Biology Chapter 4 Vocab
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/25
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
26 Terms
1
New cards
Nucleus
Site where the chromatin is located
2
New cards
Chromatin
Combination of DNA and histone proteins
3
New cards
Nucleus envelope
Phospholipid bilayer surrounding the nucleus
4
New cards
Nucleolus
Area of condensed chromatin. Site where ribosomes are produced.
5
New cards
Ribosome
Site of intracellular protein synthesis.
6
New cards
Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum
Site of extracellular protein synthesis. Composed of folded membranes covered in ribosomes.
7
New cards
Smooth ER
Site where lipids are produced. Also helps clean (detoxify) the cell. *No ribosomes here*
8
New cards
Cytosol
The liquid of the cell that the organelles are found in
9
New cards
Golgi complex
Site of protein modification and packaging for extracellular shipment
10
New cards
Lysosome
Site of intracellular digestion. Contains hydrolytic enzymes.
11
New cards
Vacuole
Site of water storage in plants. Fills with water for more structural support.
12
New cards
Mitochondria
Site of aerobic respiration and ATP production
13
New cards
Chloroplast
Carbohydrate producing organelle. Site of photosynthesis.
14
New cards
Peroxisome
-turns toxins into hydrogen peroxide of H2O2
Contains the enzyme catalase which turns H2O2 into water
Contains the enzyme catalase which turns H2O2 into water
15
New cards
Cytockeleton
Used for cellular structure and support includes microtubules > intermediate filaments > microfilaments
16
New cards
Cytoplasm
Everything outside of the nucleus but still within the cell.
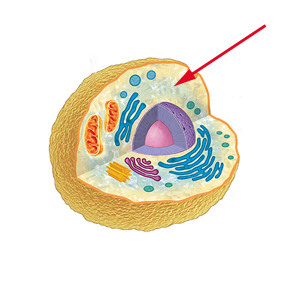
17
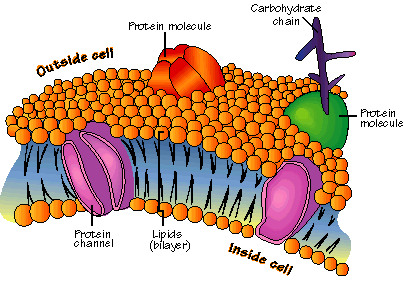
New cards
Plasa membrane
Phospholipid bilayer surrounding the cell. Is selectively permeable.
18
New cards
Light Microscope (Compound Microscope)
light passes through a specimen producing an enlarged image of the object of the specimen
-the lenses bend the light so the image of the specimen is magnified
-the lenses bend the light so the image of the specimen is magnified
19
New cards
Electron Microscope
focuses a beam of electrons through the specimen or onto its surface
-distinguishes biological structures as small as 2 nm
-distinguishes biological structures as small as 2 nm
20
New cards
Transmission Electron Microscope (TEM)
used to see 2-D image of internal structures
21
New cards
Scanning Electron Microscope (SEM)
used to see the 3-D image of a surface
22
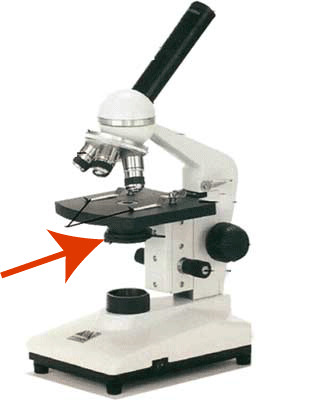
New cards
Coarse Focus Knob
23
New cards
Fine Focus Knob
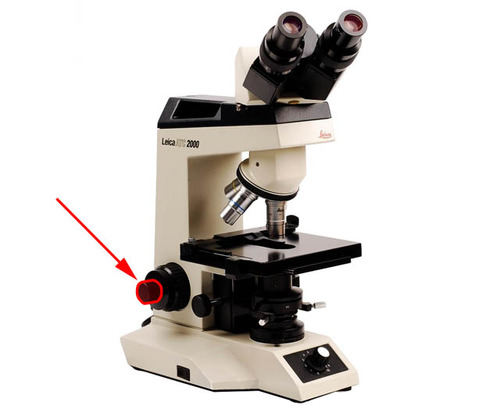
24
New cards
Objective Lenses
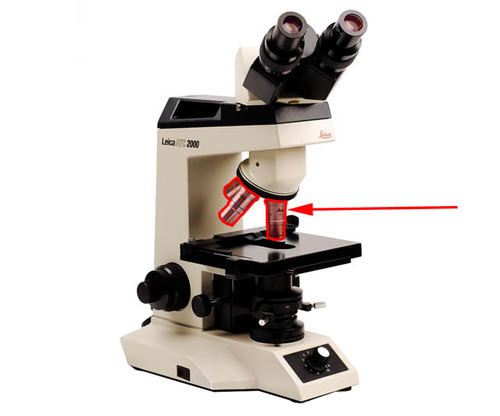
25
New cards
Condenser
focuses light through the specimen
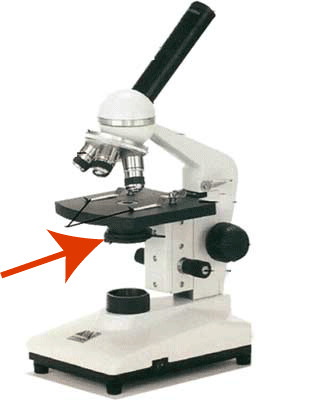
26
New cards
Iris Diaphragm
controls the amount of light passing through the specimen