Wave Speed
1/39
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
40 Terms
Linear Density (μ)
The mass per unit length of a string, defined as μ = m / l.
Constant Linear Density
A condition where the mass per unit length of a string is uniform along its entire length.
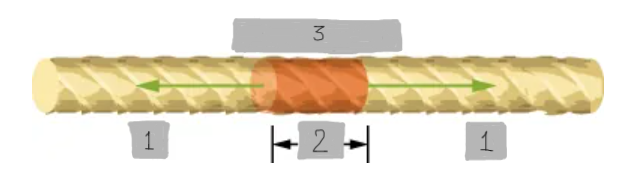
Mass Element of a String
A small segment of a string with mass Δm = μΔx, used for analyzing wave motion.
Tension in a String (F1)
The force that keeps a string taut and provides the restoring force for transverse waves.
Transverse Wave
A wave in which elements of the medium oscillate perpendicular to the direction of wave propagation.
Restoring Force
The force that acts to return a displaced string element toward its equilibrium position.
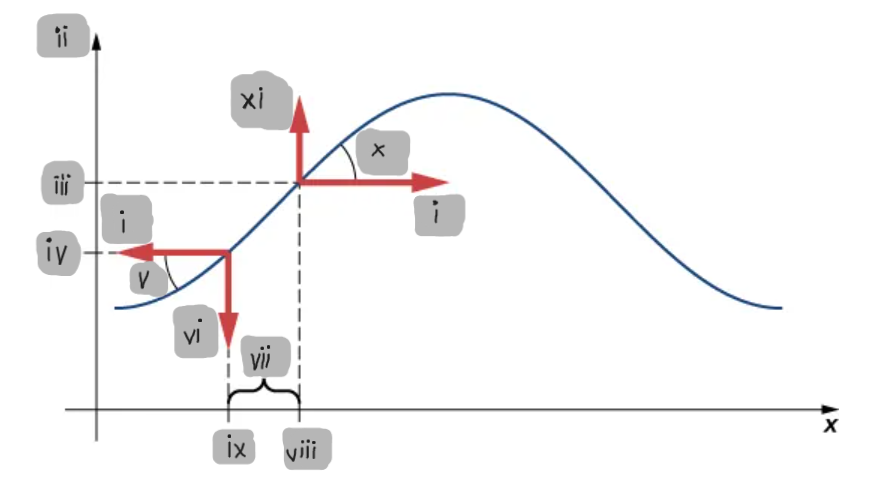
Small-Angle Approximation
The assumption that the slope of the string is small, allowing tanθ ≈ sinθ ≈ ∂y/∂x.
Net Force on a String Element
The difference between the vertical components of the tension forces acting on either side of a small mass element.
Linear Wave Equation
A differential equation describing wave motion, given by
∂²y/∂x² = (1/v²) ∂²y/∂t².
Wave Speed on a String
The speed at which a wave travels along a string, determined by tension and linear density.
Wave Speed Formula (String)
v = √(Fₜ / μ), where Fₜ is the string tension and μ is the linear density.
Dependence of Wave Speed (String)
Wave speed increases with greater tension and decreases with greater linear density.
Elastic Property of a Medium
A measure of how strongly a medium resists deformation and returns to its original shape.
Inertial Property of a Medium
A measure of how strongly a medium resists changes in motion.
General Wave Speed Relation
Wave speed is proportional to the square root of the elastic property divided by the inertial property.
F_T
(1)
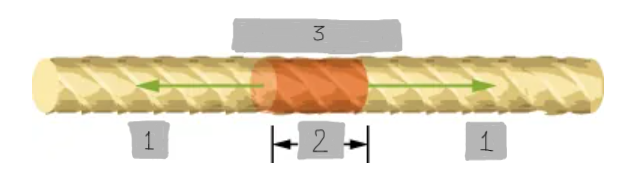
Δx
(2)
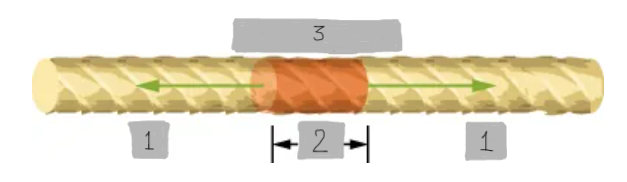
Δm = μΔx
(3)
Longitudinal Wave
A wave in which particles of the medium oscillate parallel to the direction of wave propagation.
Bulk Modulus (B)
A measure of a material’s resistance to compression, defined as
B = −ΔP / (ΔV / V₀).
Density (ρ)
Mass per unit volume of a material, defined as ρ = m / V.
Speed of Compression Waves in a Fluid
The speed of a longitudinal wave in a fluid, given by v = √(B / ρ).
Speed of Sound
The speed at which mechanical compression waves propagate through a medium.
Temperature Dependence of Sound Speed
The speed of sound in air varies with temperature because air density depends on temperature.
Wavelength (λ)
The distance between successive points of identical phase in a wave.
Frequency–Speed Relationship
The frequency of a wave is proportional to its speed when the wavelength is fixed.
Tuning of Guitar Strings
Adjusting the tension of strings to change wave speed and therefore the frequency produced
Boundary Conditions
Constraints at the ends of a string that determine allowed wavelengths
Changing Pitch on a String
Altering pitch by changing the effective length of the string while tension remains fixed.
F_T
(i)
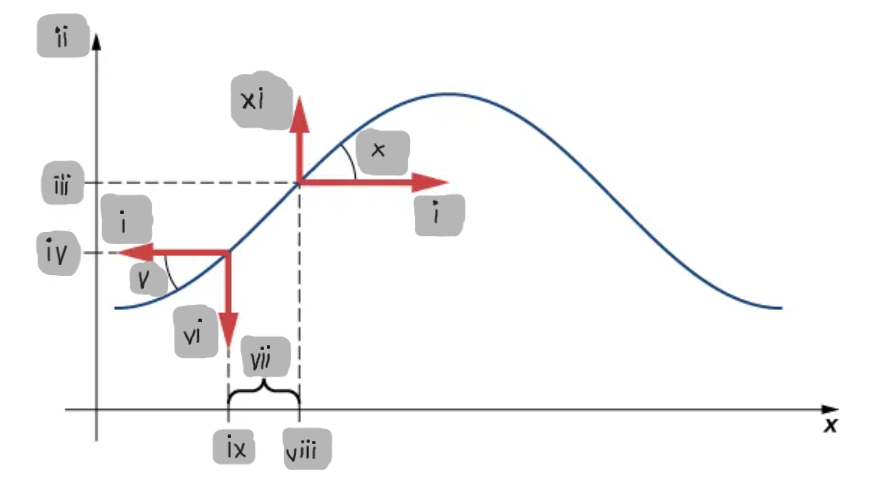
y
(ii)
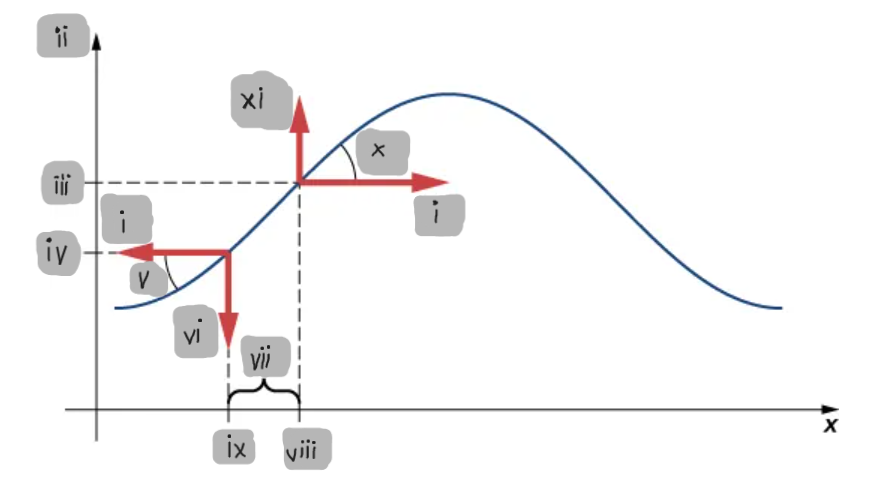
y2
(iii)
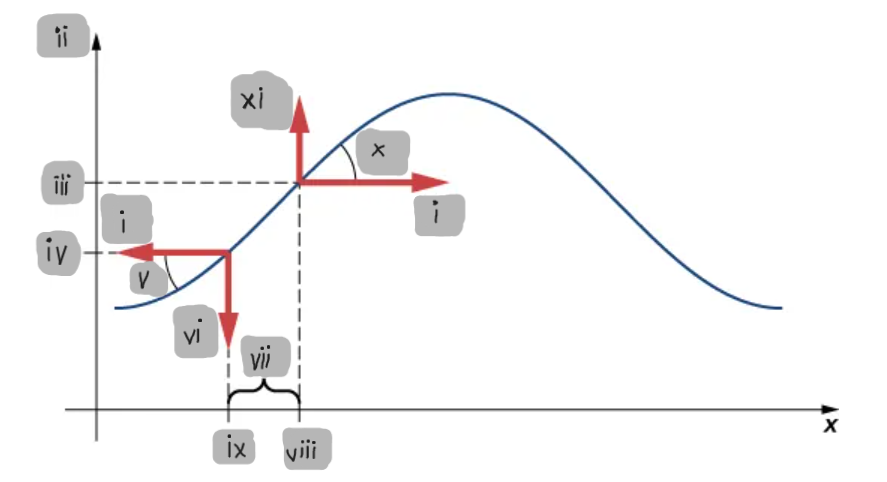
y1
(iv)
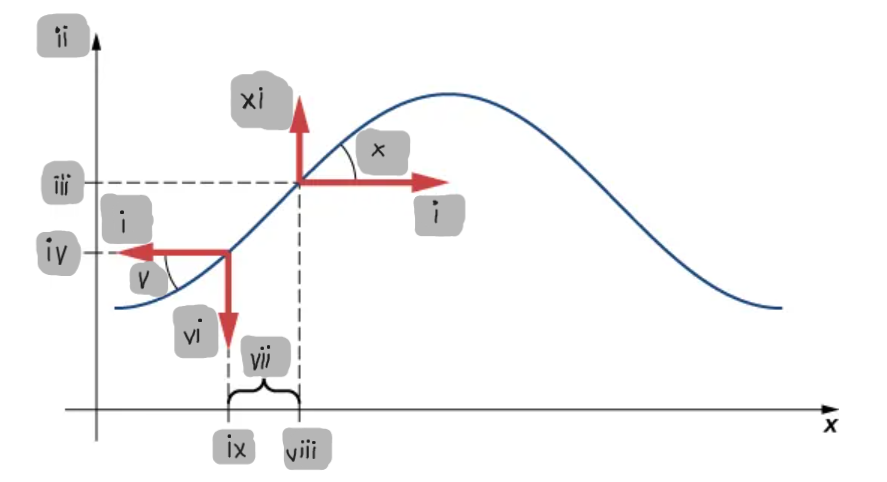
θ1
(v)
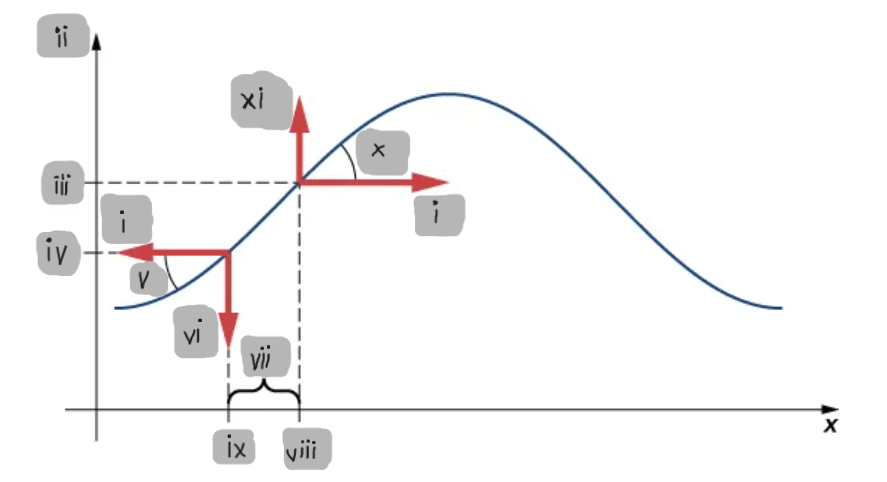
F1
(vi)
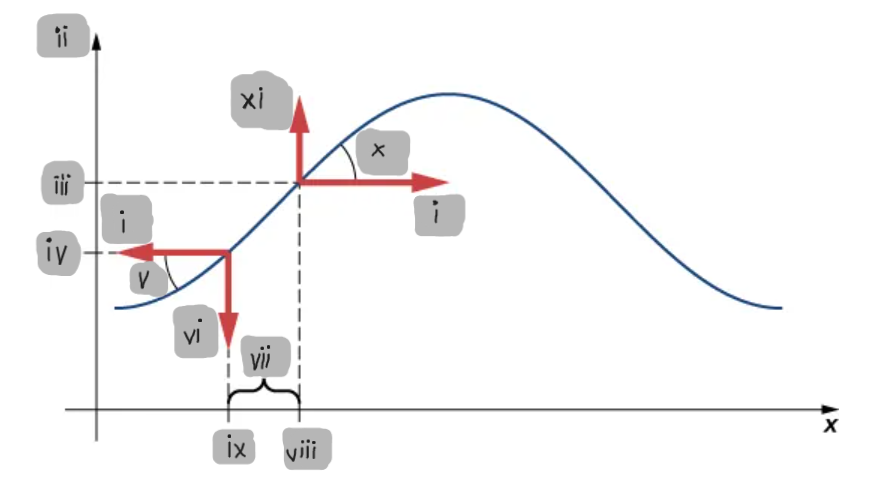
Δx
(vii)
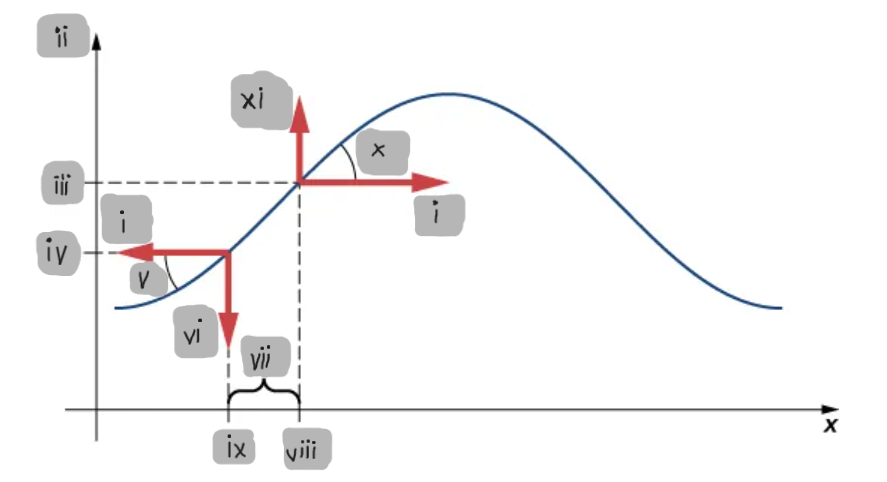
x2
(viii)
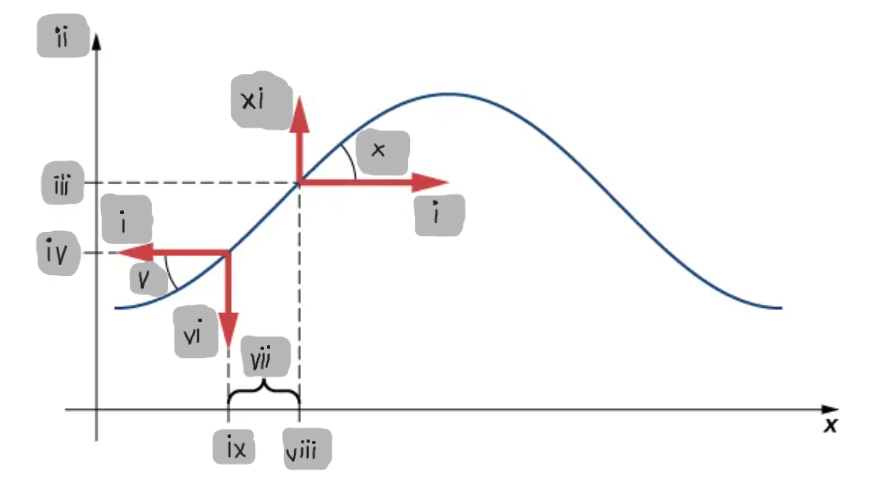
x1
(ix)
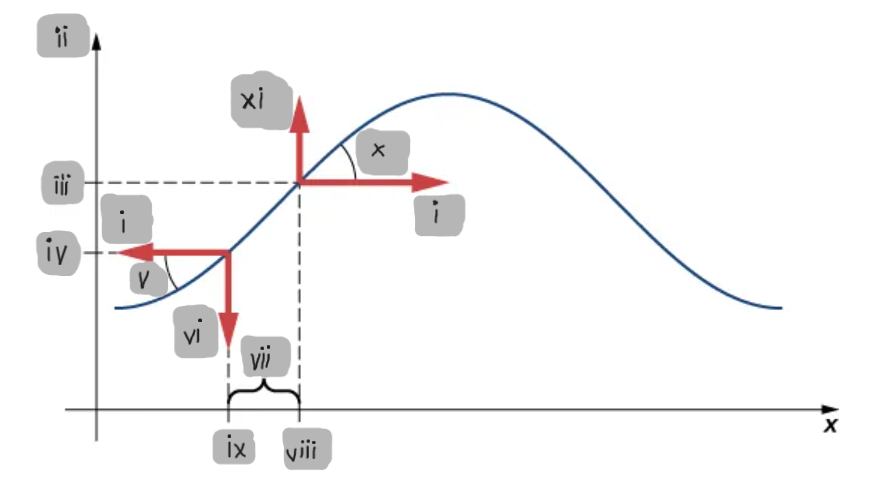
θ2
(x)
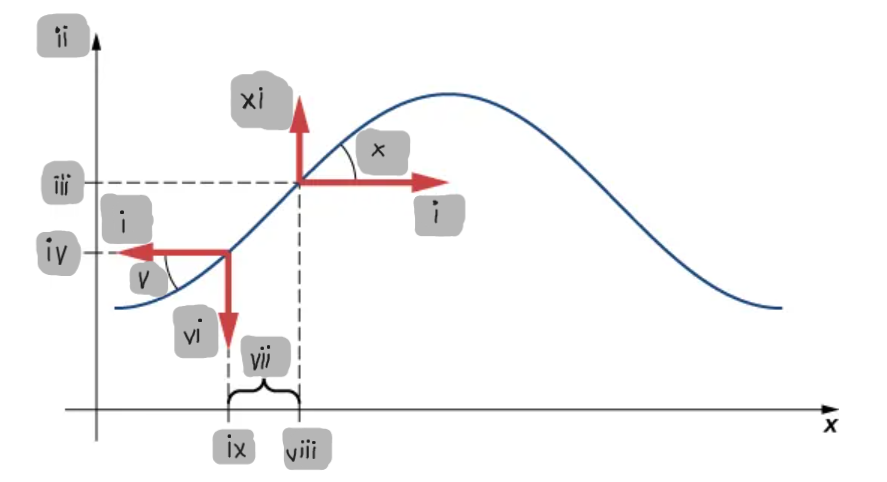
F2
(xi)