FPQC: SEMI-SOLID DOSAGE FORMS, LIQUID DOSAGE FORMS (Solutions, Emulsions, Suspensions)
1/76
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
77 Terms
Minimum Fill
SEMI-SOLID DOSAGE FORM
-Determination of the weight or volume of filled container.
-For preparations with labelled amount of not more than 150 g or 150 mL.
ACCEPTANCE CRITERIA OF MINIMUM FILL
SEMI-SOLID DOSAGE FORM
-Average of 10 containers is not less than the labelled amount.
-Individual content not less than 90% ( if label <60mL or < 60 g) or not less than 95% (if label = 60-150g or 60-150mL) of the labelled amount.
-If criteria is not met, test additional 20 containers.
Appearance
SOLUTIONS
Visual inspection to check for the presence impurities of and floating matter.
Physical Attributes
Viscosity, Clarity, Color, Odor, Taste
Emulsions
It is a two-phase liquid system combining 2 immiscible liquids.
-Dispersion Medium/External/Continuous Phase
-Dispersed/Internal/Discontinuous Phase
-Emulsifying Agents
Enumerate the general components of emulsions
Dispersion Medium/External/Continuous Phase
GENERAL COMPONENTS OF EMULSIONS
A solvent on which the dispersed phase is distributed; can be a liquid or semisolid (e.g., creams, lotions)
Dispersed/Internal/Discontinuous Phase
GENERAL COMPONENTS OF EMULSIONS
The substance distributed in the dispersion medium (API)
Emulsifying Agents
GENERAL COMPONENTS OF EMULSIONS
-Stabilizer of the droplet forms (globules) of the internal phase.
-Acts as a bridge between the 2 phases while at the same time providing a protective film around the globules and retards coalescence.
-Dye Solubility Test
-Dilution Test
-Conductivity Test
-Cobaltous Chloride in Filter Paper Test
-Fluorescence Test
Enumerate the types of emulsions
Dye Solubility Test
TYPE OF EMULSIONS
-Water soluble dye will dissolve in the aqueous phase
Methyl red
Methylene blue
Methyl orange
Malachite green
Crystal violet
Examples of water soluble dye in dye solubility test
Sudan red
Examples of oil soluble dye in dye solubility test
Water
DILUTION TEST
-o/w emulsion can be diluted with?
Oil
DILUTION TEST
-w/o emulsion can be diluted with
O/W: +
W/O: -
TESTS FOR EMULSIONS
Conductivity Test
O/W: Spotty Fluorescence
W/O: Continuous Fluorescence
TESTS FOR EMULSIONS
Fluorescence Test
O/W: Pink
W/O: Pink Spots
TESTS FOR EMULSIONS
Cobaltous Chloride in Filter Paper
Breaking
Coalescence
Sedimentation
Flocculation
Creaming
Phase Inversion
What are the common problems that always encountered in emulsions?
Breaking (completely irreversible)
Phase Inversion (partially irreversible)
What are the problems of emulsion that is irreversible?
Coalescence
Creaming
Flocculation
Sedimentation
What are the problems of emulsion that is reversible?
Ideal Characteristics of Suspensions
-Should not settle rapidly & should be readily redispersed upon gentle shaking of the container.
-Particle size of suspensoid should remain fairly constant throughout long periods of undisturbed standing.
-Should pour readily and evenly from its container.
Flocculated Suspension
Deflocculated Suspension
What are the two types of suspensions?
Flocculated Suspension
-A flocculated suspension is a suspension in which particles have undergone flocculation
-Has floccules
-The rate of sedimentation is high
-The volume of sediment is high
-Form porous sediments
-The re-dispersion of a sediment can easily be done by agitation
Deflocculated Suspension
-A deflocculated suspension is a suspension where no flocculation has taken place
-Has no floccules
-The rate of sedimentation is low
-The volume of sediment is low
-Form non-porous sediments
-The re-dispersion of a sediment is difficult by agitation
Sedimentation Volume (VS)
SUSPENSIONS
-Checking if the suspension settles rapidly
-Ratio of height of sediment settled after standard condition (Vf) and the initial height/volume of the suspension (Vi).
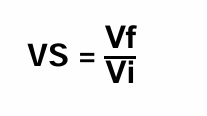
Ideal
SUSPENSIONS
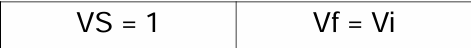
Always
SUSPENSIONS
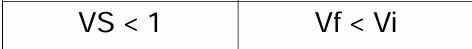
Not Possible
SUSPENSIONS
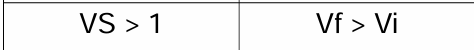
Deliverable Volume
FOR ALL LIQUID DOSAGE FORMS
-Provides assurance that liquids will, when transferred from the original container, deliver the volume of dosage form that is declared on the label of the article.
-For products with labelled amount not exceeding 250mL.
-Gently drain liquid contents from bottle for a period not to exceed 30 minutes for Multiple Unit Containers and 5 seconds for Single-unit containers.
ACCEPTANCE CRITERIA (Multiple Unit Containers)
-Average volume obtained from 10 containers is NLT 100%.
-No individual container is less than 95% of labelled amount.
-If criteria is not met, test to another 20 containers.
ACCEPTANCE CRITERIA (Single Unit Containers)
-Average volume obtained from 10 containers is NLT 100%.
-Each individual container is within the range of 95-110% of the volume declared in the label.
-If criteria is not met, test to another 20 containers.
Sterility Test
STERILE PRODUCTS
Test which confirms that the products are free from the presence of microorganisms.
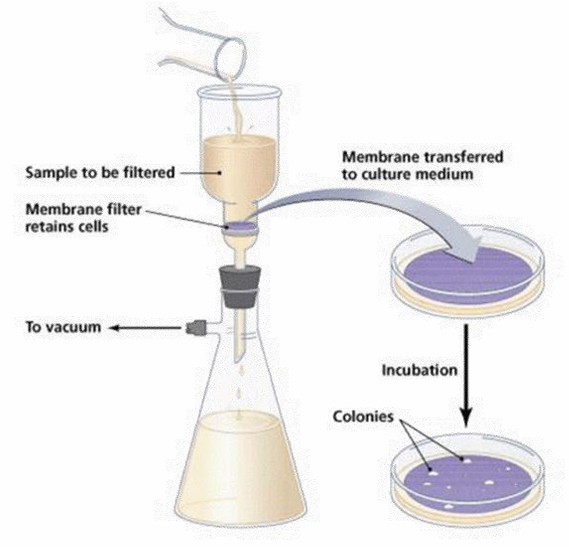
-Membrane Filtration
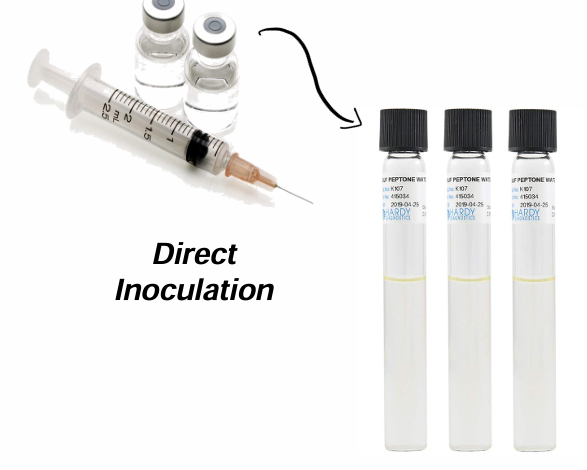
-Direct Inoculation
Enumerate the test performed in the sterility test:
Membrane Filtration
Direct Inoculation
ANAEROBIC BACTERIA
-Clostridium sporogenes
-Pseudomonas aeruginosa
-Staphylococcus aureus
STERILE PRODUCTS
Use of Fluid Thioglycolate Medium
14 days
STERILE PRODUCTS
Incubation period of Fluid Thioglycolate Medium and Soybean-Casein Digest Medium
30-35 degree Celsius
STERILE PRODUCTS
Temperature of Fluid Thioglycolate Medium
Fungi and Aerobic Bacteria
-Aspergillus brasiliensis
-Bacillus subtilis
-Candida albicans
STERILE PRODUCTS
Use of soybean-casein digest
20-25 degree Celsius
STERILE PRODUCTS
Temperature of Soybean-Casein Medium
Pyrogen Test
STERILE PRODUCTS
-Pyrogen- fever producing substances.
-Based on the response of human leukocytes which release inflammatory mediators in response to pyrogen contamination.
-Endotoxins = lipopolysaccharides found in the cell membrane of Gram-negative bacteria.
-In not more than 30 minutes before the injection of the test dose, determine the “control temperature” of each rabbit.
-The test solution is warmed to 37± 0.2°C prior to injection.
-Inject to the vein of the ear of each of 3 rabbits 10 ml of the test solution per kg body weight. Record the temperature at 30 minute intervals between 1 and 3 hours after the injection.

Pyrogen
Fever producing substances.
Endotoxins
Lipopolysaccharides found in the cell membrane of Gram-negative bacteria.
Rabbit Pyrogen Test
Test Animals: Healthy, Mature Rabbits
-Use only those rabbits whose control temperatures between them is ≤ 1°C
-Do not also use any rabbit having a temperature exceeding 39.8 ⁰C.
-Stage 1: 3 rabbits
-Stage 2: Additional 5 rabbits
Sample Size of Rabbit Pyrogen Test
Apparatus and Diluents
PYROGEN TEST
Depyrogenated at 250°C for NLT 30 minutes; treatment of diluents and solutions used for washing and rinsing
Temperature Recording
PYROGEN TEST
Use an accurate temperature-sensing device such as clinical thermometer or thermistor probes.
Stage 1
PYROGEN TEST
-Rise in temperature ≥ 0.5 degree Celsius any of the rabbits
If YES: Continue test using additional 5 rabbits
If NO: Passed the Pyrogen test
Stage 2
PYROGEN TEST
-The rise in temperature ≥ 0.5 degree Celsius in not more than 3 of the rabbits
-Sum of individual rise in temperature not exceed 3.3 degree Celsius
If YES: Passed
If NO: Failed
Limulus Amoebocyte Lysate (LAL) Test
Bacterial Endotoxin Test is also known as?
Bacterial Endotoxin Test
This test depends on the gelling property of the limulus amoebocyte lysate (LAL) obtained from the aqueous extract of circulating amoebocytes of Limulus polyphemus or Limulus Tachypleus tridentatus (horseshoe crab).
Advantages over Rabbit Pyrogen
BACTERIAL ENDOTOXIN TEST
-Greater sensitivity and simplicity
-Can quantify the amount of endotoxin in the sample
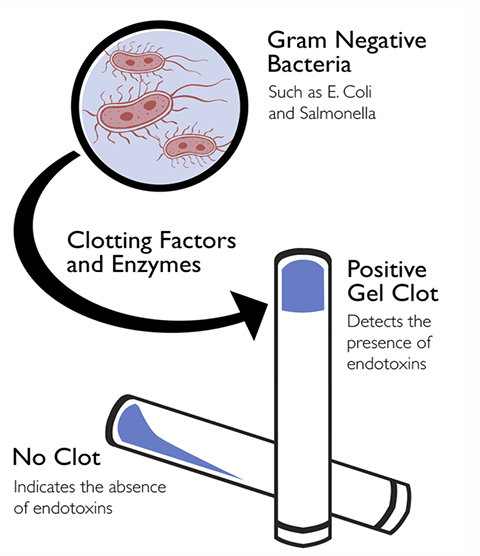
Gel Clot Technique
BACTERIAL ENDOTOXIN TEST
-This is to detect based on clotting of the LAL reagent in the presence of endotoxin
-To test the integrity of the gel, take each tube in turn directly from the incubator and invert it through about 180° in one smooth motion.
Positive: a firm gel forms upon inversion
Negative: no gel is formed
Turbidimetric Method
Chromogenic Method
Enumerate the methods of bacterial endotoxin test
Turbidimetric Method
BACTERIAL ENDOTOXIN TEST
It is based on the development of turbidity after cleavage of an endogenous substrate.
Chromogenic Method
BACTERIAL ENDOTOXIN TEST
It is based on the development of color after cleavage of a synthetic peptide-chromogen complex.
Leaker Test
This test usually is performed by producing a negative pressure within an incompletely sealed ampoule while the ampoule is submerged entirely in a deeply colored dye solution (0.5-1% Methylene Blue)
Blister Packs
The leaker test is also used in leak test for?
Test for particulate matter
Limits the presence of particulate matter
Mobile
Randomly-sourced
Extraneous substances
Other than gas bubbles.
The particulate matter is consists of?
Electronic Particle Counters/ Light Obscuration Test
Microscopic Particle Count Test
Enumerate the two methods that are used in the test for particulate matter:
-Extrinsic
-Intrinsic
-Inherent
Enumerate the types of particulate matter
External to the process
TYPES OF PARTICULATE MATTER
Origin of Extrinsic
Extrinsic
TYPES OF PARTICULATE MATTER
Material that is not part of the formulation, package or assembly process
-Glass and Stopper fragments
-Metals
-Silicone Oil
-Filter and Process particles
-Fibers form clothing and hair
-Skin Flakes and Dirt particles
TYPES OF PARTICULATE MATTER
Examples of Extrinsic
Part of the process or products
TYPES OF PARTICULATE MATTER
Origin of Intrinsic
Intrinsic
TYPES OF PARTICULATE MATTER
Material from sources related to the formulation, package or assembly process
-Active ingredients
-Ingredient degradation
-Protein aggregation
-Ingredient anomalies
-Immiscible droplets
-Any other process related to particle
TYPES OF PARTICULATE MATTER
Examples for Intrinsic
Part of the formulation
TYPES OF PARTICULATE MATTER
Origin of Inherent
Inherent
TYPES OF PARTICULATE MATTER
-Material expected from drug substance and formulation components
-Adjuvant material in suspension products
-Certain excipients
-Mannitol crystallization
-Proteinaceous aggregates
TYPES OF PARTICULATE MATTER
-Examples for Inherent
Electronic Particle Counters/Light Obscuration Test
TEST FOR PARTICULATE MATTER
It uses an electronic instrument designed to count and measure the size of particles by means of a shadow cast by the particle as it passes through a high intensity light beam.

Advantages and Disadvantages for Electronic Particle Counters/Light Obscuration Test
• Constant in process measurement
• Quickly identify size and number of particles
• Cannot identify source of particle
• Requires routine preventive maintenance and calibration
• Air bubbles cannot be differentiated
Microscopic Particle Count Test
TEST FOR PARTICULATE MATTER
-Enumerates subvisible, essentially solid particulate matter after collection on microporous membrane filter.
Stereomicroscope
TEST FOR PARTICULATE MATTER
-Apparatus that is used in the Microscopic Particle Count Test
-Composed of filter assembly for retaining particulate matter
Advantages and Disadvantages for Microscopic Particle Count Test
• Allows collection of particles larger than rated pore size.
• Microscope identification of particle types and materials.
• Slow counting and sizing on the membrane surface.
• Requires top and bottom lighting to distinguish particles.