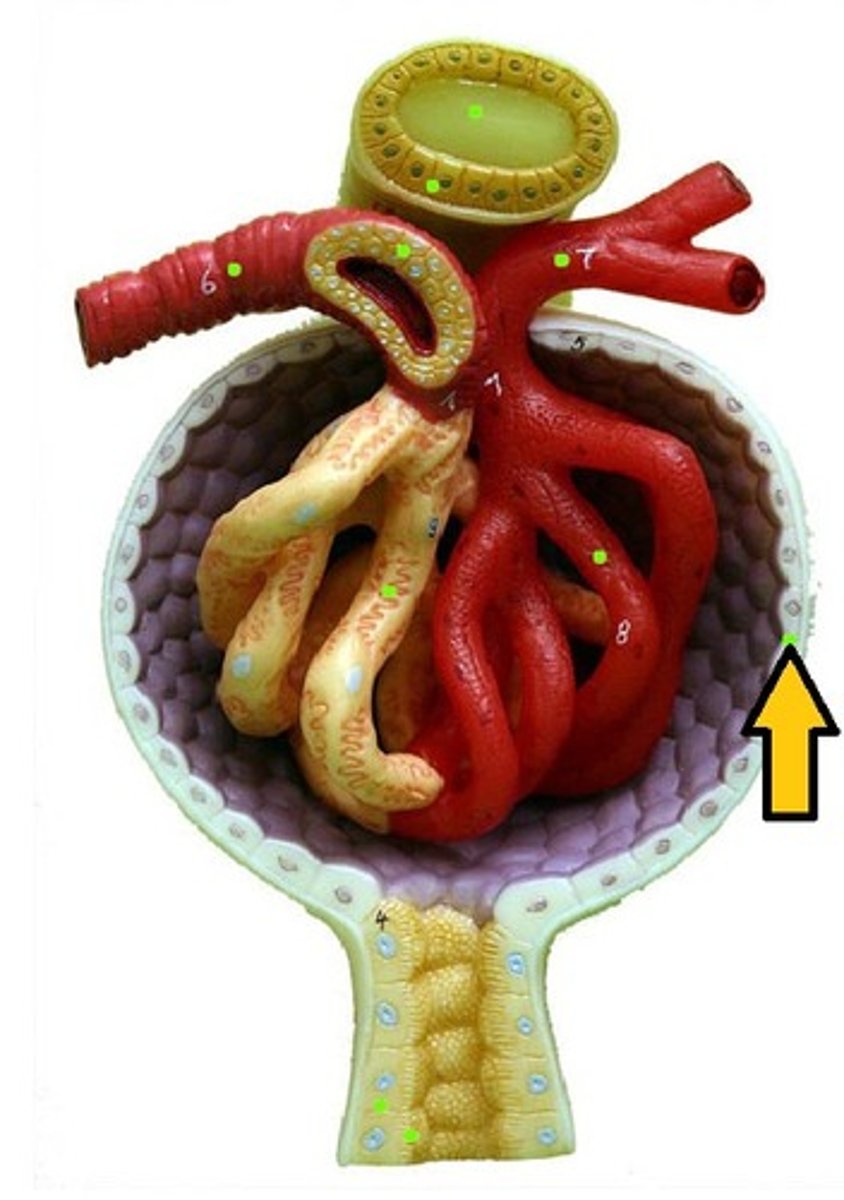
excretory system
1/56
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
57 Terms
conformer
-evolutionary path for organisms
-conform to external environment
-allow internal conditions to fluctuate along with external changes
regulator
-evolutionary path for organisms
-regulate internal environment
-maintain relatively constant internal conditions
thermoregulation
-the maintenance of physiologic core body temperature by balancing heat generation with heat loss
osmoregulation
-the maintenance by an organism of an internal balance between water and dissolved materials regardless of environmental conditions
homeostasis
-Keeping the balance
-animal body needs to coordinate many systems all at once: temperature, blood sugar levels, energy production, water balance & intracellular waste disposal, nutrients, ion balance, cell growth
-maintaining a "steady state" condition
circulatory system
-supports multicellular organisms
-distributing nutrients
excretory system
-supports multicellular organisms
-removing wastes
osmoregulation
-water balance
-freshwater (hypotonic)
-saltwater (hypertonic)
-land
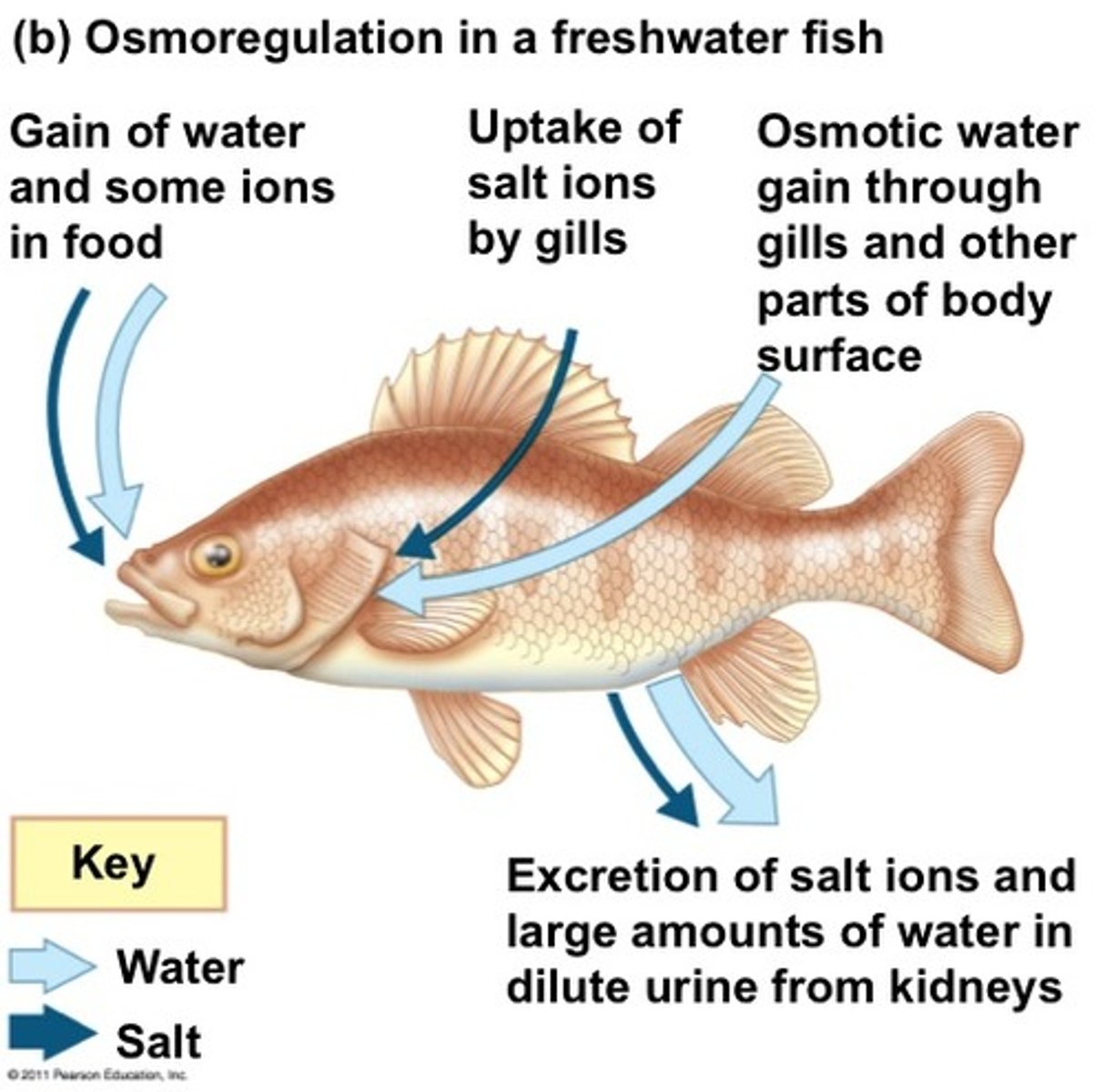
freshwater osmoregulation
-hypotonic
-water flow into cells & salt loss
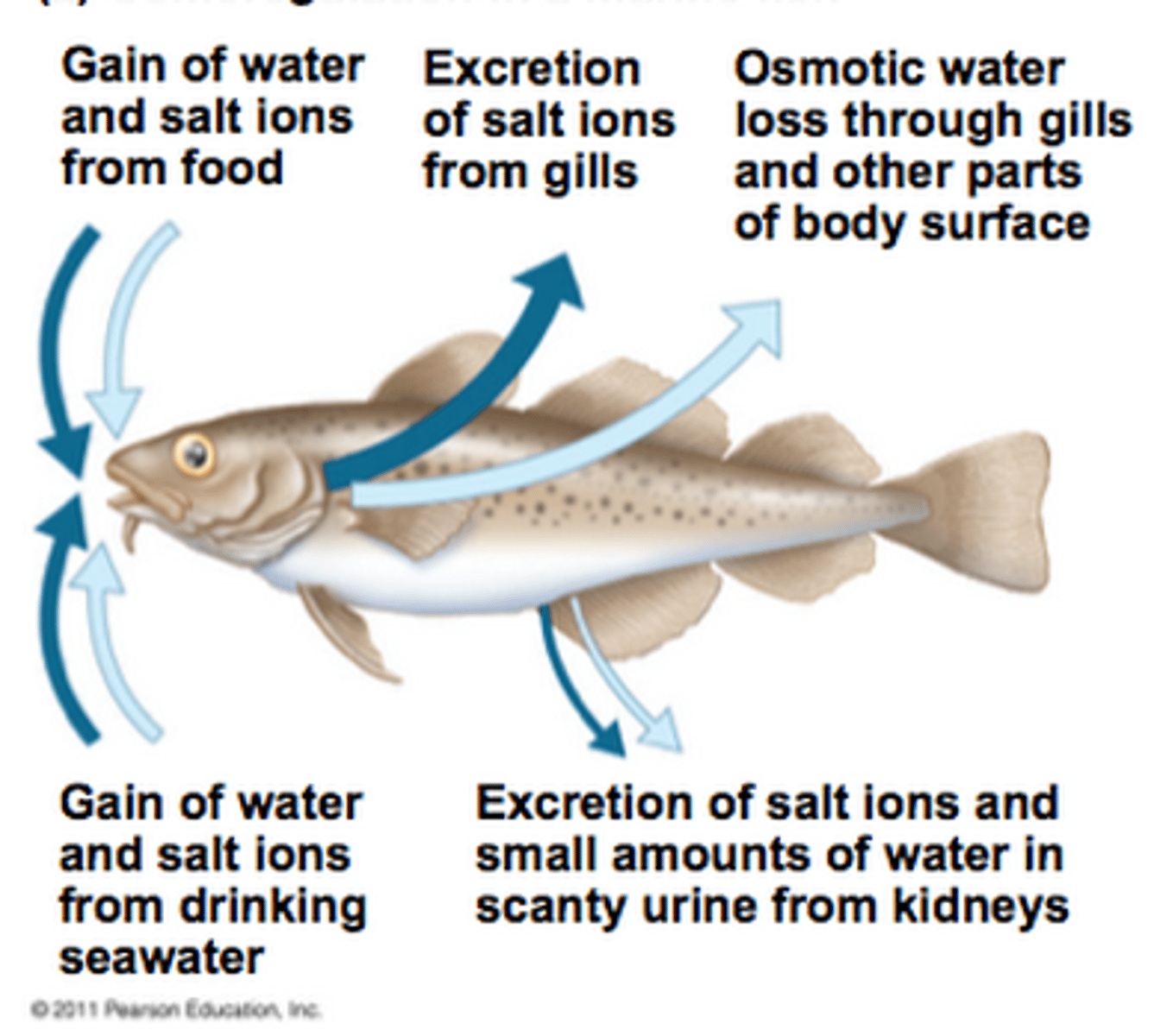
saltwater osmoregulation
-hypertonic
-water loss from cells
land osmoregulation
-dry environment
-need to conserve water
-may also need to conserve salt
why do all land animals have to conserve water?
-always lose water (breathing & waste)
-may lose life while searching for water (desiccation/ drying out)
what do we digest our food into?
-carbohydrates = CHO --> CO2 + H2O
-lipids = CHO --> CO2 + H2O
-proteins = CHON --> CO2 + H2O + N (lots of N)
-nucleic acids = CHOPN --> CO2 + H2O + P + N (very little N)
intracellular waste
-waste products from cells
-NH2 = ammonia
-CO2 + H2O
what can animals store?
-sugars
-lipids
-NOT proteins (animals do not have a protein storage system & ?poison themselves from the inside by digesting proteins, slide 8)
what does how you get rid of nitrogenous wastes depend on?
-who you are (evolutionary relationship)
-where you live (habitat)
aquatic nitrogen waste
-can afford to lose water
-ammonia (most toxic)
ammonia (NH3)
-nitrogenous waste
-very toxic (carcinogenic)
-very soluble (easily crosses membranes)
-must dilute it & get rid of it... fast!
terrestrial nitrogen waste
-need to conserve water
-urea (less toxic)
-soluble wastes can diffuse out of a shell-less amphibian egg (ammonia) or be carried away by the mother's blood in a mammalian embryo (urea)
terrestrial egg layers nitrogen waste
-need to conserve water
-need to protect embryo in egg
-uric acid (least toxic)
-the shelled eggs of birds and reptiles are not permeable to liquids, which means that soluble nitrogenous wastes trapped within the egg could accumulate to dangerous levels (even urea is toxic at very high concentrations)
-uric acid precipitates out of solution and can be stored within the egg as a harmless solid left behind when the animal hatches
freshwater animals
-water removal & nitrogen waste disposal
-remove surplus water
-overcome loss of salts
freshwater animals - surplus water removal
-use surplus water to dilute ammonia & excrete it
-need to excrete a lot of water so dilute ammonia & excrete it as very dilute urine
-also diffuse ammonia continuously through gills or through any moist membrane
freshwater animals - overcome loss of salts
-reabsorb in kidneys or active transport across gills
mammals
-nitrogen waste disposal on land
mammals - nitrogen waste disposal
-need to conserve water
-must process ammonia so less toxic
kidney (mammals)
-filter solutes out of blood
-reabsorb H2O (+ any useful solutes)
-excrete waste (urine)
urea (mammals)
-larger molecule = less soluble = less toxic
-2NH2 + CO2 = urea
-produced in liver
-costs energy to synthesize, but worth it
-low toxicity (about 100,000 times less toxic than ammonia)
-can be transported and stored safely at high concentrations (reduces the amount of water needed for nitrogen excretion when releasing a concentrated solution of urea rather than a dilute solution of ammonia)
urine (mammals)
-urea, salts, excess sugar, and H2O
-very concentrated
-concentrated NH3 would be too toxic
egg-laying animals
-birds, reptiles, insects
-Nitrogen waste disposal in egg
-no place to get rid of waste in egg
-need even less soluble molecule (uric acid)
uric acid (egg-laying animals)
-BIGGER = less soluble = less toxic
-largely insoluble in water and can be excreted as a semisolid paste with very small water loss
-even more energetically expensive to produce than urea
-polymerized urea
polymerized urea (uric acid pt 2)
-large molecule
-precipitates out of solution
-doesn't harm embryo in egg (white dust in egg)
-adults still excrete N waste as white paste (no liquid waste, uric acid = white bird "poop"!)
mammalian system
-Filter solutes out of blood & reabsorb H2O + desirable solutes
-Key functions: filtration, re-absorption, secretion, excretion
filtration (mammalian system)
-fluids (water & solutes) filtered out of blood
re-absorption (mammalian system)
-selectively reabsorb (diffusion) needed water + solutes back to blood
secretion (mammalian system)
-pump out any other unwanted solutes to urine
excretion (mammalian system)
-expel concentrated urine (N waste + solutes + toxins) from body
blood contains
-Cells
-Plasma
-H2O (want to keep)
-proteins (want to keep)
-glucose (want to keep)
-salts / ions (want to keep)
-urea (want to excrete)
mammalian kidney
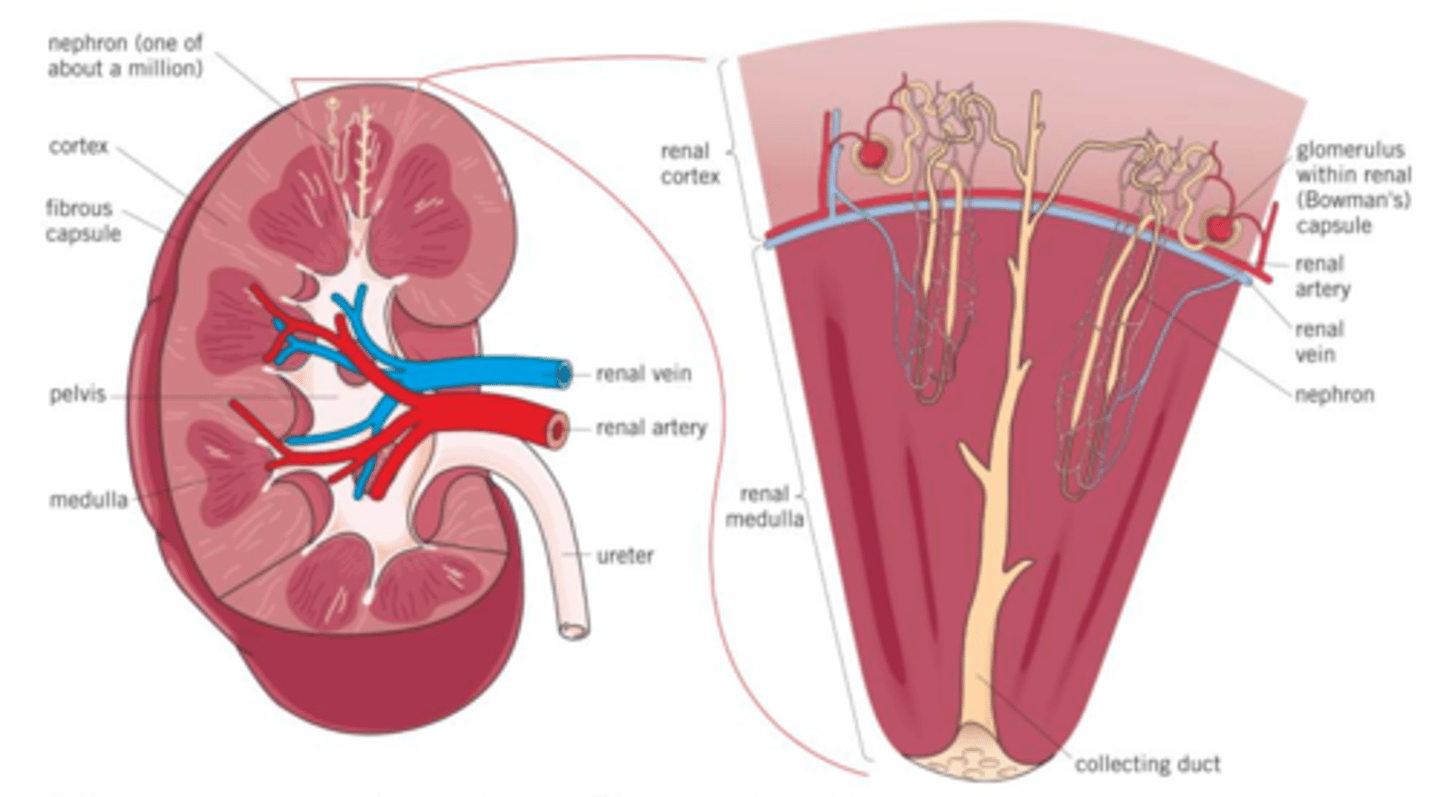
nephron
-Functional units of kidney
-1 million nephrons per kidney
-filter out urea & other solutes (salt, sugar...)
-blood plasma filteredinto nephron
-selective re-absorption ofvaluable solutes & H2O back into bloodstream
the glomerulus (nephron)
-a single long tubule and a ball of capillaries
-each nephron consists of this
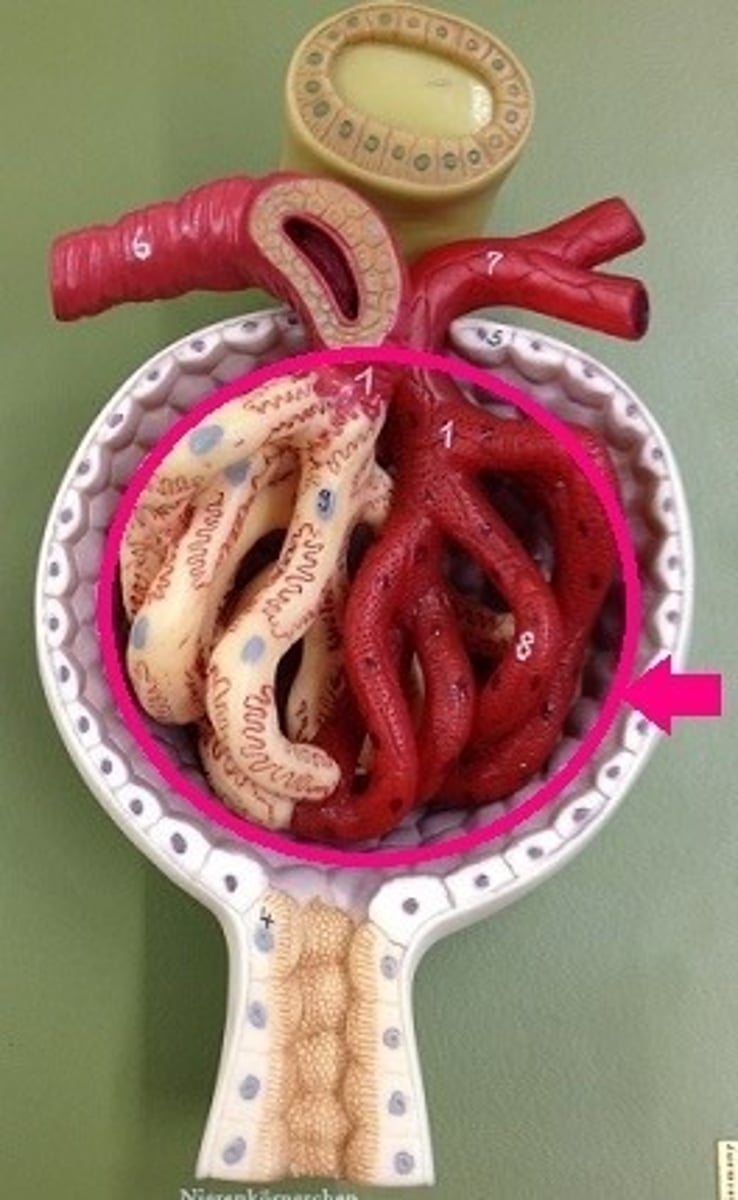
Bowman's capsule (nephron)
-the blind end of the tubule forms a cup-shaped swelling that surrounds the glomerulus
nephron: filtration
-Glomerulus (filters blood)
-occurs as blood pressure forces fluid from the blood in the glomerulus into the lumen of Bowman's capsule
-filtered out of blood: H2O, glucose, salts / ions, urea
-not filtered out: cells, proteins
-filtrate from Bowman's capsule (contains salt, glucose, vitamins, nitrogenous wastes, and other small molecules) flows through the nephron and collects ducts as it becomes urine
-high blood pressure in kidneys force to push (filter) H2O & solutes out of blood vessel (BIG problems when you start out with high blood pressure in system, hypertension = kidney damage)
podocytes
-specialized capsule cells
-permeable to water and small solutes, but not to blood cells or large molecules such as plasma proteins
nephron: re-absorption
-Proximal tubule
-reabsorbed back into blood: NaCl, H2O, glucose, HCO3- bicarbonate (buffer for blood pH)
-loop of henle
-distal tubule
proximal tubule
-reabsorb of most of the NaCl and water from the initial filtrate volume
-epithelial cells actively transport Na+ into the interstitial fluid (this transfer of positive charge is balanced by the passive transport of Cl- out of the tubule)
-as salt moves from the filtrate to the interstitial fluid, water follows by osmosis
-reabsorb about 90% of the important buffer bicarbonate (HCO3-)
loop of henle
-descending limb
-reabsorbed: H2O (high permeability to H2O)
-ascending limb
-reabsorbed: salt (filtrate becomes more dilute as it moves)
-re-absorption of water continues as the filtrate moves into the descending limb
-this transport epithelium is freely permeable to water but not very permeable to salt and other small solutes
distal tubule
-reabsorbed: salts, H2O, HCO3- bicarbonate
-More surface area means more re-absorption
-plays a key role in regulating the K+ and NaCl concentrations in body fluids by varying the amount of K+ that is secreted into the filtrate and the amount of NaCl reabsorbed from the filtrate.
-like the proximal tubule, also contributes to pH regulation by controlled secretion of H+ and the re-absorption of bicarbonate (HCO3-)
nephron: re-absorption & excretrion
-Collecting duct (reabsorbed H2O)
-excretion (concentrated urine passed to bladder)
collecting duct (nephron re-absorption & excretion)
-by actively reabsorbing NaCl, the transport epithelium of the collecting duct plays a large role in determining how much salt is actually excreted in the urine
-the epithelium is permeable to water but not to salt or (in the renal cortex) to urea
-as the collecting duct traverses the gradient of osmolarity in the kidney, the filtrate becomes increasingly concentrated as it loses more and more water by osmosis to the hyperosmotic interstitial fluid
-in the inner medulla, the duct becomes permeable to urea, contributing to hyperosmotic interstitial fluid and enabling the kidney to conserve water by excreting a hyperosmotic urine
nephron (summary)
-Not filtered out: cells, proteins
-Re-absorbed (active transport): Na+, amino acids, Cl-, glucose
-Re-absorbed (diffusion): Na+, Cl-, H2O
-Excreted: urea, excess H2O, excess solutes (glucose, salts), toxins, drugs, "unknowns"
urinalysis
-test that evaluates a sample of your urine
-detects wide range of disorders
-involves examining the appearance, concentration and content of urine
dialysis
-Patient's blood is pumped through a dialysis machine, cleansed, and pumped back into the body
-usually happens when you have only 10 to 15 percent of your kidney function left
kidney stones (common urinary tract disease)
-Calcium, magnesium, or uric acid salts in the urine crystallize and form stones
-can block a ureter
proteinuria (common urinary tract disease)
-abnormal quantities of protein in the urine
gout (common urinary tract disease)
-arthritis caused by excess uric acid that crystallizes in the joints (usually the big toe)
urinary tract infections (UTI) (common urinary tract disease)
-infection in your kidneys, ureters, bladder and urethra
kidney failure (common urinary tract disease)
-Kidney cannot cleanse blood and maintain homeostasis
-Generally caused by diabetes or high blood pressure
-When 80-85% of function is lost dialysis or kidney transplant is needed