chapters 7 and 11 (week 4) learning objectives
1/43
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
44 Terms
What are bio elements
basic requirements for life (carbon, hydrogen, oxygen, phosphorus, potassium, nitrogen, sulfur, calcium, iron, sodium, chlorine, magnesium)
What are essential nutrients
substance (element or compound) an organism must get from a source outside its cells
What are macronutrients
required in large quantities; play principal roles in cell structure and metabolism (proteins, carbohydrates)
What are micronutrients
required in small amounts; involved in enzyme function and maintenance o f protein structure (manganese, zinc, nickel)
What are organic nutrients?
contain carbon and hydrogen atoms and are usually the products of living things
What are inorganic nutrients
atom or molecule that contains a combination of atoms other than carbon and hydrogen
Environmental factors in microbial growth
Temperature
Oxygen requirements
pH
Osmotic pressure
Barometric pressure
What are the three adaptations of temperature for microbial growth
Minimum temperature
Maximum temperature
Optimum temperature
What is minimum temperature
lowest temperature that permits a microbe’s growth and metabolism
What is maximum temperature
highest temperature that permits a microbe’s growth and metabolism
What is optimum temperature
promotes the fastest rate of growth and metabolism
What is the threshold for the psychrophiles adaptation group
optimum temperature below 15°C; capable of growth at 0°C
What is the threshold for the mesophiles adaptation group
optimum temperature 20°-40°C; most human pathogens
What is the threshold for the thermophiles adaptation group
optimum temperature greater than 45°C
What aerobe microbes
Microbe that can grow in the presence of oxygen, and may even require it.
What are Obligate aerobe microbes
Microbes that require oxygen to grow.
What are facultative microbes
Microbes that can grow with or without oxygen.
What are anaerobe microbes
Microbes that do not use oxygen to grow.
What are acidophiles
grow in extremely acidic environments like the human stomachs
What are alkalinophiles
grow in extremely basic environments
What is binary fission
A simple, asexual reproduction method where a single parent cell duplicates its genetic material and then divides, resulting in two identical daughter cells
What are the four stages in population growth
Lag phase
Exponential growth phase
Stationary phase
Death phase
What occurs in the lag phase of population growth
Less than exponential growth rate; period of adjustment, enlargement
What occurs in the exponential growth phase of population growth
a period of maximum growth when cells have adequate nutrients and a favorable environment
What occurs in the stationary phase of population growth
rate of cell growth equals rate of cell death caused by depleted nutrients and O2, excretion of organic acids and pollutants
What occurs in the death phase of population growth
as limiting factors intensify, cells die rapidly
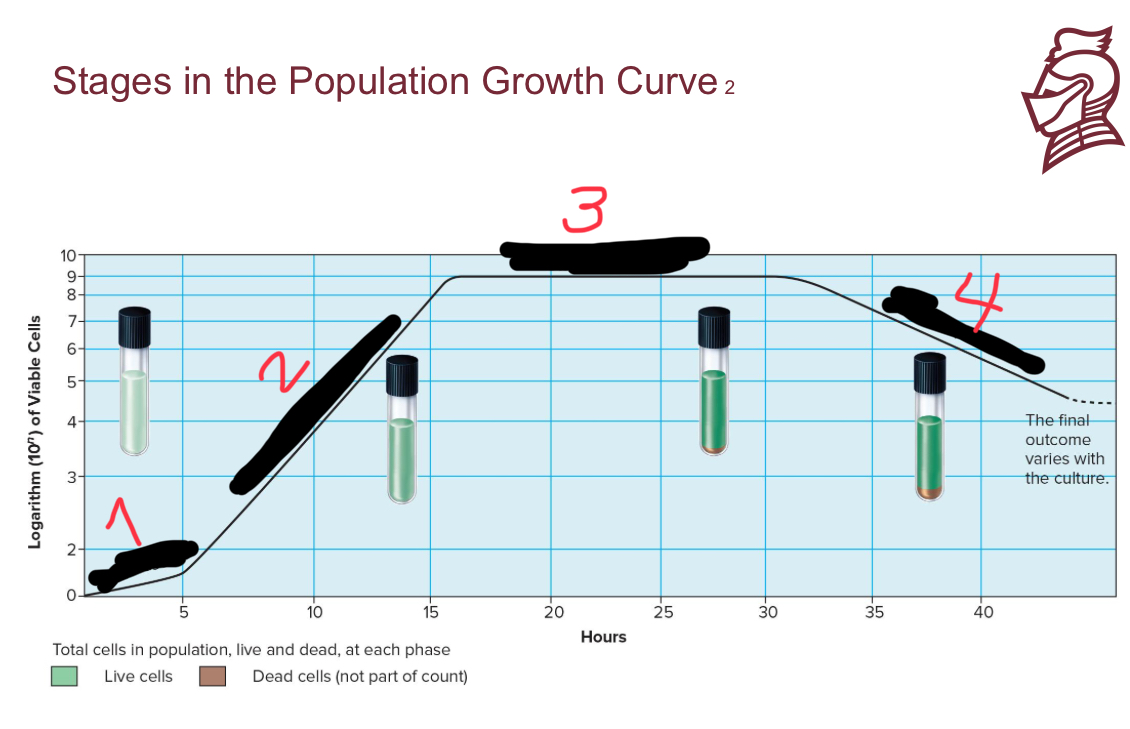
What is the name of number 3
Stationary phase
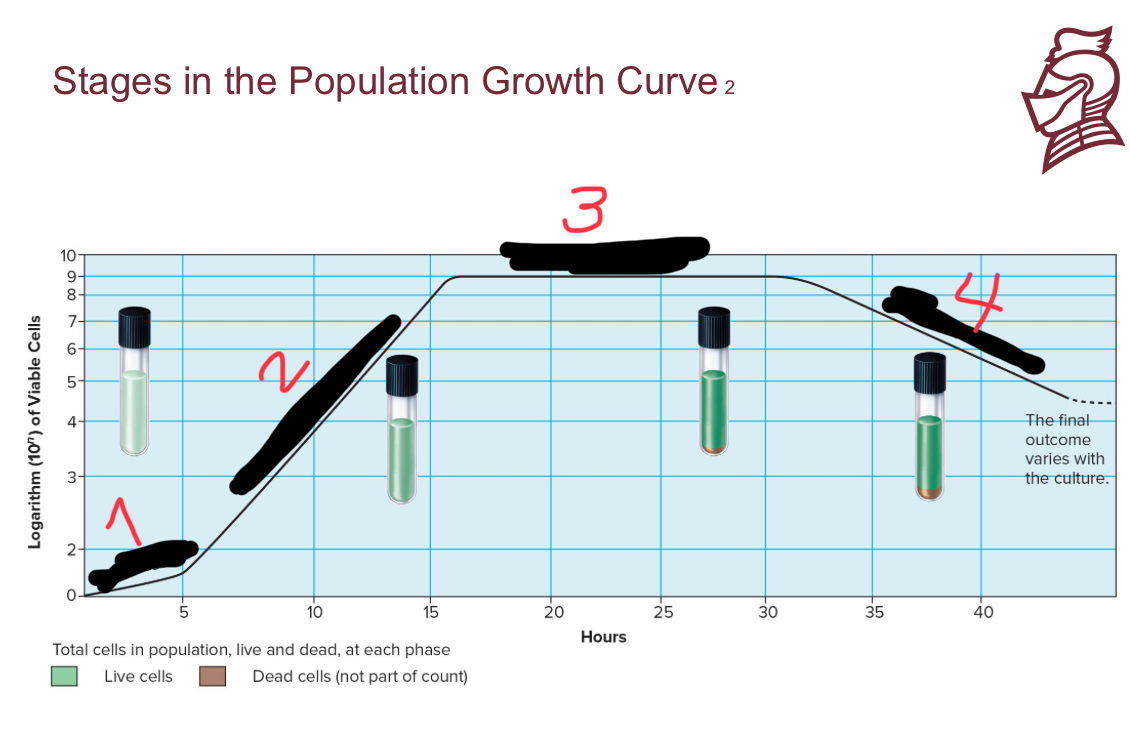
What is the name of number 4
Death phase
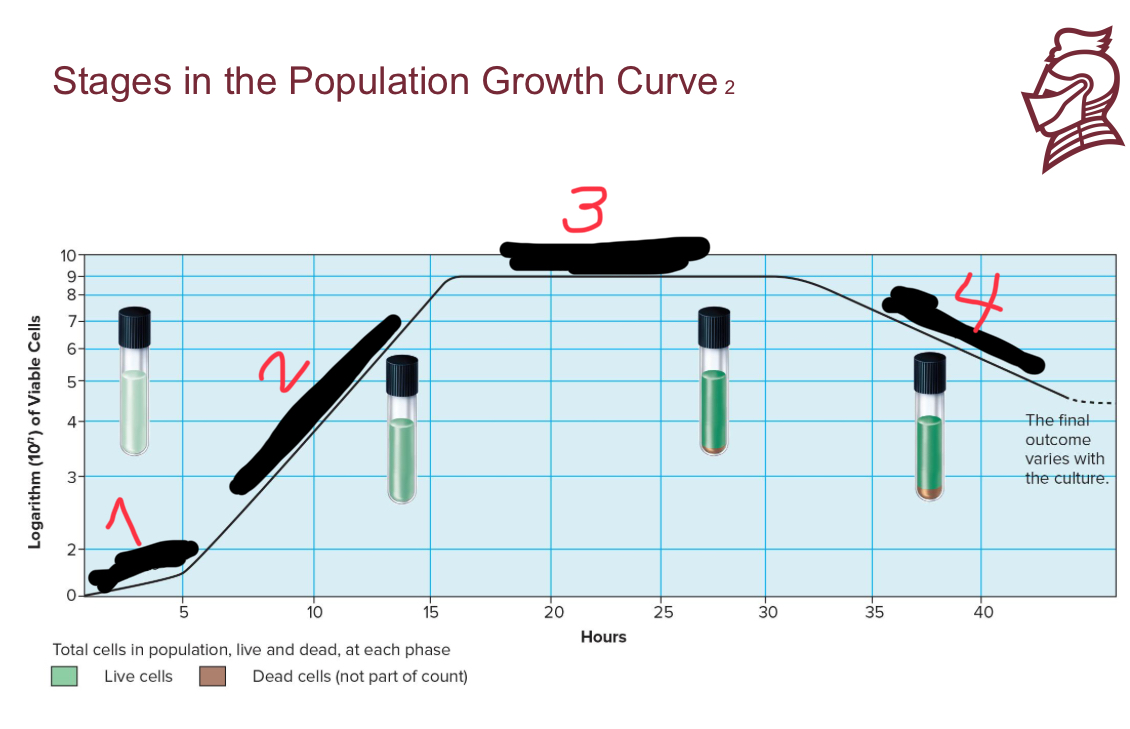
What is the name of number 2
Exponential growth phase
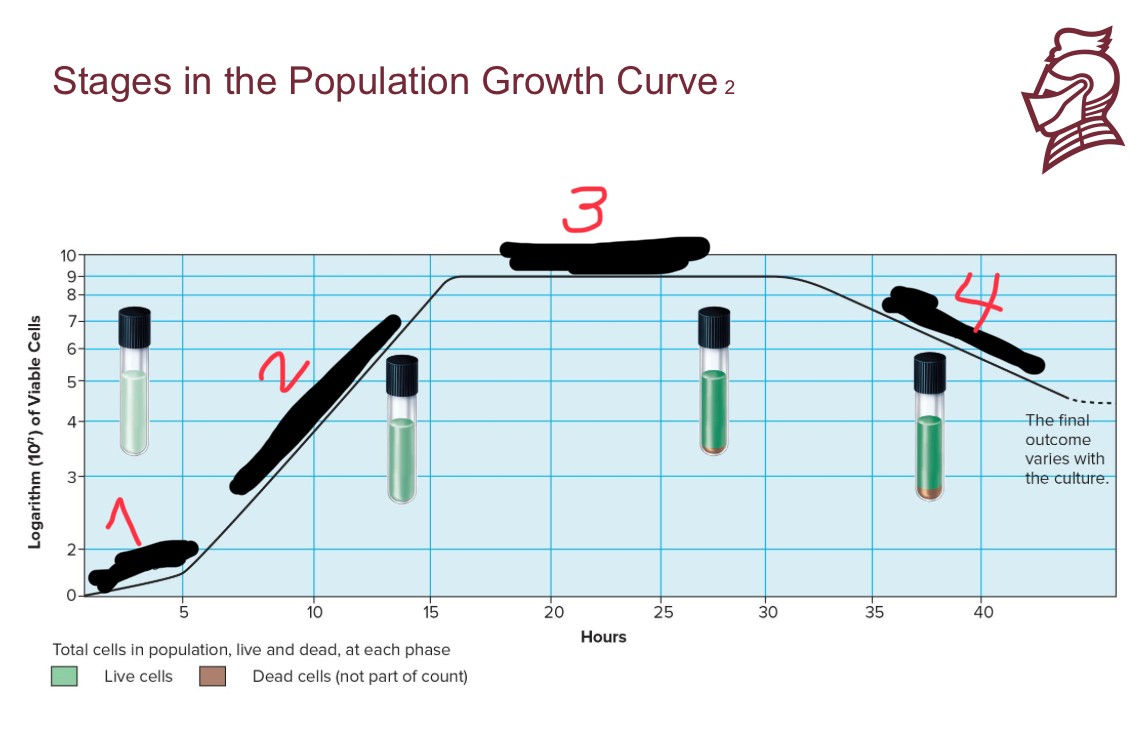
What is the name of number 1
Lag phase
What is sterilization
process to destroy all viable microbes
What is disinfection
Use of a physical process or a chemical agent (disinfectant) to destroy vegetative pathogens but not bacterial endospores
What is antisepsis
application of chemical agents directly to exposed body surfaces, wounds, and surgical incisions to destroy or inhibit vegetative pathogens
What is decontamination
physical, chemical, and mechanical methods that destroy or reduce undesirable microbes in a given area.
Factors that affect microbial death
Number of microbes
Nature of microbes in the population
Temperature and pH of environment
Concentration or dosage of agent
Mode of action of the agent
Presence of solvents, organic matter, or inhibitors
What are the 4 modes of action for chemical agents
Cell walls
Cell membranes
Protein and nucleic acid synthesis
Protein structure and function
____kills microbes at lower temperatures and over a shorter period of time than dry heat
Moist heat
What happens when the cell wall is targeted
becomes fragile and cell lyses
What happens when the cell membrane is targeted
It loses integrity
What happens when protein and nucleic acid synthesis is targeted
prevention of replication, transcription, translation, peptide bond formation, protein Synthesis
What happens when protein function is targeted
It disrupts and denatures proteins
What are the 3 importantphysical methods of control
-temp
-radiation
-filtration
What is filtration
Physical removal of microbes by passing a gas or liquid through filter