Comprehensive Guide to Cardiovascular Disease, ECG Interpretation, and Emergency Care
1/117
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
118 Terms
Cardiovascular Disease (CVD)
CVD mortality in both Canada and NL accounts for 30% of all causes of death.
CVD morbidity
CVD results in significant morbidity from MIs and CVAs.
CVD costs in Canada
CVD costs in Canada over $22 billion.
Hospitalizations cost
Hospitalizations inpatient 2.4 billion.
Lost productivity and disability from stroke
Lost productivity and disability from stroke 3.6 billion.
CV drugs utilization
6/10 major drugs are CVD related.
Risk factors for CVD
Hypertension, Family history, Ethnicity, Age, Stress, Lack of physical activity/sedentary behaviour, Poor nutrition, Sleep apnea, Obesity, High alcohol consumption, Smoking or vaping, Substances, e.g. cocaine, Dyslipidemia, Diabetes, Chronic kidney disease.
Sex and Gender Considerations
Risk factors for cardiovascular diseases.
Types of CVDs
CAD (IHD) decreased blood supply to the coronary vessels and muscle causes chest pain/angina.
Heart Failure
Left or right-sided decreased perfusion chronic tiredness, reduced physical activity and shortness of breath, edema.
Cardiomyopathy
Thickened or stiffness affects contractility and cardiac output.
Valvular heart disease
Heart valve dysfunction due to calcification, drugs, infection.
PAD/PVD
Decreased circulation, coolness, paresthesia and limb pain.
Renal perfusion
Decreased.
Social determinants of health (SDOH)
Social, economic, and environmental influences on health.
Health inequities
Unfair or unjust and modifiable.
Access to nutritious foods
Canadians who live in remote or northern regions do not have the same access to nutritious foods such as fruits and vegetables as other Canadians.
Increased screening for risk factors
Decreased morbidity and mortality and decreased costs and promote healthy aging.
CVD emergency care
Discuss the care of an adult patient experiencing 'chest pain' during a CVD emergency.
Professional practice guidelines
Explore professional practice guidelines for chest pain and arrhythmias.
Cardiac arrhythmias
Review cardiac arrhythmias, etiologies, signs and symptoms, and recommended treatments.
Effective communication
Communicate and collaborate effectively as a member of the health care team.
Congenital disorders
Disorders of the heart or central blood vessels present at birth that lead to heart failure, pulmonary HTN, delayed growth.
Electrical conduction dysfunction
Can lead to blood pressure issues, decreased cardiac output, and death.
ECG Interpretation
To understand the electrical conduction of the heart and to identify and interpret normal sinus rhythm and common abnormal cardiac rhythms or arrhythmias.
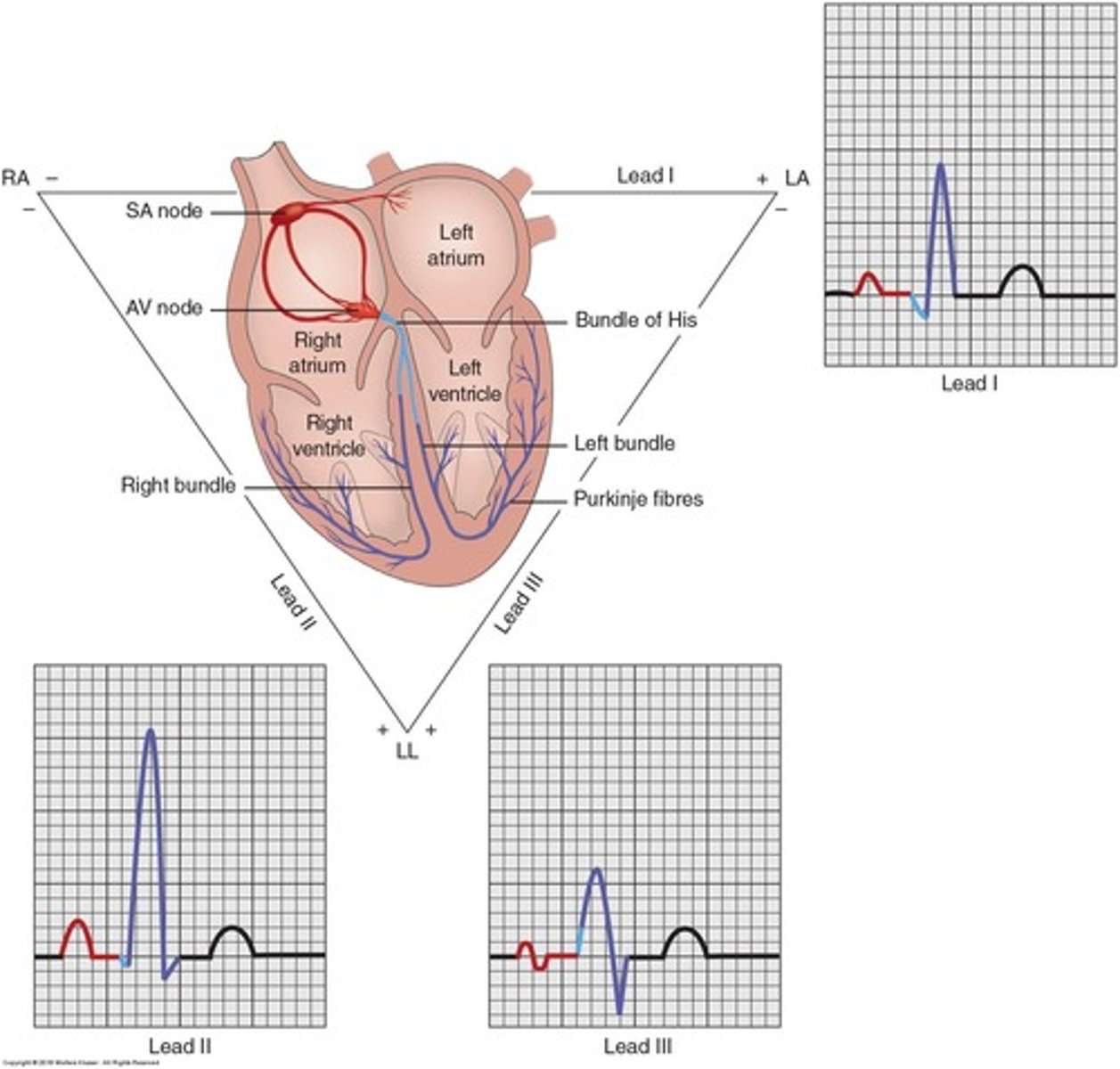
P wave
Atrial depolarization.
QRS complex
Ventricular depolarization.
T wave
Ventricular repolarization or the 'resting state'.
EKG Paper
Used for EKG interpretation.
8 Step Approach
A systematic approach for consistency with each strip that you interpret.
Heart rhythm
Regular or irregular; determined by the evenness of small boxes between each R wave.
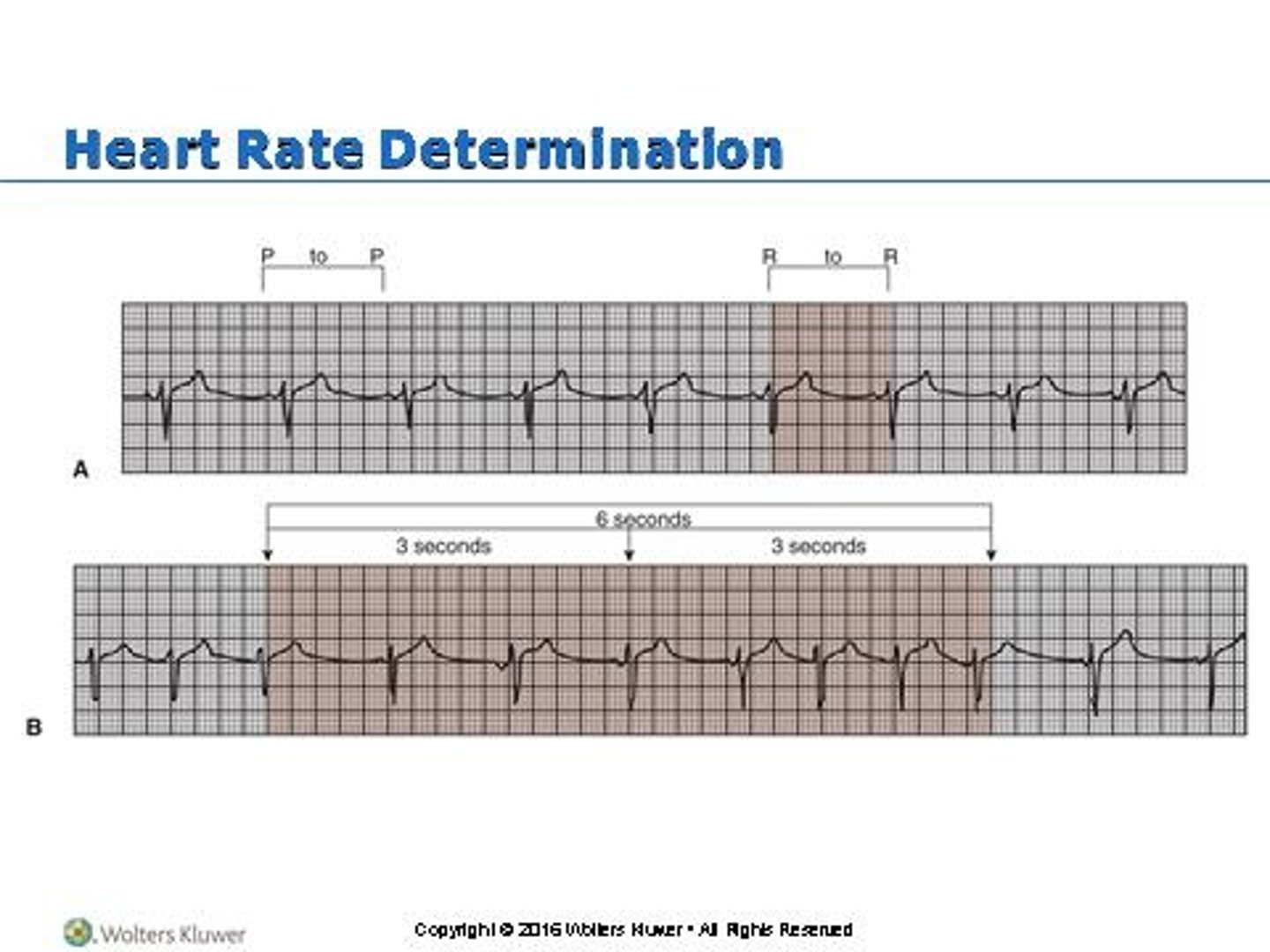
Heart rate
6 second strip method: count number of QRS complexes in six seconds and multiply by 10.
Presence of P wave
P wave should be rounded and upright, indicating SA node pacing.
PR interval
Measured from the beginning of P to the start of QRS, should be 0.12-0.20 seconds.
Width of QRS complex
Should be 0.08-0.12 seconds (1½ to 3 small boxes) and less than <0.12 sec.
ST segment
Should be at the isoelectric line; deviations may indicate myocardial ischemia or infarction.
QT interval
0.34-0.42 seconds; time required for depolarization and repolarization of the ventricles.
T wave abnormalities
Peaked T waves could indicate high potassium or hyperkalemia.
Normal sinus rhythm
1. Rhythm: regular; 2. Rate: 80 (60 -100); 3. P wave: one in front of every QRS, round, consistent shape; 4. PR interval: 0.16 sec (0.12-0.20); 5. QRS: 0.04 sec (<0.12 sec); 6. ST Segment: no depression or elevation; 7. QT interval: 0.36 sec (0.34-0.42).
Normal Sinus Rhythm (NSR)
Interpretation of T wave
Sinus Bradycardia
Same as NSR except for RATE <60 bpm
Sinus Tachycardia
Same as NSR except for RATE >100 bpm
Atrial Arrhythmias
When the SA node does not generate an impulse, atrial tissues in various locations may initiate impulses
Atrial flutter
Caution: may cause thromboemboli
Atrial fibrillation
Caution: may cause thromboemboli
Supraventricular tachycardia
1. Rhythm: Usually regular 2. Rate: 150-250 bpm 3. P wave may be buried in the previous T wave 4. PR interval: less than < 0.12 sec 5. QRS complex: less than < 0.12 sec 6. ST segment: cannot assess 7. QT interval: unable to assess 8. T wave: difficult to assess; impulse originates at or above the AV node
Ventricular Arrhythmias
No P waves because there is no atrial activity or depolarization; SA node and the AV junctional tissues do not generate an impulse & ventricles **************** of the 'pacemaker'; QRS complex > 0.12 sec; QRS has 'bizarre shape'
Premature Ventricular Contractions
Includes Bigeminy: every second beat PVC
Ventricular Tachycardia (VT)
3 PVC's, rate >100 bpm; can have a pulse or be pulseless; if not treated patient may go into cardiopulmonary arrest; 1. Rhythm: mostly regular 2. Rate: ventricular 100-250 bpm; can't tell atrial 3. P wave: can't see, not associated with QRS wave 4. PR interval: can't measure 5. QRS > 0.12 sec, wide and abnormal shape; hard to determine P: QRS ratio, QT interval, T wave; Monomorphic or polymorphic
Ventricular Tachycardia (Polymorphic)
Torsades de pointes
Ventricular Fibrillation
No pulse or cardiac output; Cardiopulmonary arrest; 'quivering ventricles'; Rate: ventricles > 300 bpm; Rhythm: Irregular; QRS: bizarre...no shape; P wave: none; PR interval: none; Coarse or Fine
Asystole
Check Your Patient !! No QRS; check in two leads; No pulse, no respirations; Patient is clinically dead
Heart blocks
First degree block, Second degree block (type I and type II), Third degree block
Third degree heart block
No atrial impulse conducted via AV node to ventricle; Two pulses generated: one stimulates ventricle and one stimulates the atria, thus AV dissociation; No association between P waves and QRS or atria and ventricle; Rate: depends on atrial and ventricular underlying rhythm; Rhythm: PP interval and RR interval both regular but not equal so 'beating out of sync'; QRS & duration: normal or abnormal; PR interval irregular; More P waves than QRS complexes
Ventricular pacemaker rhythm
Single chamber
Atrioventricular pacemaker rhythm
Dual chamber
Chest Pain
Chest pain is one of the most common presentations to the emergency department and outpatient settings.
Acute Coronary Syndrome (ACS)
Chest pain is the most common symptom of myocardial ischemia in both men and women.
Severity Scale
Scale of 1-10.
Chest Pain Symptoms
Heaviness, tightness, pressure, fatigue.
Chest Pain Location
Varies: central, left arm, right arm, neck, jaw, shoulder, back.
Chest Pain Timing
Occurs during strenuous activity, mild activity, or at rest.
Chest Pain Duration
A few seconds, minutes, hours.
Aggravating Factors
Cold, exercise.
Alleviating Factors
Rest, medications.
Chest Pain Treatment
Immediate implementing the Chest Pain Protocol.
Chest Pain Medications
Long-acting nitrates, beta blockers, calcium channel blockers.
Chest Pain Investigations
Exercise stress test, coronary angiogram, echocardiogram, other.
ST-Elevation Myocardial Infarction (STEMI)
Ischemia 6/7 - STEMI on ECG.
STEMI Treatment
ECG monitor, oxygen, morphine IV, nitroglycerine IV, ASA orally, clopidogrel or Plavix orally, anticoagulation (enoxaparin/Lovenox s/c and/or IV), bloodwork (troponin level, CBC, Lytes, UN, Cr, arterial blood gas (ABG)).
Nitroglycerin IV Indications
ACS, MI.
Nitroglycerin IV Dosage
Available in: 25mg/250 mL, 50mg/250 mL, 100 mg/250 mL bottle, 5mg/mL injectable solution.
Nitroglycerin IV Administration
5-200 mcg/min starting at 5 mcg/min, titrate to effect, keep BP >90mmHg.
Sinus Bradycardia Symptoms
Dizziness, chest pain, shortness of breath, exercise intolerance, cool, clammy skin.
Sinus Bradycardia Treatment
Prevent vagal response, hold medications e.g., beta blockers, atropine, epinephrine, dopamine.
Pacemaker
Treat the underlying cause
Hypoglycemia
Consider cardiac history
Hypothermia
Medications
Hypothyroidism
Electrolyte imbalance
Atropine IV

Epinephrine IV
Indications: Bradycardia, 2-10 mcg/min IV infusion
Dopamine IV
Indications: Low dose - renal perfusion, Increase cardiac output, Bradycardia, Vasoconstriction to raise BP. Available in: 400 mg/250 mL, 800 mg/250 mL, 800 mg/500 mL. Dose: 2-5 mcg/kg/min up to 20 mcg/kg/min
Sinus tachycardia S & S
Dizziness, SOB, Heart palpitations, Fast pulse, Chest pain
Sinus tachycardia Treatment
Treat symptoms & underlying cause: Adenosine, Diltiazem, Beta blockers, Ablation of SA node
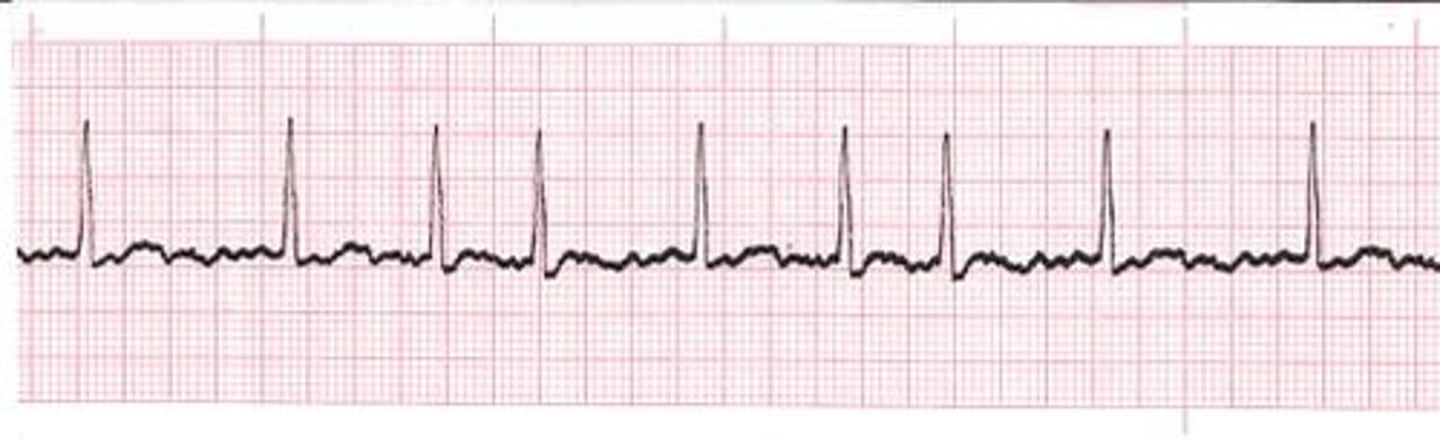
Atrial flutter S & S
Palpitations, SOB, Anxiety, Weakness, Chest pain, Hypotension
Atrial Flutter Causes
> 60 years of age, Heart disease (Valve dysfunction), Ischemia, Cardiomyopathy, COPD, Emphysema, Post CV surgery, Hyperthyroidism
Atrial Flutter Treatment
Anticoagulation therapy usually required, Cardioversion: If symptomatic & onset <48 hours, Meds to slow rate (beta blockers, calcium channel blockers), Ablation
Atrial Fibrillation Symptoms
Palpitations 'racing heart', Irregular pulse, Chest pain, Dizziness, Fainting, Decrease LOC, Fatigue, SOB
Atrial Fibrillation Causes
Hypoxia, Hypertension, Stimulants, Heart failure, CAD/Valve dysfunction, SA node problem, Rheumatic heart disease, Pericarditis, Hyperthyroidism, Post CV surgery
Atrial Fibrillation Treatment
If hemodynamically stable: anticoagulant therapy (heparin, lovenox, xarelto, warfarin) and may consider other treatments to stop fibrillation. If hemodynamically unstable: cardioversion (Electrical, Pharmacological (beta blockers, amiodarone, digoxin)). If onset >48 hours: need anticoagulant therapy or risk of thrombus formation and emboli. Pacemaker or Ablation
Amiodarone IV
Indications: atrial fibrillation. Dose: 150-300 mg IV push, then 150 mg IV q 3-5 min. Dose dependent on severity of symptoms. IV infusion.
Metoprolol IV
Indications: Atrial fibrillation, Narrow complex tachycardia. Dose: 5 mg over 1-2 min, and repeat q5 min to a max dose of 15 mg.
Digoxin IV
Used for atrial fibrillation, atrial flutter and heart failure. Dose: 8-12 mcg/kg total loading dose, give 50% of dose first then q6-8h after give remaining loading dose in 2 separate doses.
Adenosine IV
Used for: SVT. Dose: 6mg rapid IV push over 1-3 seconds followed by NS flush and then if rhythm persists, 6 mg rapid IV push followed by NS flush.
Bigeminy
every second beat PVC
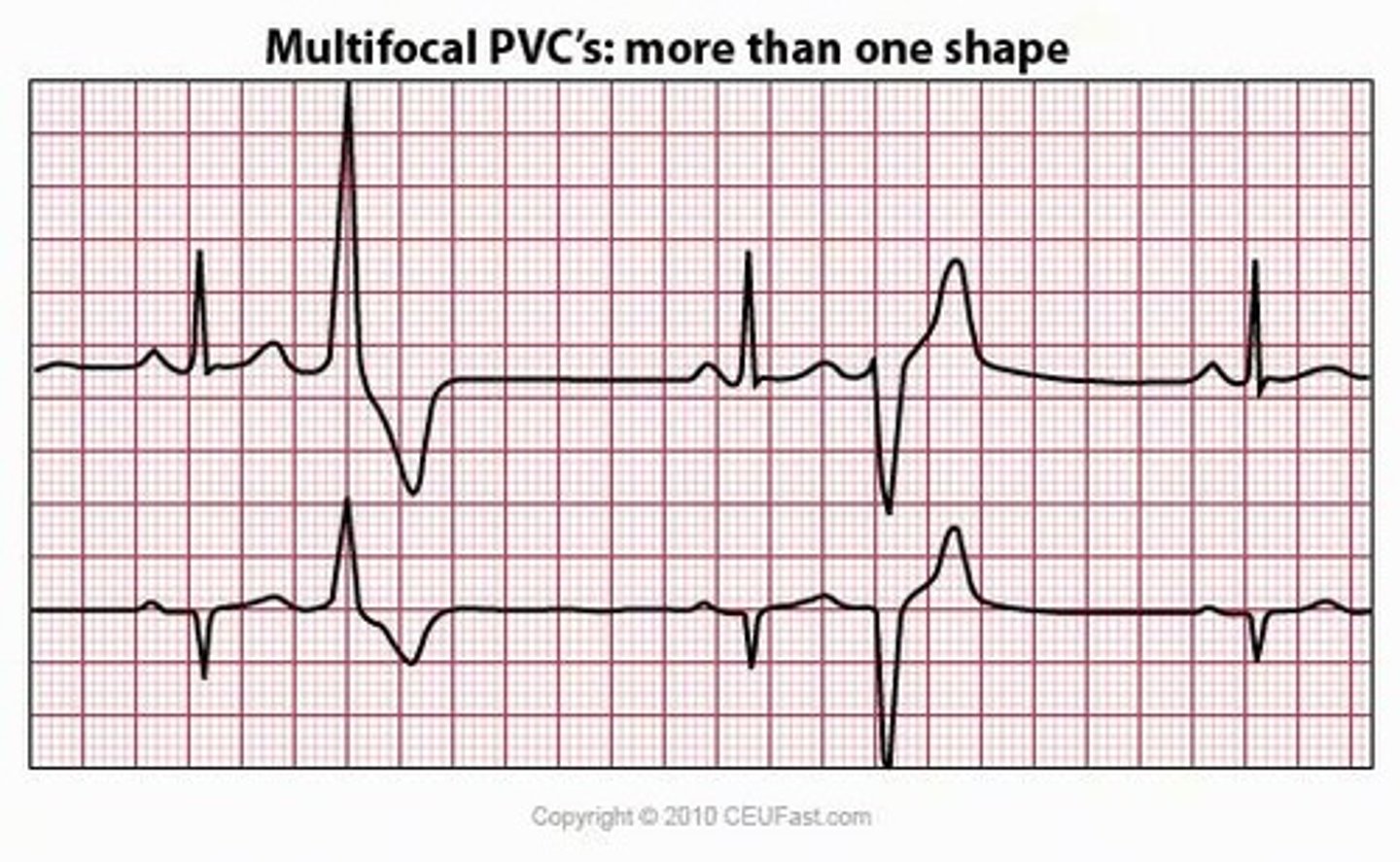
Premature Ventricular Contractions Causes
Exercise, Stress, Stimulants, Heart disease, Electrolyte imbalances, Hypoxia, Tricyclic antidepressants, Digitalis toxicity
Premature Ventricular Contractions Symptoms
Palpitations, Weakness/Dizziness, Hypotension, SOB
Treatment for Premature Ventricular Contractions
depends on frequency or if multifocal; Amiodarone, Lidocaine
Ventricular Tachycardia (Monomorphic) Treatment
Amiodarone IV
Ventricular Tachycardia (Monomorphic) Indications
ventricular tachycardia, ventricular fibrillation