E109 Physiology
1/19
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
20 Terms
ephithielium
barrier between cellular lumen (environment) and cell interior
blood
least rigid connective tissue, composed of WBCs, RBCs, cell fragments (platelets), and liquid matrix (plasma)
adipose tissue
Cushions and insulates, stores energy. Two types: ground fat (plays a role in thermodynamic insulation) and white fat.
Loose connective tissue
surrounds blood vessels and internal organs
cartilage
elastic tissue, absorbs shock
dense connective tissue
regular: tendons (connects muscle to bone) and ligaments (connects bone to bone)
irregular: muscle and nerve sheaths
bone
most rigid connective tissue, structural support, organ protection, force transmission (without it, the muscles in the arm wouldn’t be enough to bend the arm)
Exchange epithelia
Found in lungs, lining of blood vessels; helps with exchange of materials; also called leaky epithelia
Transport epithelia
found in intestine, kidney, some exocrine glands; specialized for absorption and controlled transport of substances; more selective than exchange epithelia
Ciliated epithelia
found in nose, trachea, upper airways and female reproductive tract
Protective epithelia
found in skin and lining of cavities open to environment. In skin, cells are anchored to basal lamina by hemidesmosomes.
Secretory epithelia
found in cells that secrete chemicals such as mucus and hormones (think goblet cells)
Na+ K+ ATPase
primary active transport: uses ATP to move Na+ and K+ against concentration gradients
Na+ glucose symporter
secondary active transport: uses Na+ gradient to transport glucose, carrier protein
GLUT transporter
facilitated diffusion: transports glucose via facilitated diffusion
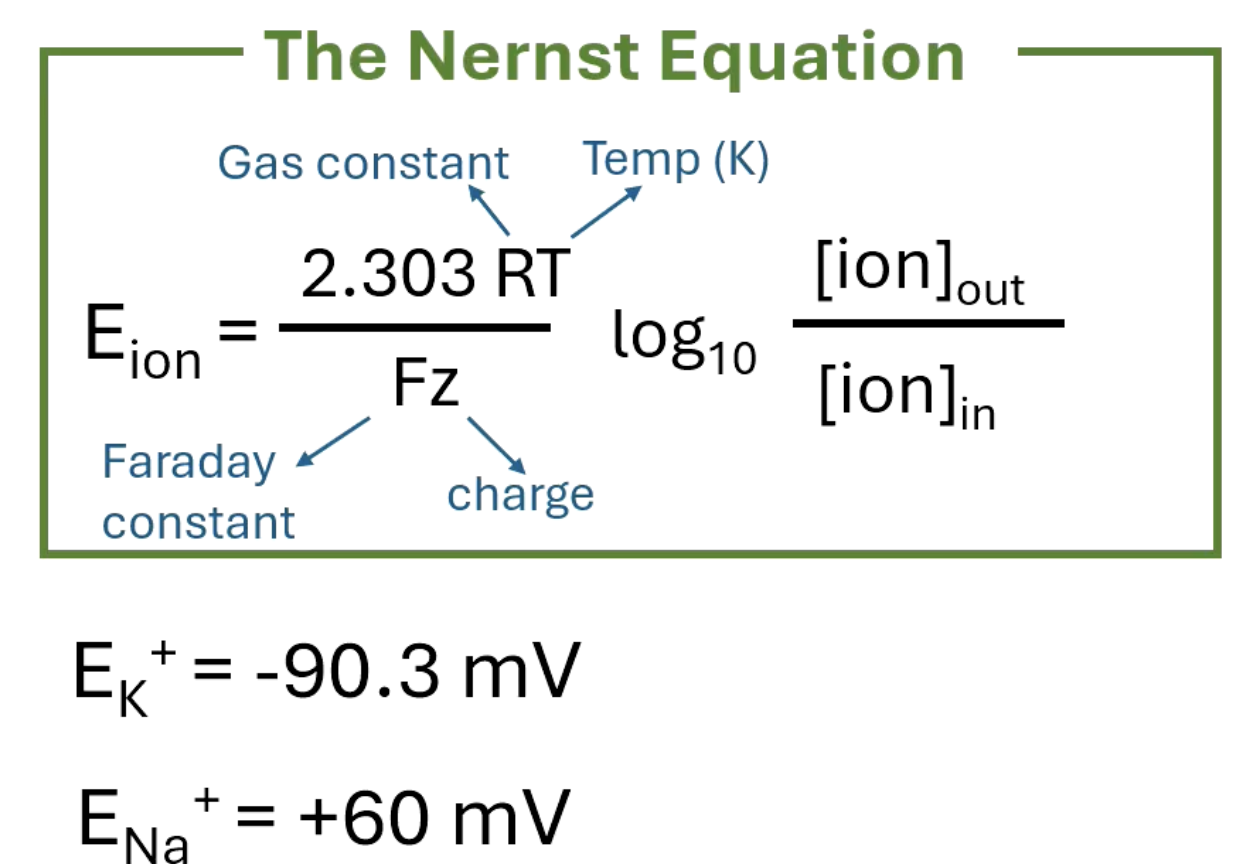
Nernst equation
concentration difference and charge of ions determine equilibrium potential
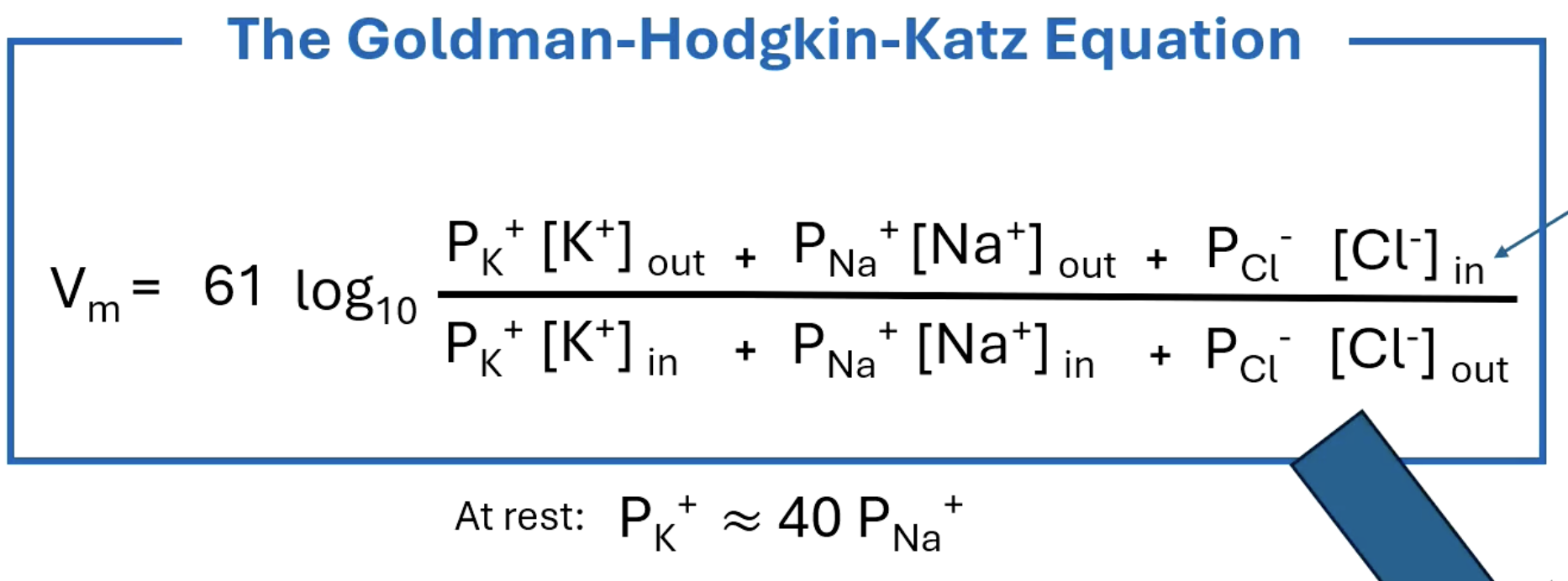
Goldman-Hodgkin-Katz equation
Permeability dictates how close the membrane potential is to the equilibrium potential of an ion
polarization
resting potential of an excitable cell, where the inside of the cell is negative compared to the outside
depolarization
difference in membrane potential is reduced, so the inside of the cell becomes more positive than prior
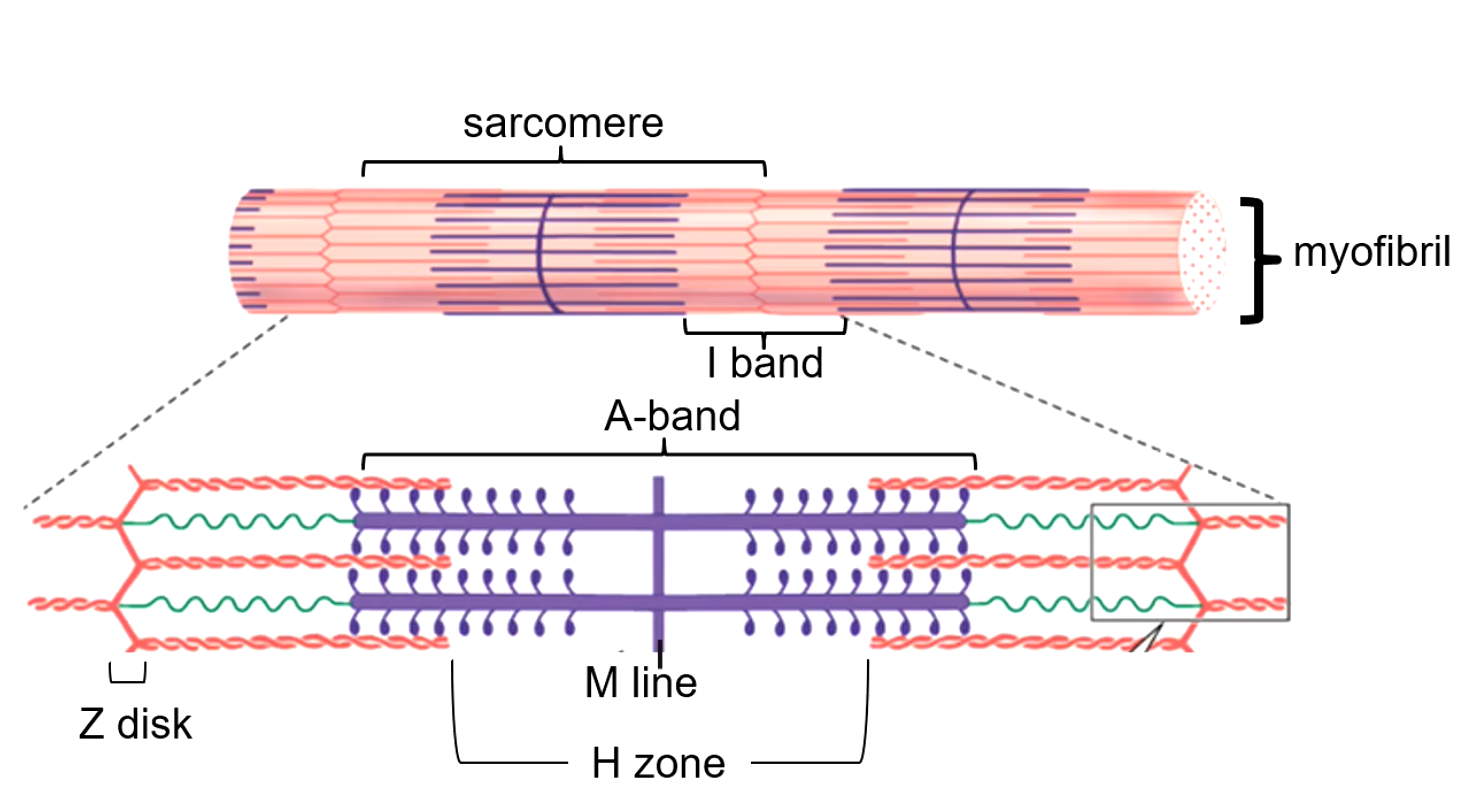
myofibril
embedded in muscle fibers which are embedded in muscle fascicles, sarcomeres are in series along myofibrils