ALEVEL Biology AQA- "Cells"
5.0(1)
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/124
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
125 Terms
1
New cards
What type of cells are more complex organisms?
eukaryotic cells
2
New cards
Fill in the gap: "prokaryotic cells are often ____________ __________ ______________"
single celled organisms
3
New cards
Where is a cell membrane found?
found on the inside of cell walls
4
New cards
What is a cell membrane compromised of?
lipids and proteins
5
New cards
What does the cell membrane do?
regulates the movement of substances into and out of the cell
6
New cards
Why does the cell membrane have a receptor?
to respond to chemicals
7
New cards
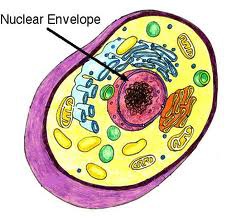
What is the nucleus surrounded by?
a double membrane
8
New cards
What is the double membrane surrounding the nucleus called?
Nuclear envelope
9
New cards
What does the nuclear envelope have?
nuclear pores
10
New cards
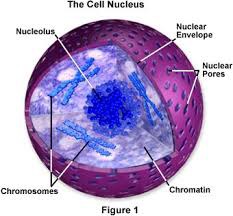
What does the nucleus contain?
Linear DNA in the form of chromatin
11
New cards
What is chromatin wrapped around? What is this called?
A protein, called Histones
12
New cards
What is embedded in the nucleoplasm?
nucleolus
13
New cards
What does a nucleus do?
Controls the cells activities
14
New cards
What does the DNA within the nucleus do?
DNA codes for the formation of proteins via mRNA which is released through nuclear pores
15
New cards
Where are ribosomes made?
nucleolus
16
New cards
Describe the structure of a mitochondria?
oval shape with a double membrane
17
New cards
What does the inner membrane do in mitochondria? what is the name of what is formed?
folds to make structures called cristae
18
New cards
What is the fluid inside mitochondria called?
matrix
19
New cards
What does the matrix fluid inside the mitochondria contain?
contains enzymes, needed for aerobic respiration
20
New cards
What does the mitochondria contain?
its own DNA and ribosomes
21
New cards
What is the function of mitochondria?
The site of aerobic respiration to release energy
22
New cards
What is golgi?
stack of fluid filled, membrane bound sacs
23
New cards
What is seen at the edge of golgi?
Vesicles
24
New cards
What does golgi modify?
proteins
25
New cards
What does Golgi make?
lysosomes
26
New cards
Describe the structure of Vesicles
small membrane bound, fluid filled, sac
27
New cards
What is vesicles produced from?
Often produced from the golgi apparatus
28
New cards
What do vesicles do?
store and transports proteins and lipids around and out of the cell
29
New cards
Describe the structure of Lysosomes.
circular organelle with a single membrane
30
New cards
What is a lysosome?
A vesicle which contain digestive enzymes
31
New cards
What is the name of the digestive enzymes lysosomes contain?
lysozymes
32
New cards
What is lysosomes used for?
Is used to separate digestive enzymes from the other parts of the cell, used to digest foreign material and 'worn' organelles
33
New cards
What do centrioles do?
creates microtubes during mitosis (prophase) to attach to centromeres on sister chromotids to separate them
34
New cards
What are spindle fibers made of?
microtubules
35
New cards
Describe the size of ribosomes
small
36
New cards
Where are ribosomes found?
often found free in the cytoplasm or attached to endoplasmic reticulum (rough)
37
New cards
What are ribosomes a compromise of?
proteins and RNA
38
New cards
Do ribosomes have a membrane?
no membrane
39
New cards
what are ribosomes the site of?
protein synthesis
40
New cards
What is the rough endoplasmic reticulum?
conjoined fluid filled membranes which are embedded with ribosomes
41
New cards
What does the rough endoplasmic reticulum do?
folds and processes polypeptides into proteins which have been created by ribosomes
42
New cards
What is the smooth endoplasmic reticulum?
conjoined fluid filled membranes which are without ribosomes
43
New cards
What does the smooth endoplasmic reticulum do?
synthesis and process of lipids ad carbohydrates
44
New cards
What are the 3 main types of filament proteins that make up the cytoskeleton?
actin filaments
microtubes
intermediate filaments
microtubes
intermediate filaments
45
New cards
What is the cytoskeleton needed for?
Needed to moe organelles around a cell to specific locations
46
New cards
What do the filaments that make up the cytoskeleton provide for the cell?
Provides support for the cell
47
New cards
What does the cytoskeleton allow?
Allows cells to change shape for movement
48
New cards
What cells are chloroplasts found in?
plant and algal cells
49
New cards
What surrounds chloroplasts? What is it called?
double membrane
chloroplast envelope
chloroplast envelope
50
New cards
What is the fluid inside the chloroplast envelope called?
stroma
51
New cards
What does chloroplast contain? What is this called?
flattened sacs individually called thylakoids
52
New cards
What do thylakoids contain?
chlorophyll
53
New cards
What is lamellae?
the interconnections between grana
54
New cards
What is grana?
stack of thylakoids
55
New cards
What are chloroplasts the site of?
photosynthesis
56
New cards
What can be found in chloroplasts? Why?
starch grains, as it is the site of photosynthesis
57
New cards
What 2 things do chloroplasts also contain?
their own DNA
ribosomes
ribosomes
58
New cards
Why do chloroplasts contain ribosomes?
to synthesise their own proteins for photosynthesis
59
New cards
What is a vacuole?
single membrane bound organelle, containing cell sap
60
New cards
What is the name of the membrane surrounding the vacuole?
tonoplast
61
New cards
What does cell sap consist of?
consists of a solution of mineral salts, sugars, amino acids, wastes and some pigments
62
New cards
What does a vacuole contain? What is this used for?
contains the pigments which may colour petals used to attract pollinators
63
New cards
What is the vacuole in plants cells for?
tugor support
64
New cards
What does the vacuole act as?
a temporary food store
65
New cards
What cell types are cell walls found in?
bacteria
plants
fungi
algae
plants
fungi
algae
66
New cards
In plant and alage cells, what is the cell wall composed of?
cellulose
67
New cards
Describe the location of cellulose fibres.
the cellulose fibres are embedded in a matrix
68
New cards
What is the cell wall compromised of in fungi cells?
chitin
69
New cards
What is the middle lamellae?
the layer between the adjecent cell wall
70
New cards
What does the middle lamellae do?
cements cells together
71
New cards
What is the cell wall needed for?
cellular support under turgor pressure from osmosis
72
New cards
What is plasmodesmata?
pores in cell wall
73
New cards
What plasmodesmata allow?
allows the flow of water from one plant cell to the next
74
New cards
Algal cells have a cell wall of what?
cellulose and chloroplasts
75
New cards
What is special about alagal cells?
they can be unicellular or multicellular
76
New cards
What is the difference between plant and algal cells? (in terms of chloroplast)
alagal cells often have one large chloroplast rather than many smaller ones like plant cells
77
New cards
What is special about fungal cells?
they can be multicellular or unicellular
78
New cards
Give an example of a unicellular fungal cell.
yeast
79
New cards
Give an example of a multicellular fungal cell.
mushroom
80
New cards
True or False: Fungal cells have chloroplast
False; fungal cells do not have chloroplasts
81
New cards
What makes up an organism?
cell → tissue → organ → organ system → organism
82
New cards
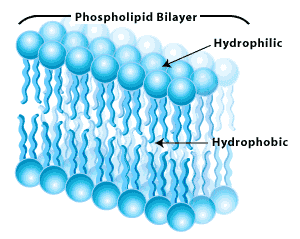
Phosolipid bilayer membrane diagram
83
New cards
Nucleus diagram
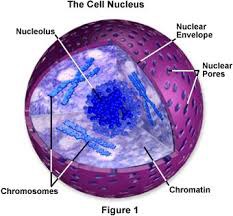
84
New cards
Mitochondrian diagram
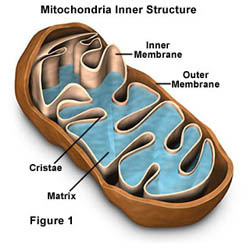
85
New cards
Golgi diagram

86
New cards
Chloroplast diagram
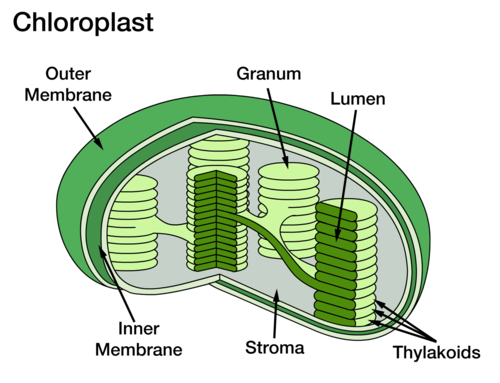
87
New cards
Vesicles diagram
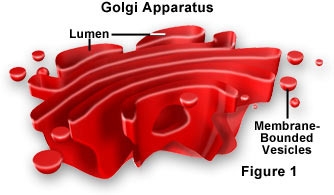
88
New cards
Ribosomes diagram
89
New cards
Rough endoplasmic reticulum diagram
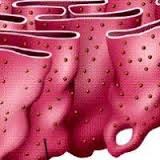
90
New cards
Smooth endoplasmic reticulum diagram
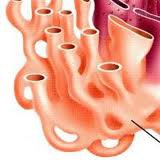
91
New cards
Vacuole diagram

92
New cards
Cell wall diagram
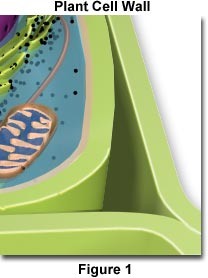
93
New cards
Compare eukaryotic cells to prokaryotic cells. (in terms of size)
prokaryotic cells are much smaller than eukaryotic cells
94
New cards
What type of cells are unicellular (single celled)?
prokaryotic cells
95
New cards
Compare the structure of eukaryotic and prokaryotic.
prokaryotic cells are much simpler in structure than eukaryotic cells
96
New cards
state one difference between prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells.
prokaryotic cells have no membrane bound organelle
97
New cards
Where is bacterial DNA found?
nucleoid
98
New cards
describe the DNA in a nucleoid
the DNA is free in the cell wall and not associated with proteins. It exists as a single circular chromosome.
99
New cards
What are plasmids?
smaller circular pieces of DNA that can replicate independently from the main chromosomal DNA
100
New cards
Where are the genes of antibiotic resistance often found?
Plasmids