OPT 116 Energy Production of Fatty acids and amino acids
1/39
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
40 Terms
beta oxidation of fatty acids
beta carbon is oxidized to a carbonyl group (carbon atom removed from the first carbon that attaches to a functional group)
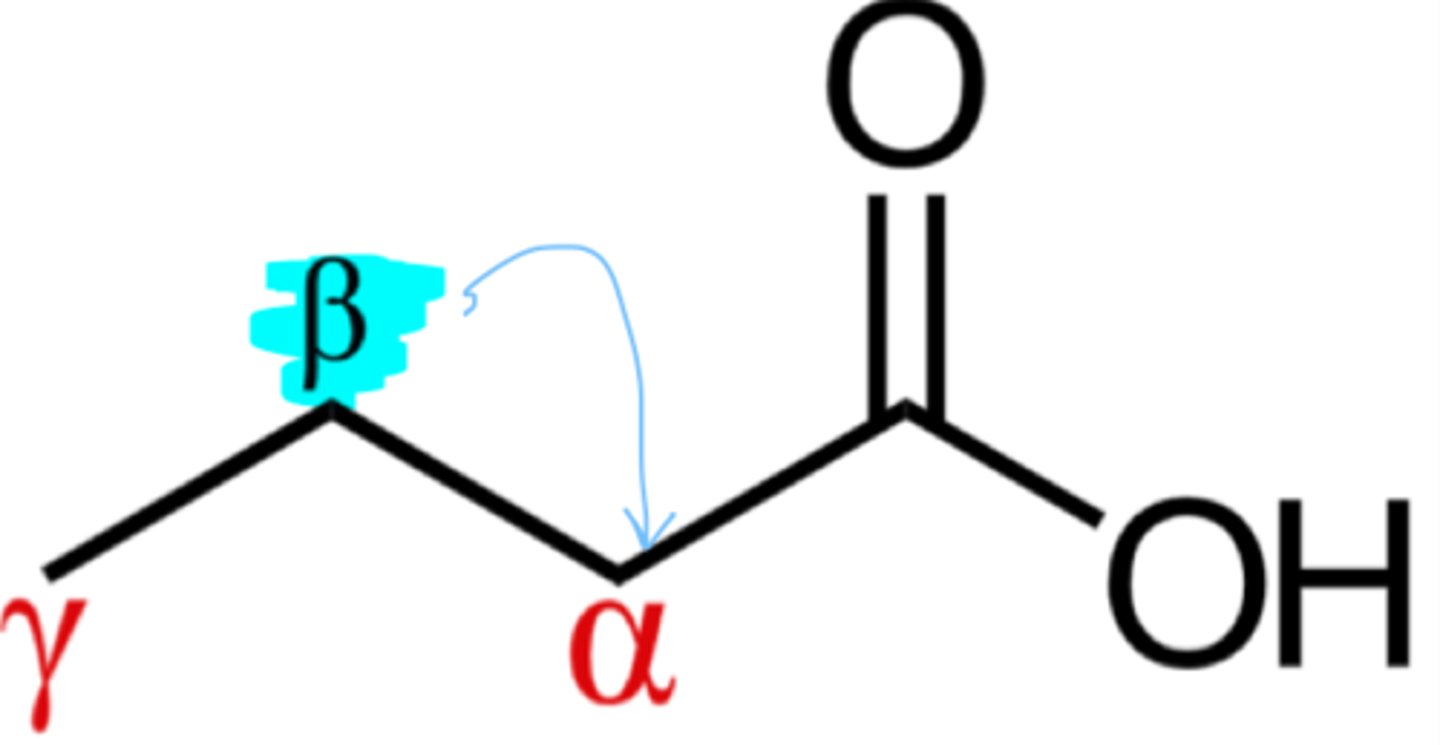
How does beta oxidation generate ATP?
based on the number of carbon atoms
What are the three stages of fatty acid oxidation
1. b oxidation
2. citric acid cycle
3. electron transport chain

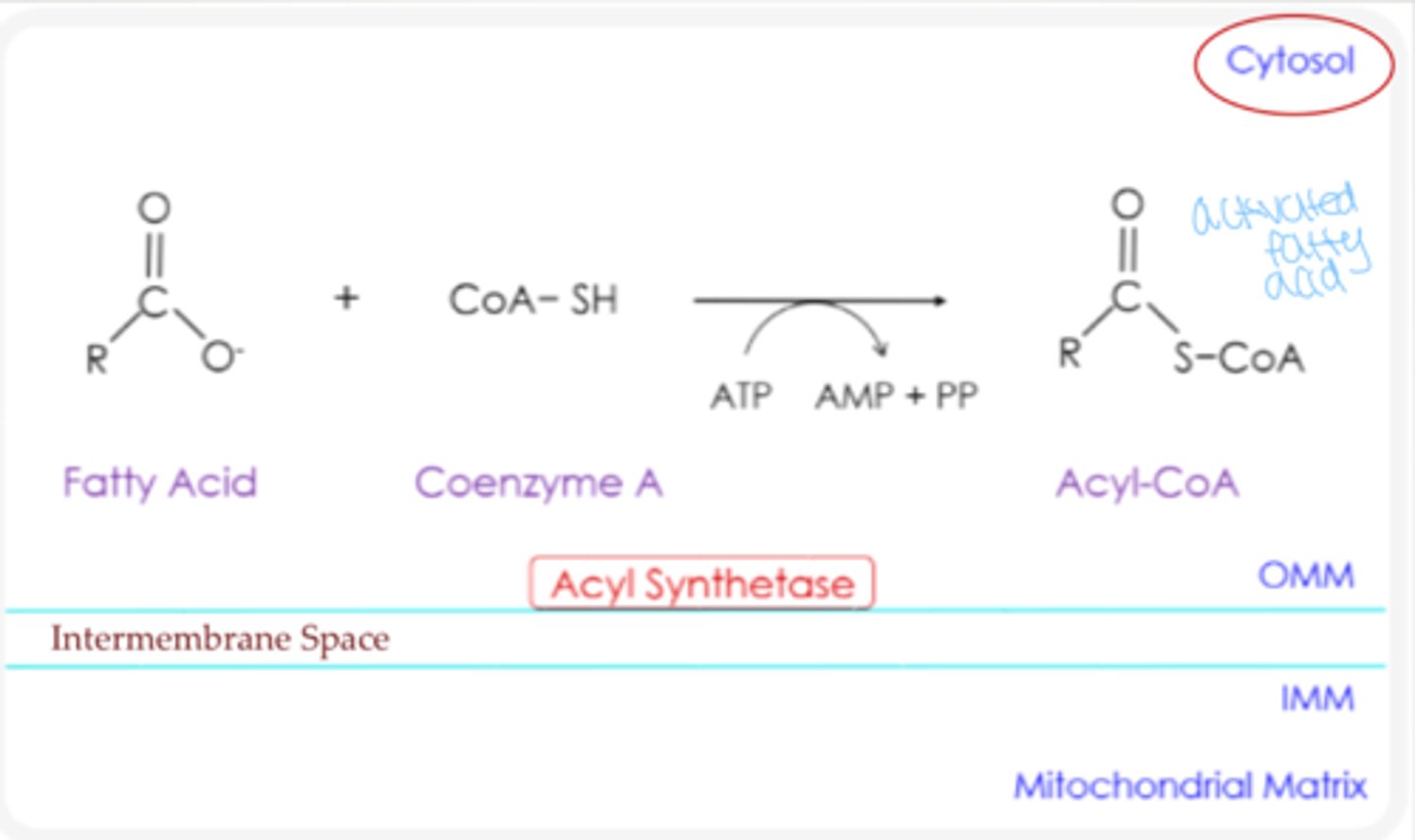
Fatty acid activation
Coenzyme A (CoA) is added to the fatty acid to form Acyl CoA... requires ATP
What is the activated form of a fatty acid?
acyl-CoA
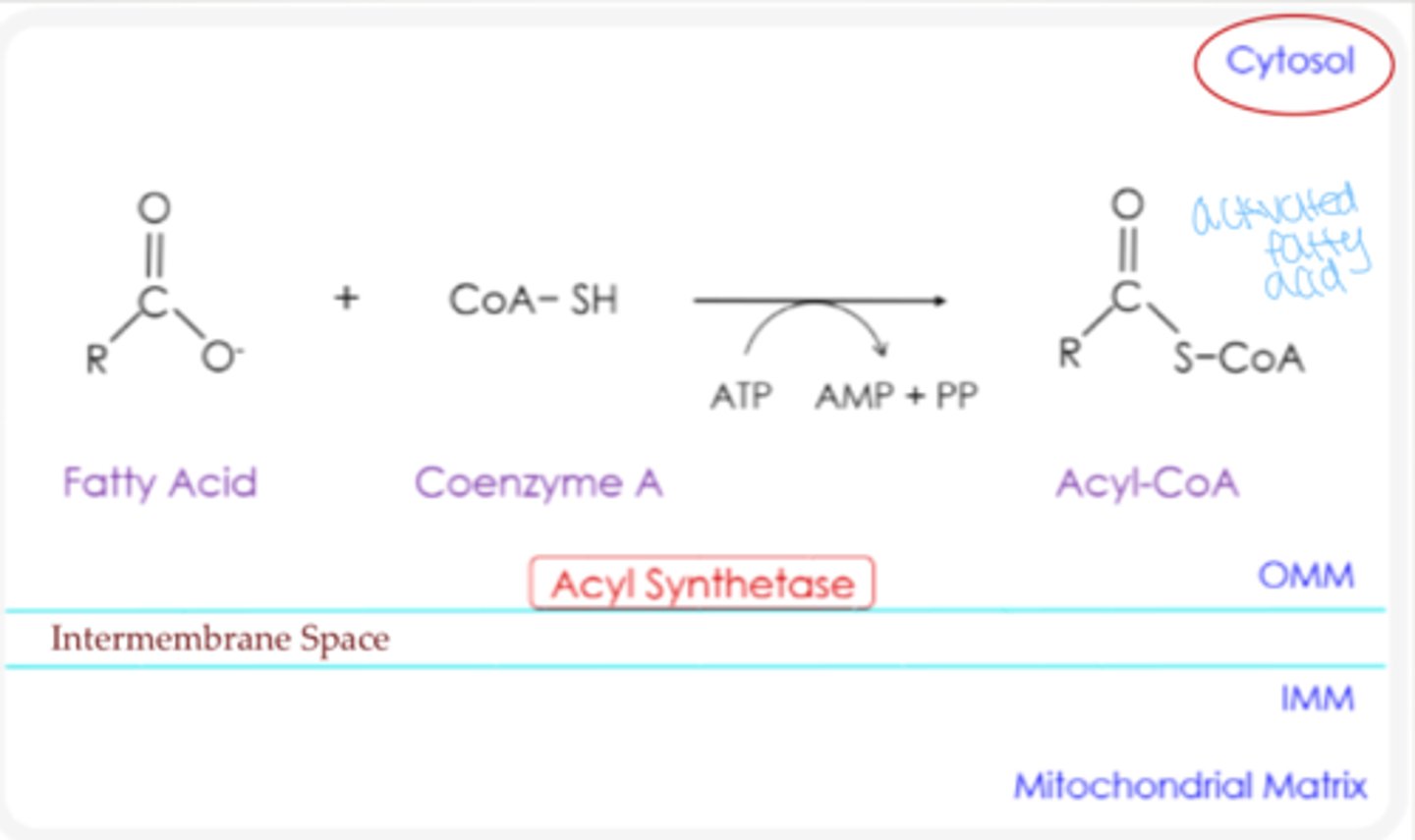
Where does fatty acid activation occur?
cytosol
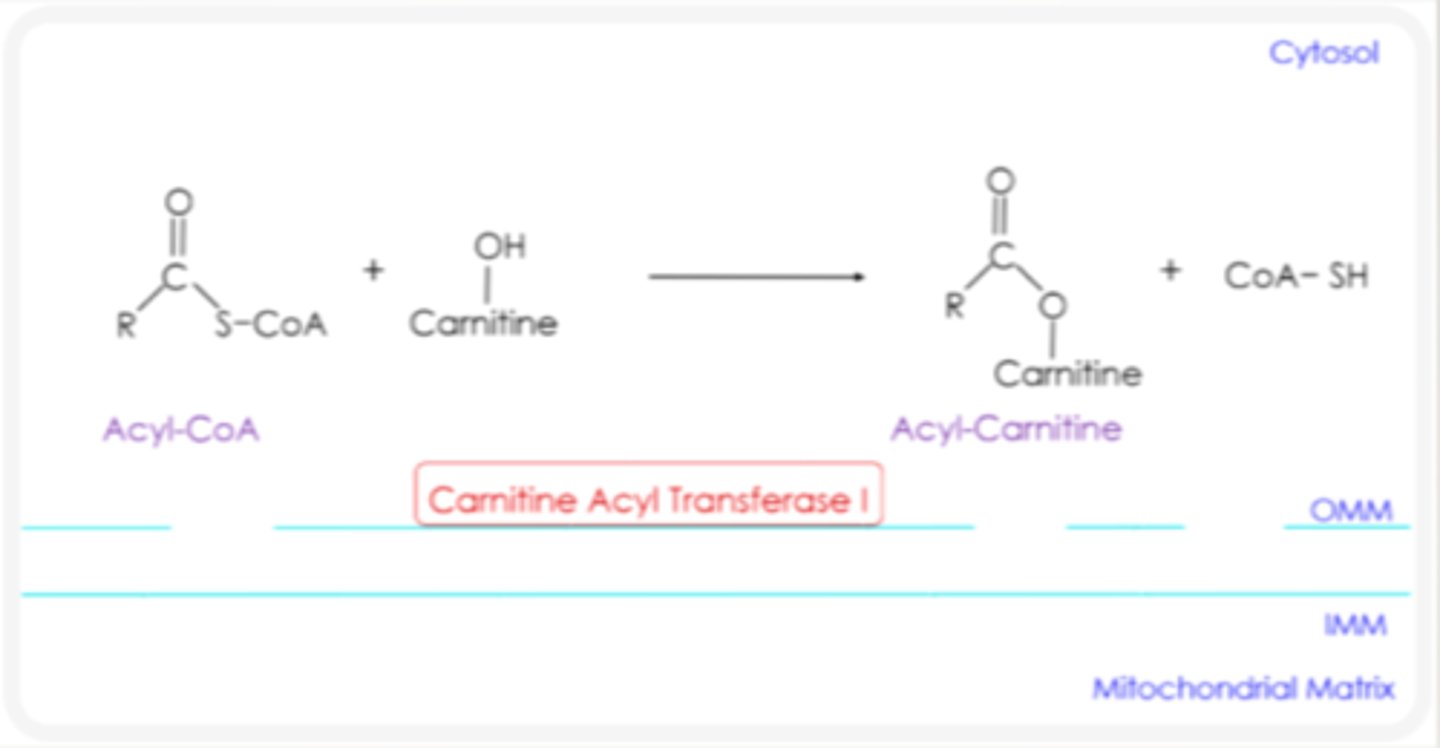
How is a fatty acid transported from the cytosol to mitochondrial matrix?
converted to Acyl Carnitine
How does Acyl Carnitine pass through the outer mitochondrial matrix?
through pores
What transports Acyl carnitine across the inner mitochondrial membrane ?
Acyl Carnitine Translocase
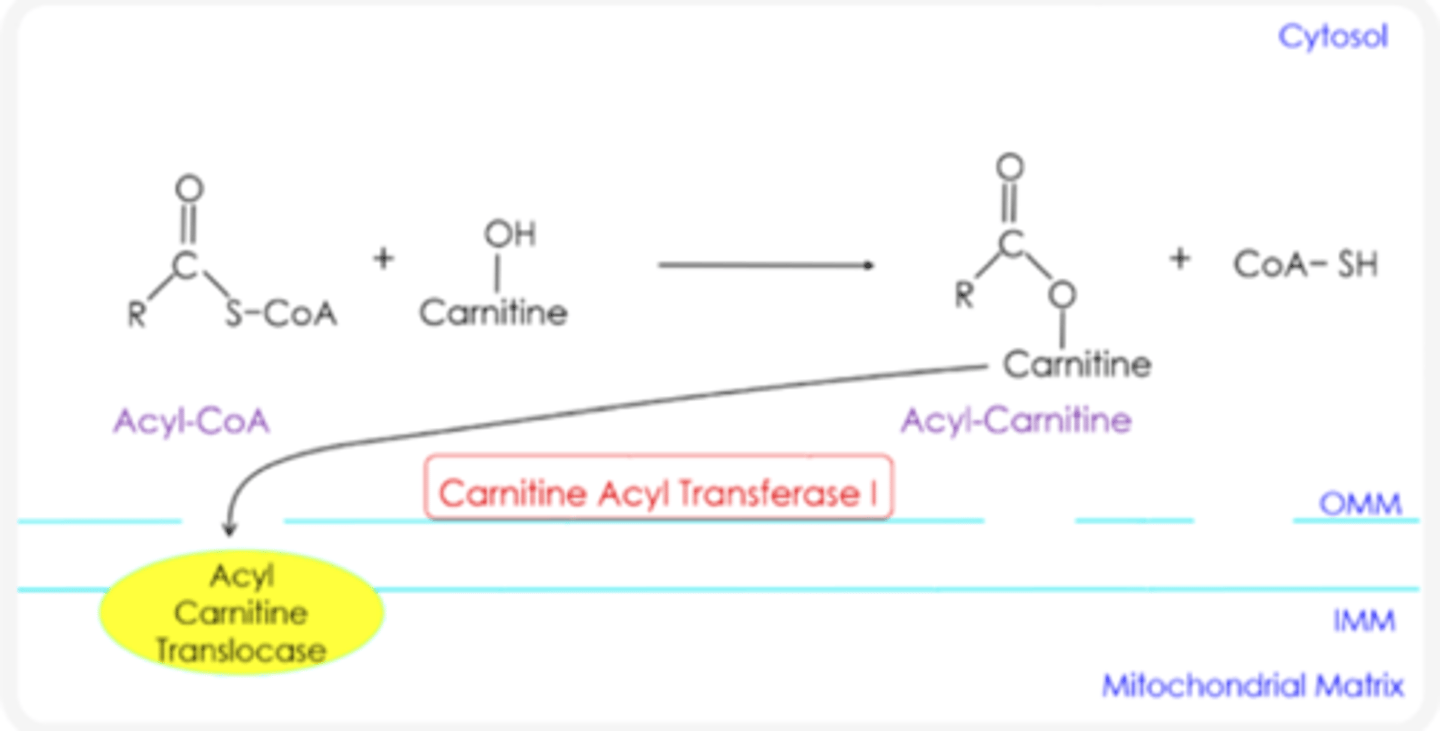
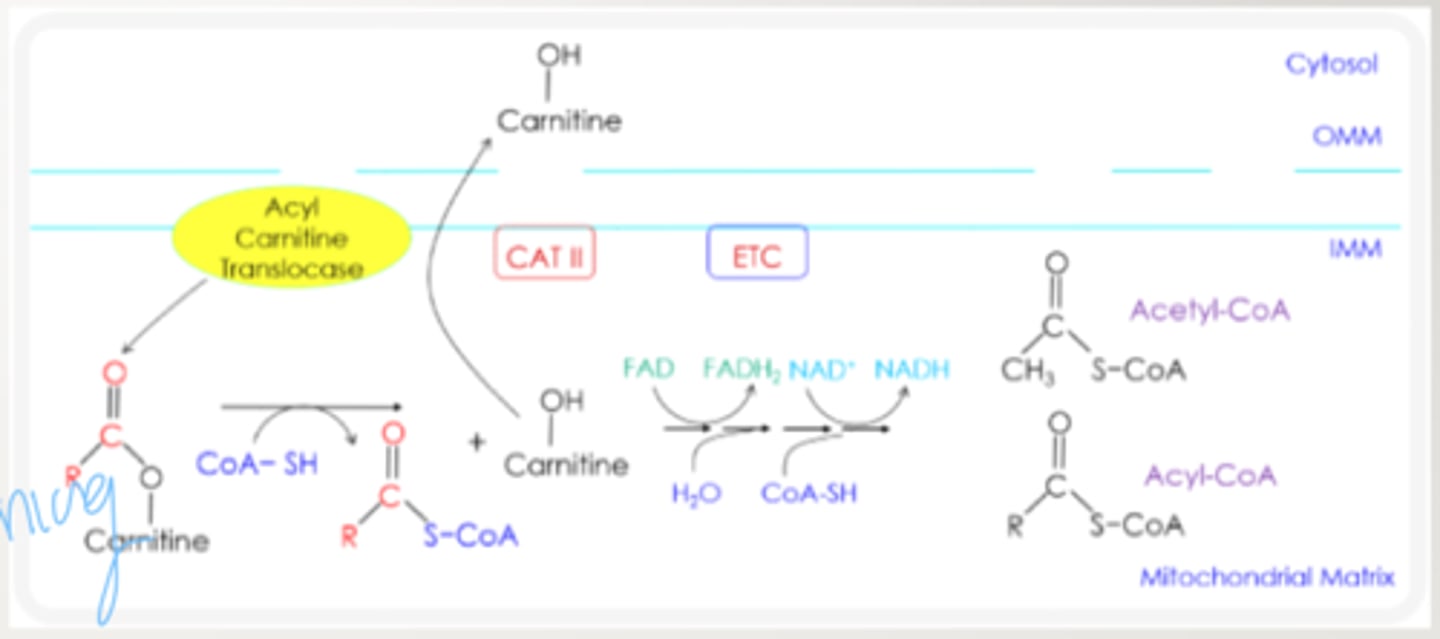
Acyl carnitine is converted back into ________ during the next step of fatty acid oxidation
Acyl CoA
What catalyzes the conversion of Acyl carnitine back to Acyl CoA?
Carnitine Acyl Transferase II
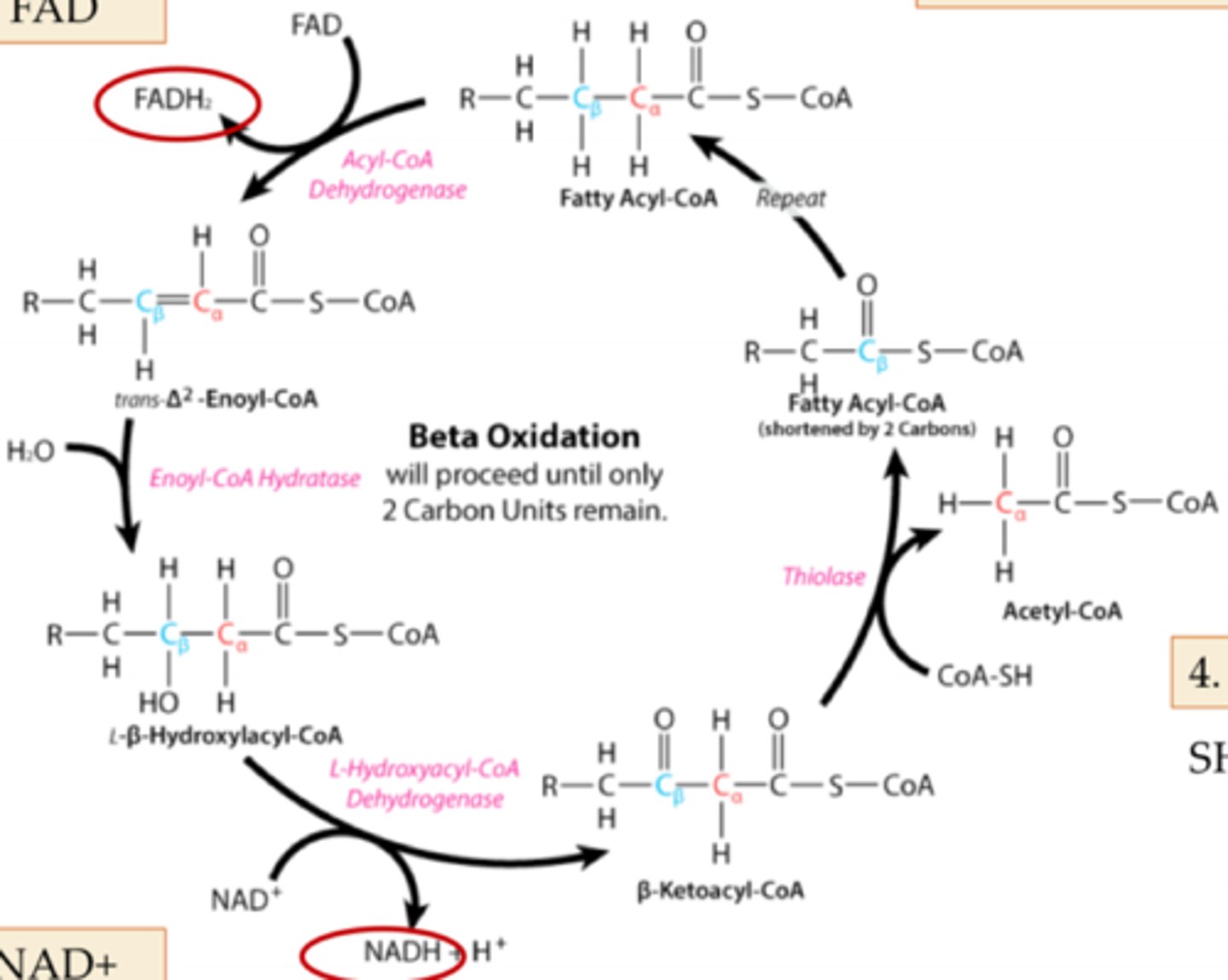
When Acyl CoA is oxidized, each cycle removes ______ from the fatty acid chain
2 carbons
The 2 carbons that are removed from fatty acid chain are converted to
Acyl CoA and Acetyl coA
Each cycle of oxidation transfers electrons to ______ and ______
1 NAD+ and 1 FAD
Which cells utilize fatty acids for energy even in the presence of glucose?
liver cells, heart, and resting skeletal muscle
Steps of beta oxidation
1. Dehydrogenation
2. Hydration
3. Oxidation of NAD+
4. Thiolytic Cleavage
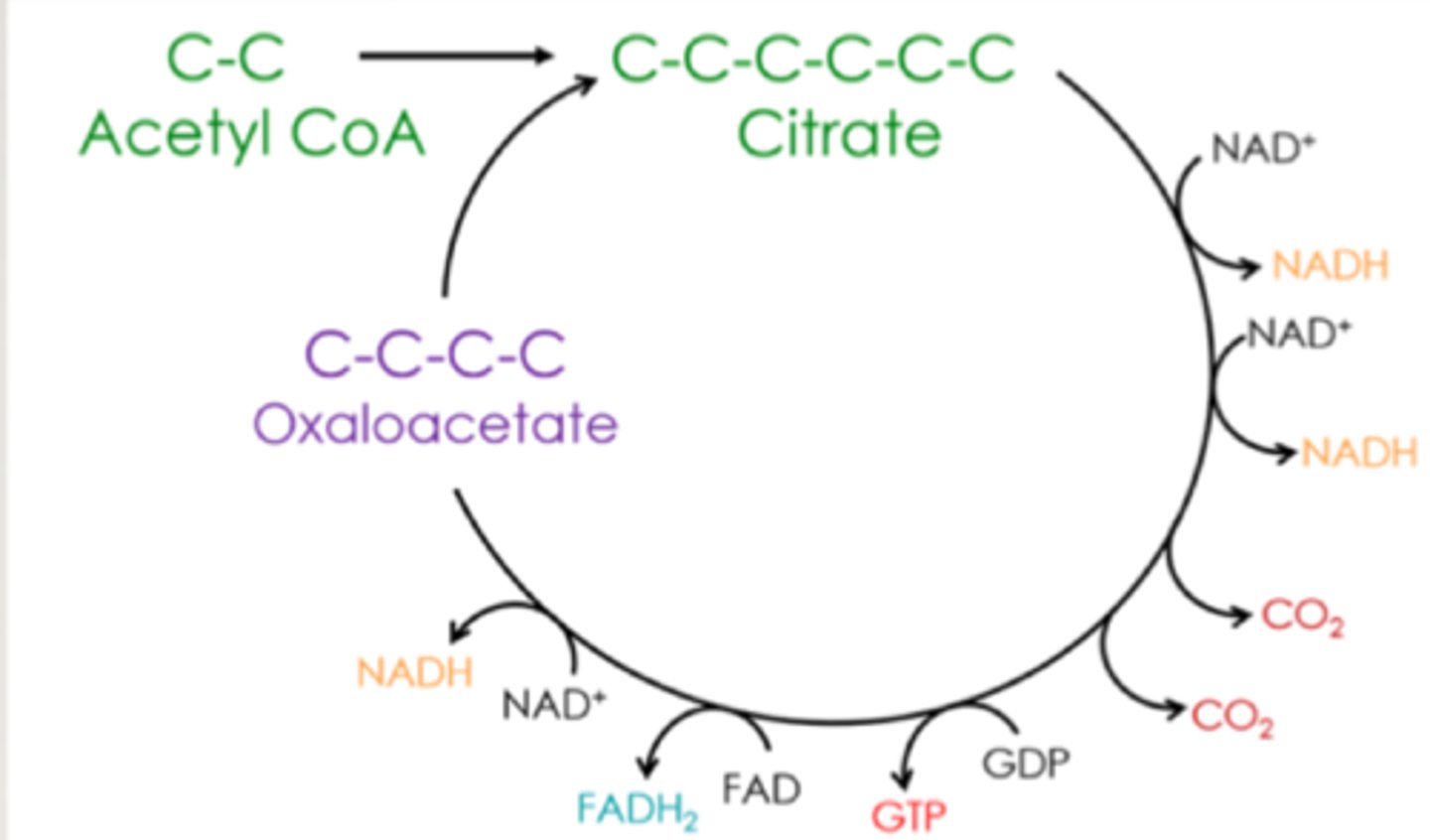
How many NADH, FADH2, and GTP are produced from acetyl CoA entering the citric acid cycle?
3 NADH, 1 FADH2, 1 GTP
How many oxidation cycles are required for even numbered fatty acid chains? (99% are even)
(n/2)-1

How much total ATP is produced during fatty acid oxidation cycle?
14 ATP (1.5 from FADH2, 2.5 from NADH, 10 from acetyl CoA)
How many NADH and FADH2 are produced through fatty acid beta oxidation of a 16 carbon fatty acid?
7 NADH, 7 FADH2
How many ATP are produced from NADH and FADH2 entering the electron transport chain?
7* 2.5= 17.5
7* 1.5= 10.5
28 ATP
If you have a 16 carbon fatty acid, how many acetyl CoA are produced through fatty acid beta oxidation?
8 acetyl CoA
How many acetyl CoA go through the citric acid cycle?
8--> 10 ATP each
(17.5 + 10.5 + 60 + 12 + 8)- 2= 106
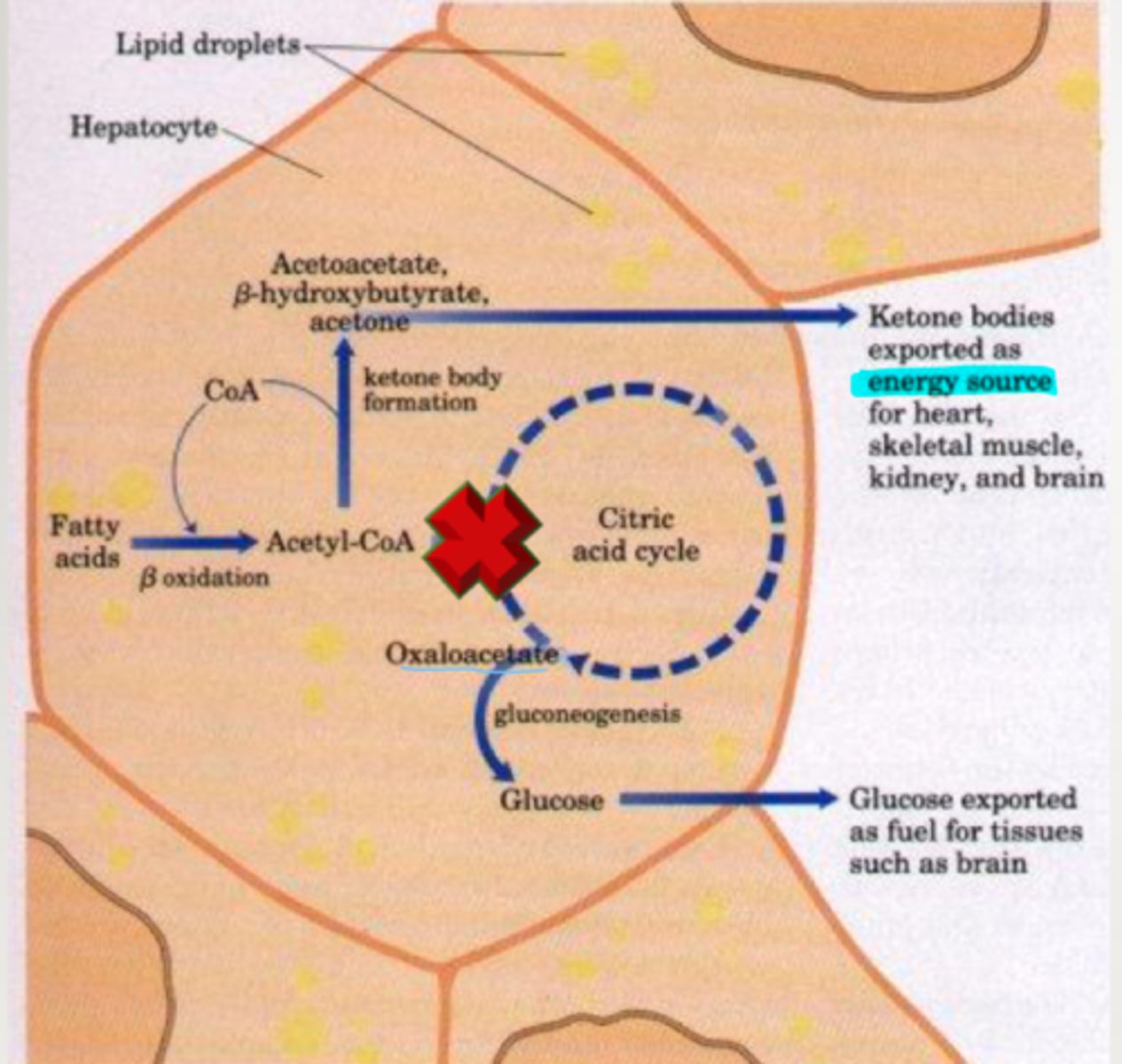
ketone bodies
the by-products of the incomplete breakdown of fat
If there is not a sufficient amount of oxaloacetate to bind with acetyl coA
acetyl coa will build up and excess is converted in the liver to ketone bodies which enter the blood stream

hyperglycemia
excessive sugar in the blood, leads to dehydration
hyperketonemia
excess circulating ketone bodies, decreased alkaline buffer leads to acidosis
What uses ketone bodies as fuel source?
brain, heart, kidneys, skeletal muscles
What is the normal ketone concentration in the blood?
<0.6 mmol/L
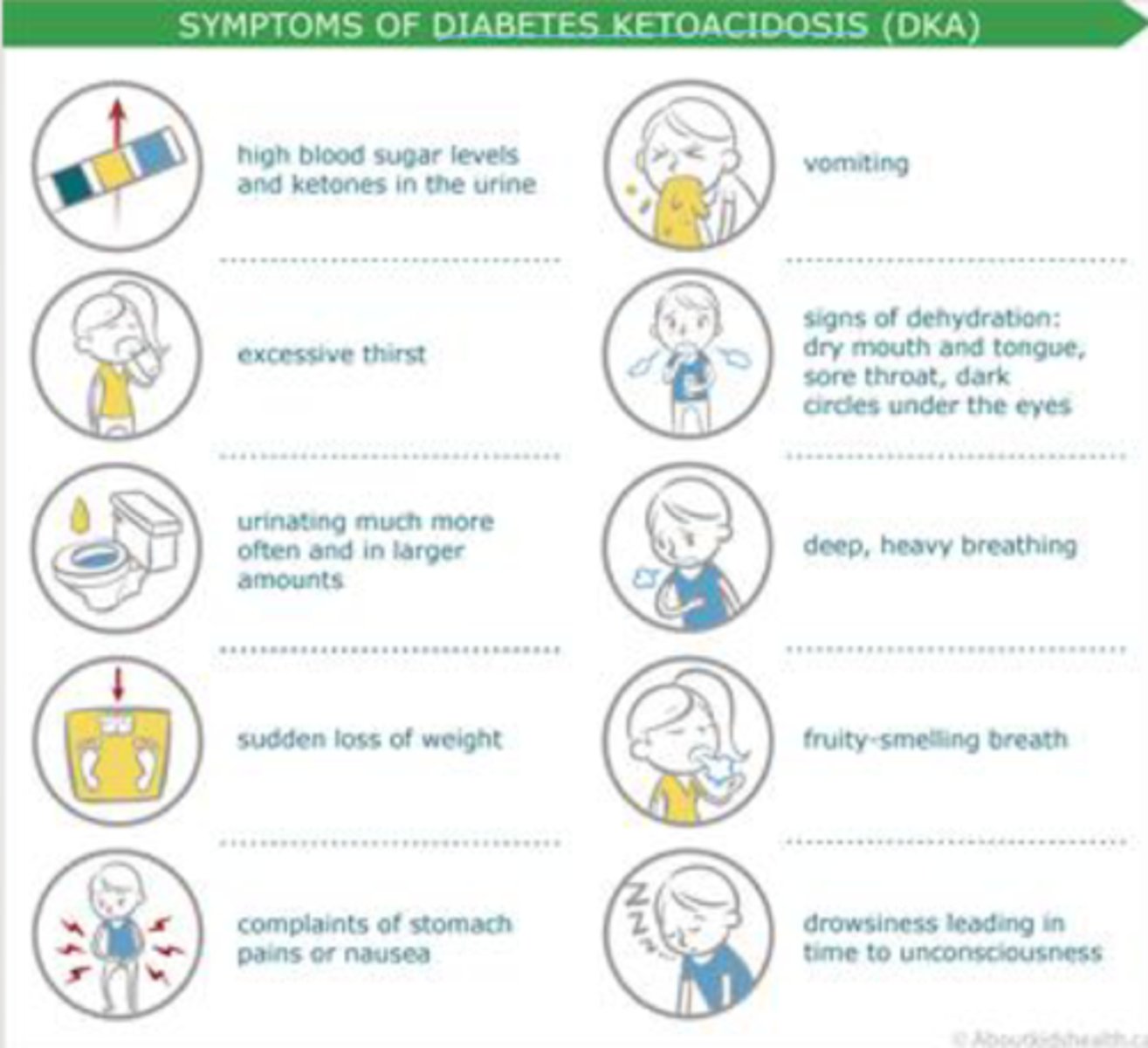
If ketone concentration in the blood exceeds 3 mmol/L the result is
ketoacidosis which can lead to dehydration, coma, or death
ketonemia
increased ketones in blood
ketonuria
presence of ketone bodies in the urine, acetone breath results
Ketogenic diets result in
excess ketone bodies which can be harmful
ketosis
low levels of ketones in blood but enough to support function

ketoacidosis
dangerously high levels of ketones in the blood which can be fatal

amino acids in excess of immediate body requirements
cannot be stored for later use and is therefore converted to other molecules to be used for energy production
During amino acid catabolism, the amino group is removed to release
nitrogen (ammonium)
Ammonium
- synthesizes amino acids, nucleotides, and biogenic amines
-converted to urea to be excreted in the urine
-carbon skeleton still remains
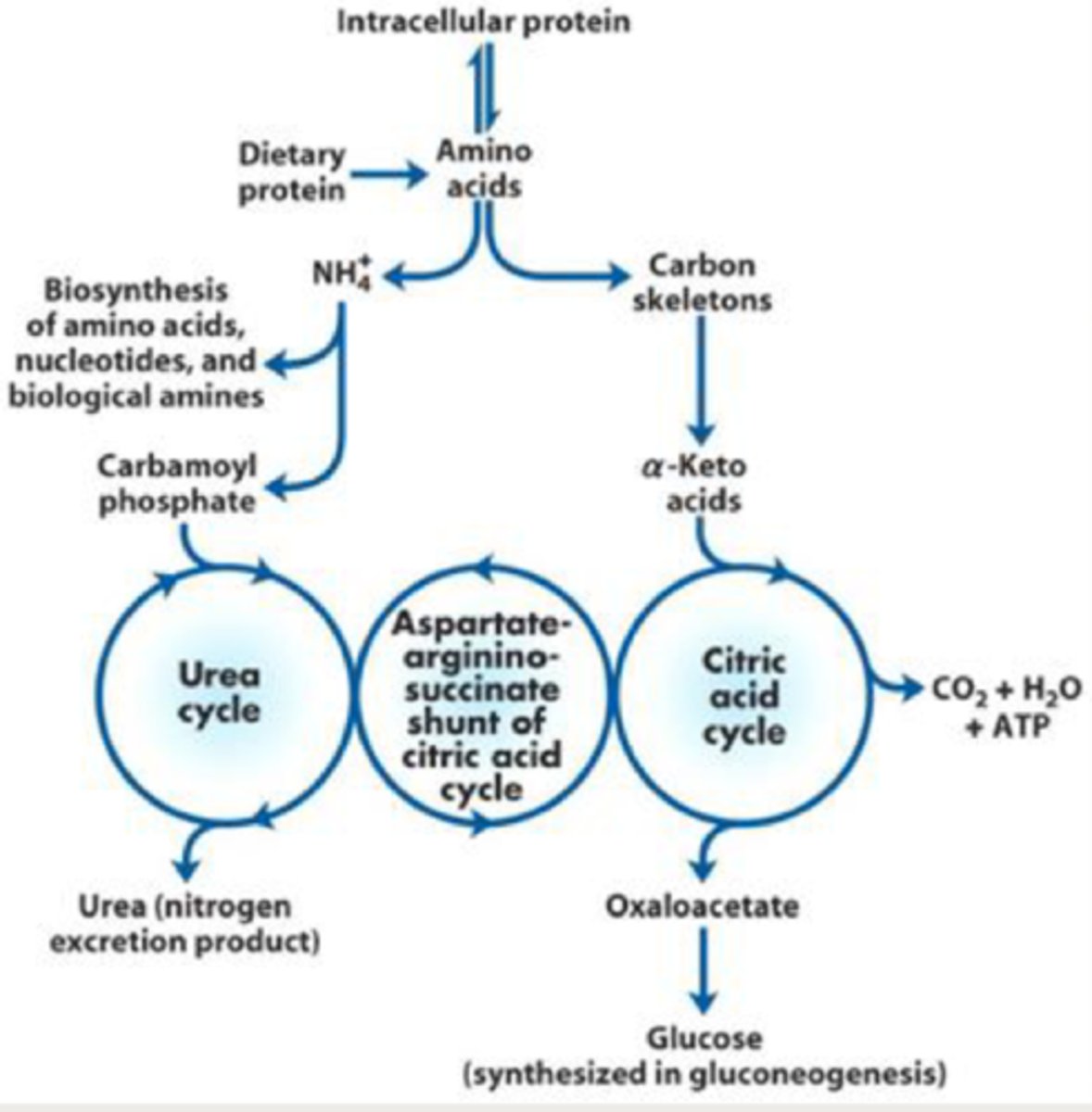
glucogenic
converted to pyruvate or an intermediary of krebs cycle which can then be used to produce glucose (glucose is used to produce energy)
ketogenic
converted to acetyl CoA which is used to produce ketone bodies that can be used for energy production