Pediatric Dermatology: Newborn to Infectious Rashes
1/20
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
21 Terms
benign, epidermal, papules, cheeks, Epstein, spontaneously
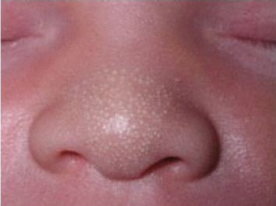
Milia: Background
-______ rash most common in newborns
-Tiny ________ cysts filled with keratinous material
-1-2 mm white _________ occurring mostly to face (nose, _______)
Intraoral version are ________ pearls
-No treatment necessary
-____________ resolves over a few weeks
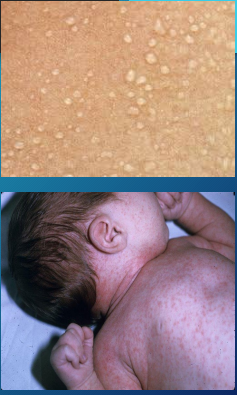
rubra, blockage, sweat, sweating, fever
Miliaria (Heat Rash): Background
-Types → crystallina, ______, profunda
-Pathophysiology → _________ of eccrine _____ glands, sometimes accompanied by inflammation
-Etiology → anything that causes ___________ like hot/humid environment, physical activity, _____, or occlusion of the skin
-Most beneficial treatment is to avoid sweating
newborns, stratum corneum, vesicles, without, head, epidermis, leakage, inflammatory, erythematous, axilla
Miliaria: Crystallina and Rubra
-Crystallina
Common in ___________ but can happen at any age
Blockage of duct within the _______ ________
Small, thin walled _________ “dew drops” _________ inflammation
Most common on the _____, neck, and upper trunk
-Rubra
Most common type
Blockage of duct within the ________ or dermis
_________ of sweat into surrounding tissue → _____________ response
Small, ____________ papular, papulovesicular, or papulopustular lesions
Most common in skin folds of the neck, _______, or groin
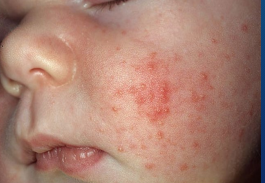
first few, Malassezia, inflammatory, absence, 4, cleansing, ketoconazole
Neonatal Cephalic Pustulosis
-Appears ______ ____ weeks of life (most commonly between 2-4 weeks)
-Inflammatory reaction to ____________ species
-Characterized by ___________ papules and pustules, _________ of comedomes, and distribution limited to the face (especially cheeks) and scalp
-Spontaneously resolves within _ months
-Treatment → Medications are not always recommended for treatment
________ with mild baby cleansers
Avoid oils and lotions
2% ___________ twice daily
1% hydrocortisone once daily (optional)
3-4, males, sebaceous, androgenic, comedomes, scarring, 1, benzoyl peroxide, bactrim, tumor, puberty
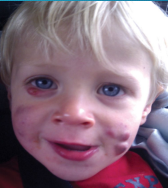
Infantile Acne
-Presents around __-__ months
-Uncommon but presents more often in ______
-Results from hyperplasia of __________ glands, secondary to _________ stimulation
-Inflammatory papules, pustules, _________, and sometimes nodules (can lead to _________)
-Typically resolves spontaneously by _ year old
-Treatment
Mild to Moderate → keratolytic agents (2.5% ______ _______), topical antibiotics (clinda or erythromycin), topical retinoids
Severe → oral antibiotics (erythromycin or ________), could also try oral isotretinoin
-Severe, unremitting cases need to be evaluated for CAH, gonadal or adrenal _______, and precocious _________
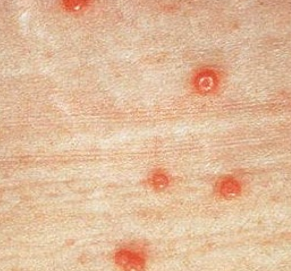
higher, 72, erythematous, pustules, trunk, week
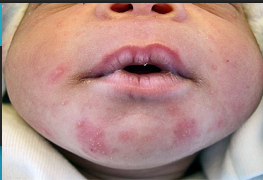
Erythema Toxicum Neonatorum
-Common newborn rash → most common in _______ birthweight or greater gestational age infants
-Appears within the first __ hours of life
-Multiple ____________ macules and papules → progress to _________ on an erythematous base, most commonly on the _____ and proximal extremities
-Spontaneously resolves within a ______, so no treatment is necessary
Asian, delayed, melanocytes, macule, ill, sacral-gluteal, shoulders, benign
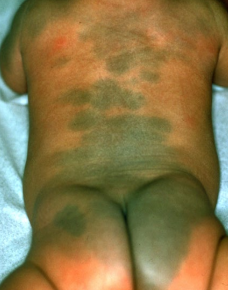
Mongolian Spot (Congenital Dermal Melanocytosis)
-Most common in _______, AA, and Native American populations
-Results from ________ disappearance of dermal _____________
-Blue-gray, pigmented ________ or patch with ___-defined borders
Most common over ________-__________ region followed by the _________
-_______ and fades during the first couple years of life and most disappear between ages 6 and 10
-Don’t confuse with bruising
macules, benign, McCune-Albright, large, Neurofibromatosis, 6
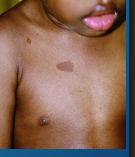
Cafe au Lait Macule
-Usually present at birth or appear in early childhood, can be found anywhere on the body
-Flat, tan-brown _________ or patches (coffee with cream) that range from a few mm to > 15 cm. These can grow with the child
-Usually _______
-Can be associated with _________-__________ Syndrome, which has a _____, unilateral cafe au lait macule
-Can be associated with ______________ Type 1, which usually has > _ spots over 0.5 cm before puberty or 1.5 cm after puberty
dilation, capillaries, irregular, nape, 1
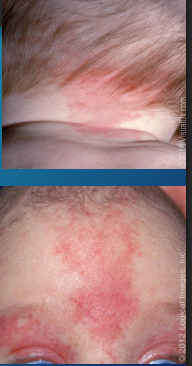
Salmon Patch (Nevus Simplex)
-Common vascular birthmark
-Results from _______ of dermal __________
-Red, ________, macular patches that are commonly found on _____ of neck, eyelids, and glabella
-Most facial lesions fade by _ y/o, but nuchal lesions may persist through life
low, malformation, venules, blanchable, purple, face, complications, laser, capillary vessel
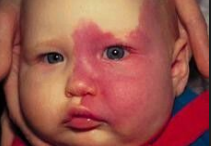
Port Wine Stain
-____ flow vascular ____________ of dermal capillaries and postcapillary _______
-Unilateral, ___________, pink-red, sharply demarcated macule/patch
May darken to _______ and develop a pebbly or thickened surface
Most common on ____
-Typically isolated but can occur as part of complex malformation syndromes
-If eye is involved, refer to ophthalmology and maybe neurology
-Treatment
Cosmetic improvement and prevention of ____________ (thickening, nodularity, bleeding)
Pulsed dye _______ therapy, which irreversibly damages _______ ______
females, white, telangiectasia, plaque, 6-8, 12-14, 3-10, ulceration, obstruction, beta blocker
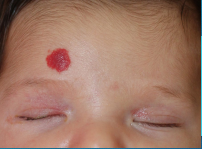
Infantile Hemangioma
-More common in _________; increased incidence in low birth weight or preterm infants
-Present at birth or develop within the first few weeks of life
-May initially appear as pale ______ macule with ____________ proliferating to a bright red, lobulated ________/nodule
-Superficial → reach max size by __-__ months
-Deep → may grow for ___-___ months
-Most spontaneously resolve over __-___ years
-Risks → __________, bleeding, amblyopia or pressure on globe if periorbital, may accompany other malformations
If subglottic, airway _________ can occur. Subglottic hemangiomas are also associated with Beard hemangiomas
-If treatment needed, you can try oral or topical _____ _________ or pulsed dye laser treatment
benign, lymphatic, cysts, birth, translucent, cervicofacial, axilla, lateral, chromosomal, proximal, oral, resection
Lymphatic Malformations
-_______, slow flow vascular lesions composed of dilated __________ channels
-Macrocystic (cystic hygroma)
Collection of large, interconnected lymphatic ______
Present at birth
Large, ___________, soft mass covered by normal skin
Most commonly located in ____________, _____, or ______ chest wall
½ are associated with __________ abnormalities
-Microcystic (lymphangioma circumscriptum)
Cluster of clear, translucent or hemorrhagic vesicles
May present at birth or appear within the first few years of life
Most commonly located on ________ extremities, trunk, axilla, or ____ cavity
-Treatment → surgical _________ (MC) or percutaneous chemoablation
staph aureus, red, pustules, crusts, face, young, bullae, brownish, trunk, dermis
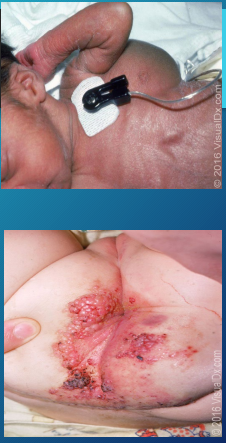
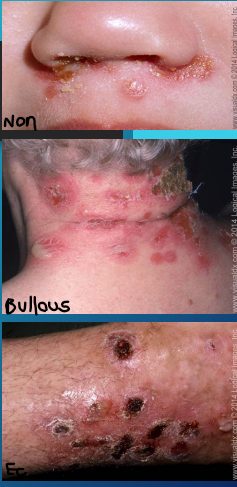
Impetigo: Background
-Most frequently seen in children ages 2-5 years old
-Commonly caused by _____ ________ or GAS
-Non-Bullous (MC)
____ papules → vesicles → _________ → enlarge then break down → forms thick yellow/honey colored ______
Most commonly affects the _____ and extremities
-Bullous
Seen mostly in ______ children
Vesicles enlarge → form _____ with clear, yellow fluid → ruptures → leaves a ________ crust
Usually affects the _____
-Ecthyma
Ulcerative form, where the lesion extends into the ______
clinical, culture, Mupirocin, Cephalexin, bactrim, ecthyma, 24
Impetigo: Diagnosis and Treatment
-Diagnosis
Almost always ________
Gram stain and ________ (if unsure or concerned for MRSA or resistant pathogen)
-Treatment
Topical therapy → _________ or retapamulin, indicated if limited skin involvement
Oral therapy → _________ (DOC for oral therapy), dicloxacillin, _______ or clindamycin if concern for MRSA. Indicated if extensive skin involvement or _______ subtype
-Return to school or daycare __ hours after starting therapy
feet, scalp, T. rubrum, direct, pruritic, scaling, clearing, raised, KOH, hyphae, antifungal, fluconazole, nystatin
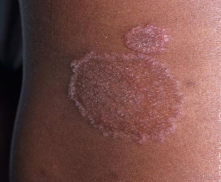
Tinea Corporis
-Found anywhere on the body except ____, groin, face, ______, or nails
-Most common organism is __.______. Could also be T. mentagrophytes or M. canis
-Infected by _____ skin contact w/infected person or animal, contact with fomites, secondary spread
-Begins as _______, circular/oval, erythematous, _______ patch/plaque followed by central _________ with _______ border “ringworm”
-___ prep of skin scraping shows segmented _______
-Treatment
Topical _________ agents of azoles, allylamines
Oral antifungals of terbinafine, ___________, griseofulvin if extensive skin involvement or failure of topical treatment
Do not use ________
scalp, pruritic, alopecia, black, hyphae, Griseofulvin, CBC, ketoconazole
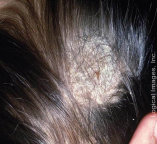
Tinea Capitis
-Fungal infection of the _____ most common in prepubertal children
Most commonly with trichophyton or microsporum species
Contracted from infected person, animal, or contaminated object
-_______, scaly patches with ________
May also be associated with visible _____ dots (broken hair) in areas of alopecia
-KOH prep may show fungal spores and/or _______. Could also do a fungal culture if diagnosis is uncertain
-Treatment
Systemic antifungal agents → ____________ (DOC) x 6-12 weeks. Check LFTs and ___ if therapy > 8 weeks
Selenium sulfide or __________ shampoo twice daily
moisture, diaper, maceration, frictional, irritants, urease, pH, enzymes, inflammation, pH, colonization, candida
Diaper Dermatitis: Pathogenesis
-Increased ________ due to the occlusive ________ as well as stool and urine → leads to __________ of the skin → impairs skin barrier → more susceptible to _________ damage by diaper → leads to further impairment of skin barrier → increased affect of chemical ______ (stool/urine) and microorganisms
-Fecal bacteria produce the enzyme _______ → interacts with urine → increases __ → activates other fecal _________ (protease/lipase) → leads to further irritation and ____________ of the skin
-Elevated __→ alters skin microbiome → more susceptible to ___________ of skin and stool organisms (staph aureus, strep pyogenes, _______ albicans)
sparing, erythematous, asymptomatic, maceration, erosions, pain, glossy, painful, nodules, C. albicans, folds, diaper, red, papules, pustules
Diaper Dermatitis: Presentation
-Irritant diaper dermatitis → occurs in diaper area ______ skin folds
-Mild → scattered ___________ papules, ___________
-Moderate → more extensive erythema with __________ or superficial skin _______, some ____ and discomfort
-Severe → extensive erythema with a ______ appearance, _______ erosions, papules and _______
-Secondary infections (Candida, S. aureus, S. pyogenes) → _._______ most common. Typically involves skin ______ as well as _______ area. Described as beefy ___ plaques, satellite ________, and superficial _________
clinical, diaper changes, cleansing, corticosteroids, nystatin, mupirocin
Diaper Dermatitis: Diagnosis and Treatment
-Diagnosis → almost always clinical
-Treatment
General measures → frequent ______ ______, air exposure, gentle _________, barrier preparations (petroleum, zinc oxide)
Low potency topical ____________ (1% hydrocortisone) for more severe cases
Topical antifungal (_____, clotrimazole, miconazole) if candida superinfection
Topical antibiotics (_______) if bacterial superinfection
Poxvirus, palms/soles, trunk, popliteal, dome-shaped, umbilication, pruritus
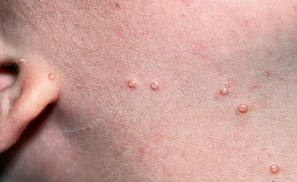
Molluscum Contangiosum: Background and Presentation
-Etiology → _________ family
-Epidemiology → most common in childhood, but it can occur in adolescents and adults
-Symptoms → appear anywhere on the body (except _____/______), but the _____, axilla, antecubital/_______ fossa, crural folds are most common
Firm, ____-______ papules with central ____________
Polypoid with stalk like base
________
clinical, 2, 6-12, curettage, salicylic
Molluscum Contagiosum: Diagnosis and Treatment
-Diagnosis → _________, maybe a biopsy with histologic exam
-Treatment
Starts to resolve within _ months with complete clearing within _-__ months in immunocompetent patients
Cryotherapy
_________
Cantharidin (topical blistering agent)
________ acid (topical keratolytic agent)