ECON 202- Final Exam Study Guide
1/99
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Flashcards for review
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
100 Terms
If U.S. speculators gained greater confidence in foreign economies so that they wanted to move more of their wealth into foreign countries, what would happen to the dollar?
depreciate which would cause aggregate demand to shift right.
In which case can we be sure aggregate demand shifts left overall?
People want to save more for retirement and the Fed decreases the money supply.
Most economists agree that money changes real GDP in both the short and long run. True or False?
False
The term business cycle implies that economic fluctuations follow a regular, predictable pattern. True or False?
False
A decrease in the price level makes consumers feel wealthier, so they purchase more. This logic helps explain why the aggregate demand curve slopes downward. True or False?
True
The primary purpose of the aggregate demand and aggregate supply model is to demonstrate the classical dichotomy. True or False?
False
All explanations for the upward slope of the short-run aggregate supply curve suppose that the quantity of output supplied increases when the actual price level exceeds the expected price level. True or False?
True
Technological progress shifts the long-run aggregate supply curve to the right. True or False?
True
Which of the following alone can explain the change in the price level and output during World War II?
Aggregate demand shifted right.
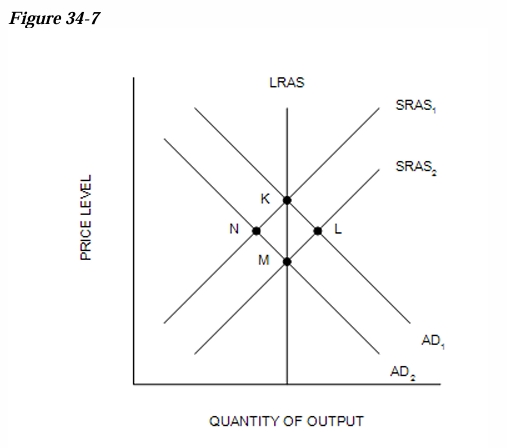
Refer to Figure 34-7. If the economy starts at point K, a short-run fall in output would be consistent with a movement to point which point?
N
An increase in the money supply causes output to rise in the long run. True or False?
False
The aggregate demand and aggregate supply model helps us to understand both short-run economic fluctuations and how the economy moves from the short to the long run. True or False?
True
Suppose workers notice a fall in their nominal wage but are slow to notice that the price of things they consume have fallen by the same percentage. They may infer that the reward to working is temporarily…
low and so supply a smaller quantity of labor.
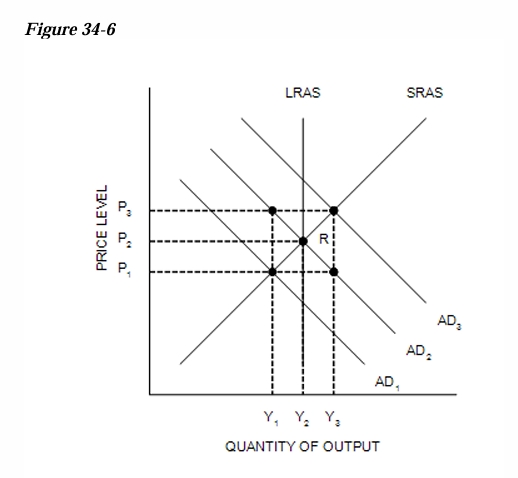
Refer to Figure 34-6. Suppose the economy starts at R. If changes occur that move the economy to a new short-run equilibrium of P1 and Y1 , then it must be the case that…
aggregate demand has decreased.
The recession of 2008-2009 was in many ways the worst macroeconomic event in more than half a century. True or False?
True

Refer to Scenario 34-1. What would happen to the dollar?
It would appreciate in foreign exchange markets making U.S. goods more expensive compared to foreign goods.
If the central bank increased the money supply in response to a decrease in short-run aggregate supply, unemployment would return towards its natural rate, but prices would rise even more. True or False?
True
The initial impact of an increase in an investment tax credit is to shift aggregate…
demand right.
We can explain continued increases in both output and the price level by supposing that only aggregate demand shifted right over time. True or False?
False
The price level rises in the short run if…
aggregate demand shifts right or aggregate supply shifts left.
Refer to Figure 34-6. Suppose the economy starts at R. Stagflation would be consistent with the move to…
P3 and Y1.
When the Fed buys bonds the supply of money…
increases and so aggregate demand shifts right.
If aggregate demand and aggregate supply both shift right, we can be sure that the price level is higher in the short run. True or False?
False
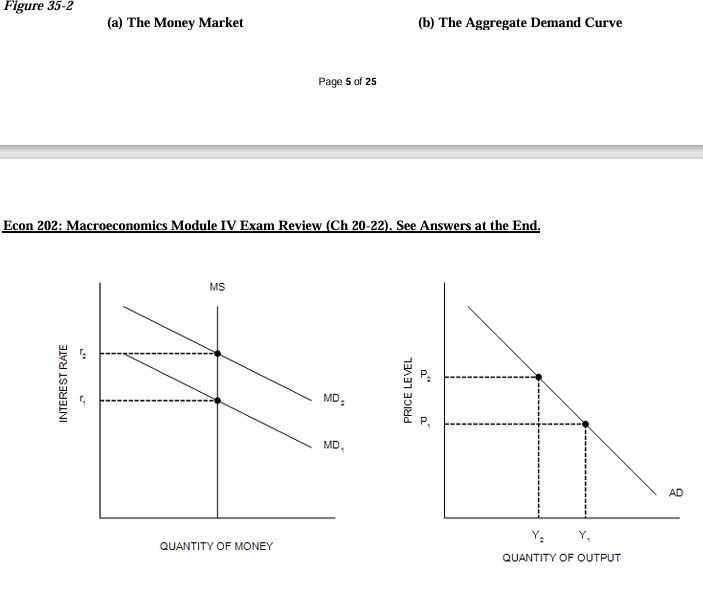
Refer to Figure 35-2. A decrease in Y from Y1 to Y2 is explained as follows…
An increase in P from P1 to P2 causes the money-demand curve to shift from MD1 to MD2; this shift of MD causes r to increase from r1 to r2; and this increase in r causes Y to decrease from Y1 to Y2.
Initially, the economy is in long-run equilibrium. Aggregate demand then shifts leftward by $50 billion. The government wants to increase its spending in order to avoid a recession. If the crowding-out effect is always one-third as strong as the multiplier effect, and if the MPC equals 0.6, then by how much do government purchases have to increase in order to offset the $50 billion leftward shift?
By $30 billion
Changes in the interest rate…
shift aggregate demand if they are caused by fiscal or monetary policy, but not if they are caused by changes in the price level.
While a television news reporter might state that "Today the Fed raised the federal funds rate from 1 percent to 1.25 percent, " a more precise account of the Fed's action would be as follows:
"Today the Fed told its bond traders to conduct open-market operations in such a way that the equilibrium federal funds rate would increase to 1.25 percent."
In a certain economy, when income is $100, consumer spending is $60. The value of the multiplier for this economy is 4. It follows that, when income is $101, consumer spending is…
$60.75.
An increase in the price level shifts the money demand curve to the left, causing interest rates to increase. True or False?
False
The Federal Open Market Committee is…
the group at the Federal Reserve that sets monetary policy.
An example of an automatic stabilizer is…
unemployment benefits.
In liquidity preference theory, an increase in the interest rate, other things the same, decreases the quantity of money demanded, but does not shift the money demand curve. True or False?
True
The multiplier effect states that there are additional shifts in aggregate demand from expansionary fiscal policy, because it…
increases income and thereby increases consumer spending.
A significant example of a temporary tax cut was the one announced in 1992 by President George H. W. Bush. The effect of that tax cut on consumer spending and aggregate demand was…
likely smaller than if the cut had been permanent.
If the inflation rate is zero, then the nominal and real interest rate are the same. True or False?
True
Monetary policy and fiscal policy are the only factors that influence aggregate demand. True or False?
False
Permanent tax cuts have a larger impact on consumption spending than temporary ones. True or False?
True
Which of the following policies would be advocated by someone who wants the government to follow an active stabilization policy when the economy is experiencing severe unemployment?
Increase government expenditures
An increase in the money supply shifts the aggregate-supply curve to the right. True or False?
False
Shifts in aggregate demand affect the price level in…
both the short and long run.
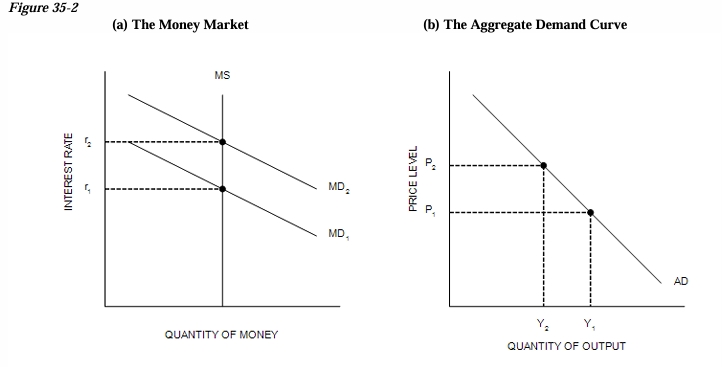
Refer to Figure 35-2. If the money-supply curve MS on the left-hand graph were to shift to the left, this would…
shift the AD curve to the left.
Monetary policy…
can be described either in terms of the money supply or in terms of the interest rate.
Which of the following is an example of crowding out?
An increase in government spending increases interest rates, causing investment to fall.
If the multiplier is 3, then the MPC is…
2/3.
An increase in the money supply decreases the equilibrium interest rate and shifts the aggregate-demand curve to the right. True or False?
True
If the marginal propensity to consume is 6/7, then the multiplier is 7. True or False?
True
According to the theory of liquidity preference, the interest rate adjusts to balance the supply of, and demand for, loanable funds. True or False?
False
As the interest rate falls to equilibrium in the market for money…
the quantity of money demanded rises, which would reduce a surplus of money.
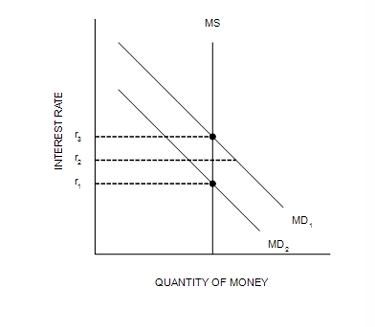
Refer to Figure 35-4. Suppose the current equilibrium interest rate is r2. If the Federal Reserve increases the money supply, and the price level does not change…
there will be an increase in the equilibrium quantity of goods and services demanded.
Using the liquidity-preference model, when the Federal Reserve decreases the money supply…
the equilibrium interest rate increases.
If an increase in inflation permanently reduced unemployment, then…
money would not be neutral and the long-run Phillips curve would slope downward.
Which of the following describes the Volcker disinflation most accurately?
Much of the public did not believe that the Fed would keep money growth low, so unemployment rose more than it would have otherwise.
If there is an adverse supply shock and the Federal Reserve responds by increasing the growth rate of the money supply, then in the short run the Federal Reserve's action…
raises inflation but lowers unemployment.
Although monetary policy cannot reduce the natural rate of unemployment, other types of government policies can. True or False?
True
A policy change that reduces the natural rate of unemployment shifts both the long-run aggregate-supply curve and the long-run Phillips curve left. True or False?
False
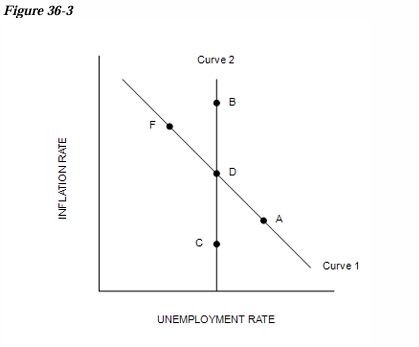
Refer to Figure 36-3. Curve 2 is the…
long-run Phillips curve.
According to the Friedman-Phelps analysis, in the long run actual inflation equals expected inflation and unemployment is at its natural rate. True or False?
True
The theory by which people optimally use all available information when forecasting the future is known as…
rational expectations.
An increase in the inflation rate permanently reduces the natural rate of unemployment. True or False?
False
If the Fed were to increase the money supply, inflation would increase and unemployment would decrease in the short run. True or False?
True
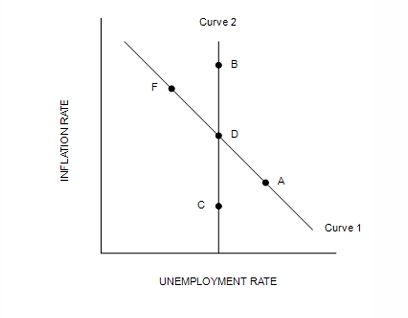
Refer to Figure 36-3. The inflation rate is greatest at…
B.
The short-run Phillips curve is based on the classical dichotomy. True or False?
False
An increase in the natural rate of unemployment shifts the long-run Phillips curve to the right. True or False?
True
The sacrifice ratio is the percentage point increase in the unemployment rate created in the process of reducing inflation by one percentage point. True or False?
False
A vertical long-run Phillips curve is consistent with…
both the conclusion of Friedman and Phelps and the classical idea of monetary neutrality.
In most of the 1970s, the Fed's policy created expectations of high inflation. True or False?
True
Neither monetary policy nor any government policy can change the natural rate of unemployment. True or False?
False
Unexpectedly high inflation reduces unemployment in the short run, but as inflation expectations adjust the unemployment rate returns to its natural rate. True or False?
True
The long-run Phillips curve is consistent with monetary neutrality implied by the classical dichotomy. True or False?
True
An increase in inflation expectations shifts the short-run Phillips curve right and has no effect on the long-run Phillips curve. True or False?
True
If the Fed reduces inflation 1 percentage point and this makes output fall 5 percentage points and unemployment rises 2 percentage points for one year, the sacrifice ratio is…
5.
According to the Phillips curve, unemployment and inflation are positively related in…
neither the long run nor the short run.
An adverse supply shock shifts the short-run Phillips curve right. If people raise their inflation expectations, the short run Phillips curve shifts farther right. True or False?
True
If unemployment is above its natural rate, what happens to move the economy to long-run equilibrium?
Inflation expectations fall, which shifts the short-run Phillips curve to the left.
Over the long run the Volcker disinflation…
shifted the short-run, but not the long-run Phillips curve left.
A goal of monetary policy and fiscal policy is to…
offset the shifts in aggregate demand and thereby stabilize the economy.
The wealth effect, interest-rate effect, and exchange-rate effect are all explanations for…
the slope of the aggregate-demand curve.
If inflation expectations rise, the short-run Phillips curve shifts…
right, so that at any inflation rate unemployment is higher in the short run than before.
A low sacrifice ratio would make a central bank less willing to reduce the inflation rate. True or False?
False
Which of the following would not be directly included in aggregate demand?
Government's tax collections
In 2008, the United States was in recession. Which of the following things would you not expect to have happened?
Increased real GDP
Suppose that a small economy that produces mostly agricultural goods experiences a year with exceptionally poor conditions for growing crops. The poor weather would…
shift the short-run aggregate supply curve to the left and the short-run Phillips curve to the right.
The proliferation of Internet usage serves as an example of a favorable supply shock. True or False?
True
The Employment Act of 1946 states that…
the government should promote full employment and production.
Opponents of active stabilization policy…
believe that the political process creates lags in the implementation of fiscal policy.
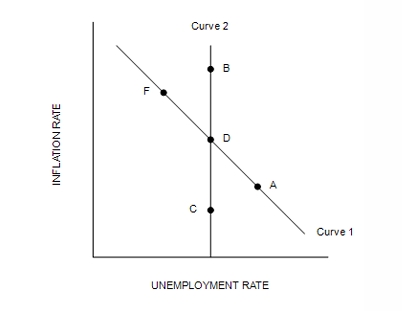
Refer to Figure 36-3. If the economy starts at D and the money supply growth rate increases, in the long run the economy…
moves to B.

Refer to Scenario 36-1. In the short run the increased prices of world commodities…
raised the price level and reduced output.
Which of the following is most commonly used to monitor short-run changes in economic activity?
Real GDP
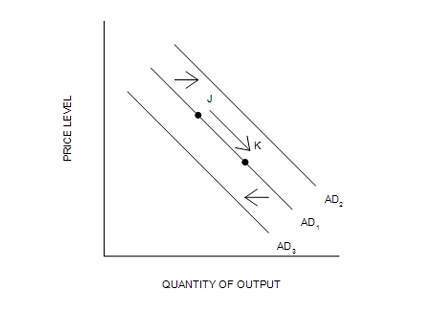
Refer to Figure 35-5. An increase in government purchases will…
shift aggregate demand from AD1 to AD2.
An improved functioning of the labor markets will shift…
the long-run Phillips curve to the left and the long-run aggregate supply curve to the right.
Other things constant, which of the following would reduce unemployment and raise inflation?
Businesses become more optimistic about the future of the economy.
Which of the following events shifts aggregate demand leftward?
A decrease in government expenditures, but not a change in the price level
Which of the following is not a determinant of the long-run level of real GDP?
The price level
An adverse supply shock will shift short-run aggregate supply…
left, making prices rise.
Other things the same, as the price level decreases it induces greater spending on…
both net exports and investment.
If taxes…
increase, then consumption decreases, and aggregate demand shifts leftward.
The government builds a new water-treatment plant. The owner of the company that builds the plant pays their workers. The workers increase their spending. Firms from which the workers buy goods increase their output. This type of effect on spending illustrates…
the multiplier effect.
Fiscal policy refers to the idea that aggregate demand is affected by changes in…
government spending and taxes.
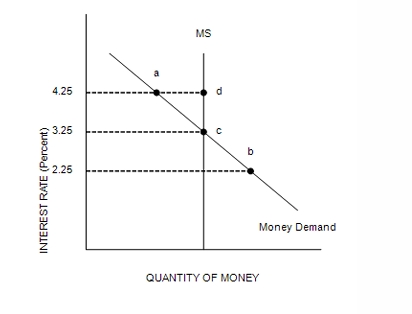
Refer to Figure 35-1. There is an excess supply for money at an interest rate of…
4.25 percent.
According to liquidity preference theory, the money-supply curve would shift leftward…
if the Federal Reserve chose to decrease the money supply.