Unit 4: Imperfect competition Ap Exam review
1/29
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
30 Terms
What are the three markets in a imperfect competition
Monopoly, Monopolistic competition, Oligopily
In imperfect competition when it comes to price, what roles do firms have
They are price setters
In a monopoly do barriers to entry exist
Yes, they are highly present and firms are barred from entering the market
What is a geographical monopoly
When a business has no competition in a certain area meaning they can charge different prices
What is a natural monopoly
When the industry features extreme economies of scale that one firm can serve the market more cheaply than any other firm
On a demand curve in a monopoly, where does the monopoly operate
On the elastic portion because it is the only firm in the market, and it wants to maximize profits and because MR would be negative and TR would be lower and Tc would continue to increase
Why is the demand MR curve below the Demand curve in a monopoly
Because to sell more output the monopolist must lower its price on each additional unit, and each previous unit
What is the profit maximization rule for monoplies
Where marginal reveune=Marginal cost
Why is a monopoly not productively efficent
because it doesn’t produce at the minimum of the ATC
Why is a monopoly not allocatively efficent
because they under-allocate resources because the market has one seller that wants to produce less and price higher
What is deadweight loss
It exists in imperfect competition when a monopoly is not being allocatively efficent
Productively efficent point
MC=Min ATC
Allocatively efficent
MC=P
What is price discrimination
The ability of monopolists to charge consumers different prices for the same good or service to maximize profits
To price discriminate what conditions must occur
The firm must be a price setter or some degree of market power
The firm must prevent reselling
The firm must be able to differentiate customers either individually or by groups
When a firm perfectly price discriminates what happens to DWL and CS
They both become Producer surplus
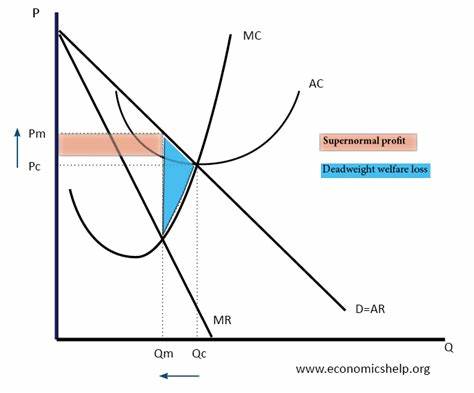
What does a monopoly graph look like?
What does a natural monopoly graph look like
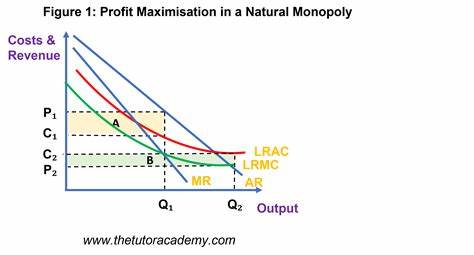
To reduce the DWL that is present in a natural monopoly what does the government do
They regulate the natural monopoly by subsidizing the monpoly
What is monopolistic competition
It is a market type with a multitude of different firms, similar to perfect comp, however, each firm has a slightly differentiated good
Is it possible to earn economic profit in the short run or long run in a monopolistic competition
In the short run yet, but in the long run, no
How is the demand curve different between monopolistic competition and a monopoly
The monopolys demand cruve is less elastic as their is only one firm in the market, while a monopolistic competitions demand curve is more elastic due to the presence of other firms
What do monopolistic competition firms do to gain an edge over each other
They advertise, however, they have to give up some of their resources
What is excess capacity
In the long run, monopolistically competitive markets do not produce enough to achieve the lowest ATC possible and therefore produce less output
What is an oligopoly
When a few firms dominate the market
How do firms act in a oligopoly
They act interdependently meaning that the firms best choices are influenced by one another decisions
What do oligopolies have the incentive to do
Collude to set prices and production
If Oligopolies are left unregulated, what could occur
A cartel which is a formal agreement to not compete but instead behave as a monopoly by determining price and quantity together
Who regulates oligopolies
The government
What is a natural limitation of forming a cartel
Firms within the cartel have an incentive to cheat to maximize profits