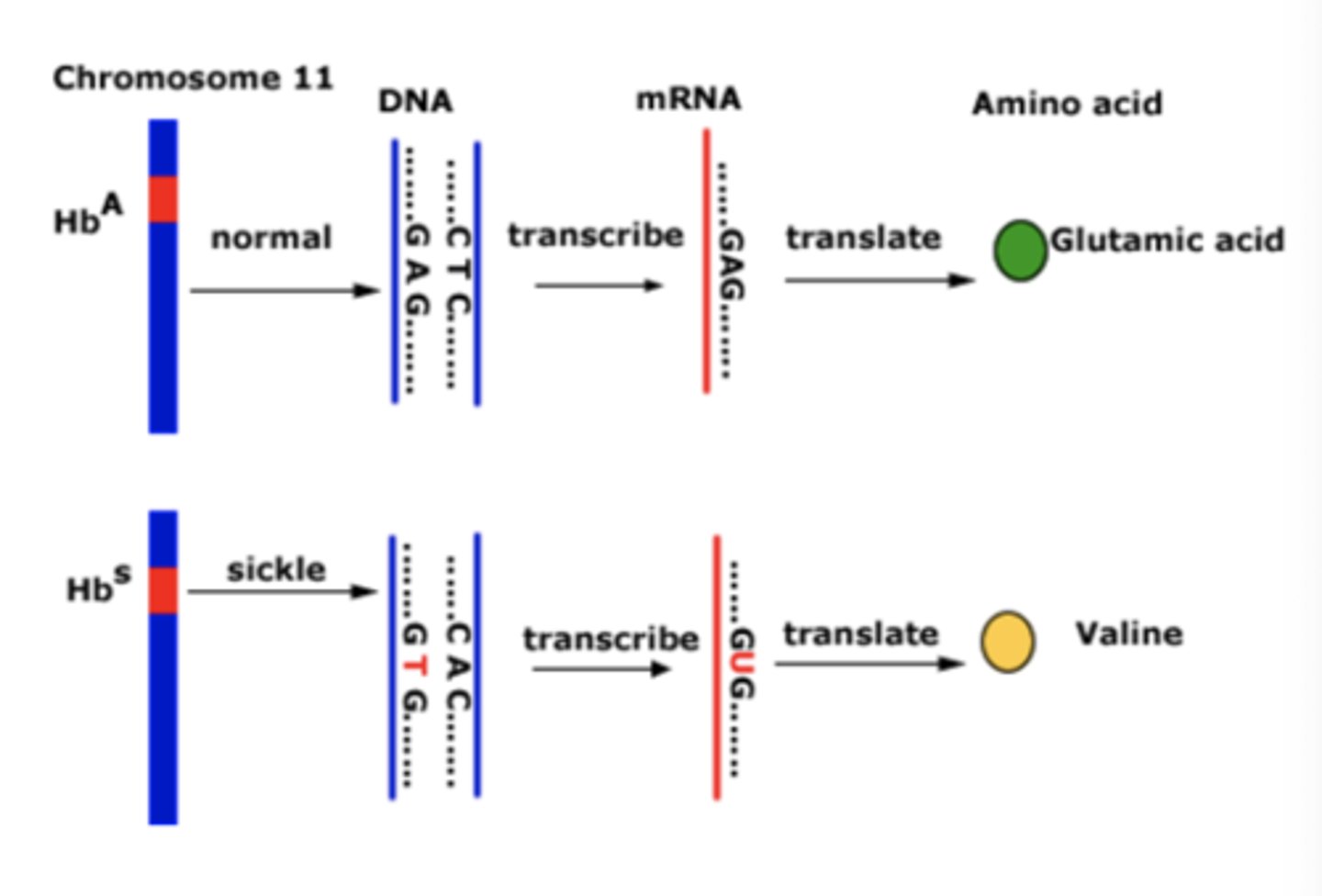
Hemoglobin S genetics
- single point mutation
- β-chain abnormalities
- co-dominant
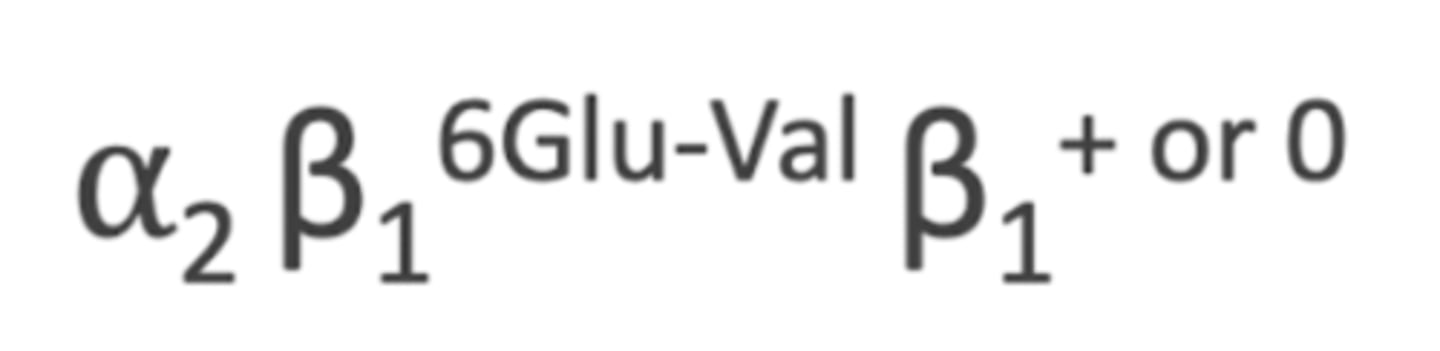
phenotype of Hgb S
- trait= AS= only one β defected
- homozygous= SS
- heteozygous= Hb SC or Hb S-B-thal
Hgb S chromosome
α2β2-6Glu-Val
- at position 6, glutamic acid is replaced with valine
- produces a +1 charge
- affects oxygen affinity
Oxygenated hgb S
does not produce a hydrophobic pocket for valine
- maintain biconcave disc
Deoxygenated hgb S
- creates a hydrophobic pocket
- form electrostatic bonds between hgb= molecules that elongate in a helical formation
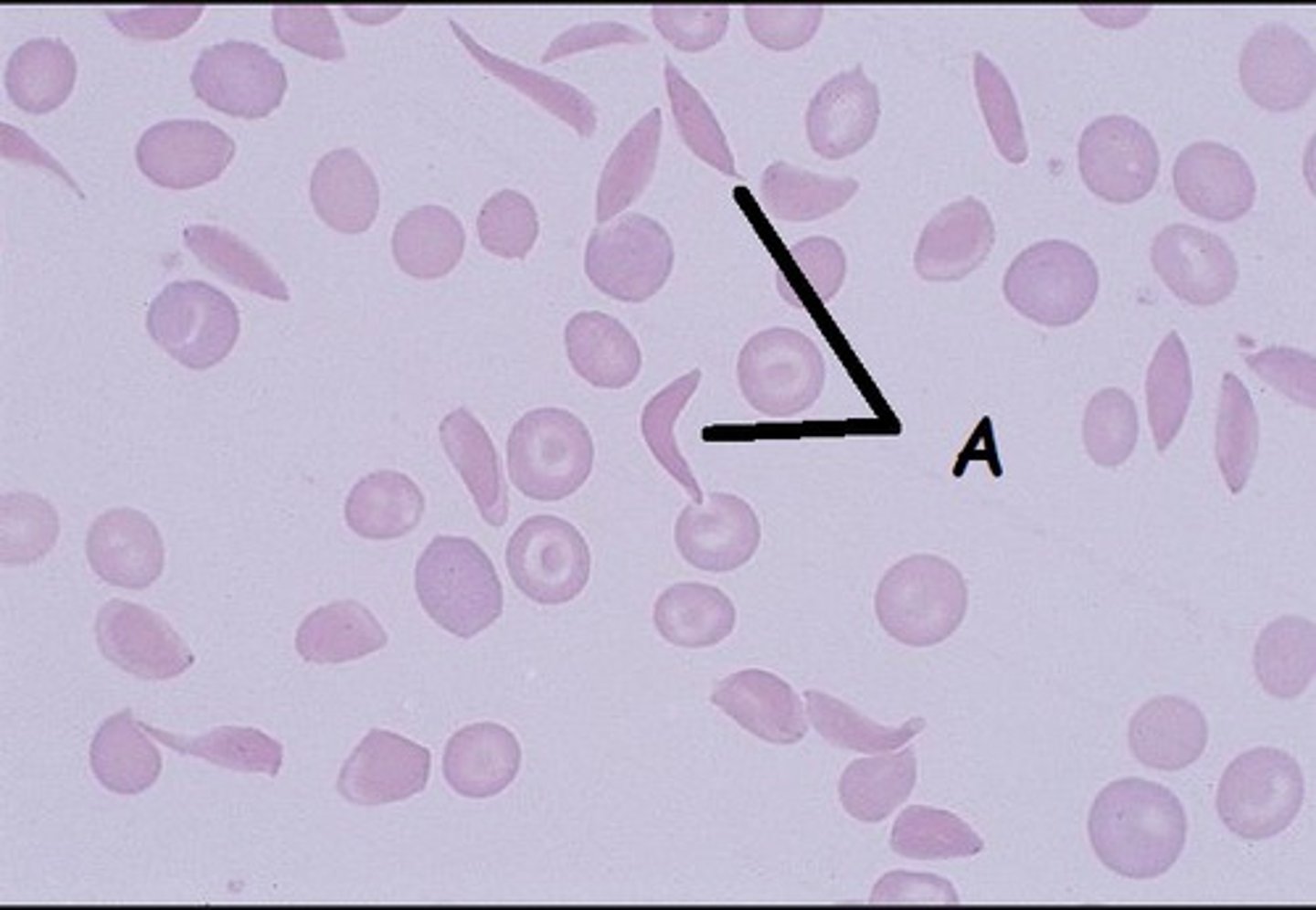
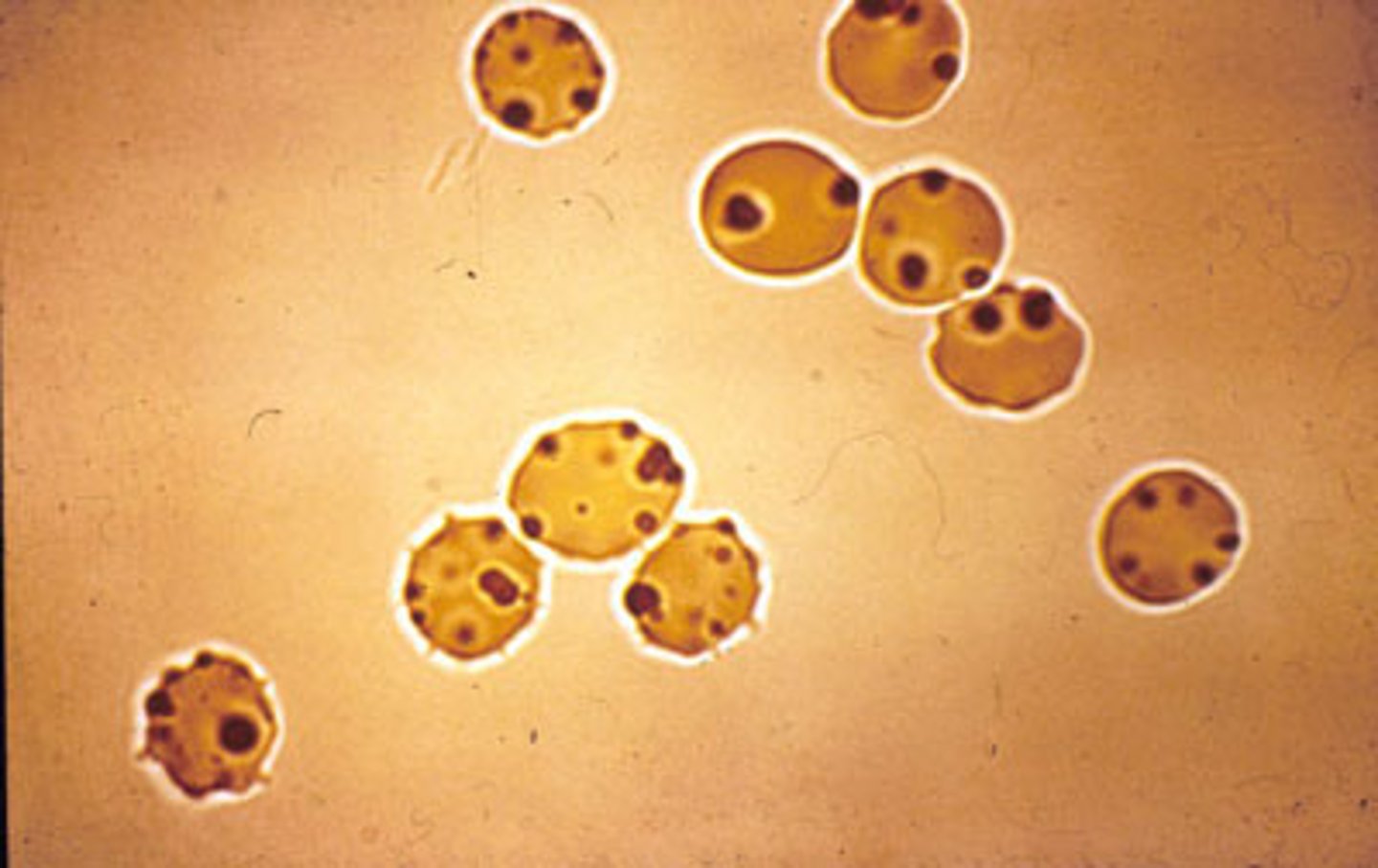
Hgb S RBCs
- Less soluble
- Rigid
- Form tactoids= liquid crystals
- Hg S polymers= sickle
O2 saturation for sickling
- Homozygous <85%
- Heterozygous <40%
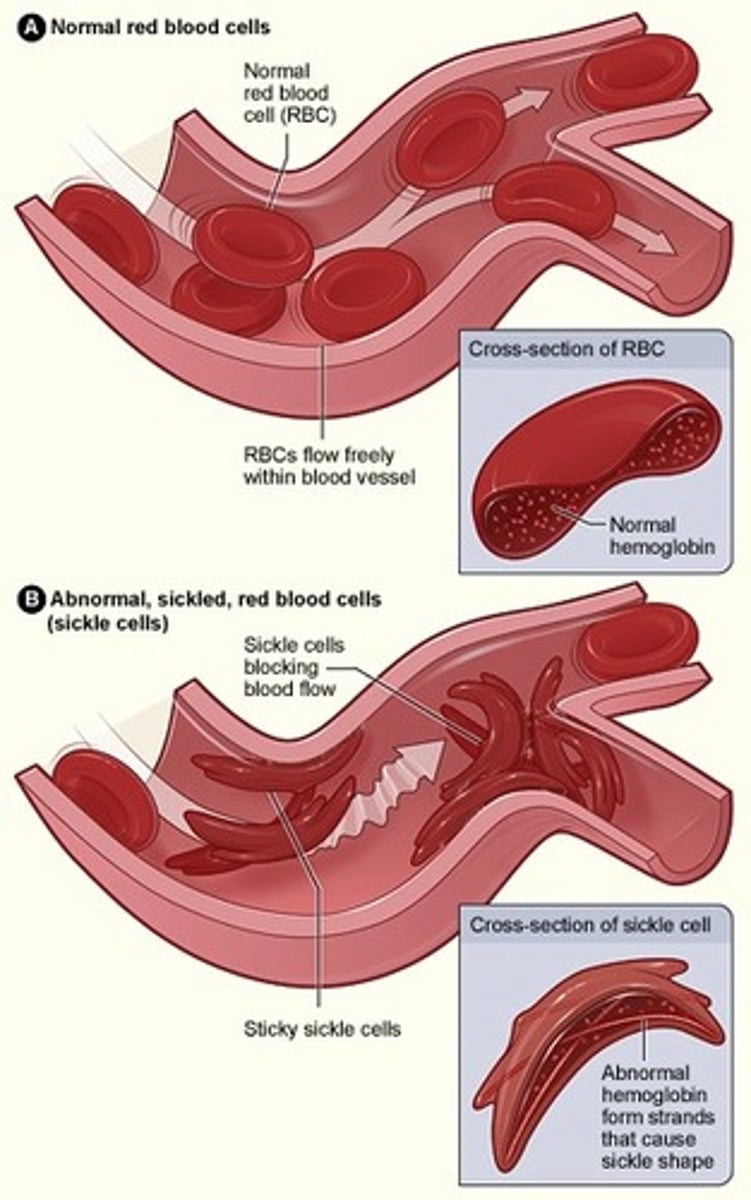
Sickle pathophys
- viscous blood= slow flow
- Decrease in O2 tension= low pH, high 2-3 BPG
- blocks capillaries
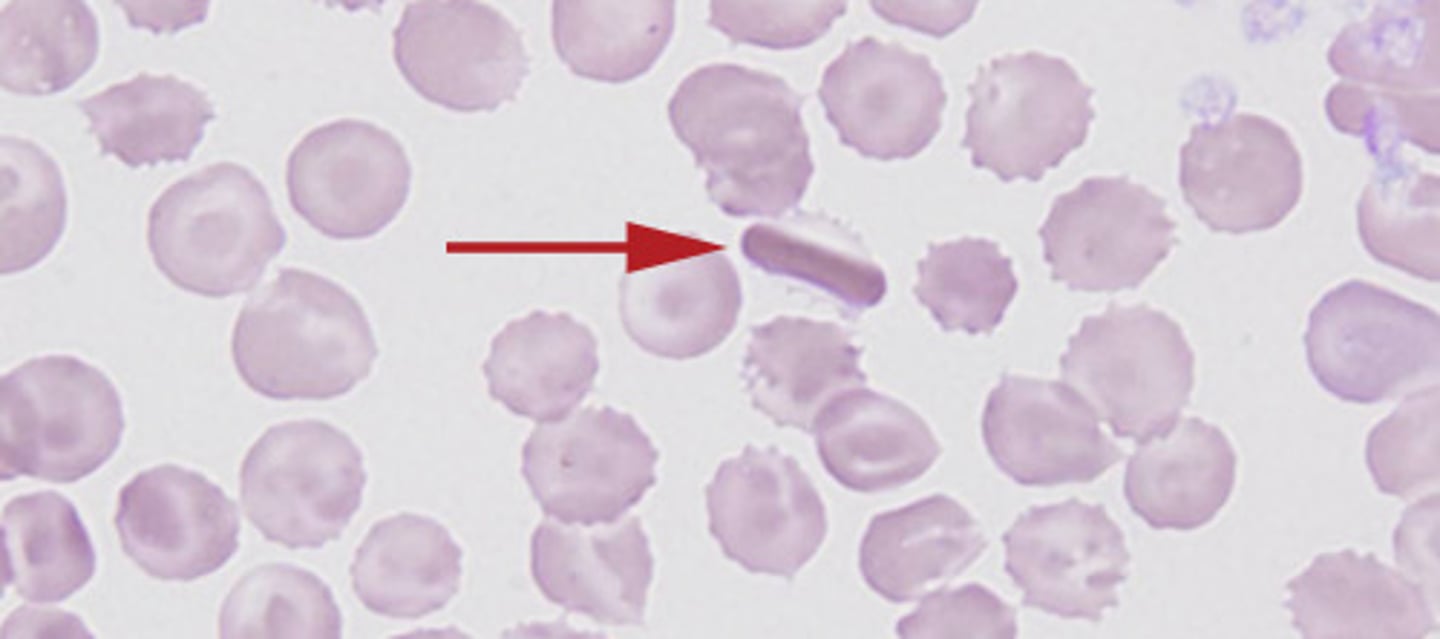
Reversible sickle cells
- change shape based on oxygen tension
- microvasculature occlusion
Irreversible
- constant shape
- recognized by abnormal spleen
sickle cell anemia
- chronic hemolysis
- hyperplastic BM
- aplastic crisis
- megaloblastic= folate defiency
- cardiac defects
- bacterial infections
Vaso-occlusive crisis
Rigid sickled cells aggregate in the microvasculature
- hypoxia, acidosis
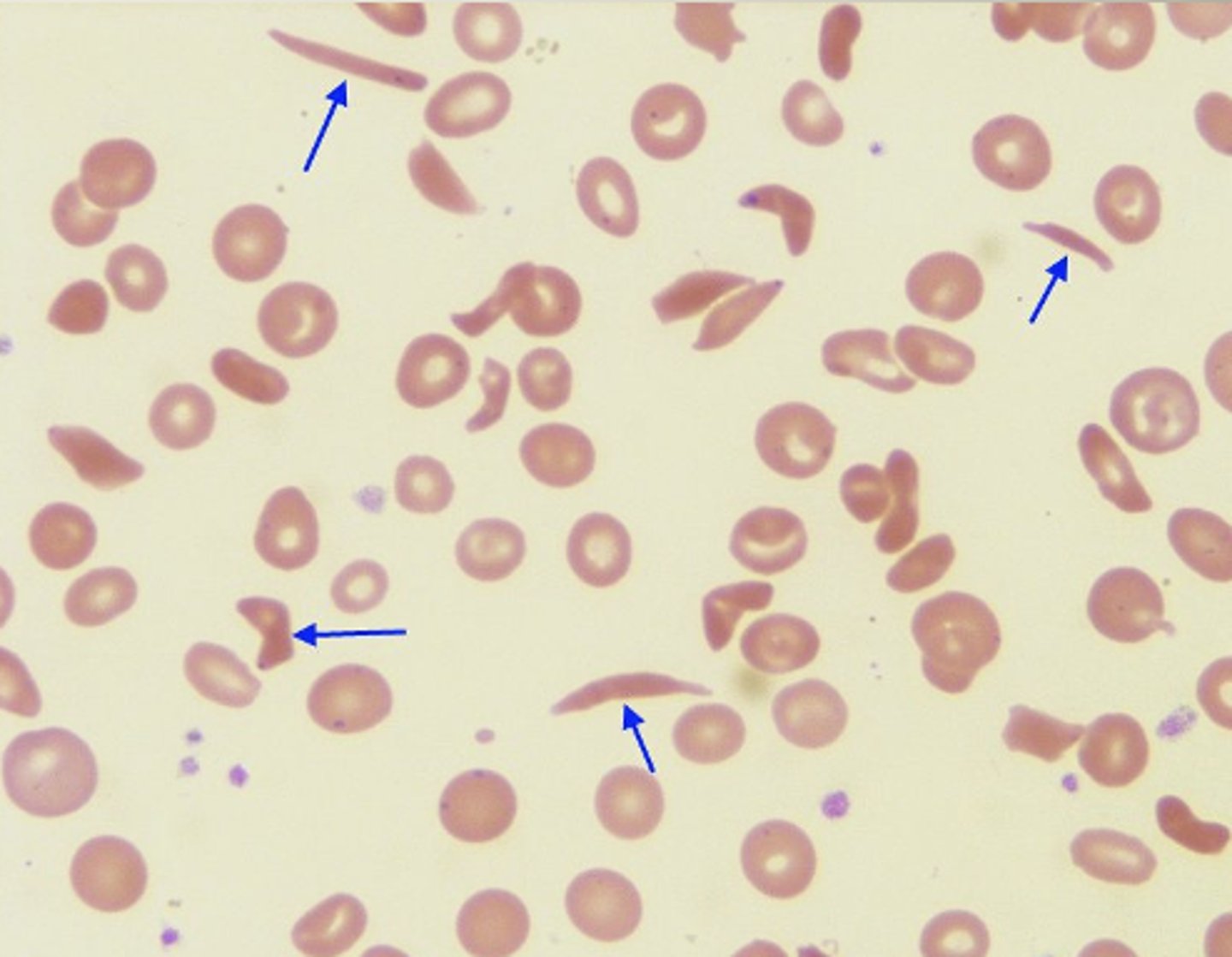
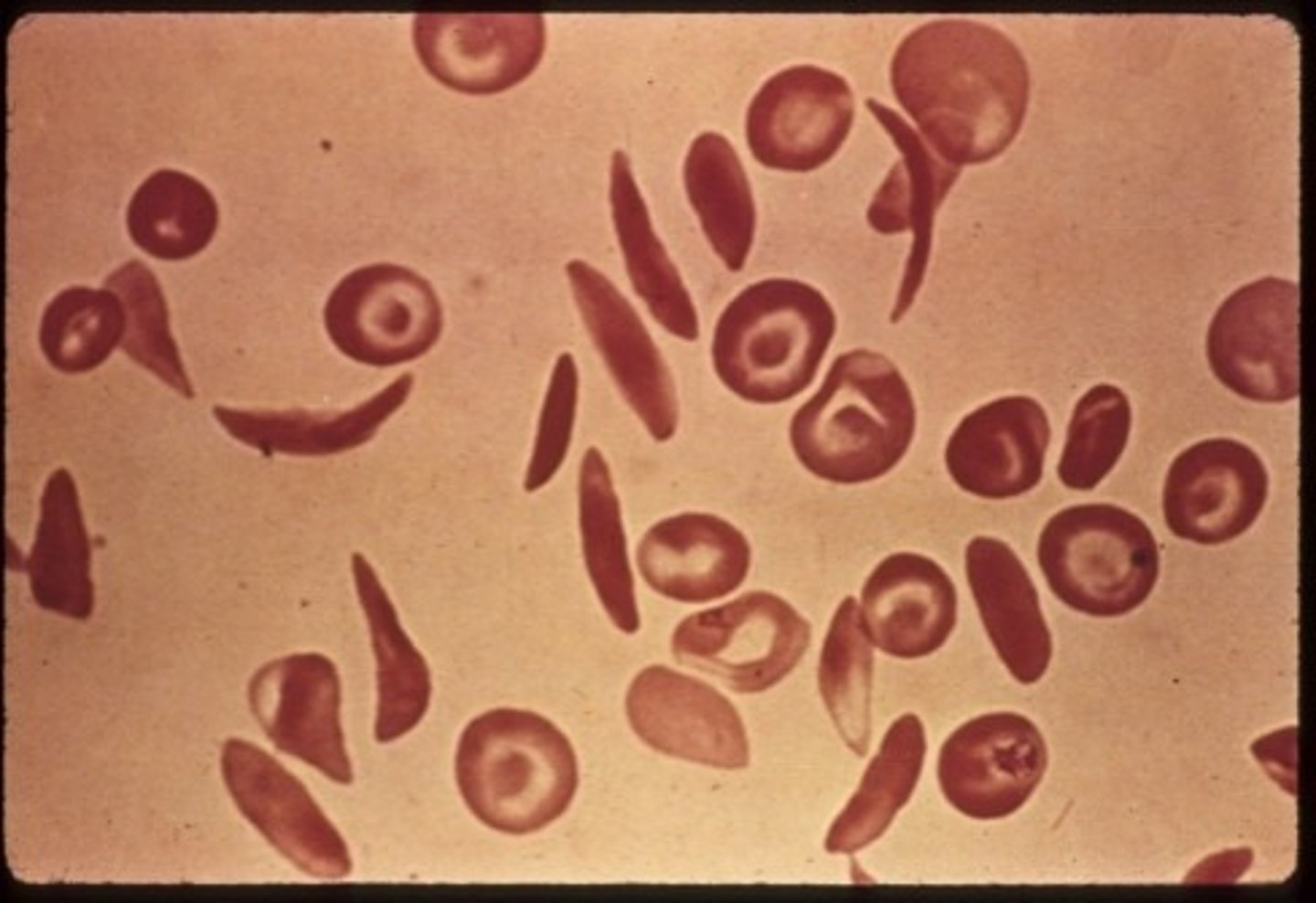
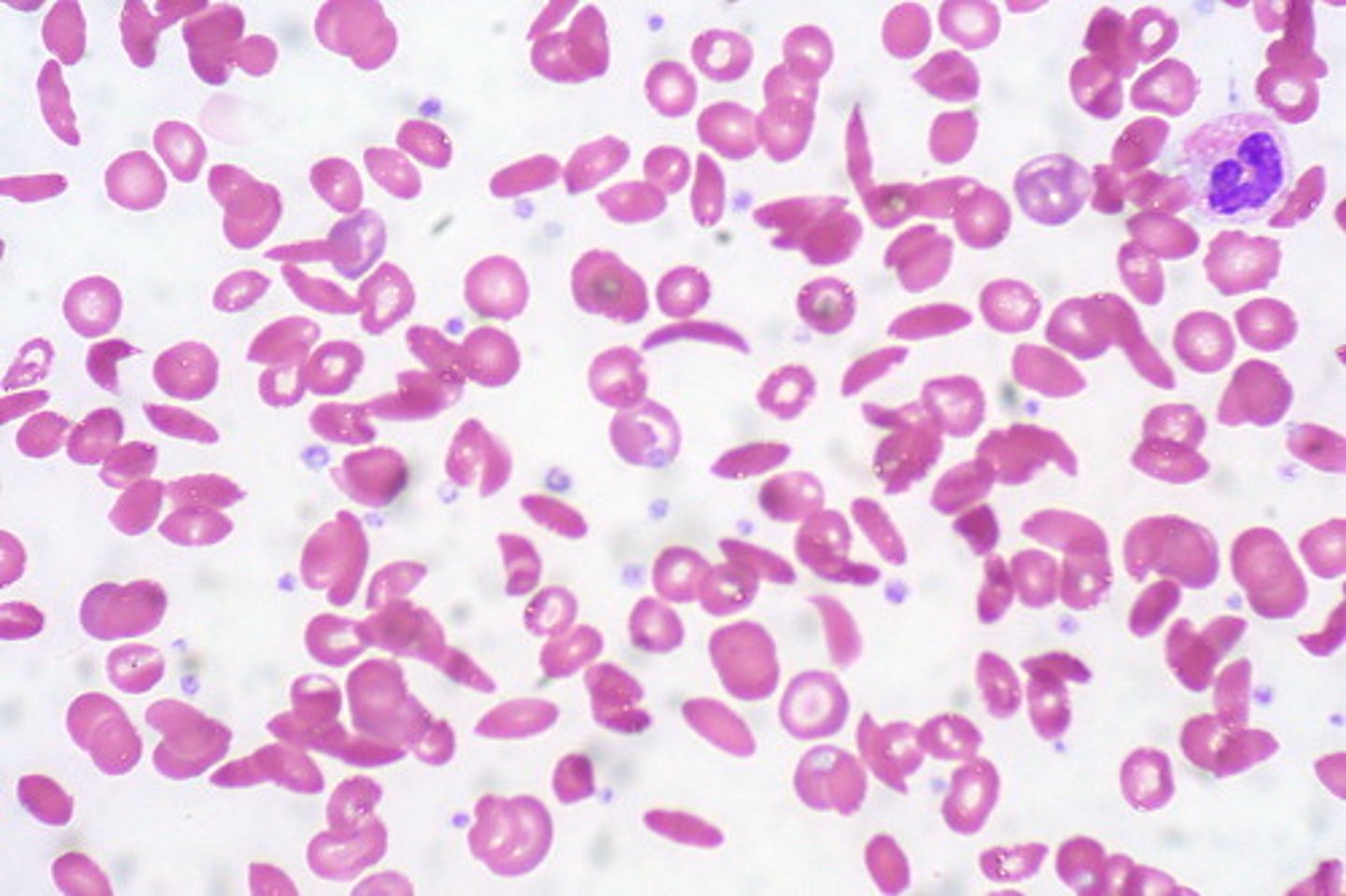
Peripheral Blood Sickle cell
- Normochrom/normocyt
- increased RDW
- Hgb 6 - 10 gm/dL
- Reticulocyte 10 - 25%**
- inclusions
- thrombocytosis
- leukocytosis left shift
- target cells**
Chemistry tests sickle cell
- Increased direct and indirect bilirubin
- Increased LD & uric acid
- Decreased haptoglobin
Diagnosis of SCD
1. insolubility of Hb S= Tactoids crystals
2. HPLC)
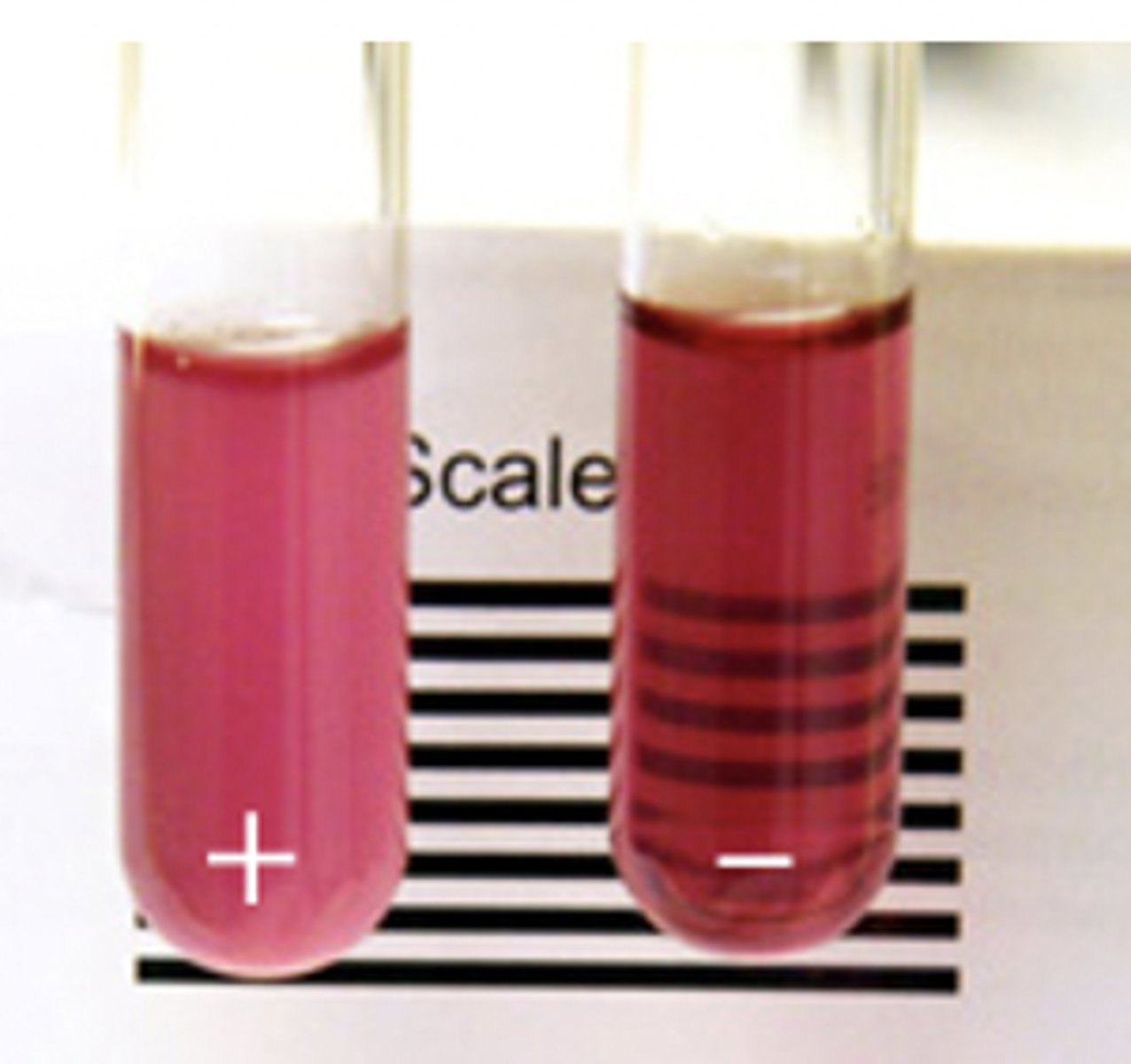
Hemoglobin Solubility Test
- adults
- decreased solubility of deoxygenated Hb S= tactoid crystals= turbidity
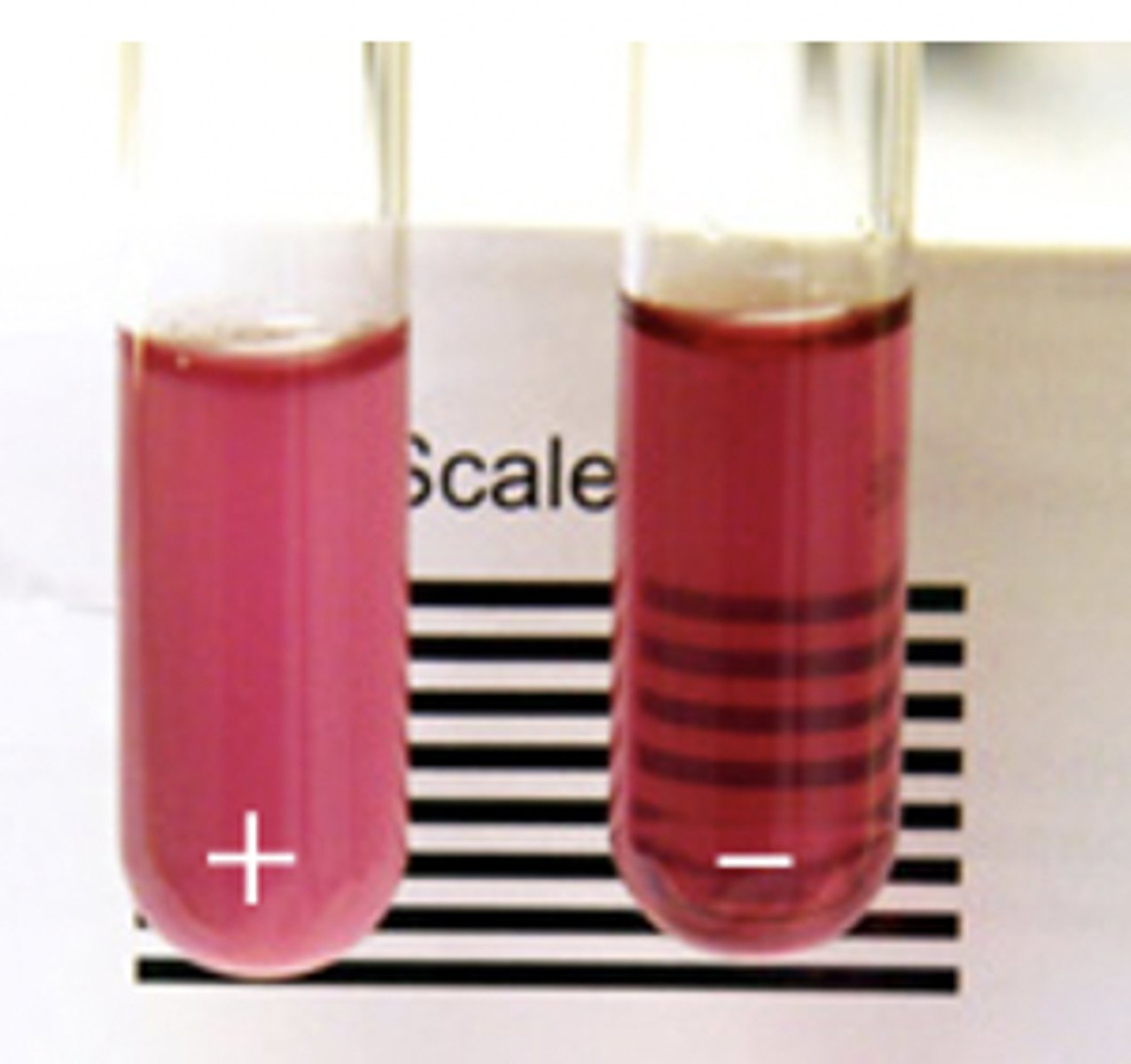
False positives Hgb solubility
- hyperlipidemia
- Too much blood added
False negatives Hgb solubility
- Infants <6 months
- Low hematocrits
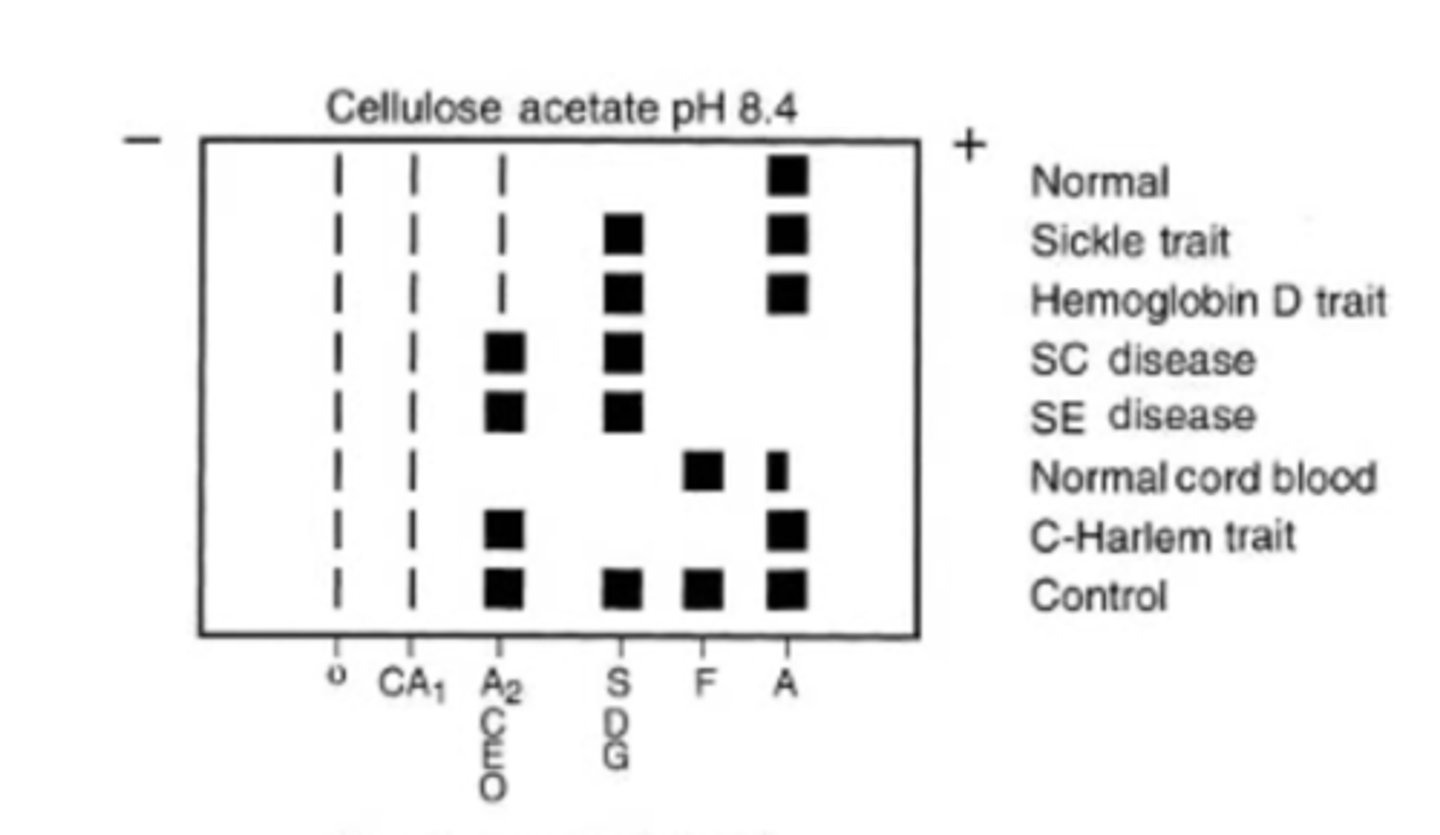
Alkaline hemoglobin electrophoresis
Hb molecules (- charge), migrate towards anode (+ pole)
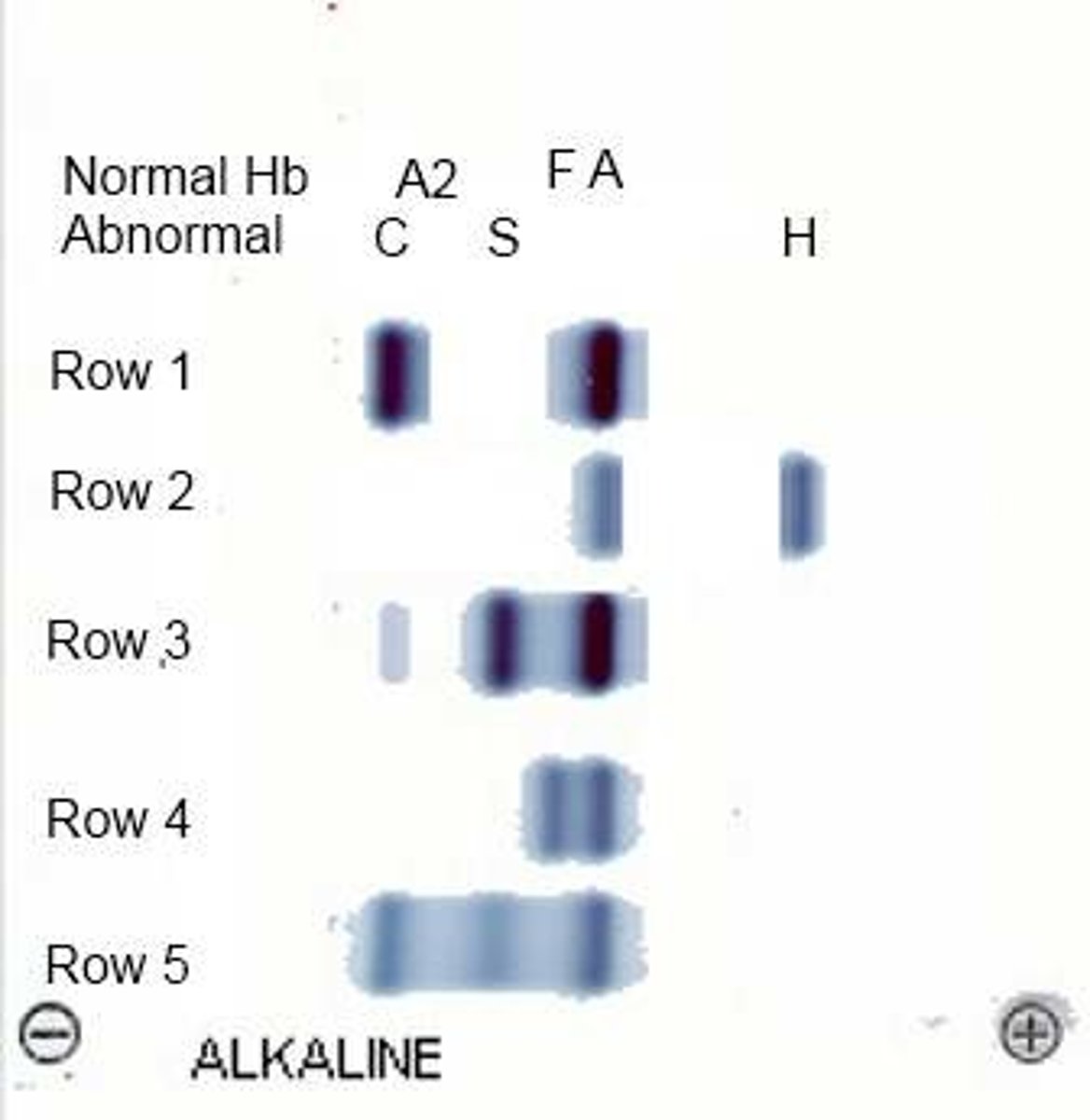
alkaline pH electrophoresis
Hb S migrates with Hb D and Hb G
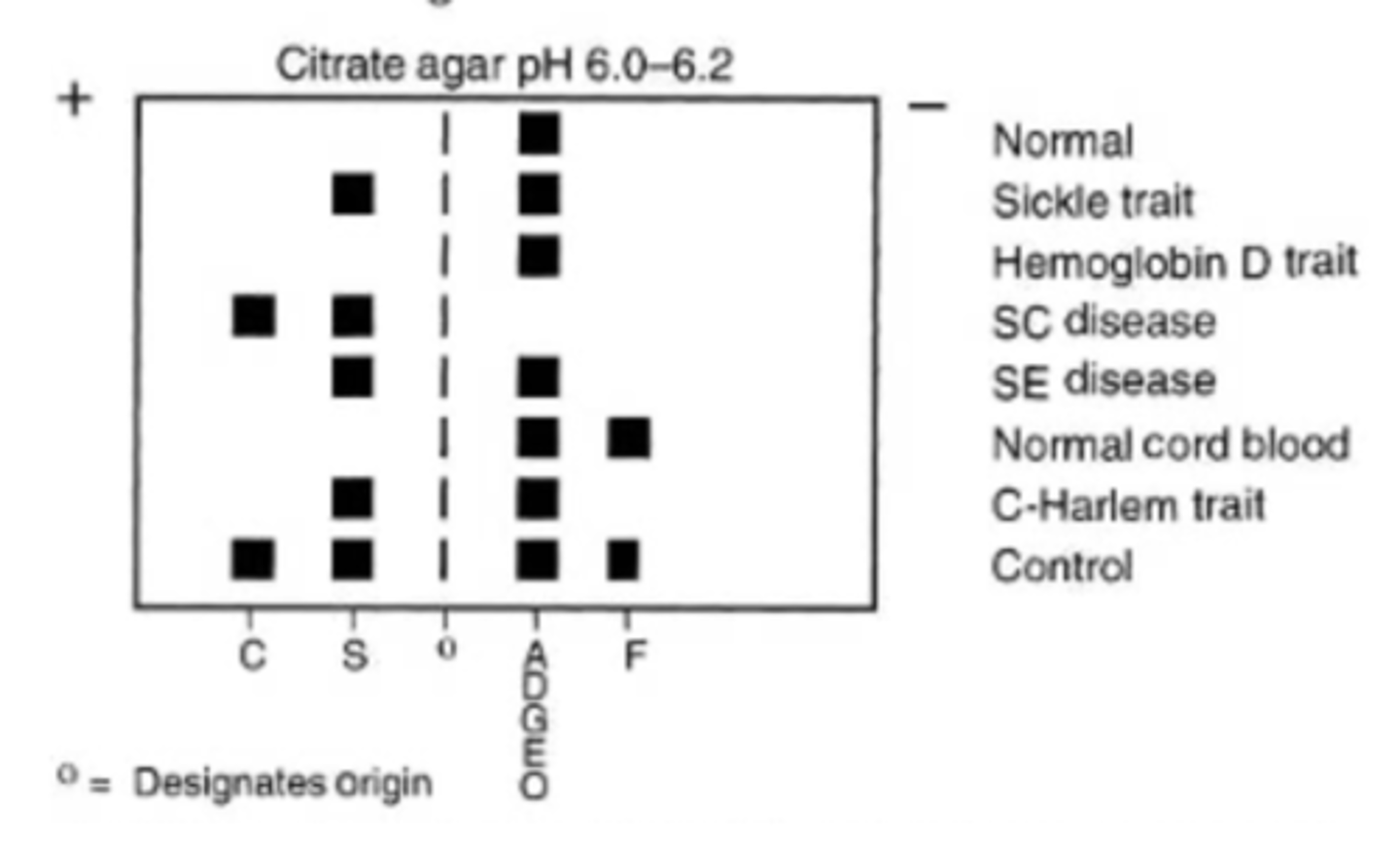
acidic pH electrophoresis
Hb S separates from D and G
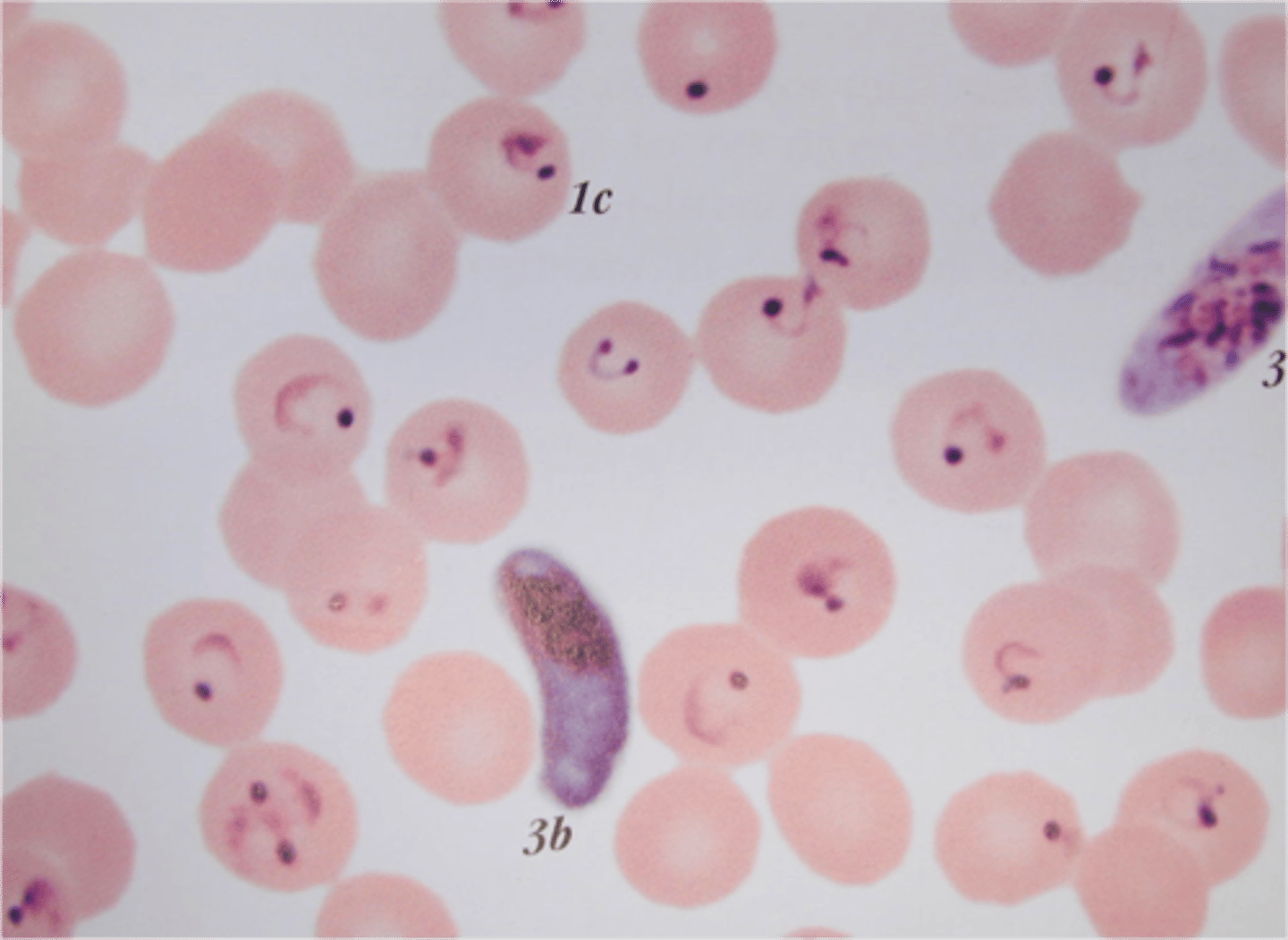
Plasmodium falciparum
HbS cells with P. falciparum sickle more quickly since the parasite uses the oxygen
- asplenic= fatal
Sickle cell treatment
- stem cell transplant
- Hydroxyurea or butyrate= increases HbF
- supportive care
Sickle Cell Trait
- Heterozygous Hb AS
- Benign and asymptomatic
SCT complication
with hypoxia
- Severe respiratory infections
- un-pressurized aircraft
- Anesthesia
- CHF
SCT test results
- few target cells
- positive Hgb solubility test
Hemoglobin C
- black population
- homozygous CC
- a2b26GluLys
- "bars of gold"
- no vaso-occlusive crisis
Hgb C Lab
- target cells
- slight reticulocytes
- Hgb C cystals
- negative Hgb solubility
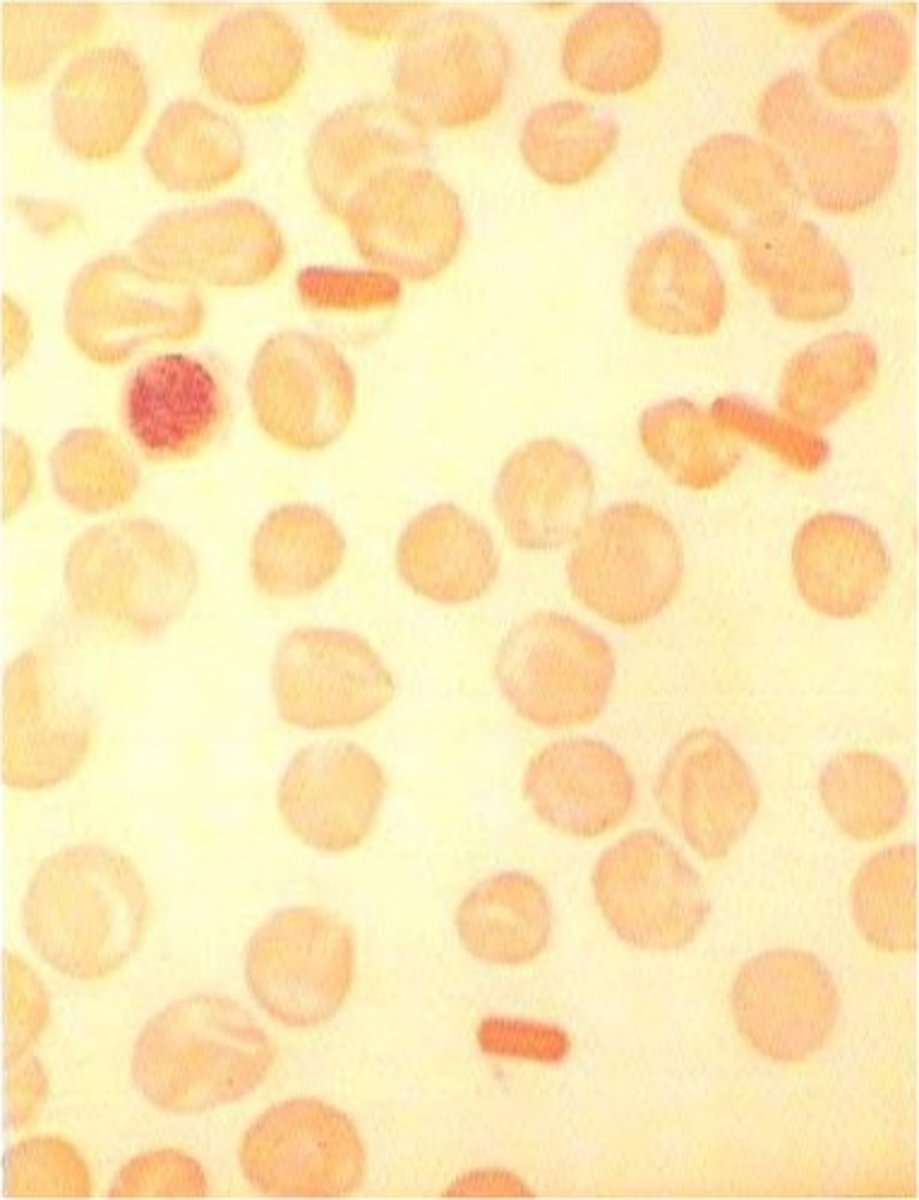
Hemoglobin E
- lowd MCV
- Microcytes and target cells
- Differentiate from IDA*
- negative Hgb solubility test
Hemoglobin D
- mild hemolytic anemia*
- splenomegaly
- No treatment is required
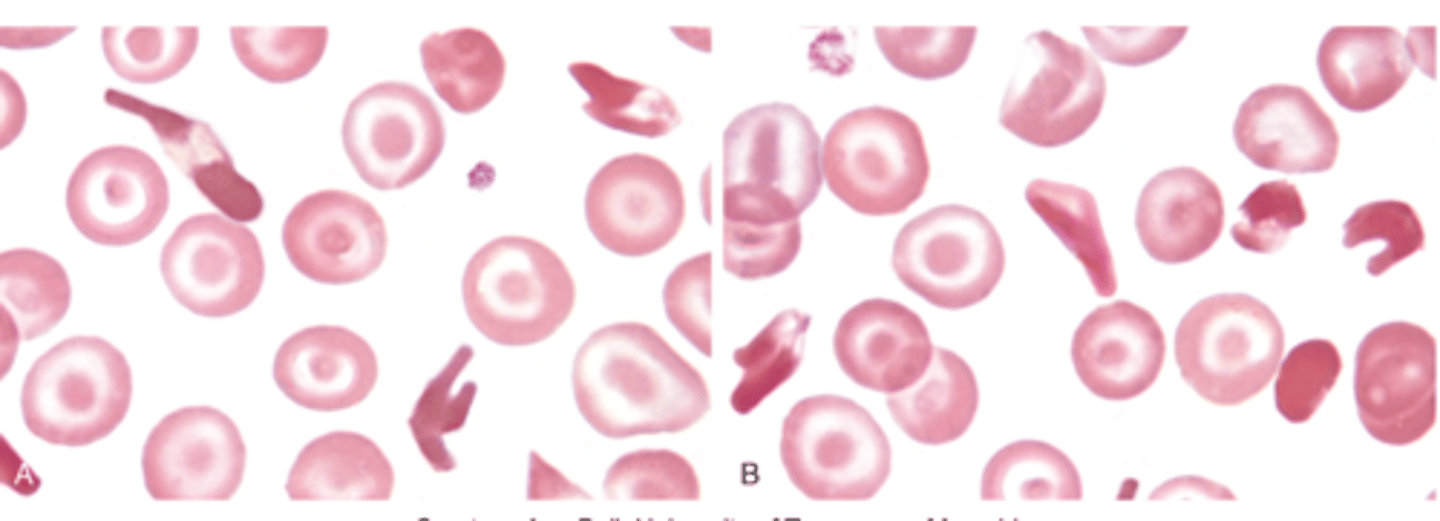
Hemoglobin SC
structural defect
- sickle and bar of gold
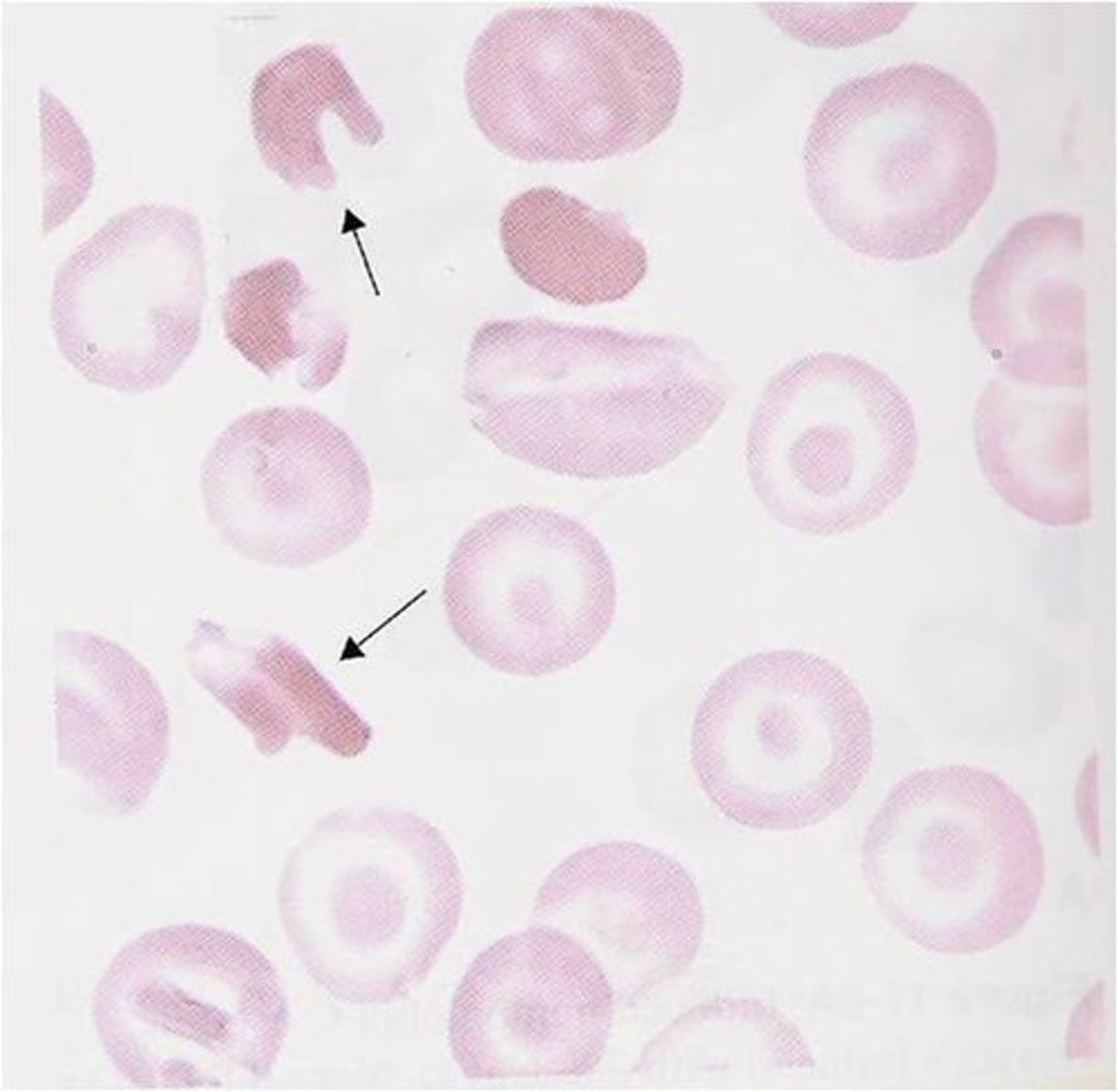
Hgb SC Lab
- normochrom/normocyt anemia
- hgb 11-13 mg/dL
- retics
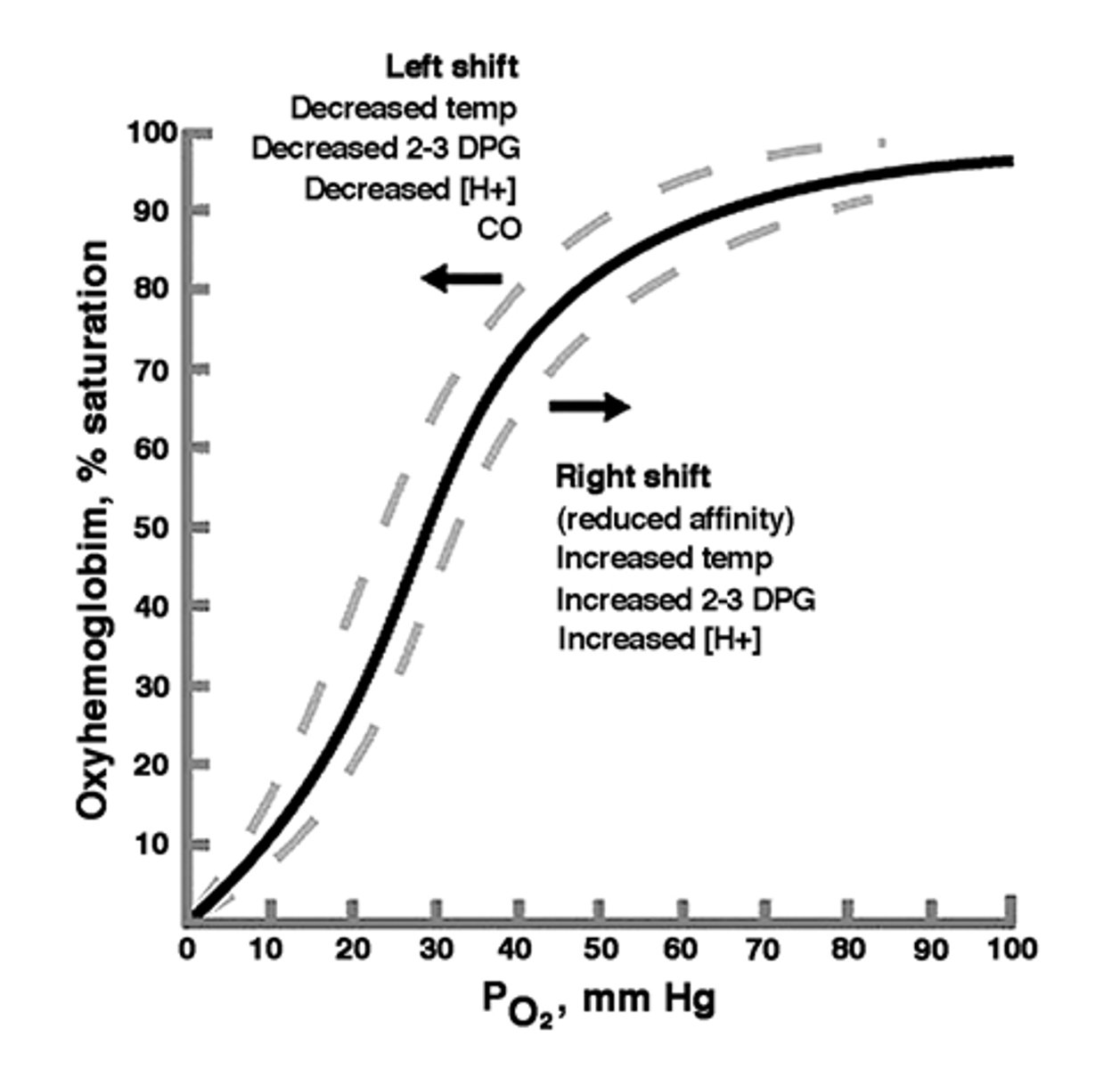
Decreased O2 affinity
Shift to right of O2 dissociation curve= quickly release O2 in tissues
- cyanosis, HbKansas
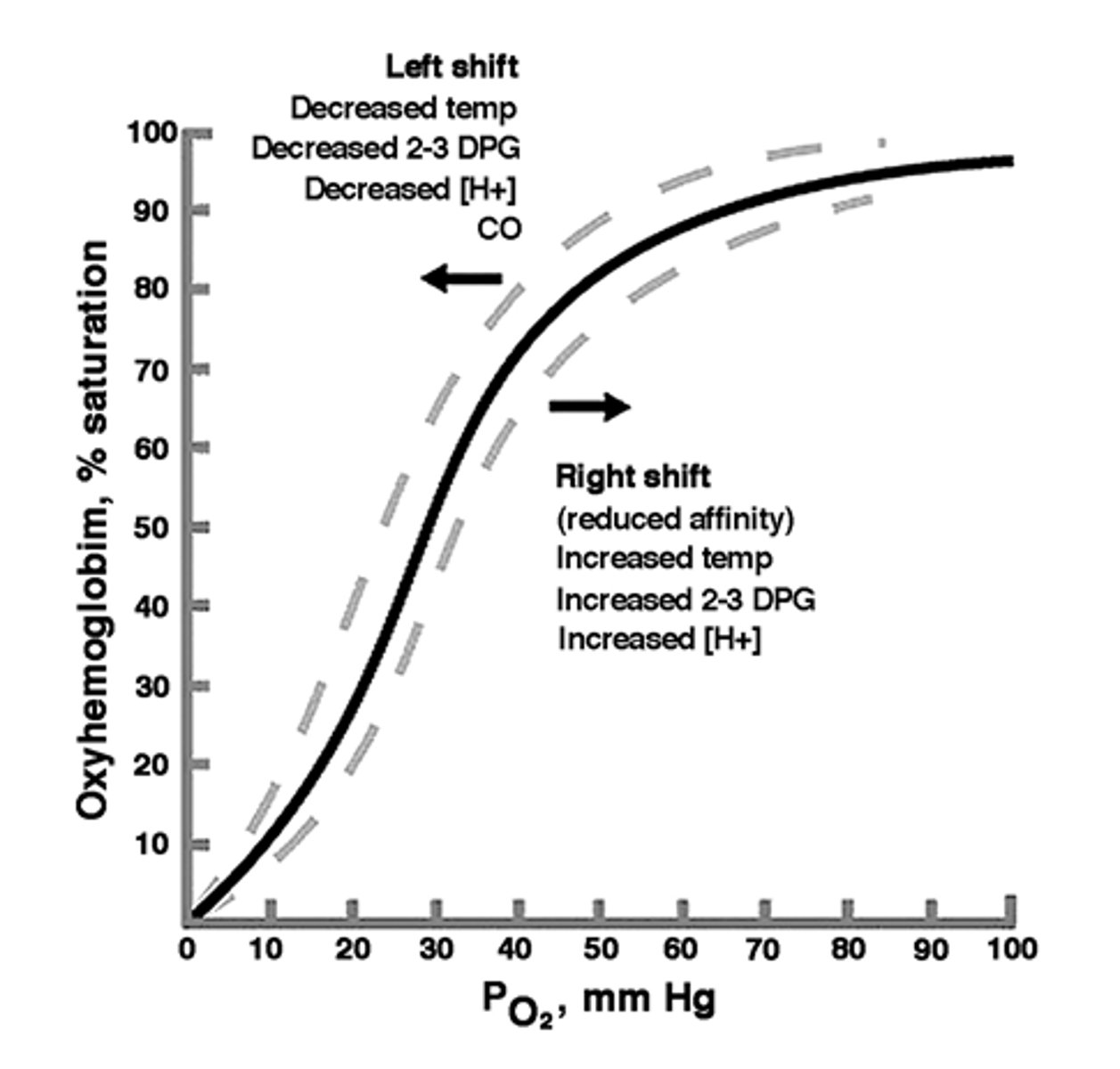
Increased O2 affinity
Shift to left of O2 dissociation curve= Fail to release oxygen on demand
- compensatory erythrocytosis
- Hgb Chesapeake
Hb M variants
AA substitution makes heme iron in ferric form= methemoglobin
- unable to bind oxygen
Unstable hemoglobin disease
Amino acid substitution or deletion have weakened the binding forces that maintain the structure of the molecule
- heinz bodies from denatured hgb