3.) Principles of Design
1/21
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
22 Terms
Overview
• Explains the impact of design on efficiency & safety.
• Describes the basic principles of design for all food facilities
• Focuses on human engineering in design.
Impact of Design
◆ On Safety
◼ Design can support safe & sanitary food handling, thereby reducing the risk of food born illness.
◼ Design can prevent employee injuries by providing a safe work environment.
-
◆ On Efficiency
◼ Labor costs are between 25% & 40% of operating expenses.
◼ Design can reduce labor requirements, reducing expenses & providing competitive advantage.
◼ Design can reduce food costs, strengthening the bottom line.
◆ On Safety
◼ Design can support safe & sanitary food handling, thereby reducing the risk of food born illness.
◼ Design can prevent employee injuries by providing a safe work environment.
◆ On Efficiency
◼ Design can support safe & sanitary food handling, thereby reducing the risk of food born illness.
◼ Design can prevent employee injuries by providing a safe work environment.
Design Principles
• Principles that lead to efficiency & a pleasant environment for the worker & customer.
• Designers weigh these principles when locating functional areas within the building, laying out equipment, & designing custom fabricated items.
• A common misconception about design is that there is only one “right” way to lay out the equipment & arrange the space.
Design Principles
•Efficient & effective designs should:
1. Consider hazard analysis & critical control point.
2. Be flexible & modular.
3. Enhance the customer’s experience.
4. Show simplicity.
5. Create an efficient flow of materials & personnel.
6. Facilitate ease of sanitation & promote food safety.
7. Create ease of supervision.
8. Use space efficiently.
Hazard Analysis & Critical Control Point
• The U.S. Food & Drug Administration has adopted hazard analysis & critical control point as the basic standard by which food service facilities are evaluated.
• HACCP is the process by which food temperatures are monitored & corrected in a foodservice facility.
• This process includes the entire system from receiving through waste removal.
There are seven basic principles of HACCP:
• Analyze hazards.
• Identify critical control points.
• Establish preventive measures with critical limits for each control point.
• Establish procedures to monitor the critical control points.
• Establish corrective actions to be taken when monitoring shows that a critical limit has not been met.
• Establish procedures to verify that the system is working.
• Establish effective record keeping.
Design Principles: Flexibility & Modularity
•Flexibility to accommodate:
•New menu items.
•New methods of preparation.
•New equipment items.
•New methods of service.
-
• Achieved through Modularity:
•Standard sizes of equipment.
•Standard utility connections.
•Ease of removal & replacement.
•Flexibility to accommodate:
•New menu items.
•New methods of preparation.
•New equipment items.
•New methods of service.
• Achieved through Modularity:
•Standard sizes of equipment.
•Standard utility connections.
•Ease of removal & replacement.
Design Principles: Simplicity
◆ Food facilities invite clutter, clutter leads to poor sanitation, confusion, & inefficiency in the work areas.
◆ Examples of simplicity:
◼ Clean, uncluttered lines.
◼ Avoiding unnecessary accessories.
◼ Simplifying & reducing the number of menu items in order to simplify the kitchen & allow for greater consistency & quality of food items being prepared
◼ Convenient server stations
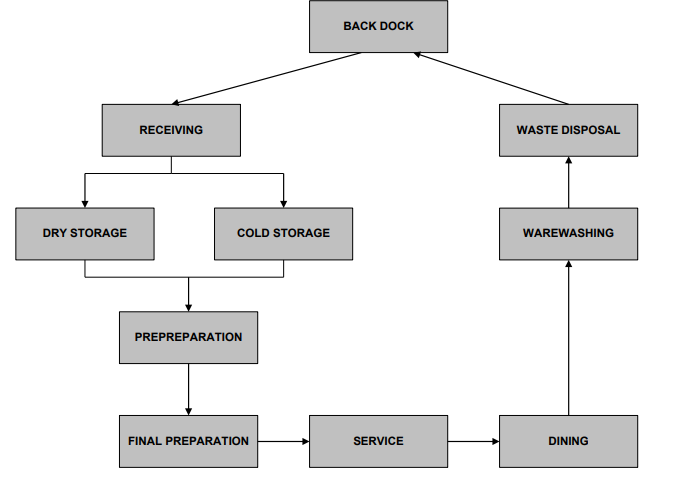
Design Principles: Flow of Materials & Personnel
• Should follow a logical sequence beginning with receiving & ending with waste disposal.
• Some flow considerations in design are:
• Movement of employees from one functional area of the kitchen to another.
• Flow of raw food from the dock, to storage, to preparation, & to service.
• Flow of dishes through the dishwashing system & back to the service area.
• Flow of customers from the entry of the facility to the dining area.
• Some flow considerations in design are:
• Movement of employees from one functional area of the kitchen to another.
• Flow of raw food from the dock, to storage, to preparation, & to service.
• Flow of dishes through the dishwashing system & back to the service area.
• Flow of customers from the entry of the facility to the dining area.
Design Principles: Flow of Materials & Personnel
Design Principles: Ease of Sanitation
• A facility designed with sanitation in mind can be cleaned more quickly & easily & thus requires fewer labor hours.
• Some examples of sanitation design considerations:
• Building finishes (walls, floors, ceilings) that are easily cleaned & sanitized.
• Providing & arranging work area so that cross contamination between raw & cooked products is unlikely.
• Using wall-hung equipment & locating utility services in the walls, so that floors are free of clutter.
• Garbage disposals in preparation areas to simplify waste disposal.
• Some examples of sanitation design considerations:
• Building finishes (walls, floors, ceilings) that are easily cleaned & sanitized.
• Providing & arranging work area so that cross contamination between raw & cooked products is unlikely.
• Using wall-hung equipment & locating utility services in the walls, so that floors are free of clutter.
• Garbage disposals in preparation areas to simplify waste disposal.
Design Principles: Ease of Supervision
• Design examples:
• Locating the Production Office with lines of sight to the preparation areas (rather than the back door).
• Minimizing the number of walls & partitions between functional areas.
• Where interior walls are necessary, as between two banks of equipment, use half-height rather than full height walls.
• Avoid separating by floor (e.g. service areas on one floor, & preparation below).
Design Principles: Space Efficiency
• Providing these components will help ensure that each section of the kitchen has the necessary equipment & storage space to enable employees to work efficiently:
• A work surface
• A food prep sink
• A hand wash sink
• A cutting surface
• Storage for utensils
• Storage for pans
• Storage for raw ingredients
• Storage for the finished product
• Proper aisle space for movement
Design Principles: Lifetime Value
•The cost of a design solution or an item of equipment is not the purchase price, but the overall cost of ownership, including:
• Operational costs.
• Maintenance Costs.
• Labor costs to operate.
• Lifetime (how long it will last).
Design Principles: Compromise
• In the process of design, conflict is inevitable & compromise is necessary.
• Budget & space constraints are frequent causes of conflict.
• If the client insists on making choices that depart from principles of good design, the designer has three choices:
• Formally express the concern & give in to the client’s demand.
• Formally express the concern, then seek a design solution that will satisfy the client & will preserve the principles of good design.
• As a last resort, resign & bill the client for the work completed as of the day of the disagreement.
Design Principles
•Efficient & effective designs should:
1. Consider hazard analysis & critical control point.
2. Be flexible & modular.
3.Enhance the customer’s experience.
4. Show simplicity.
5. Create an efficient flow of materials & personnel.
6. Facilitate ease of sanitation & promote food safety.
7. Create ease of supervision.
8. Use space efficiently.