Zool 110 Lec: Annelids and Ecdysozoans (
1/28
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
29 Terms
phylum onychophora and phylum tardigrada
what are the two phyla within the group ecdysozoans
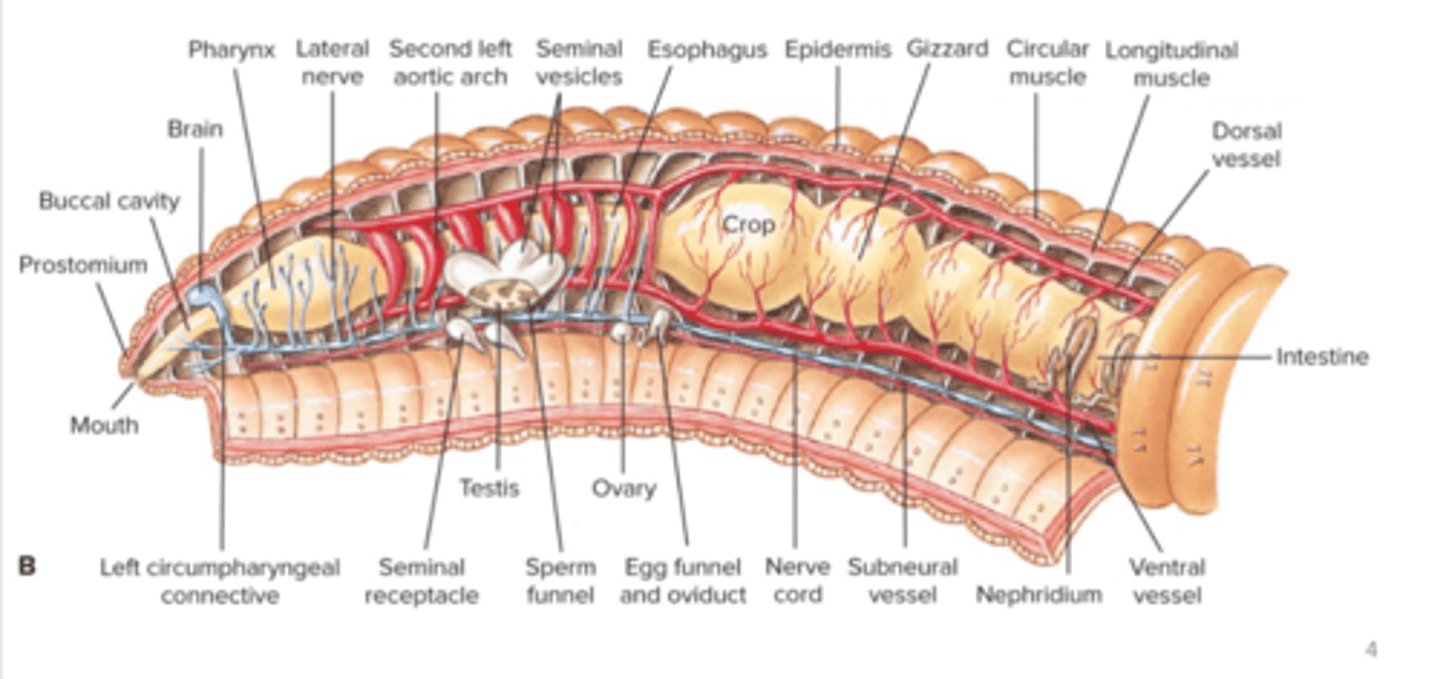
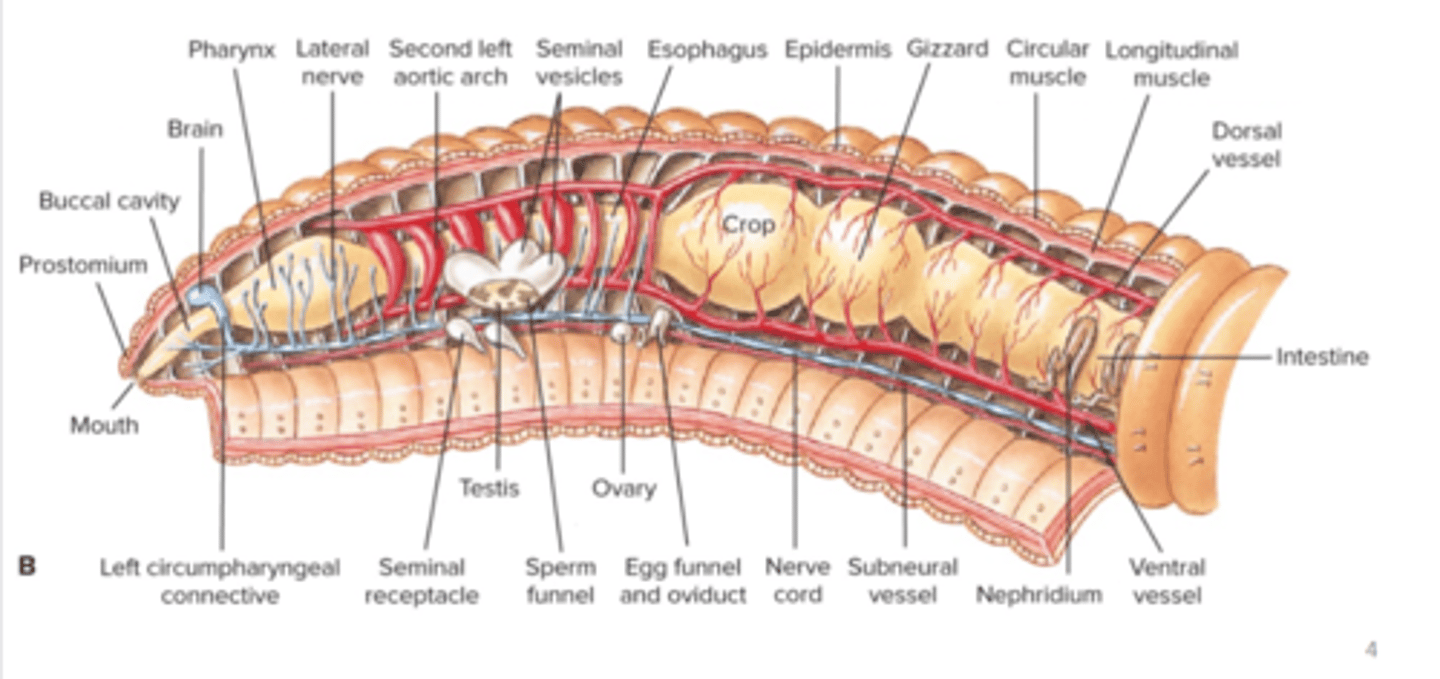
Phylum Annelida
cephalized vermiform animals with segmented (metameric body plan), triploblastic, coelomate lophotrochozoans, coelom usually divided by septa, marine/freshwater/terrestrial/most free-living/some symbionts or ectoparasites, transparent cuticle secreted by epithelial tissue
Phylum Annelida reproduction
fission and fragmentation, monoecious sexual reproduction with trochophore larva or direct development
polychaetes are what kind of group
3 multiple choice options
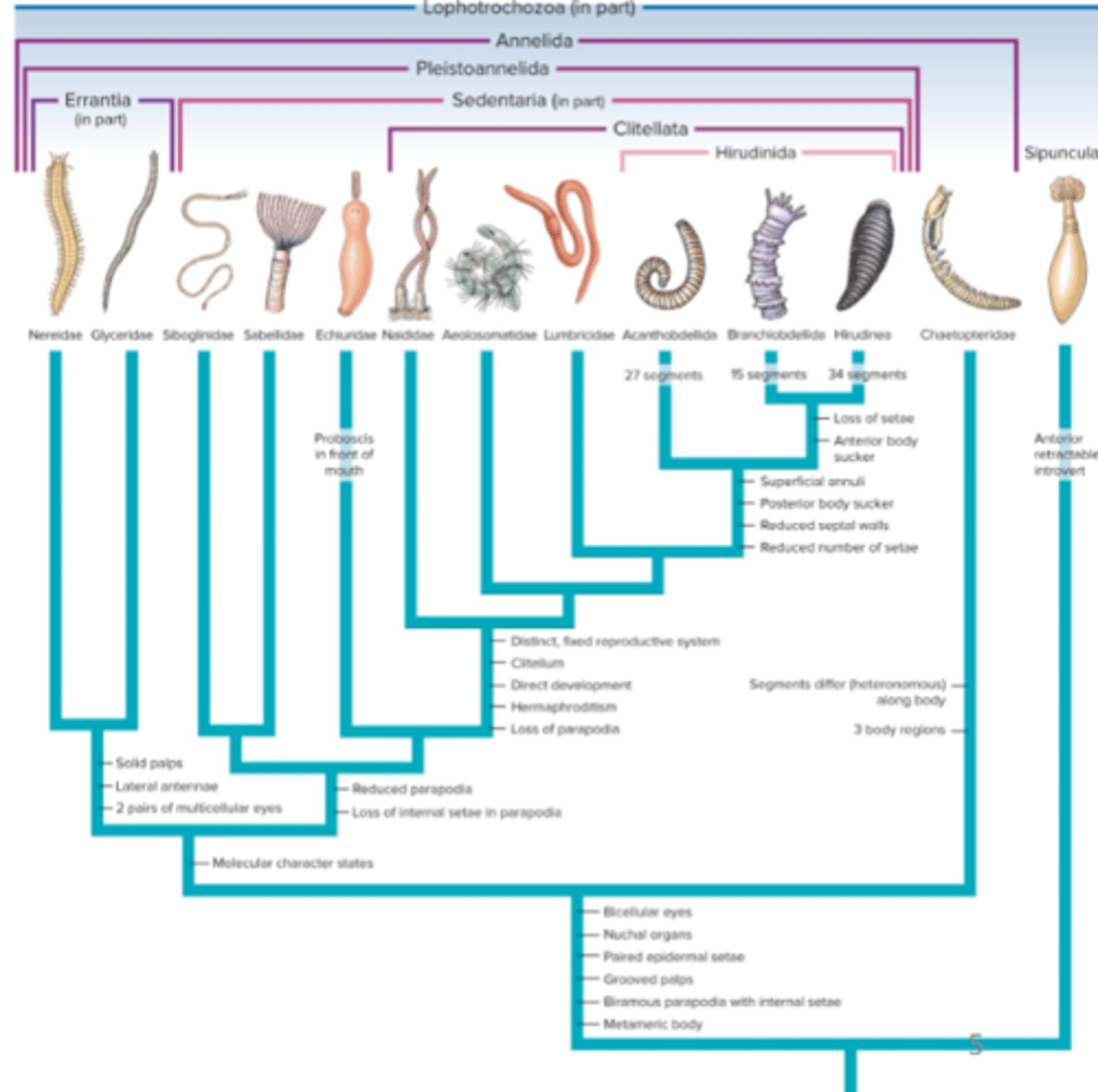
Errantia and Sedentaria
what are the two major clades in Annelida
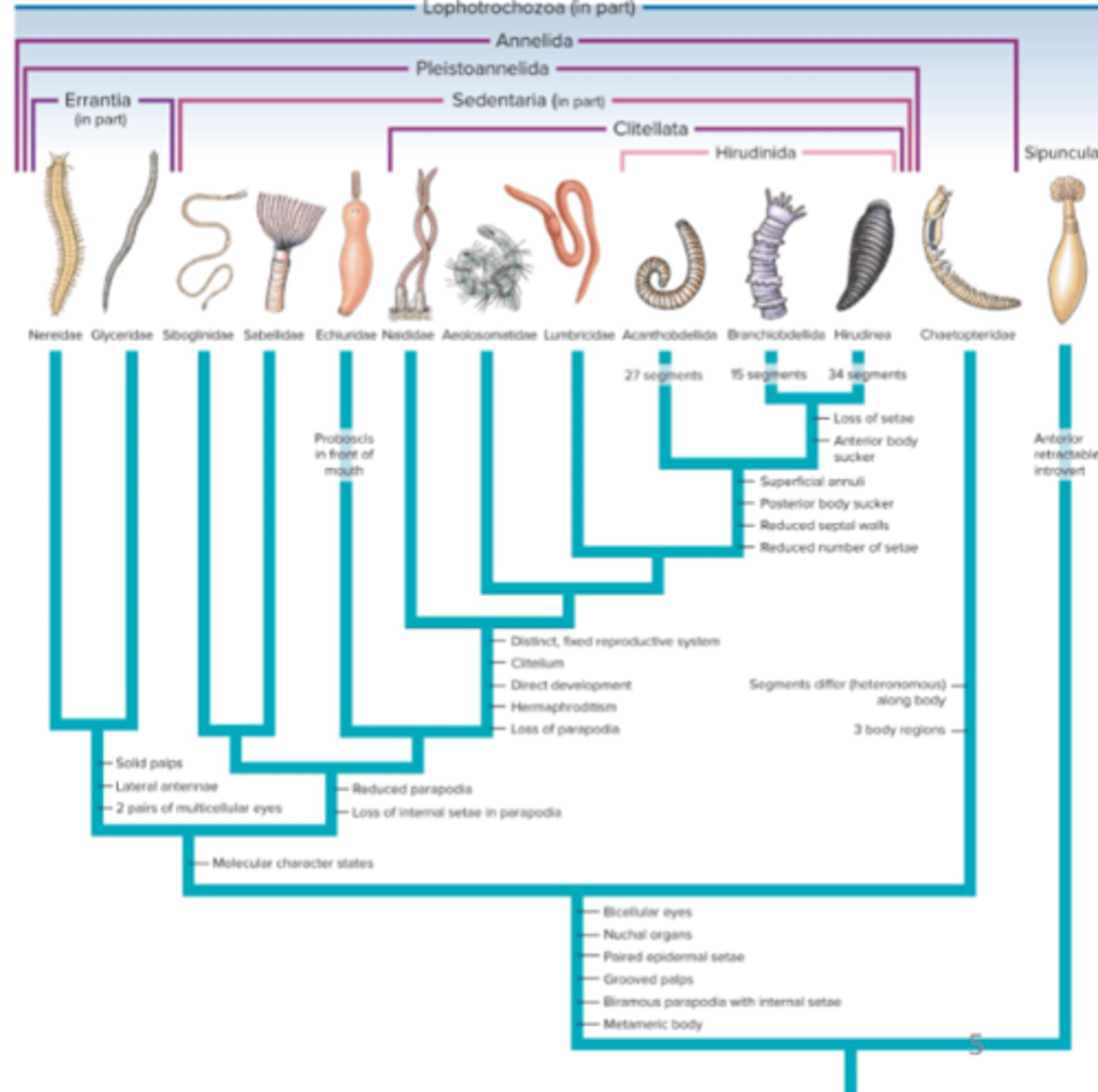
Clades of Phylum Annelida phylogenetic breakdown
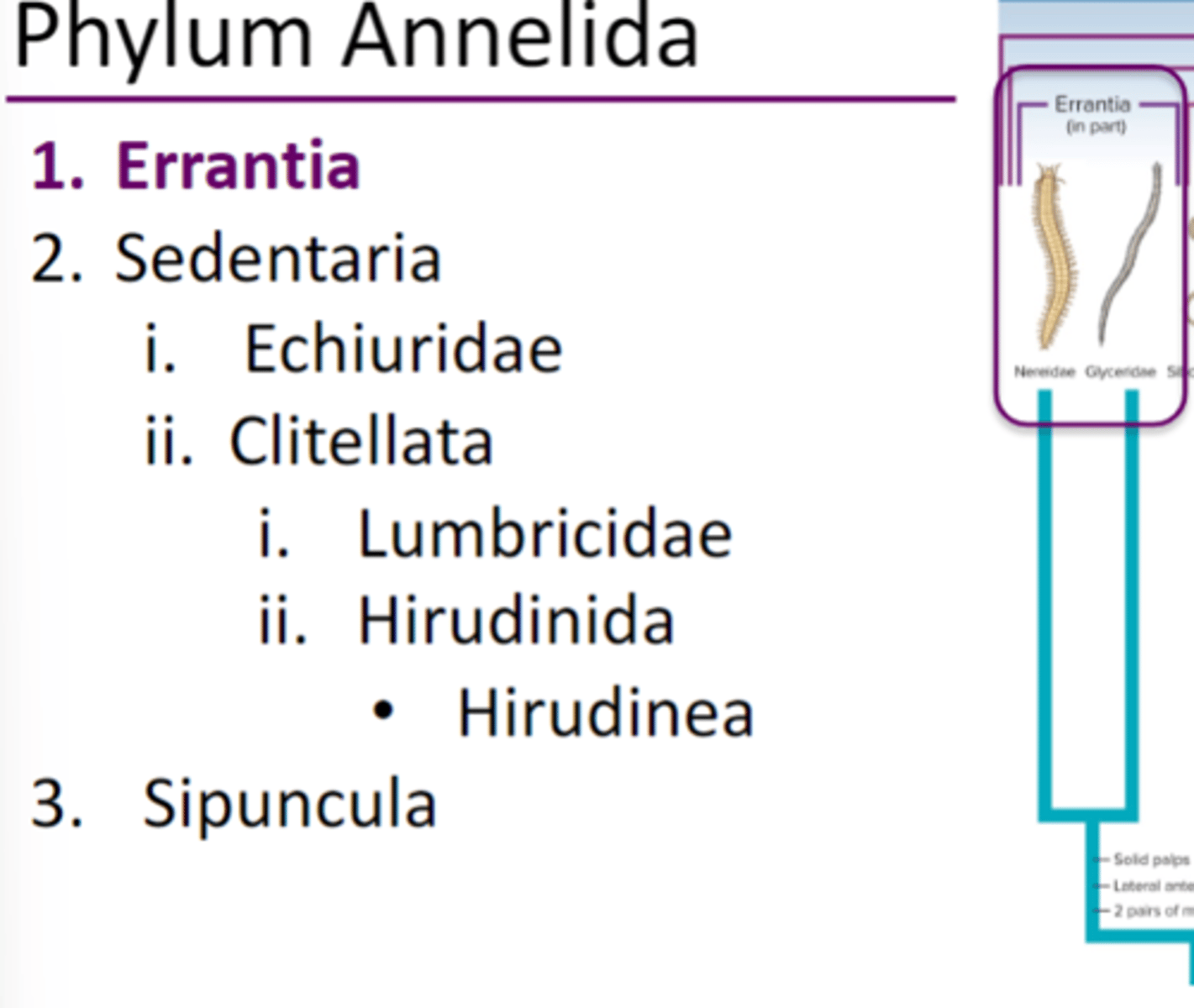
Clade Errantia (Phylum Annelida)
motile polychaete worms, many are euryhaline, well differentiated head with sense organs, parapodia (paired appendages) on each segment, many setae arranged in bundles on parapodia, no citellum

setae
Bristle-like structures that help segmented worms move
Clade Errantia body plan
prostomium = mouth, sometimes retractable, pharynx that can be everted, parapodia with setae
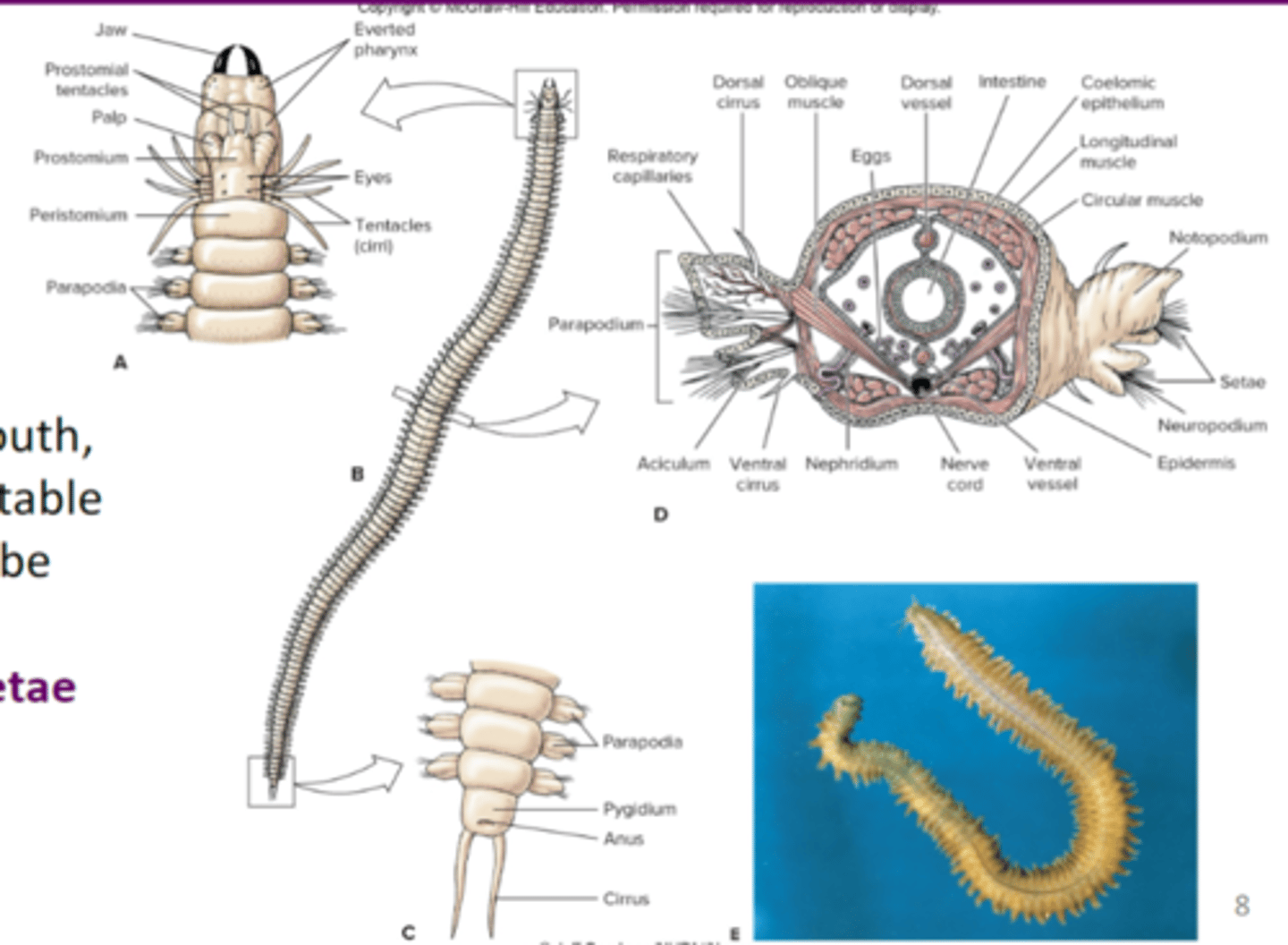
parapodia
Paddlelike appendages that assist aquatic annelids in locomotion
Clade Errantia Reproduction
no separate sex organs, usually dioecious, external fertilization
Clade Errantia Sexual Reproduction
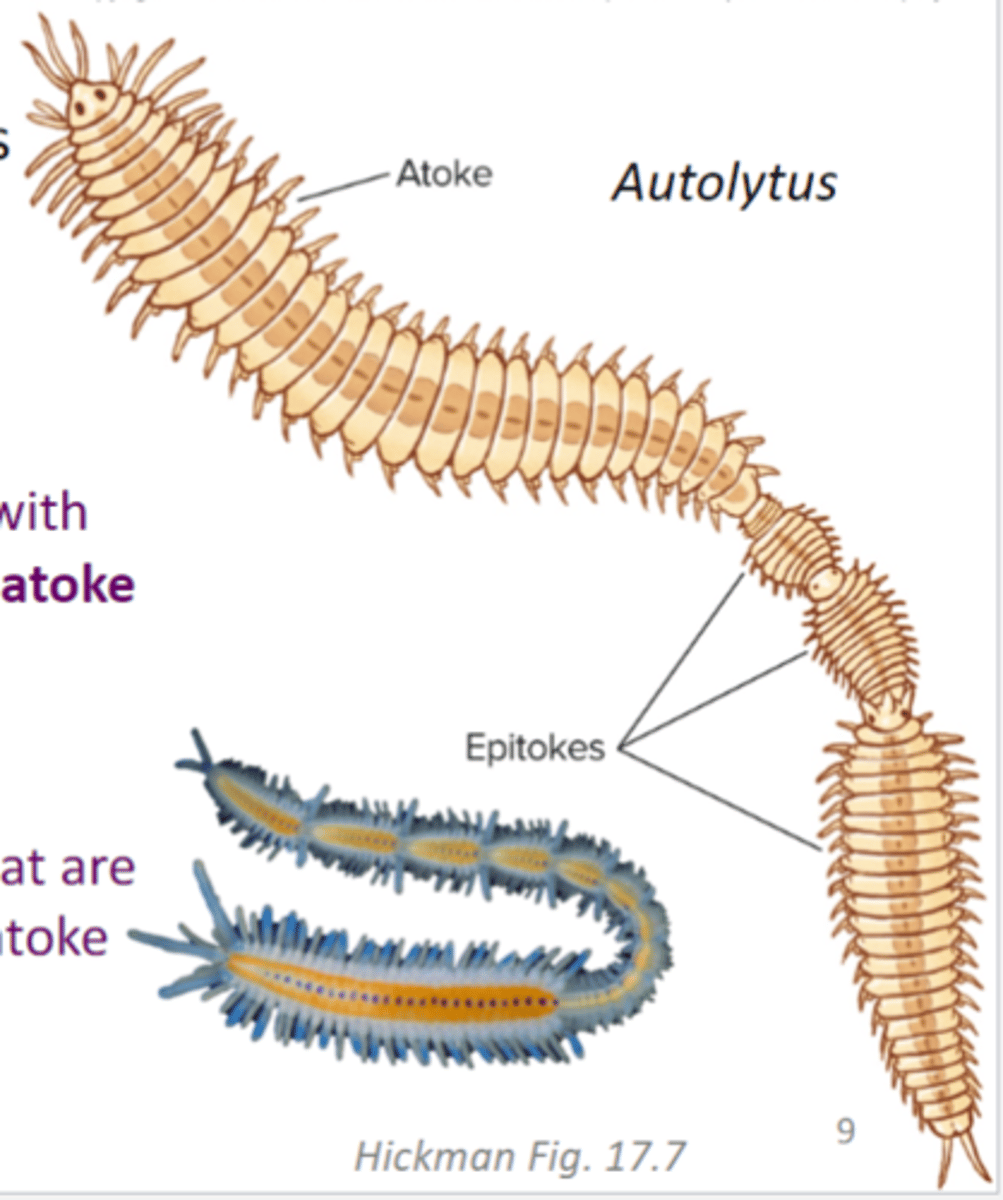
epitoke = segments packed with gametes that detach from the atoke and rise to the surface
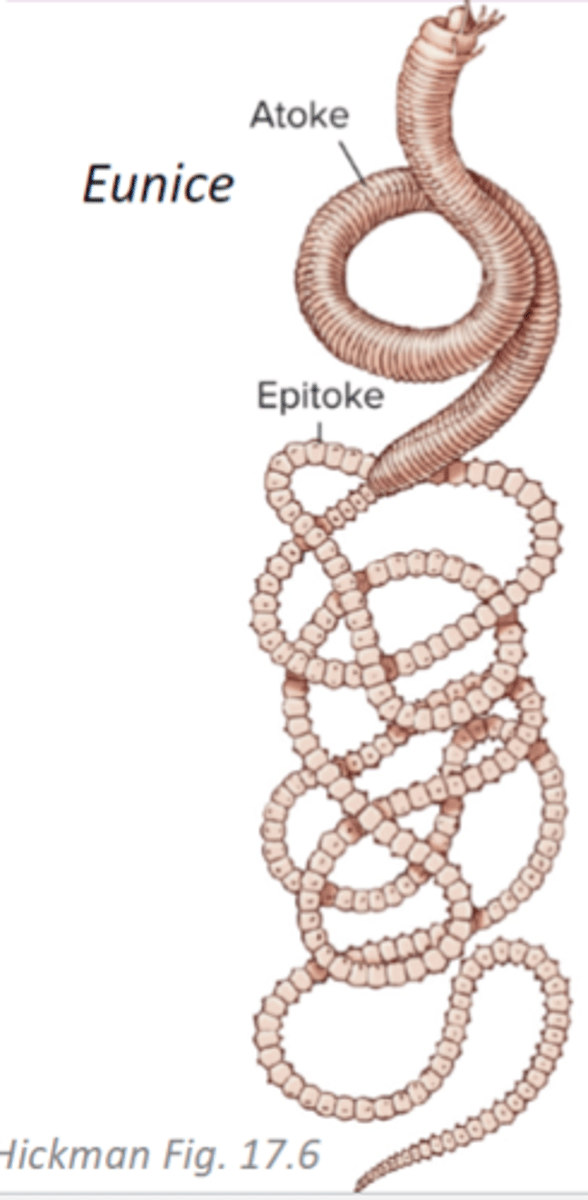
Clade Errantia Asexual Reproduction
epitokes = complete worms that are budded of posterior end of atoke
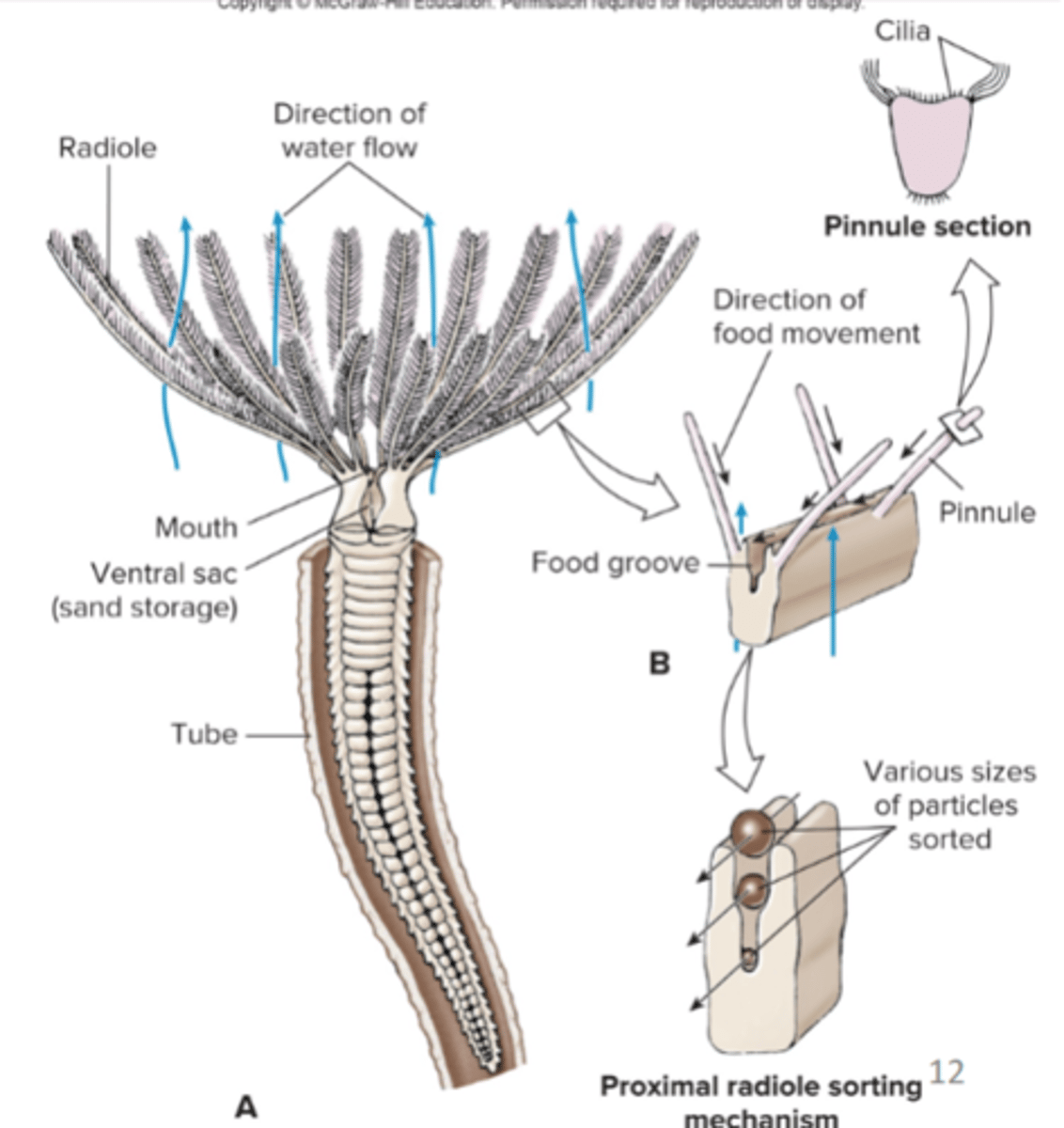
Clade Sedentaria
tubeworms, live in parchment tube
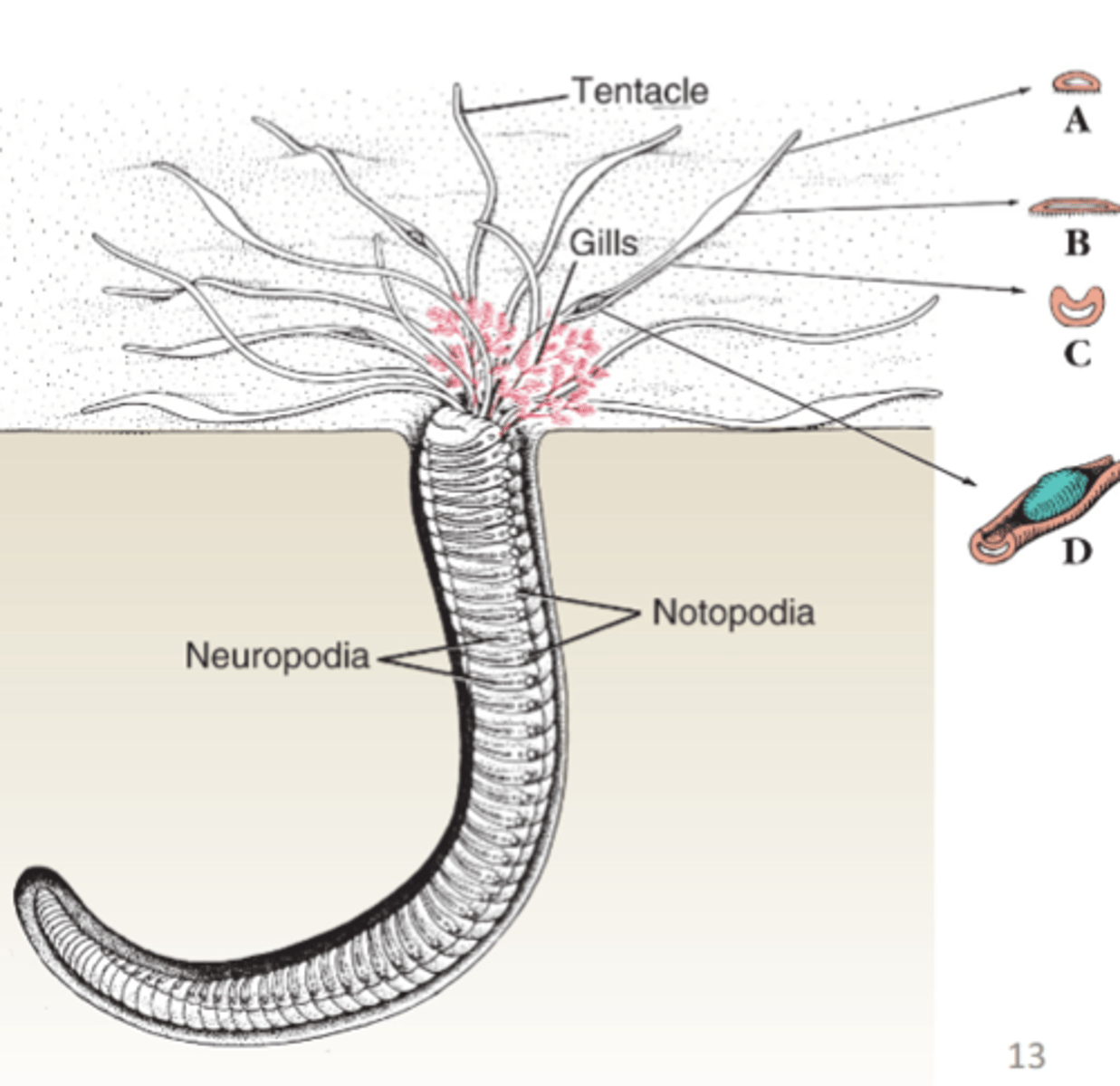
Amphitrite (terbellid) "spaghetti worm"
part of clade sedentara, tentacles extend across sand and sweep up food
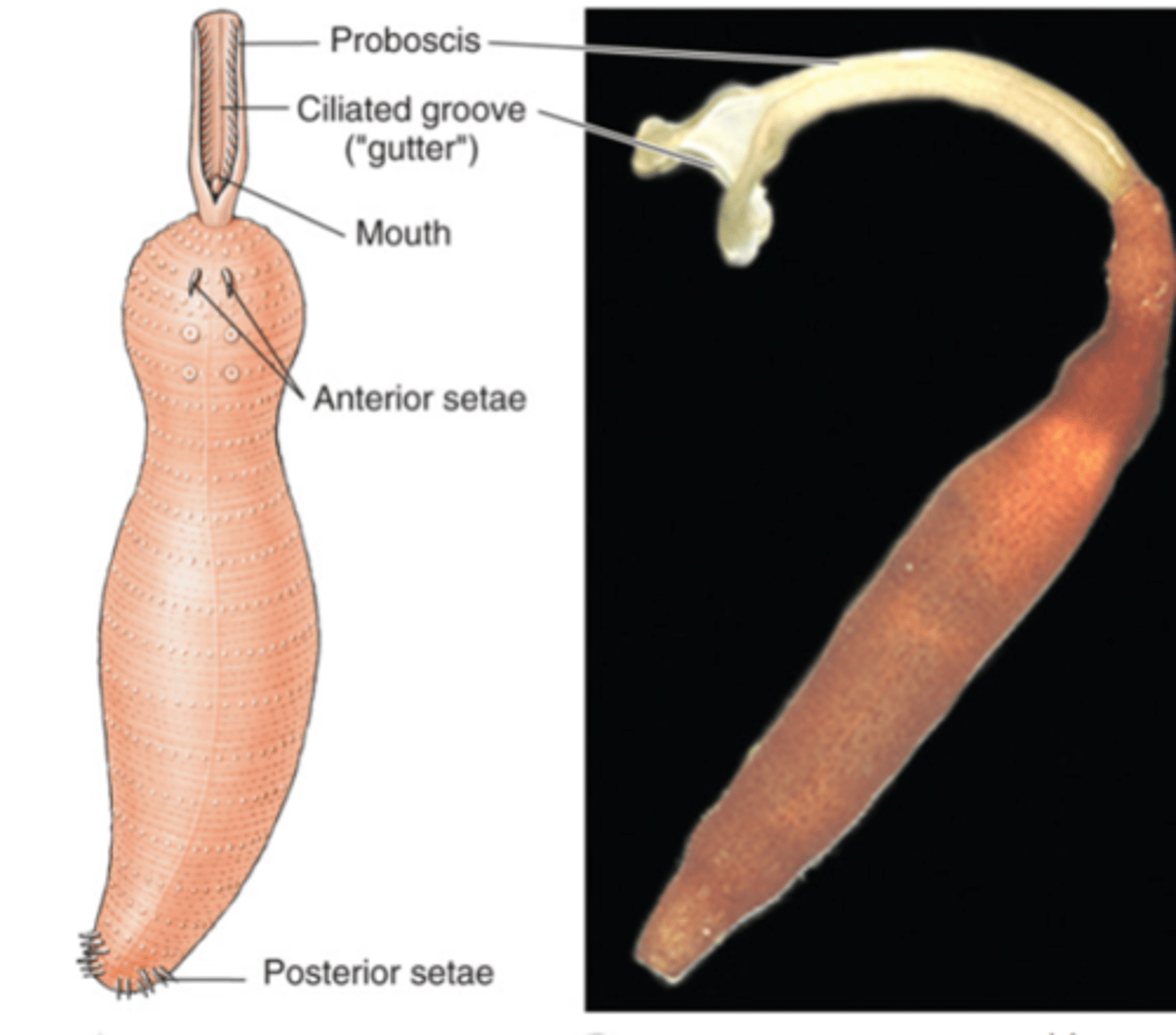
Echiurids (spoon worms)
part of clade sedentaria, proboscis with gutter
Echiuridae and Clitella
what are the two subgroups of clade Sedentaria
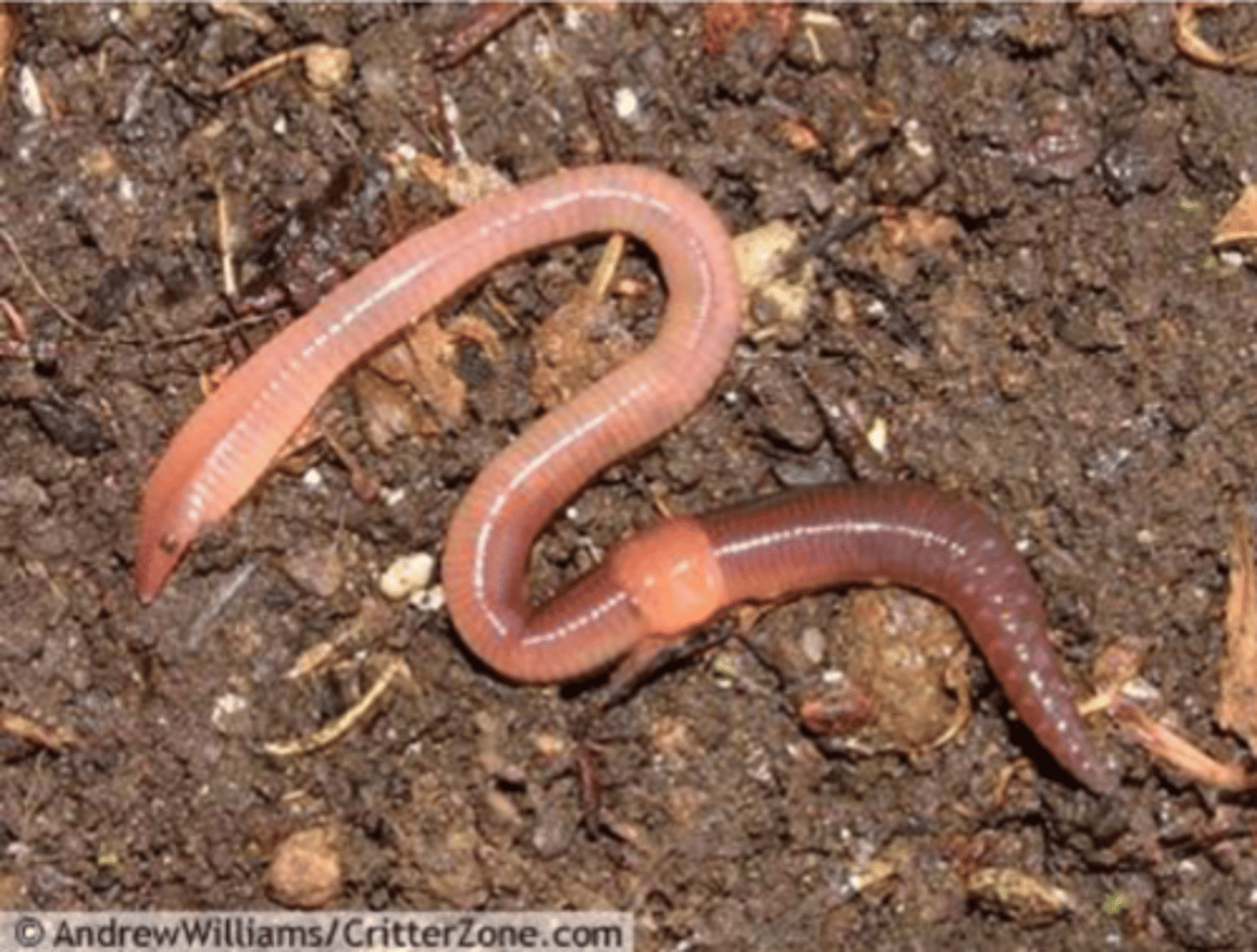
Subgroup Clitella (Clade Sedentaria)
have a clitellum, freshwater and terrestrial, oligochaetes (non-monophyletic group), class Hirudinia

Subgroup Clitella body plan (e.g. oligochaete)
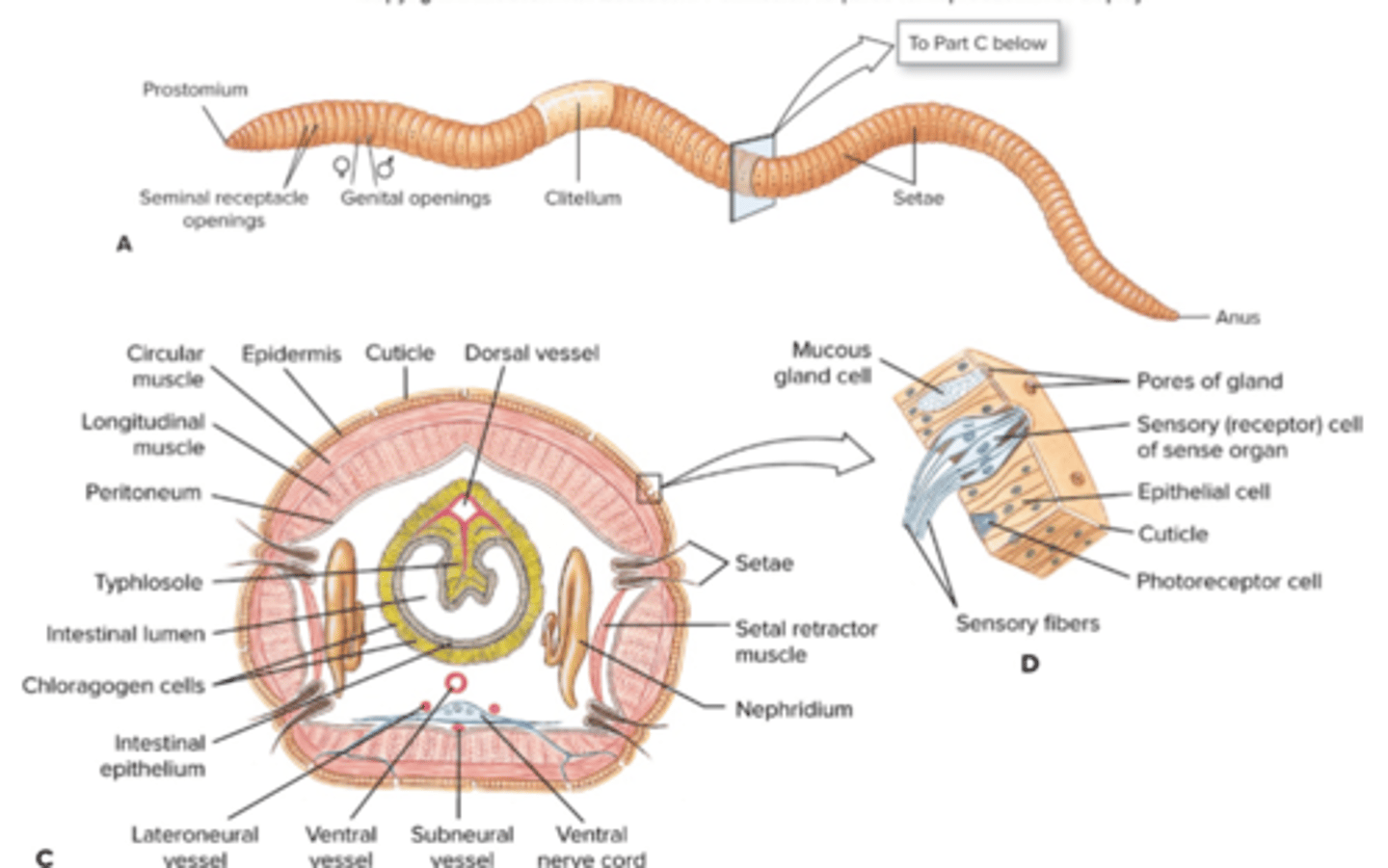
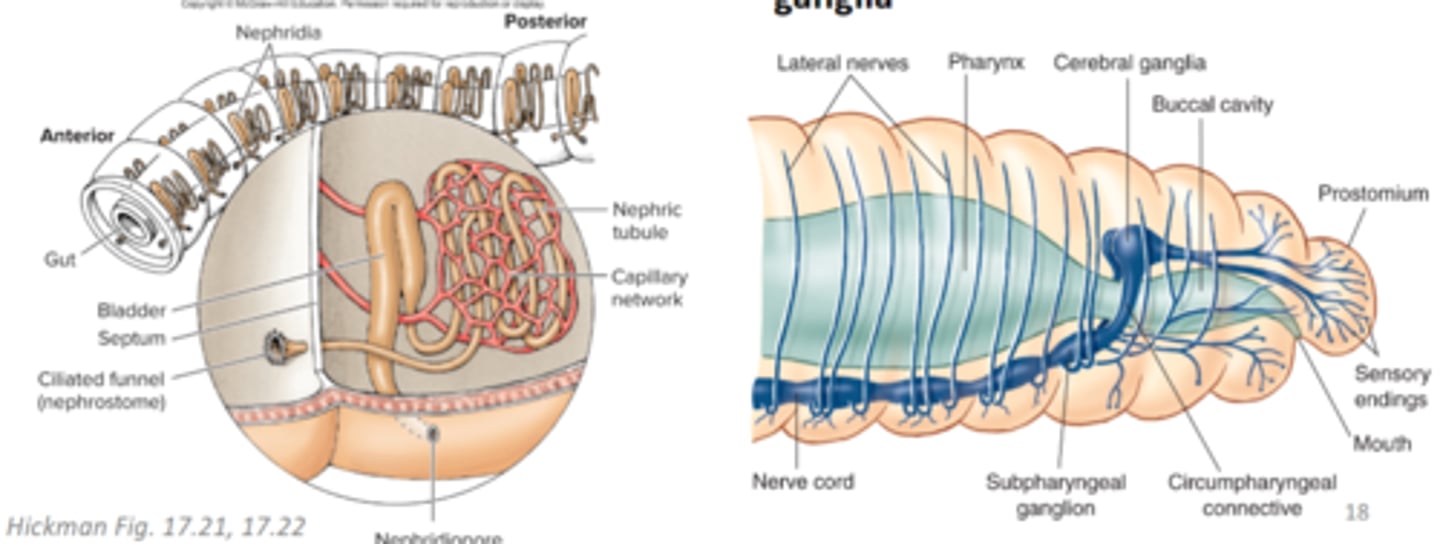
Oligochaete (subgroup clitella) excretory and nervous system
paired nephridia in each segment, cerebral ganglia (brain) above pharynx, connectives (nerves) pass around pharynx to connect brain to first pair of ganglia
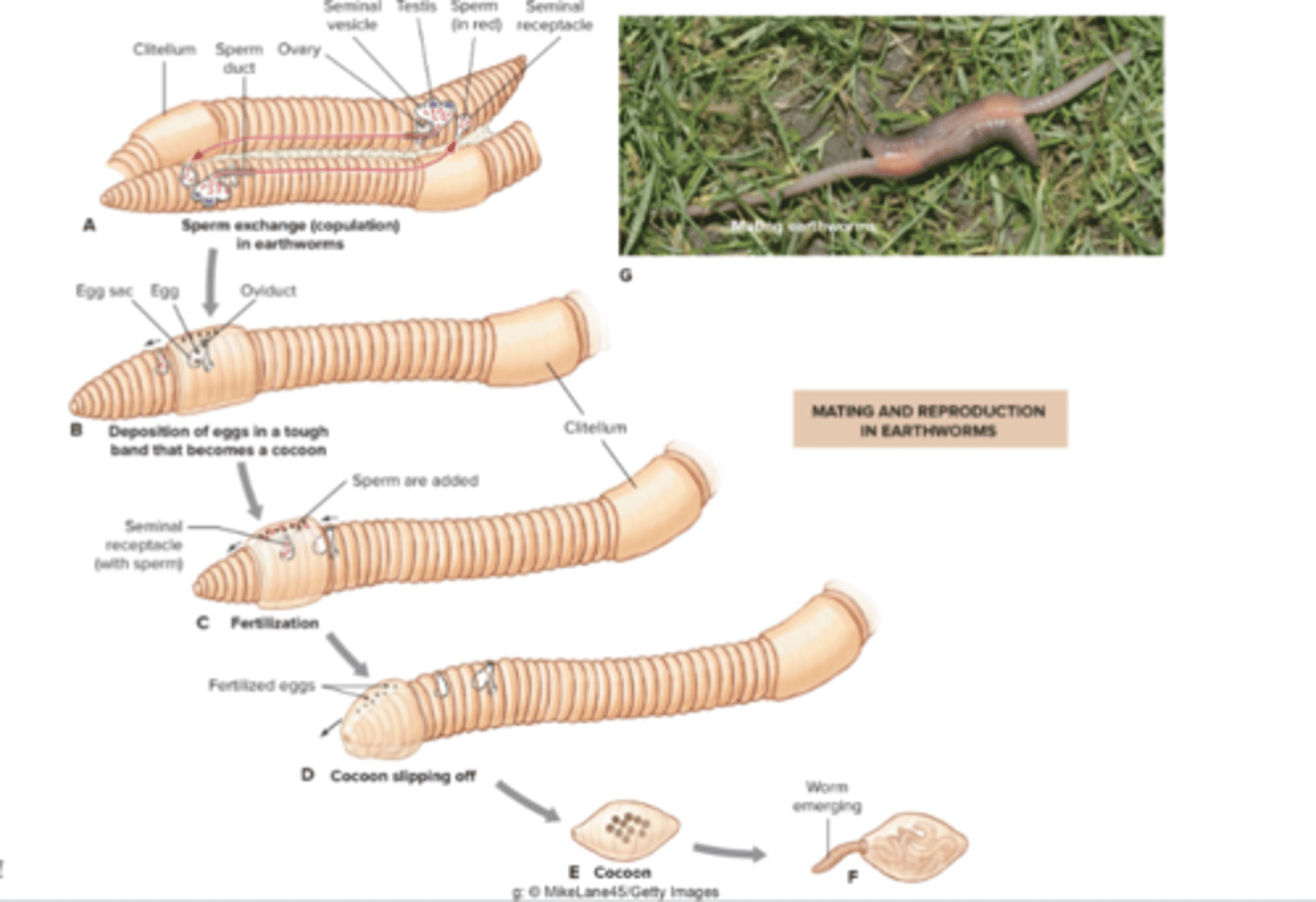
Oligochaete (subgroup clitella) reproduction
clitellum picks up eggs and sperm and fertilizes them and then it pops off and acts as a cocoon where the new worms eventually emerge from
Class Hirudinida (Clade Sedentaria Subgroup Clitella)
order Hirudinea (true leeches), no setae, anterior and posterior suckers, carnivorous on small invertebrates, temporary parasites or permanent parasites, fluid feeding = salivary glands secrete anesthetic cand anticoagulants
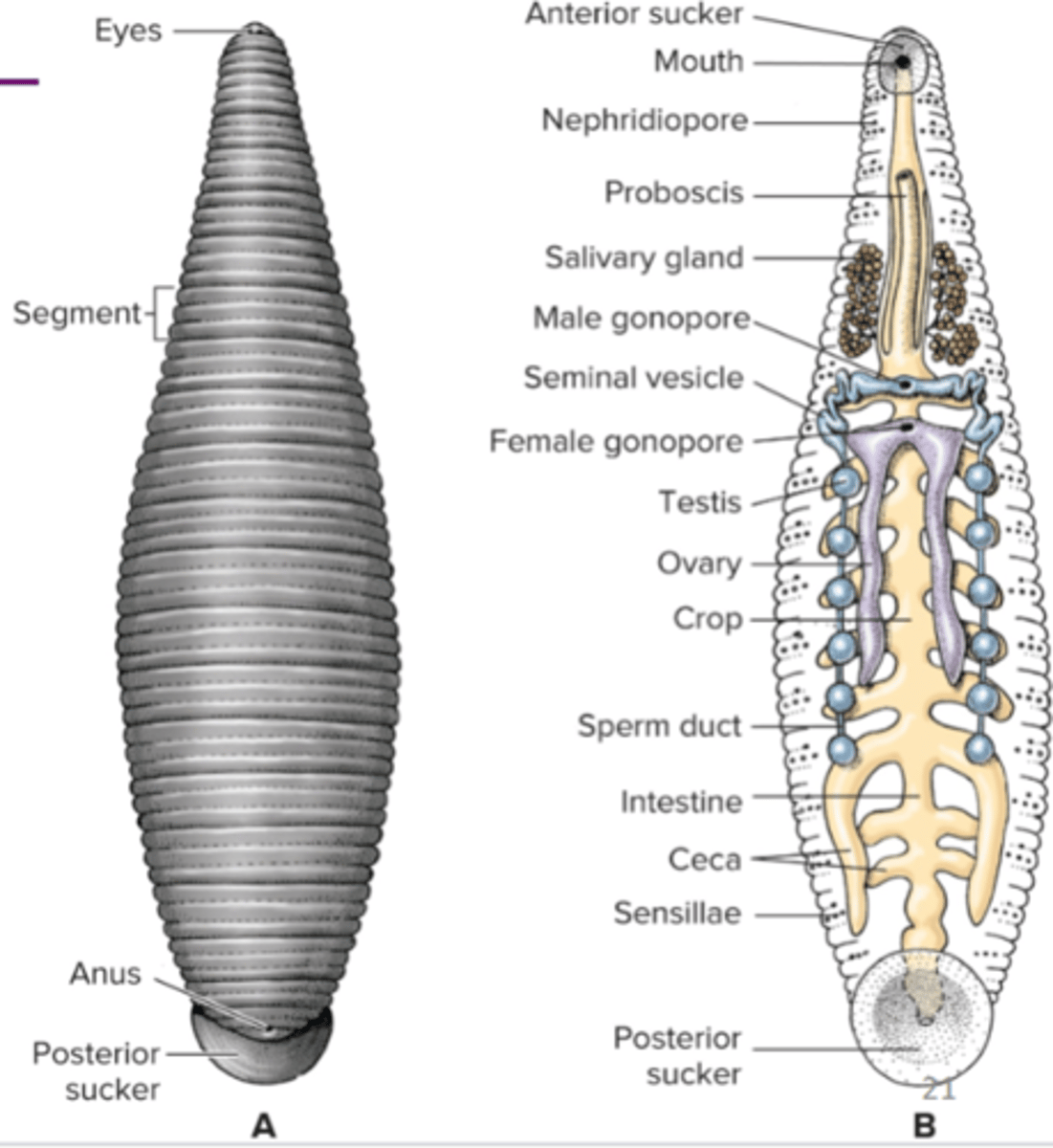
Class Hirudinida body plan (Clade Sedentaria Subgroup Clitella
hermaphroditic with clitellum only during breeding season

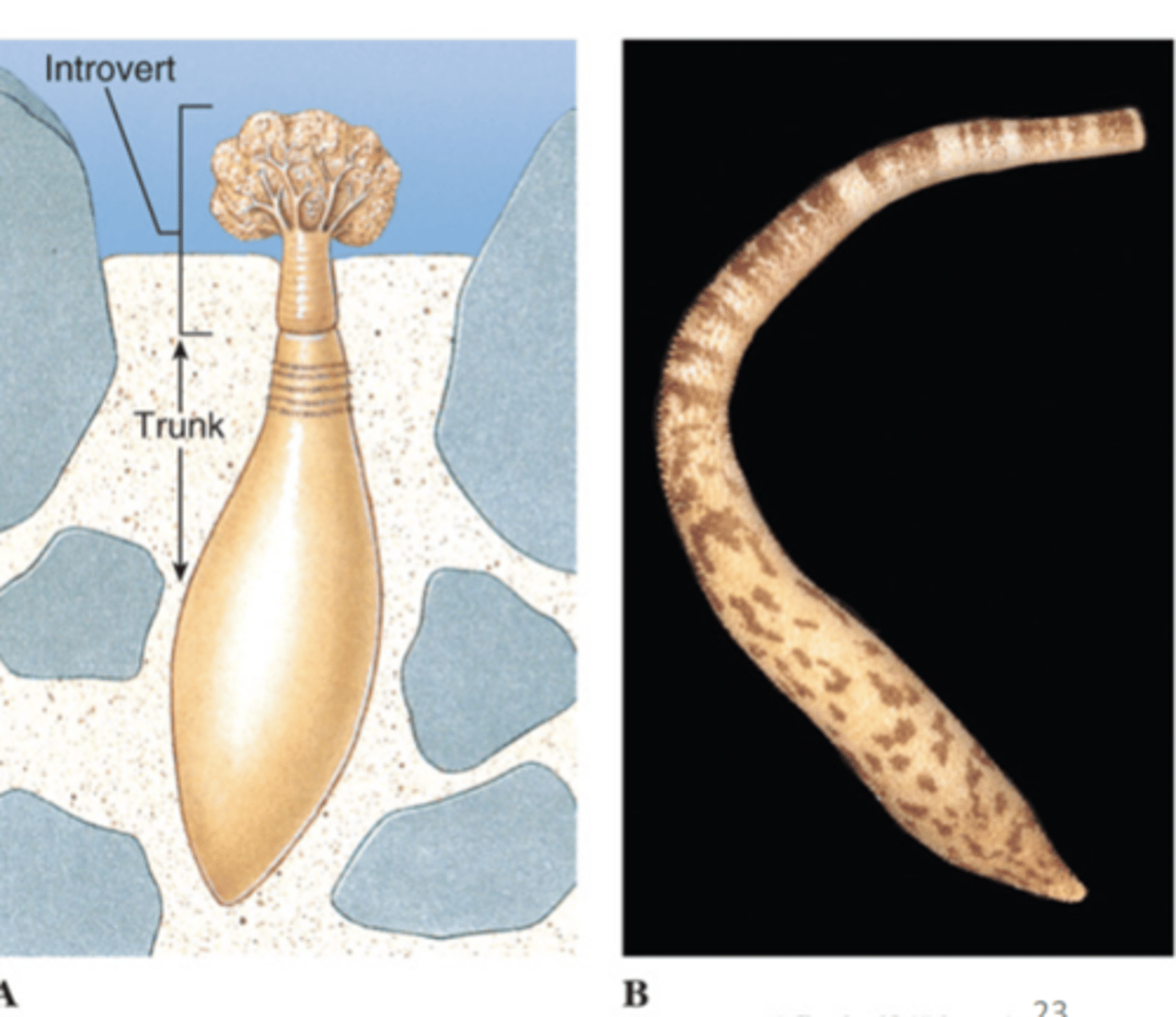
Group Spinuncula
spinunculans (peanut worms), introvert = proboscis
Clade Ecdysozoa
protostomes with a cuticle that is shed (molted) through ecdysis
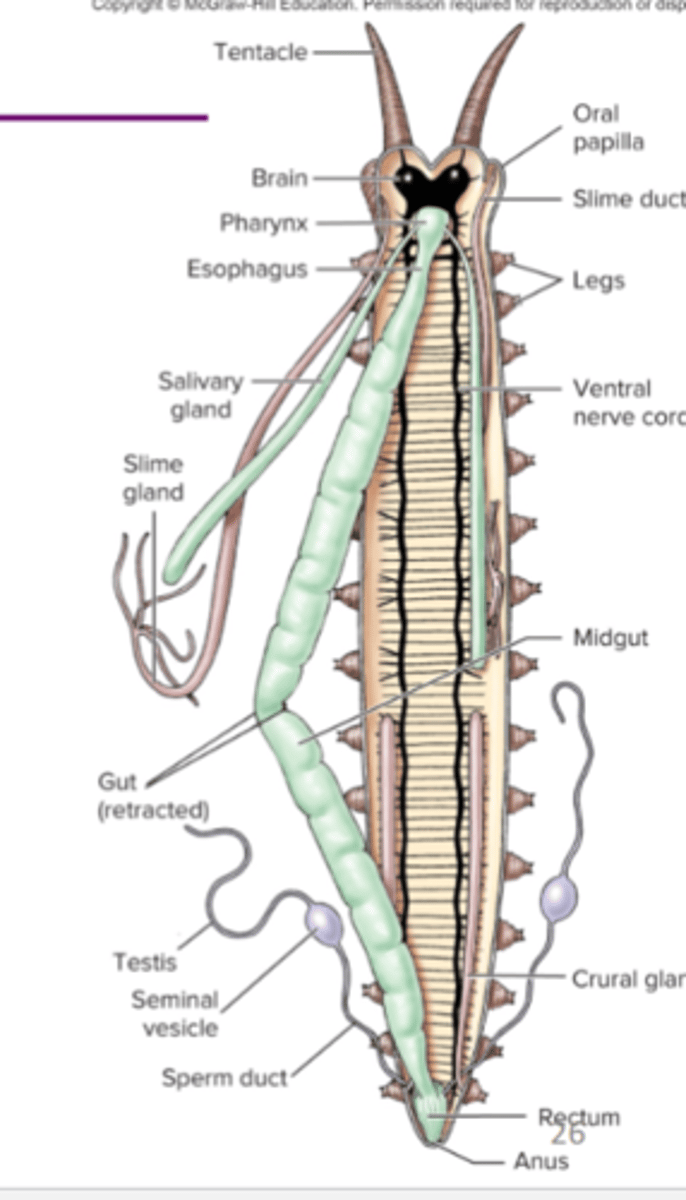
Phylum Onychophora
velvet worms, 70 species of small caterpillar like animals, terrestrial, open circulatory system, tracheal respiratory system, slime glands for hunting
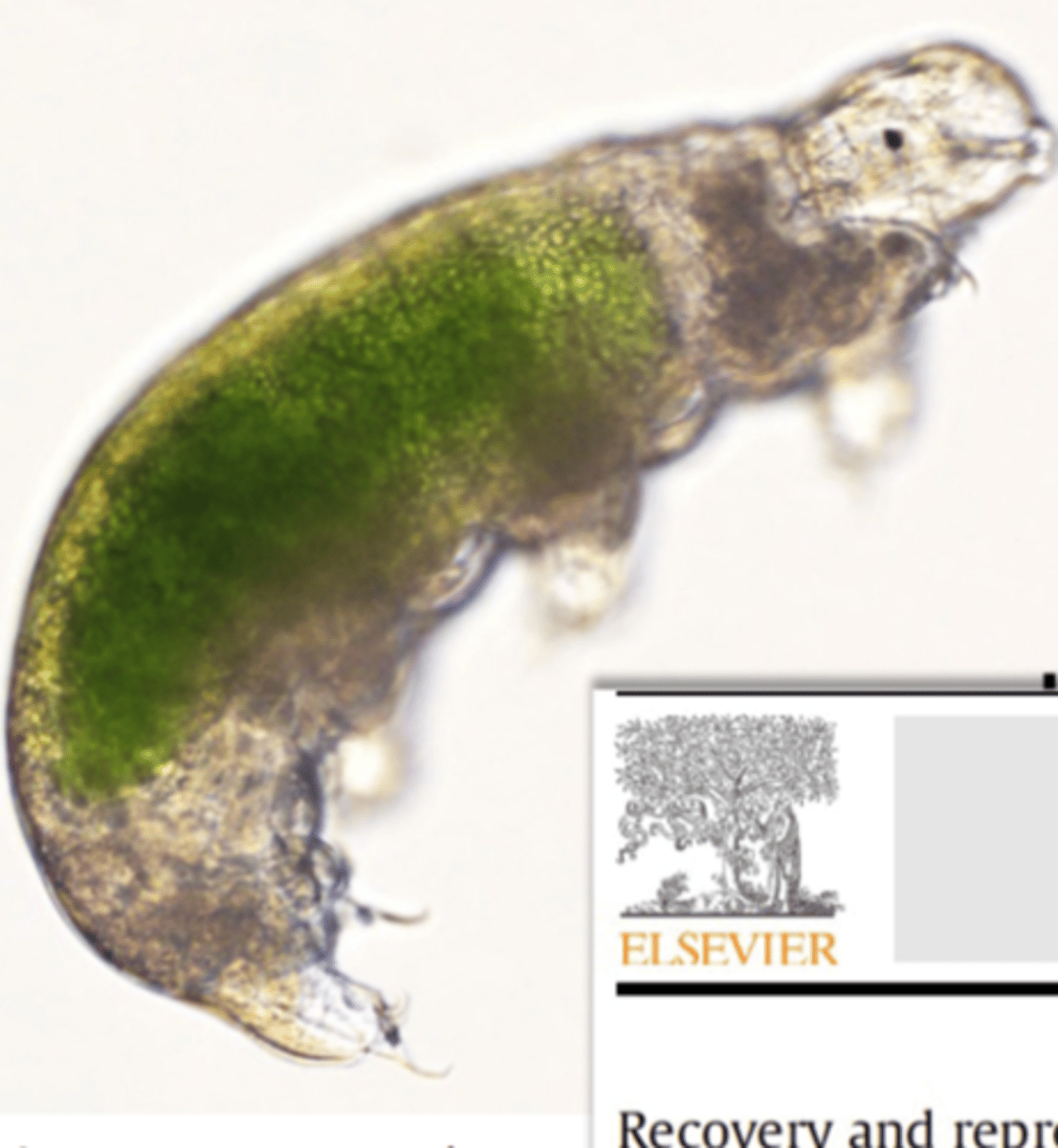
Phylum Tardigrada
water bears, 900 species, mostly terrestrial in water film around mosses and lichens, some freshwater or marine
Phylum Tardigrada body plan
elongated, unsegmented body, with stubby unjointed legs each with 4-8 claws, large brain, malpighian tubule excretory system, open circulatory system, use sharp stylet in pharynx to feed
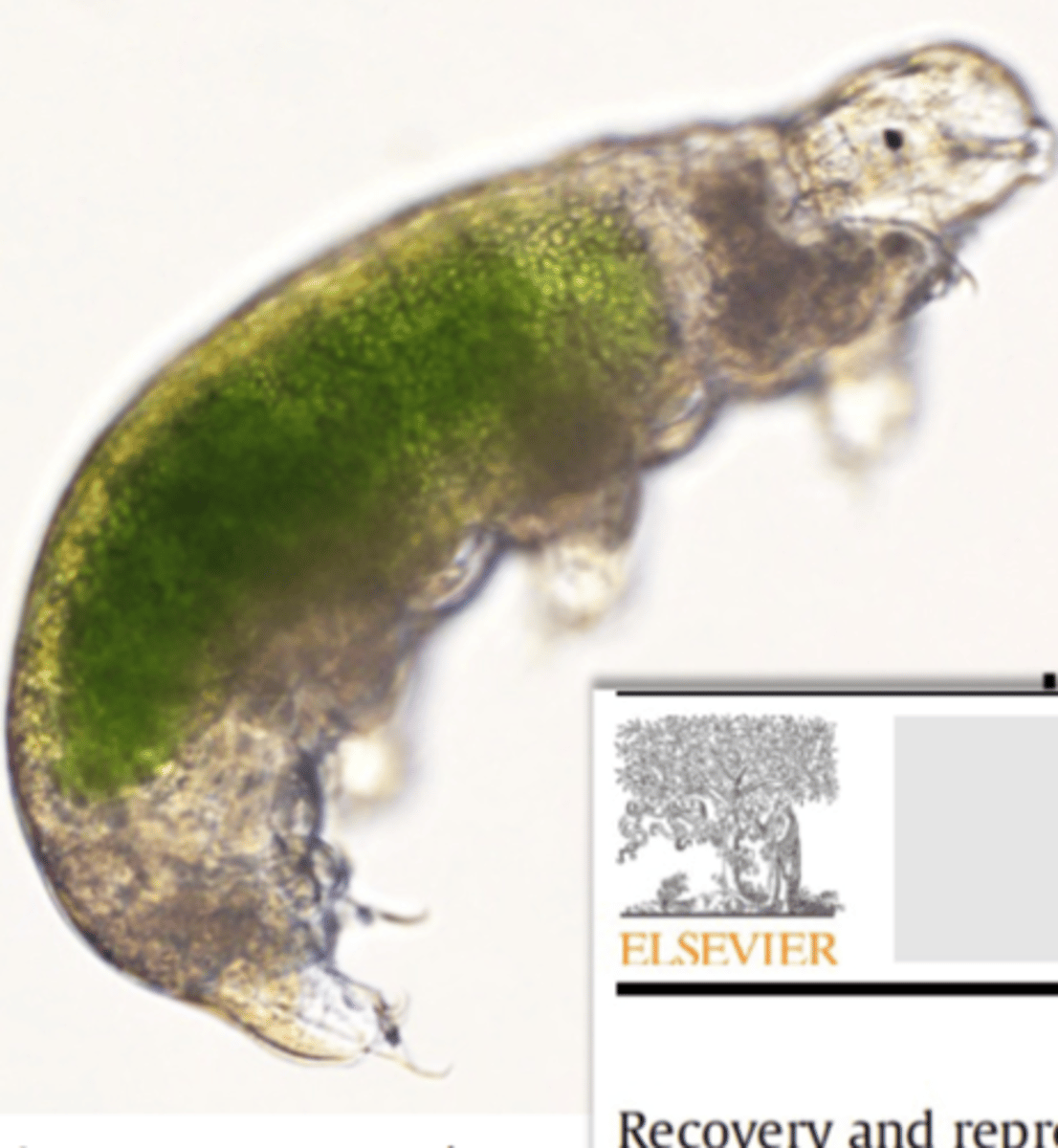
Phylum Tardigrada reproduction
dioecious, many parthenogenetic, egg-laying occurs at molting