5) Orbital Hybridisation (Valence Bond Theory)
1/24
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
25 Terms
Define hybridisation.
The combining of valence orbitals to create orbitals of equal energy (degenerate).
What is orbital hybridisation?
What is this concept a part of?
Orbital hybridisation: mixing of atomic orbitals.
The Hybrid Orbital Approach (HOA).
In HOA, how are these bonds formed?
Via the overlap of atomic orbitals.
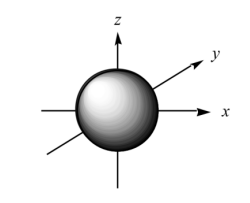
What is the name of this orbital?
State the shape and electron density distribution.
s orbital.
Spherical and electron density in all directions.
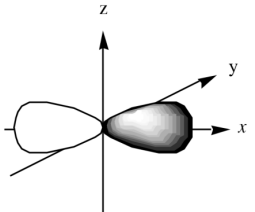
What is the name of this orbital?
State the electron density distribution.
p orbital.
Electron density greatest along x-axis.
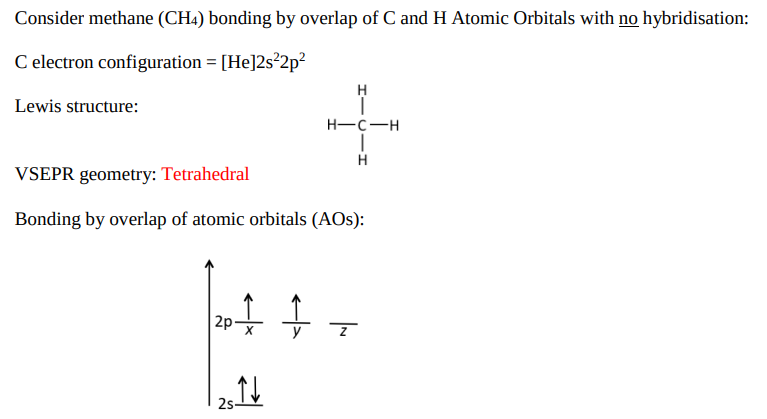
Why is the Hybridisation Model necessary for the example shown? (3)
The two p orbitals have an unpaired electron each (2 bonds to C only).
To form 4 bonds, you need 4 unpaired electrons.
As C is bonded to 4 other H atoms, we need electron promotion to occur.
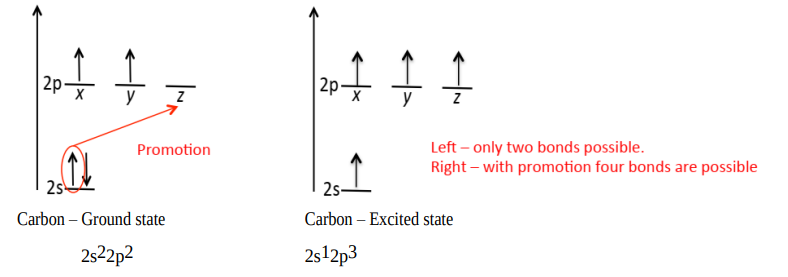
Draw the diagram of C after promotion.
What can s, p and d orbitals mix (hybridise) to form?
What does sp hybrid mean?
What does sp² hybrid mean?
What does sp³ hybrid mean?
They mix to form / give hybid orbitals.
sp - 1 x s orbital + 1 x p orbital.
sp² - 1 x s orbital + 2 x p orbitals.
sp³ - 1 x s orbital + 3 x p orbital.
Fill in the blanks:
…… in same ….. ……. (same quantum number n).
Orbitals of a type are …… equivalent in every respect.
The number pf hybrid orbitals formed equals the number of …, …, ….
All, valence shell.
Equivalent.
s, p, d.
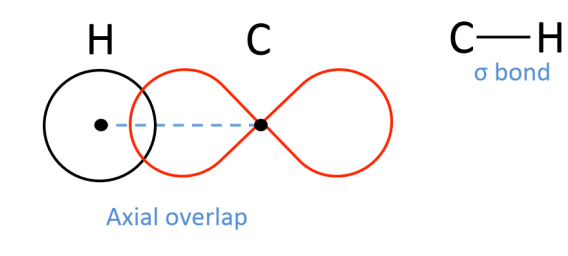
What is the name of this bond called?
How are they formed?
Is it strong or weak?
Sigma bond.
They form when you have axial orbital overlap. Overlap allows unpaired electrons to pair permitting bond formation.
Strong.
What does the axial overlap achieve in a sigma bond?
It achieves maximum orbital overlap (maximum electron density overlap).
Draw the orbital hybridisation diagram for methane, starting with it in the ground state, then the excited state and the final hybrid state.
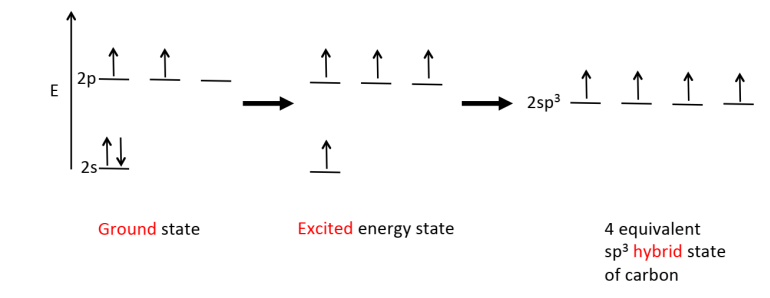
Why must orbital hybridisation of methane occur?
Without it, bonds formed from overlap of the C atom s & p AOs wouldn’t be equivalent.
After hybridisation, overlap of the 4 equivalent sp³ orbitals with 4 H atom s orbitals will give 4 equivalent bonds.
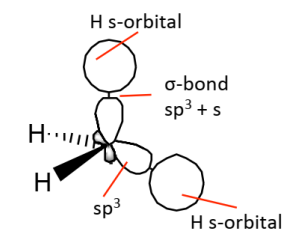
Generally, carbon is …….. ……… when it’s directly bound to 4 atoms.
sp³ hybridised
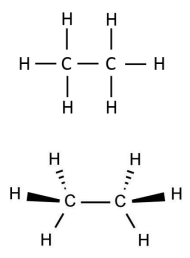
How many sigma bonds does ethane have?
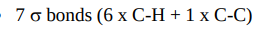
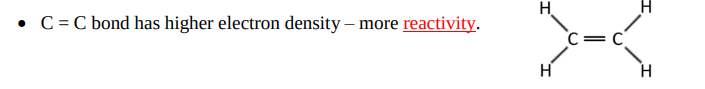
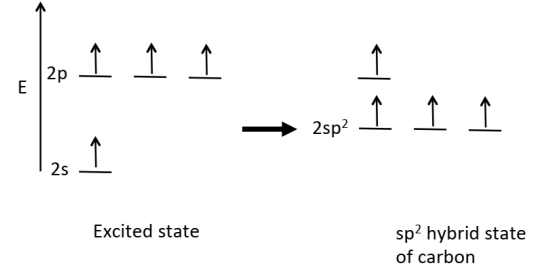
Draw the excited state and the hybrid state of ethene.
How would 3 equivalent bonds arise in ethene?
Equivalent bonds could arise if the carbon s orbital hybridises (mixes) with 2 of the p orbitals.
In ethane & ethene, what is the geometry shape around each C atom?
Ethane: tetrahedral.
Ethene: trigonal planar.
However in ethene, there is a remaining p orbital with an unpaired electron that’s perpendicular to the plane of sp² orbitals. Why can axial overlap of this remaining orbital NOT occur?
Where does overlap instead occur?
They are out of plane and there is 0 electron density along the C-C bond axis.
Above and below bond axis.
What does the overlap above and below the bond axis result in?
What does both this bond and a sigma bond make?
Results in a weaker overlap and a weaker bond called a pi bond.
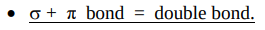
We get restricted movement around the double bond. Why is this?
What does no rotation around the double bond lead to?
Looking at the pi part of the double bond, p orbital overlap would be destroyed by rotation of C atoms as they are very weak.
Leads to isomers.
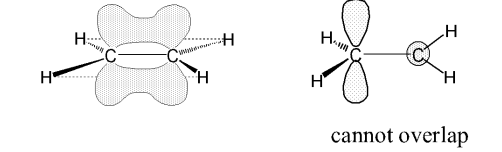
In general, carbon will be … ….. when bound directly to 3 other atoms.
sp² hybridised
How many bonds does ethyne have between C atoms?
Draw the excited electron state and the hybrid state diagrams of ethyne.
3
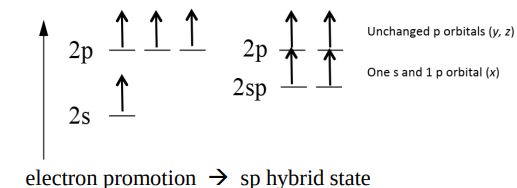
Ethyne has sp orbitals. Why do sp orbitals have a greater degree of s character?
Ethyne forms 2 equivalent sigma bonds to the H atoms and there’s also one found between C atoms. What happens to the 2 remaining 2p orbitals and their unpaired electrons?
Has a greater degree of s character due to 50% s and 50% p.
They overlap to form 2 pi bonds.
In general, carbon will be …. …. when directly bound to 2 other atoms.
sp hybridised
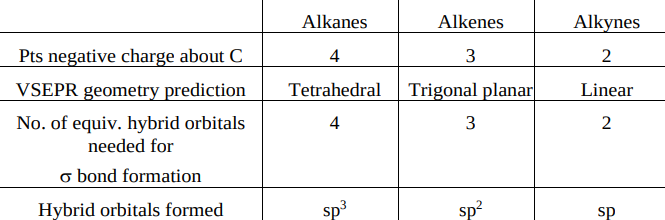
General learning table