UKMLA: Infectious Disease
1/195
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
196 Terms
Gram-Positive Bacteria
Bacteria with a thick peptidoglycan cell wall that stains violet with crystal violet stain
Gram-Negative Bacteria
Bacteria lacking a thick peptidoglycan cell wall, do not retain the crystal violet stain, and instead stain red or pink with a counterstain such as safranin.
Atypical Bacteria
Bacteria that cannot be stained or cultured using standard techniques, including organisms causing atypical pneumonia such as Mycoplasma pneumoniae and Legionella pneumophila.
Beta-Lactam Antibiotics
Antibiotics that inhibit bacterial cell wall synthesis via a beta-lactam ring; examples include penicillins, cephalosporins, and carbapenems.
Non-Beta-Lactam Cell Wall Inhibitors
Antibiotics such as vancomycin and teicoplanin that inhibit bacterial cell wall synthesis without containing a beta-lactam ring
Metronidazole Mechanism Of Action
Inhibits bacterial nucleic acid synthesis, disrupting DNA replication and leading to bacterial death.
Ribosome-Targeting Antibiotics
Macrolides→ -mycin
Tetracyclines→ doxycycline
Gentamycin
Folic Acid Pathway In Bacteria
Para-aminobenzoic acid (PABA) converted to dihydrofolic acid (DHFA)→ tetrahydrofolic acid (THFA)→ folic acid
Blocked by sulfamethoxazole
Trimethoprim Mechanism Of Action
Inhibits the conversion of dihydrofolic acid (DHFA) to tetrahydrofolic acid (THFA)
Gram Stain Procedure
Apply crystal violet stain – stains gram-positive bacteria violet.
Apply counterstain (e.g., safranin) – stains gram-negative bacteria red/pink.
Gram-Positive Cocci
Staphylococcus
Streptococcus
Enterococcus
Gram-Positive Rods
Corynebacteria
Mycobacteria
Listeria
Bacillus
Nocardia
Gram-Positive Anaerobes: CLAP Mneumonic
Clostridium
Lactobacillus
Actinomyces
Propionibacterium
Gram Negative Bacteria
Neisseria meningitidis
Neisseria gonorrhoeae
Haemophilus influenzae
Escherichia coli
Klebsiella
Pseudomonas aeruginosa
Moraxella catarrhalis
MRSA
Staphylococcus aureus that has developed resistance to beta-lactam antibiotics, including penicillins, cephalosporins, and carbapenems
MRSA Eradication Measures
Combination of chlorhexidine body washes and antibacterial nasal creams to eliminate colonisation
Extended-Spectrum Beta-Lactamase (ESBL) Bacteria
Bacteria, usually E. coli or Klebsiella, that produce beta-lactamase enzymes destroying the beta-lactam ring, causing resistance to many antibiotics. Commonly cause UTIs, pneumonia, and septicaemia.
Management Of Extended-Spectrum Beta-Lactamase (ESBL) Bacteria
Nitrofurantoin or phosphomycin
Nitrofurantoin Mechanism Of Action
exclusively for lower urinary tract infections→ bactericidal
Amoxicillin
Used for:
Streptococci
Listeria
Enterococci
Co-Amoxiclav
Used for:
Staphylococci
Haemophilus
E.coli
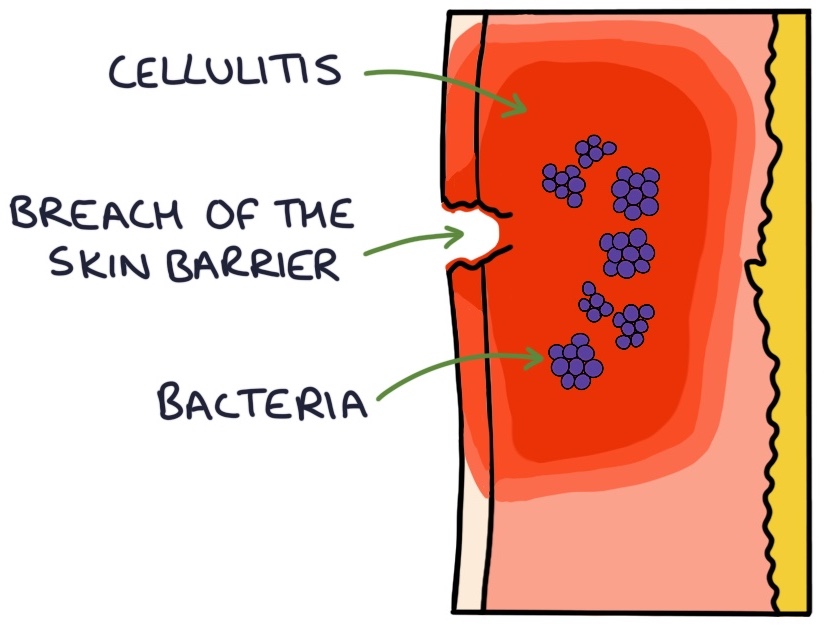
Cellulitis
When a patient presents with cellulitis, look for a breach in the skin barrier and a point of entry for the bacteria. This may be due to skin trauma, eczema, fungal nail infections or ulcers.
Presentation Of Cellulitis
Skin changes in cellulitis include:
Erythema (red discolouration)
Warm or hot to touch
Tense
Thickened
Oedematous
Bullae (fluid-filled blisters)
A golden-yellow crust indicates a Staphylococcus aureusinfection
Eron Classification For Cellulitis
The Eron classification assesses the severity of cellulitis:
Class 1 – no systemic toxicity or comorbidity
Class 2 – systemic toxicity or comorbidity
Class 3 – significant systemic toxicity or significant comorbidity
Class 4 – sepsis or life-threatening infection
Management Of Cellulitis
Class 3 and 4 cellulitis requires admission for intravenous antibiotics. Admission is also considered for frail, very young or immunocompromised patients and those with facial, periorbital or orbital cellulitis.
Flucloxacillin is the usual first-line antibiotic for cellulitis, either oral or intravenous.

Management Of Cellulitis Near Eyes Or Nose
Co-amoxiclav
Clostridium Difficile
Gram positive, rod-shaped anaerobic bacteria
Associated with repeated antibiotic or PPI use
Faecal transmission
Drugs Associated With Causing C.Difficile
Antibiotics and PPI’s:
Clindamycin
Ciprofloxacin (and other fluoroquinolones)
Cephalosporins
Carbapenems (e.g., meropenem)
Presentation Of C.Difficile
Colonisation is usually asymptomatic.
Infection presents with diarrhoea, nausea and abdominal pain.
Severe infection with colitis can present with:
Dehydration
Systemic symptoms (e.g., fever, tachycardia and hypotension)
Diagnosis Of C.Difficile
Diagnosis is based on stool samples. Stools can be tested for:
C. difficile antigen (specifically glutamate dehydrogenase)
A and B toxins (by PCR or enzyme immunoassay)
The antigen test shows whether C. difficile is present but not whether it is producing toxins. The antigen is the initial screening test and is followed up with tests for toxins if C. difficile is identified.
Management Of C.Difficile
Management is with supportive care and oral antibiotics. The options are:
Oral vancomycin (first-line)
Oral fidaxomicin (second-line)
Patients need to be isolated until 48 hours after the last episode of diarrhoea. There is a high recurrence rate.
Faecal microbiota transplantation is an option for recurrent cases. The stool microbiome from a donor is transferred to the patient via capsules, colonoscopy or enema.
Complications Of C.Difficile
Psuedomembranous colitis→ inflammation in large intestine with yellow/white plaques
Toxic megacolon→ severe inflammation. High risk of bowel rupture.
Encephalitis
The most common viral cause is herpes simplex virus (HSV). In children the most common cause is herpes simple type 1 (HSV-1) from cold sores. In neonates it is herpes simplex type 2 (HSV-2) from genital herpes, contracted during birth.
Presentation Of Encephalitis
Altered consciousness
Altered cognition
Unusual behaviour
Acute onset of focal neurological symptoms
Acute onset of focal seizures
Fever
Diagnosis Of Encephalitis
Lumbar puncture, sending cerebrospinal fluid for viral PCRtesting
CT scan if a lumbar puncture is contraindicated
MRI scan after the lumbar puncture to visualise the brain in detail
EEG recording can be helpful in mild or ambiguous symptoms but is not always routinely required
Swabs of other areas can help establish the causative organism, such as throat and vesicle swabs
HIV testing is recommended in all patients with encephalitis
Contraindications to a lumbar puncture include a GCS below 9, haemodynamically unstable, active seizures or post-ictal.
Management Of Encephalitis
Aciclovir treats herpes simplex virus (HSV) and varicella zoster virus (VZV)
Ganciclovir treat cytomegalovirus (CMV)
Repeat lumbar puncture is usually performed to ensure successful treatment prior to stopping antivirals
Complications Of Encephalitis
Lasting fatigue and prolonged recovery
Change in personality or mood
Changes to memory and cognition
Learning disability
Headaches
Chronic pain
Movement disorders
Sensory disturbance
Seizures
Hormonal imbalance
Otitis Media
Otitis media refers to infection in the middle ear
Rhinitis
Rhinitis refers to inflammation of the nasal mucosa
Common Cause Of Ear Nose And Throat Infections
Most ear, nose and throat infections are viral and resolve spontaneously within 1–3 weeks
Indications For Antibiotics In Ent Infections
Antibiotics are reserved for immunocompromised patients, those with significant comorbidities, severe infections, or infections that fail to resolve.
Backup Prescription
A backup prescription allows patients to collect antibiotics if symptoms do not improve or worsen after 3 days
Common Bacterial Cause Of Tonsillitis
Group A Streptococcus (GAS), primarily Streptococcus pyogenes.
Common Bacterial Causes Of Otitis Media Sinusitis And Tonsillitis
Streptococcus pneumoniae, Haemophilus influenzae, Moraxella catarrhalis, and Staphylococcus aureus.
A scoring system giving one point for each of the following: fever >38°C, tonsillar exudates, absence of cough, and tender anterior cervical lymph nodes. A score of 3 or more indicates 40–60% probability of bacterial infection and warrants antibiotics.
Feverpain Score For Bacterial Tonsillitis
A scoring system with one point each for: fever in previous 24 hours, purulence on tonsils, attended within 3 days of onset, inflamed tonsils, and no cough or coryza. Scores of 2–3 indicate 34–40% probability; 4–5 indicate 62–65% probability of bacterial tonsillitis.
First-Line Antibiotic For Bacterial Tonsillitis
Penicillin V (phenoxymethylpenicillin) for 10 days, effective against Streptococcus pyogenes.
Alternative Antibiotic For Tonsillitis In Penicillin Allergy
Clarithromycin
Complications Of Tonsillitis
Peritonsillar abscess (quinsy), otitis media, scarlet fever, rheumatic fever, post-streptococcal glomerulonephritis, and post-streptococcal reactive arthritis
Presentation Of Otitis Media
Reduced hearing and ear pain with a bulging red tympanic membrane on otoscopy. Perforation may cause ear discharge.
Natural Course Of Otitis Media
Usually resolves within 3–7 days without antibiotics. Admission may be required if systemically unwell.
First-Line Antibiotic For Otitis Media
Amoxicillin for 5–7 days.
Second-Line Antibiotic For Otitis Media
Co-amoxiclav if infection is not responding to amoxicillin.
Duration Of Sinusitis
Acute sinusitis typically lasts 2–3 weeks and resolves without treatment.
Management Of Sinusitis Not Improving After 10 Days
High-dose steroid nasal spray for 14 days (e.g., mometasone 200 mcg twice daily) or a backup antibiotic prescription (phenoxymethylpenicillin first-line)
Management Of Chronic Sinusitis
Saline nasal irrigation, steroid nasal sprays or drops (e.g., mometasone or fluticasone), and functional endoscopic sinus surgery (FESS)
Acute Gastritis
Stomach inflammation and epigastric discomfort, nausea and vomiting
Enteritis
Inflammation of the intestines, abdominal pain and diarrhoea
E Coli
E. coli 0157 produces the Shiga toxin. The Shiga toxin causes abdominal cramps, bloody diarrhoea and vomiting. It also destroys blood cells, leading to haemolytic uraemic syndrome (HUS)
Use Of Antibiotics With E.Coli Infection
The use of antibiotics increases the risk of haemolytic uraemic syndrome. Therefore, antibiotics should be avoided if E. coligastroenteritis is a possibility.
Campylobacter Jejuni
Campylobacter is a common cause of travellers’ diarrhoea
Most common cause of gastroenteritis
Gram-negative, curved or spiral bacteria
Spread via raw poultry, untreated water, raw milk
Symptoms Of Campylobacter Jejuni
Incubation is usually 2 to 5 days. Symptoms resolve after 3 to 6 days. Symptoms are:
Abdominal cramps
Diarrhoea often with blood
Vomiting
Fever
Management Of Campylobacter Jejuni
Clarithromycin is often first-line. Azithromycin and ciprofloxacin are alternative options.
Shigella
Spread via faeces (person or contamination)
1-2 days incubation period
Symptoms resolve within 1 week: bloody diarrhoea, cramps and fever
Manage via azithromycin
Salmonella
Raw eggs, raw poultry or animal-faeces contaminated food
12 hours to 3 days incubation period Symptoms resolve d
Symptoms: watery diarrhoea, vomiting, pain
Bacillus Cereus
Gram positive rod
Contaminated cooked food
Cerulide toxin→ cramping and vomitting within 5 hours of ingestion
The typical course is vomiting within 5 hours, diarrhoea after 8 hours and resolution within 24 hours.
Yersinia Enterocolitica
Gram-negative bacillus
Raw or undercooked pork
Typically affects children
4-7 days incubation period
Symptoms over 3 weeks: right-sided abdominal pain
Staphylococcus Enterotoxins
Eggs, meat, dairy
Symptoms of diarrhoea, vomiting, abdominal cramps and fever. These symptoms start within hours of ingestion and settle within 12 to 24 hours
Giardiasis
Parasite in small intestine of animals→ cysts in faeces contaminate food or water
Manage via tinidazole or metronidazole
Oral Rehydration Solution
These contain glucose, potassium and sodium
Anti-diarrhoeal Drug
Loperamide
Anti-emetic Drug
Metoclopramide
Hepatitis B
DNA virus→ sharing toothbrushes, sex, blood, minor cuts, vertical transmission
Hepatitis B In Children
The risk of developing chronic hepatitis Bafter exposure is:
90% for neonates
30% for children under 5
Under 10% for adolescents
Children To Test For Hepatitis B
Children of hepatitis B positive mums (screen at 12 months of age or any time after that)
Migrants from endemic areas
Close contacts of patients with hepatitis B
Hepatitis B Positive Mothers
reduce the risk of the baby contracting hepatitis B, at birth (within 24 hours) neonates with hepatitis B positive mothers should be given both:
Hepatitis B vaccine
Hepatitis B immunoglobulin infusion
Infants are given an additional hepatitis B vaccine at 1 and 12 months of age. They will also receive the hepatitis B vaccine as part of the normal 6 in 1 vaccine given to all infants aged 8, 12 and 16 weeks. They are tested for the HBsAg at 1 year to see if they have contracted hepatitis B.
Complications Of Hepatitis B
Where there is evidence of hepatitis or cirrhosis, treatment with antiviral medications may be considered.
Hepatitis B Screening
When screening for hepatitis B, test HBcAb (for previous infection) and HBsAg (for active infection). If these are positive do further testing for HBeAg and viral load (HBV DNA).
HBsAb demonstrates an immune response to HBsAg. The HBsAg is given in the vaccine, so having a positive HBsAb may simply indicate they have been vaccinated and created an immune response to the vaccine.HBV DNA).
Hepatitis C
RNA virus
NO vaccine available
Curable in adults via direct acting antiviral medications
Hepatitis C Disease Course
In adults:
1 in 4 fight off the virus and make a full recovery
3 in 4 develop chronic hepatitis C
Complications:
Liver cirrhosis and associated complications of cirrhosis
Hepatocellular carcinoma
Investigations For Hepatitis C
Hepatitis C antibody is the screening test
Hepatitis C RNA testing is used to confirm the diagnosis of hepatitis C, calculate viral load and identify the genotype
Hepatitis C And Breastfeeding/Pregnancy
Babies to hepatitis C positive mothers are tested at 18 months of age using the hepatitis C antibody test. Breastfeeding has not been found to spread hepatitis C, so mothers are free to breastfeed their babies. If nipples become cracked or bleed breastfeeding should temporarily stop whilst they heal.
Management Of Hepatitis C In Children
Medical treatment may be considered in children over 3 years. Treatment in childhood involves pegylated interferon and ribavirin
Treatment is typically delayed until adulthood unless the child is significantly affected, because children are usually asymptomatic and newly available treatment for adults is highly effective.
Infectious Mononucleosis
Infectious mononucleosis (IM) is a condition caused by infection with the Epstein Barr virus (EBV). It is commonly known as the “kissing disease”, “glandular fever” or “mono”. This virus is found in the saliva of infected individuals.
Symptoms Of Infectious Mononucleosis
Typical symptoms are fever, sore throat, fatigue, splenomegaly
May cause itchy maculopapular rash in response to amoxicillin
Monospot Test
Monospot test: this introduces the patient’s blood to red blood cells from horses. Heterophile antibodies (if present) will react to the horse red blood cells and give a positive result.
Paul-Bunnell Test
Paul-Bunnell test: this is similar to the monospot test but uses red blood cells from sheep.
Specific Epstein-Barr Virus Antibody Tests
It is possible to test for specific EBV antibodies. These antibodies target something called viral capsid antigen (VCA):
The IgM antibody rises early and suggests acute infection
The IgG antibody persists after the condition and suggests immunity
Management And Prognosis Of Infectious Mononucleosis
Infectious mononucleosis is usually self limiting. The acute illness lasts around 2 – 3 weeks, however it can leave the patient with fatigue for several months once the infection is cleared.
Patients are advised to avoid alcohol, as EBV impacts the ability of the liver to process the alcohol. Patients are advised to avoid contact sports due to the risk of splenic rupture. Emergency surgery is usually required if splenic rupture occurs.
Complications Of Epstein-Barr Virus
Splenic rupture
Glomerulonephritis
Haemolytic anaemia
Thrombocytopenia
Chronic fatigue
EBV infection is associated with certain cancers, notable Burkitt’s lymphoma.
Influenza
RNA virus
A,B,C → affects humans
D→ affects cattle
Influenza Vaccination
The flu vaccine is free on the NHS to people at higher risk of developing flu or flu-related complications:
Aged 65 and over
Young children
Pregnant women
Chronic health conditions, such as asthma, COPD, heart failure and diabetes
Healthcare workers and carers
Presentation Of Influenza
The delay between exposure and symptoms is usually around 2 days. Typical presenting features include:
Fever
Lethargy and fatigue
Anorexia (loss of appetite)
Muscle and joint aches
Headache
Dry cough
Sore throat
Coryzal symptoms
Management Of Influenza
Oral oseltamivir (twice daily for 5 days)
Inhaled zanamivir (twice daily for 5 days)
Treatment needs to be started within 48 hours of the onset of symptoms to be effective.
Malaria
Protozoan parasites→ plasmodium falciparum
Bite of female anopheles mosquitoes