carbohydrates and polysaccharides
1/98
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
99 Terms
What are carbohydrates made of
Carbon oxygen and hydrogen
What is the most common carbohydrates minimal formula
Cn(H2O)n
What is the other name of carbohydrates
Saccharides, sugars
Carbohydrates are major sources of energy, how do we take them
Intake from diet but mammals are also able to synthesize from small MW metabolites,
How do plants synthesize sugars
From CO2 and energy in the form of radiation
Synthesis is an overall reduction reaction, respiration is oxidation
What are the different types of carbohydrates
Monosaccharides, the simplest ch
Disaccharides, two covalently linked monos.
Polysaccharides, many covalently linked monos
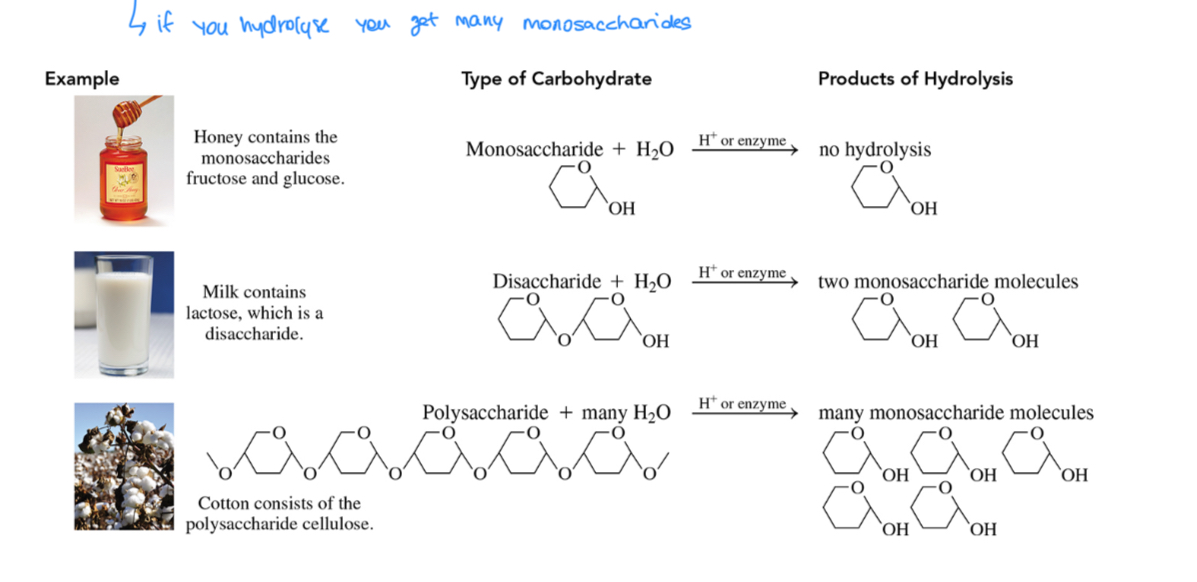
What is the structure of a monosaccharides
In simple cases it contains a carbon chain, an aldehyde (aldose) or ketone (ketose) group, and hydroxyls on each carbon atoms except the carbonyl
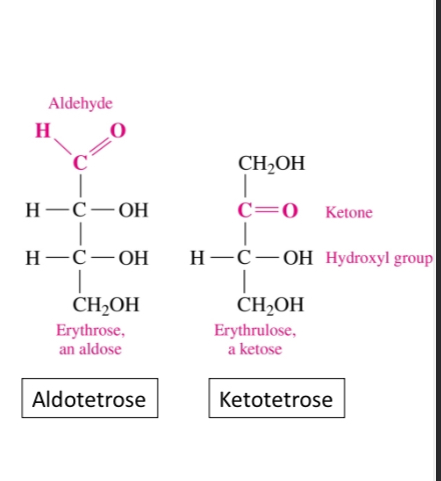
Name these monosaccharides
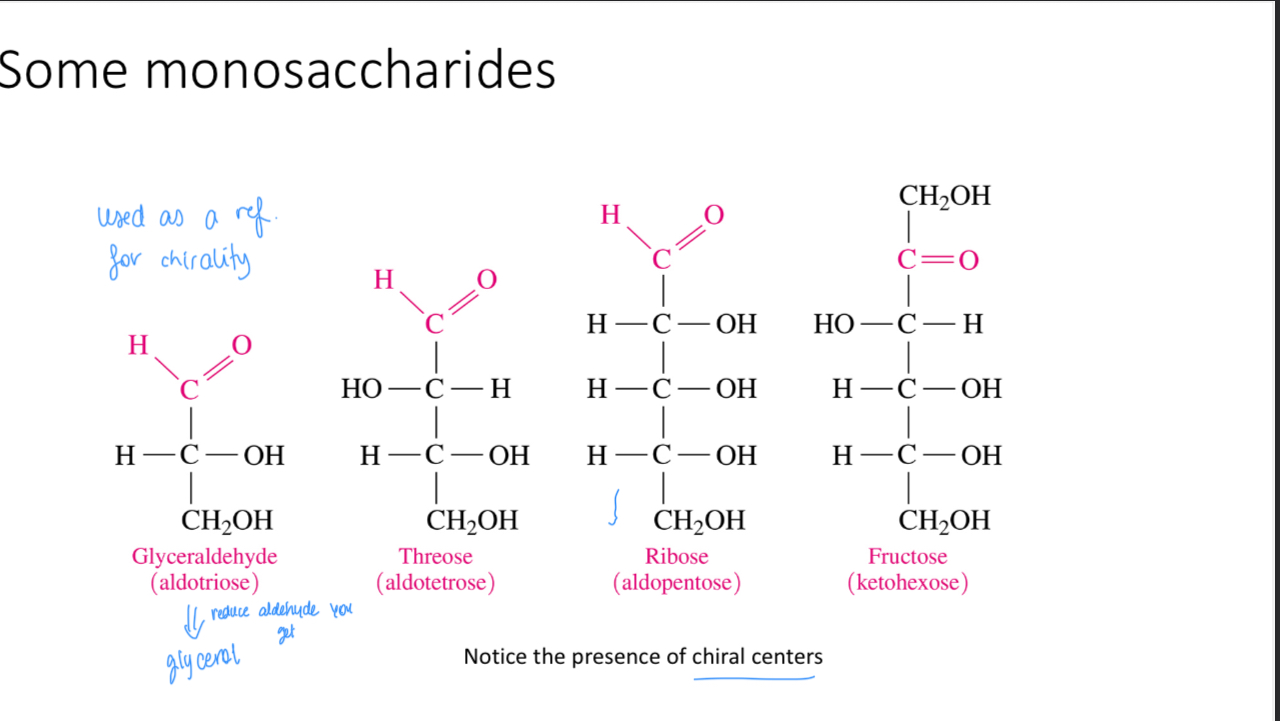
Fisher projections
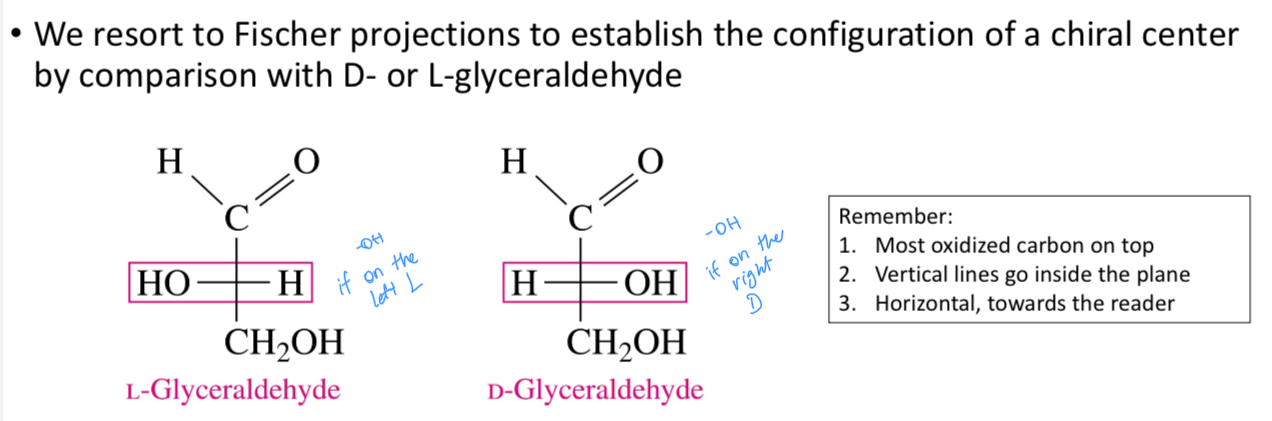
Which carbon atom decides whether it’s L or D
The one chiral carbon that’s furthest away from the most oxidized C atom (chiral carbon)
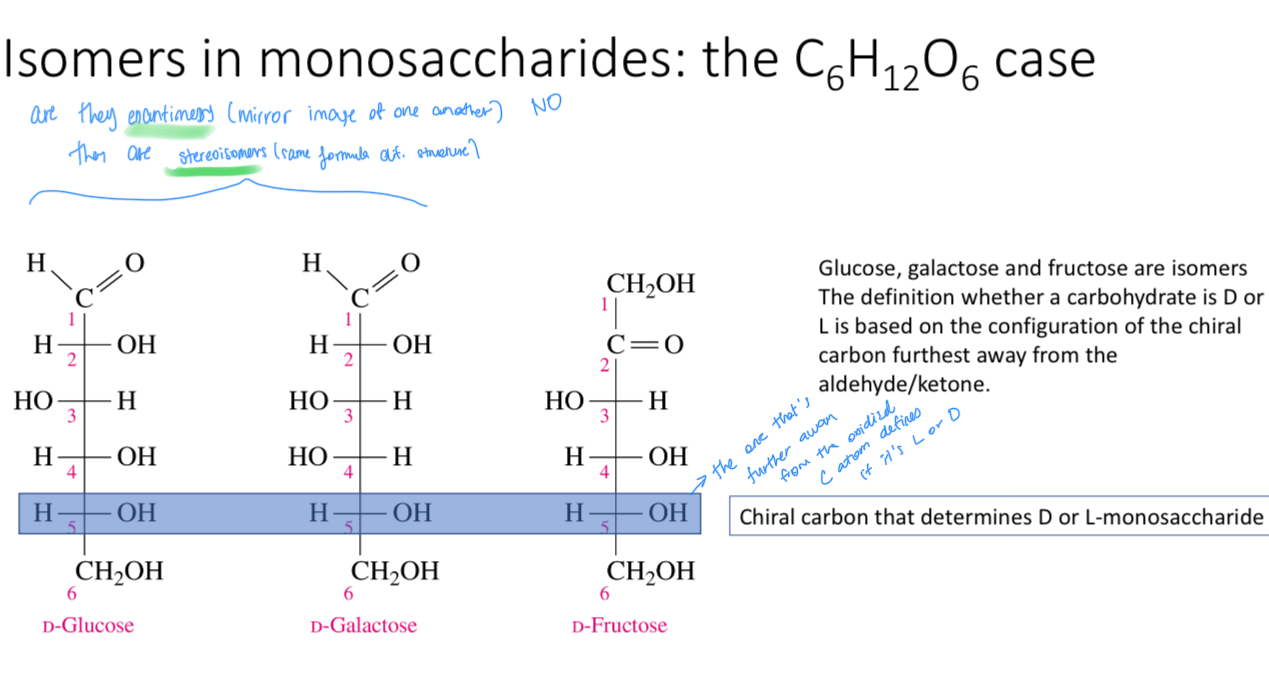
Are d-glucose, d-fructose and d-galactose enantiomers (mirror image of one another)?
No they are stereoisomers (Same formula different structure)
VERY IMPORTANT IN THE EXAM
YOU SHOULD SAY IT’S A POLYMER OF D-GLUCOSE NOT JUST GLUCOSE
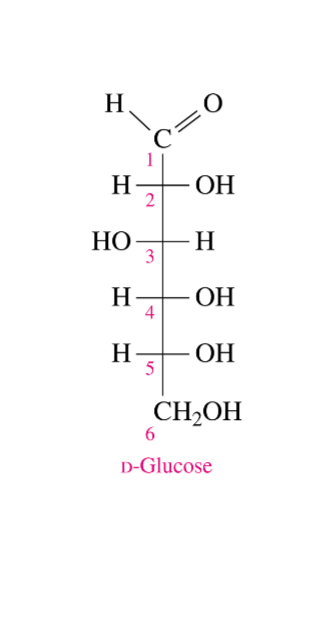
What is the most common hexose
D-Glucose
Where is D-Glucose found in
Fruits, vegetables, corn syrup and honey
What is D-Glucose also known as in the body
Dextrose and blood sugar
What is the D-Glucose the building block of
The disaccharides; sucrose, lactose and the polysaccharides such as cellulose and glycogen
What is galactosemia
High galactose in blood
What is the formula of d-galactose
It’s an aldohexose with the formula C6H12O6
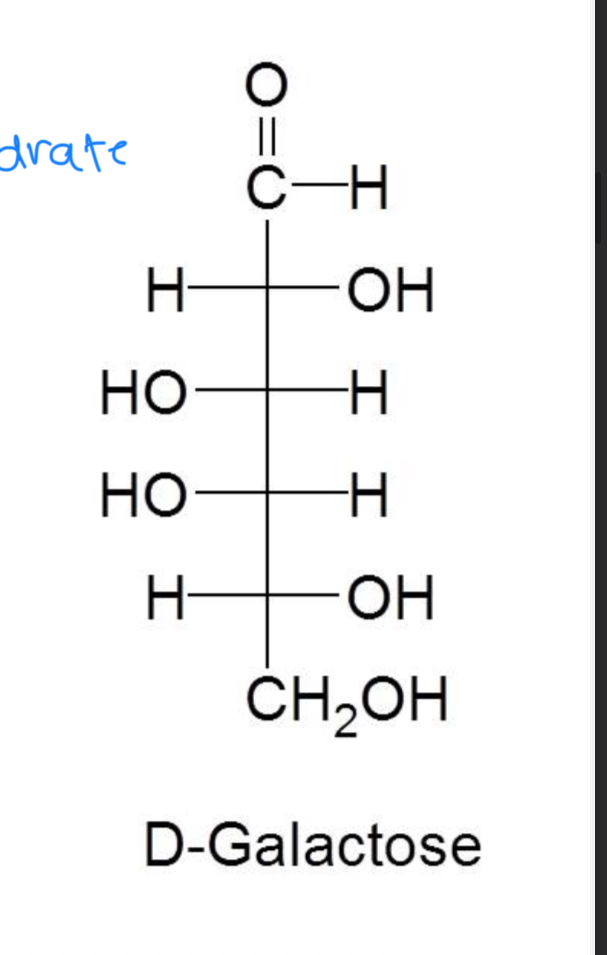
D-galactose is the building block of what
lactose
Which monosaccharide is important in the cellular membranes of the brain and nervous system
D-galactose
What happens in the condition of galactosemia
the enzyme needed to convert d-galactose to d-glucose is missing so galactose accumulates in the blood and tissue
What can galactosemia cause
The accumulation of galactose in the blood and tissue can lead to cataracts, mental retardation, failure to thrive and liver disease
D-fructose formula
Ketohexose with the formula C6H12O6
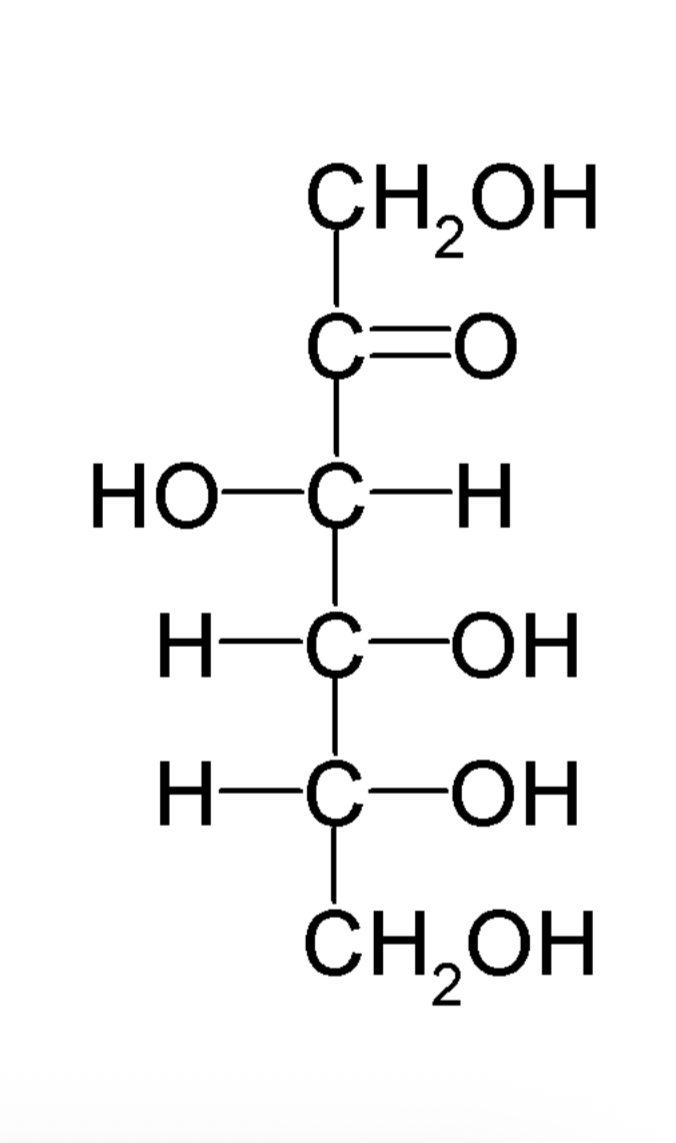
What is the sweetest carbohydrate
D-fructose
How can we obtain d-fructose
By the hydrolysis products of sucrose (so fructose isn’t the only building block of sucrose but one of them)
How can we obtain high-fructose corn syrup (HFCS)
By using an enzyme to break down sucrose to glucose and fructose
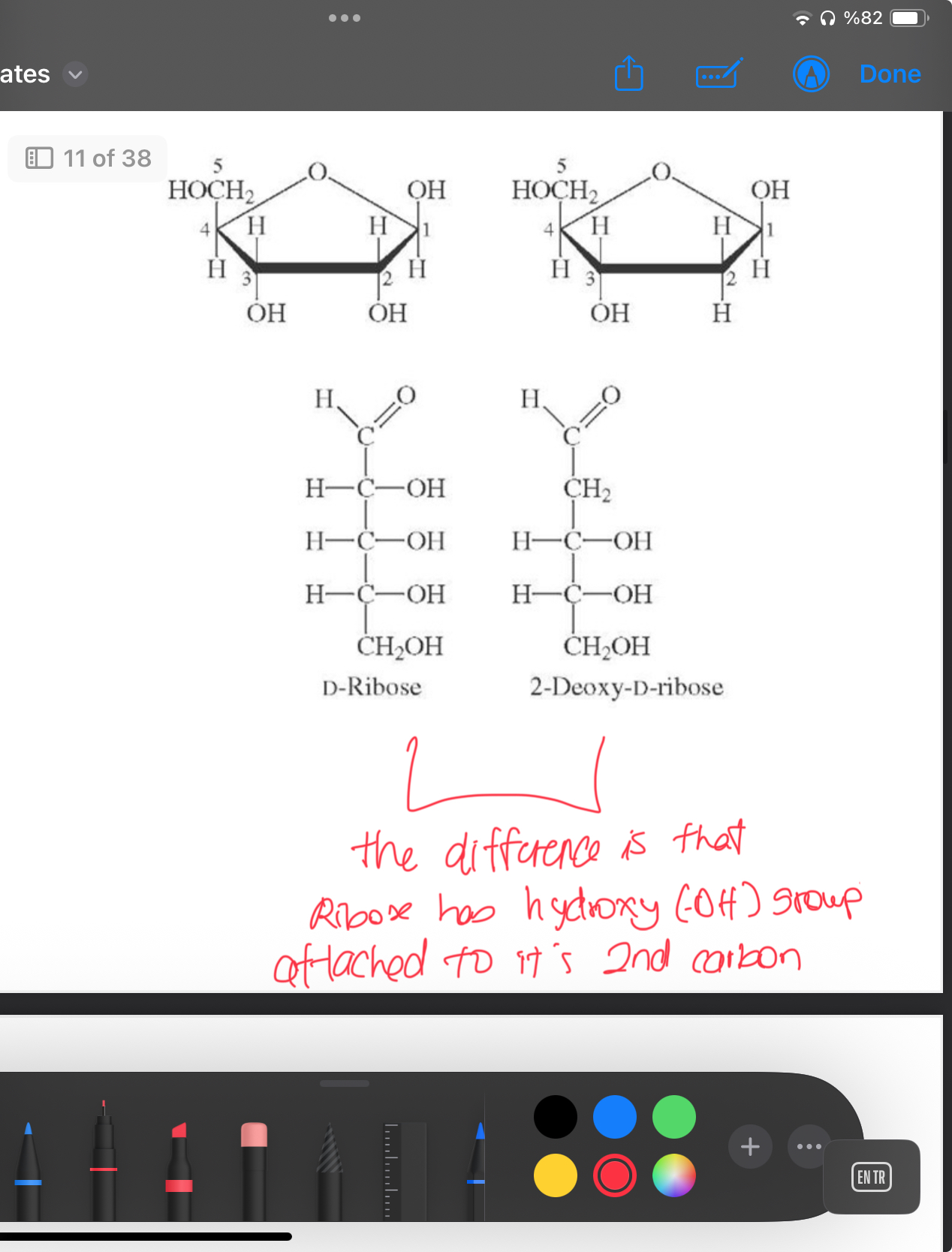
Formula of d-ribose
Aldopentose with the formula C5H10O5
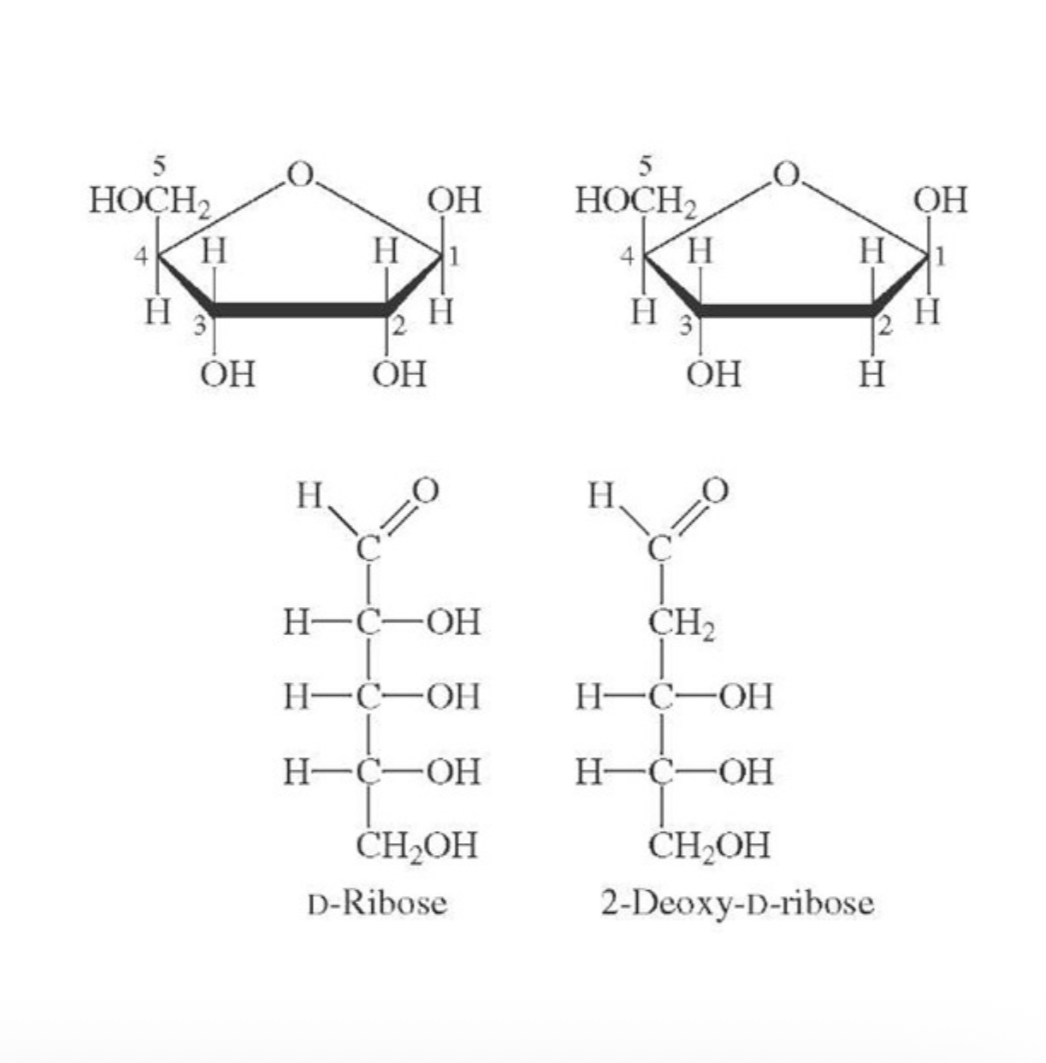
What is the d-ribose component of
Ribonucleic acid (RNA) molecules
How do we obtain d-ribose
It is reduced from 2-deoxy-d-ribose which is part of the deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) molecules
What is the difference between d-ribose and 2-deoxygenated-d-ribose
What are the reactions that monosaccharides can perform and they react as which form
-reduction
-oxidation
-aldol reaction
-reaction with amines
-formation of acetals and hemiacetals
They react as aldehydes or ketones
Reactions they can enter if they have one or more hydroxyl group and what they act as
-oxidation (Aldehydes only)
-water elimination
-formation of esters
They react as alcohols
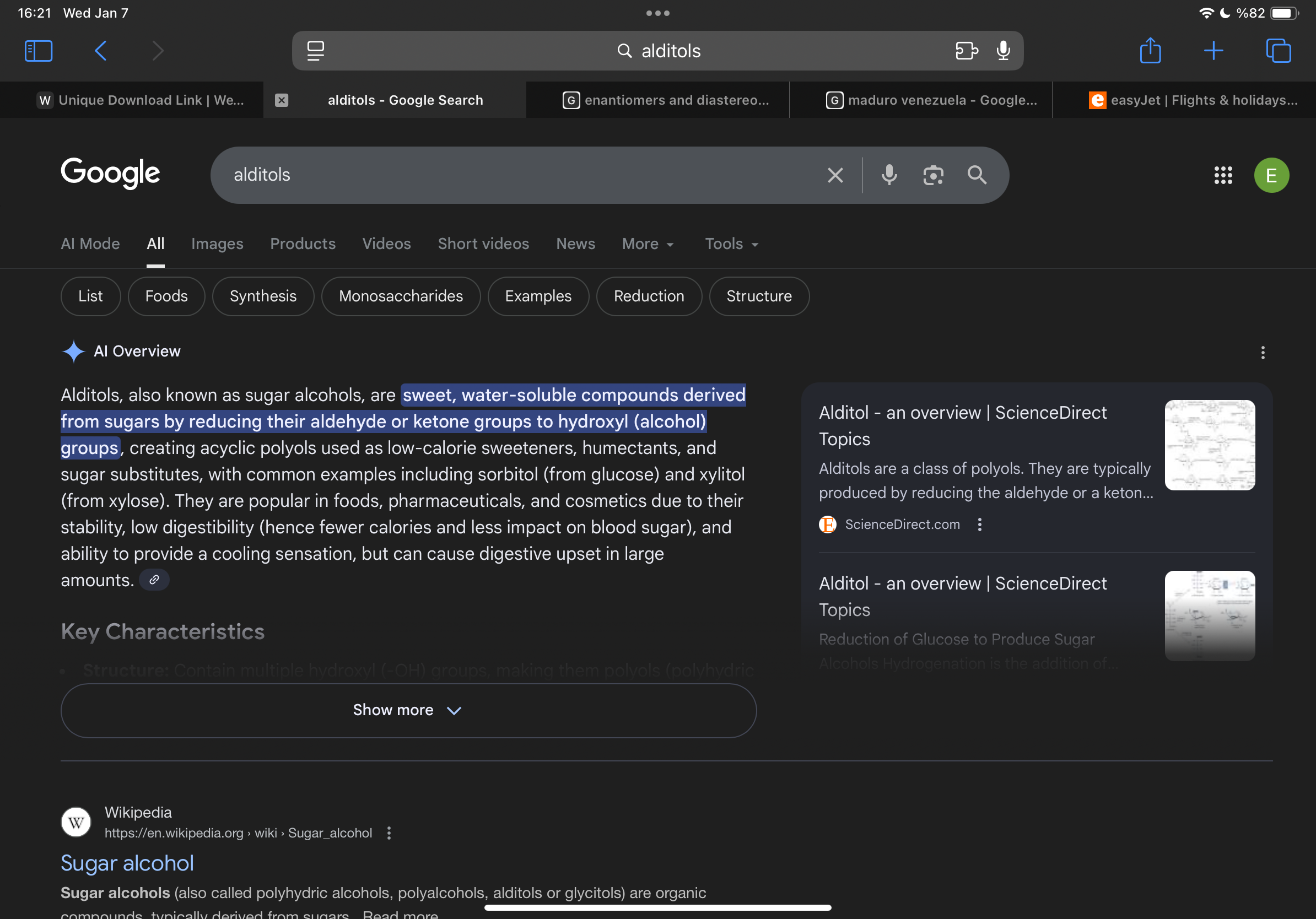
Aldoses and ketoses ar in equilibrium between the open chain and cyclic forms. The reaction is reversible
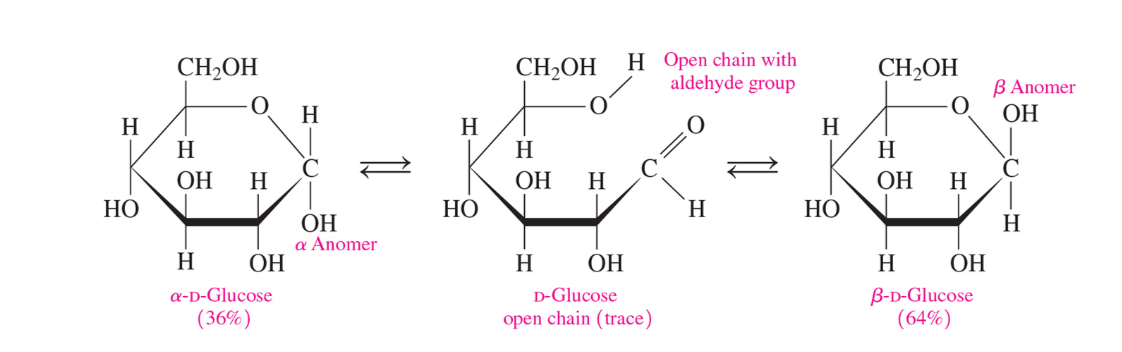
How do we get cyclic forms in aldoses and ketoses (monosaccharides)
From an intermolecular reaction between the carbonyl and a -OH group (the different ends of the monosaccharide open chain)
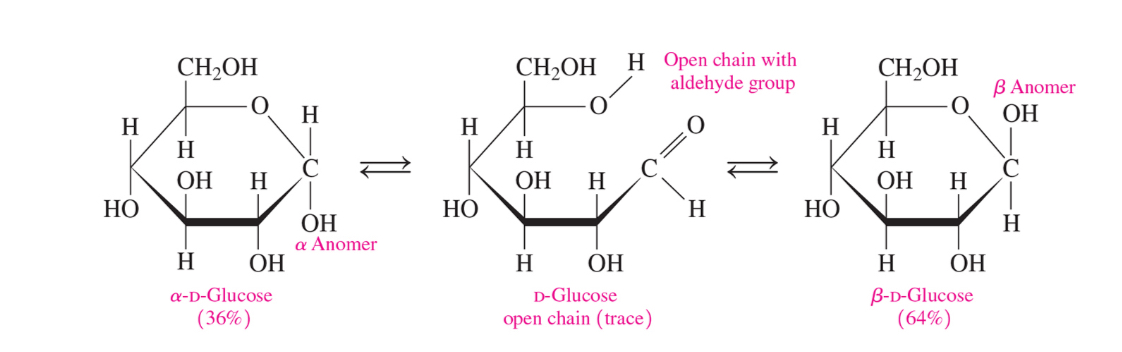
Cyclic hemiacetals yielding a five or six membered ring are stable
Self explanation: when the carbonyl group reacts with the hydroxy group on the same sugar a cyclic structure is produced and it’s called a hemiacetal.
Why do we usually find sugar in a cyclic structure
Because cyclic hemiacetals yielding a five or six membered ring are stable
What are the 5-membered and 6-membered hemiacetals called
Furanose (5-membered)
Pyranose (6-membered)
What is the difference between alpha and beta-d-glucose
alpha= -OH down
Beta= -OH up
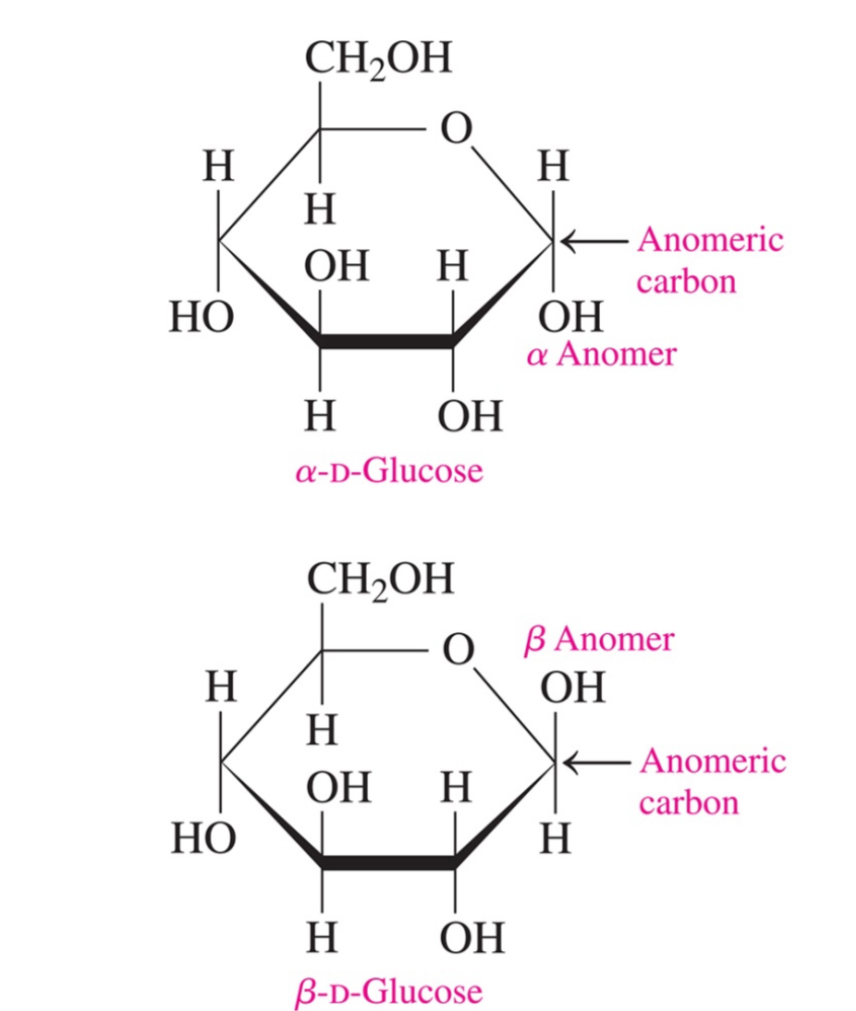
What is an anomer
A cyclic stereoisomer of a carbohydrate with isomerism involving only the arrangement of atoms or groups at the aldehyde or ketone position (meaning that it’s a stereoisomer where the only difference is on the anomeric carbon which is the carbonyl group’s carbon)
Why is the chair conformation important
-minimizes angle strain
-minimizes torsional strain
-is the lowest energy shape
(Minimize steric hindrance)
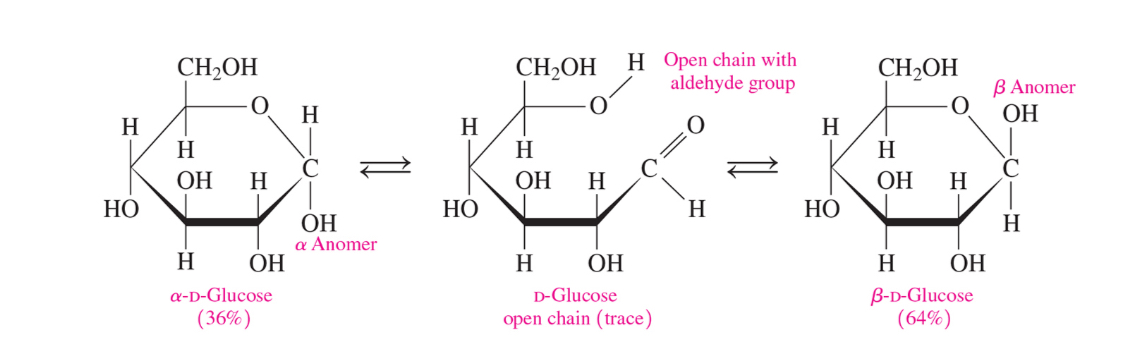
What is mutarotation
Mutarotation is the spontaneous interconversion of alpha and beta anomers of sugar in solution via the open chain form causing a gradual change in optical rotation until equilibrium is reached
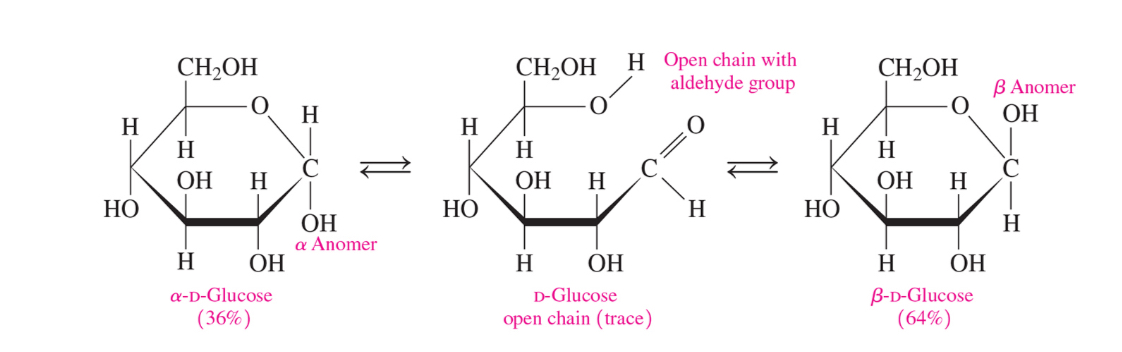
Mutarotation in fructose (ketose)
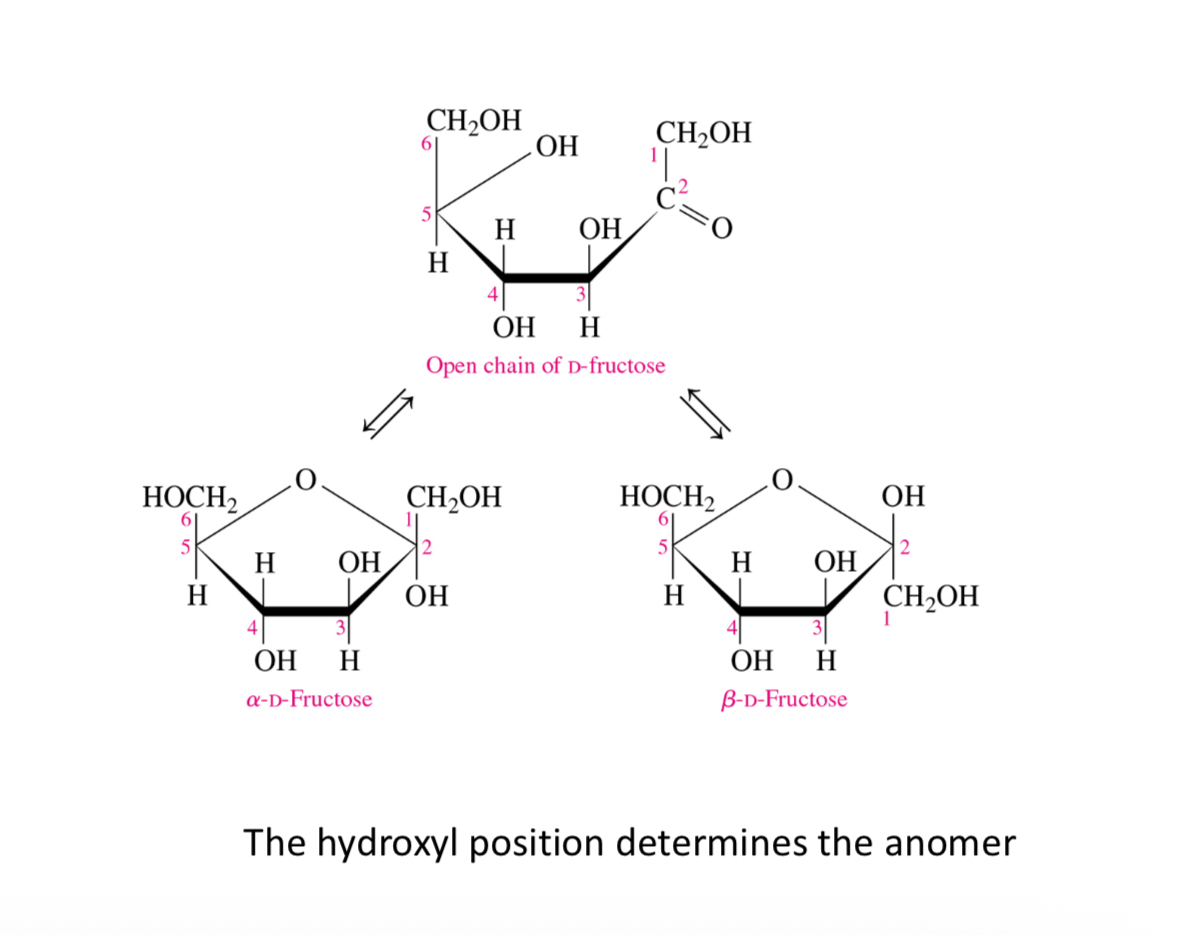
What are the common monosaccharides
1- D-Glucose (6C)
2- D-Galactose (6C)
3- D-Fructose (6C)
4- D-Ribose (5C)
What are the conditions for the oxidation of monosaccharides
1- Monos. Are mostly found in cyclic forms in solutions but the small amount of the open chain form can be oxidized
2-have an aleyhe group with adjacent hydroxyl group that can be oxidized to carboxylic acid
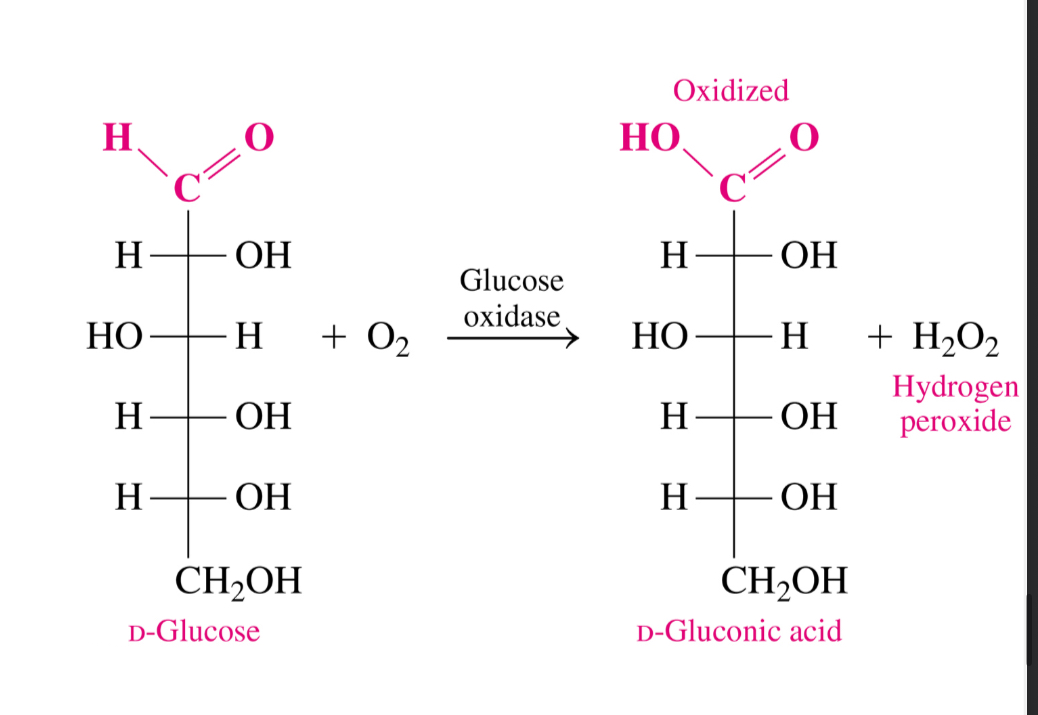
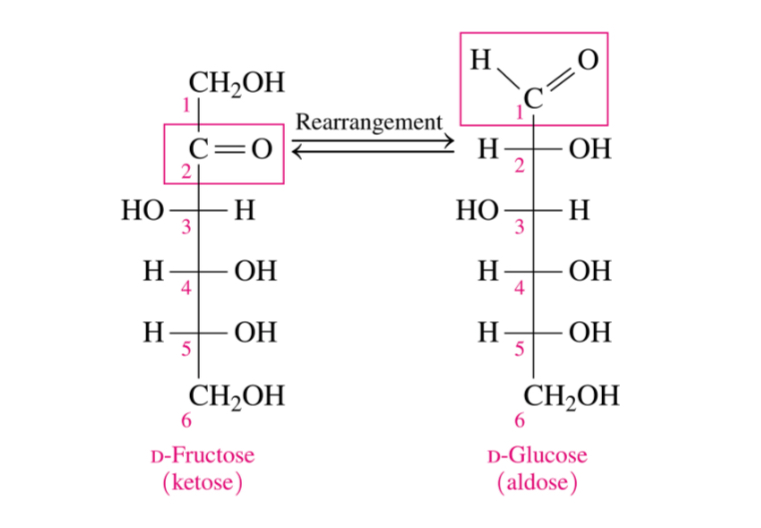
Can ketoses undergo oxidation
No normally they can’t BUT intermolecular rearrangments make monosaccharides such a s fructose oxidizable
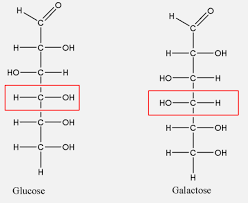
Are d-glucose and d-galactose stereoisomers
Yes, d-fructose is a structural isomer since it’s a ketose and d-ribose has 5 carbon atoms
What can be an oxidizing agent for an aldose
Benedict’s solution
Reduction of monosaccharides
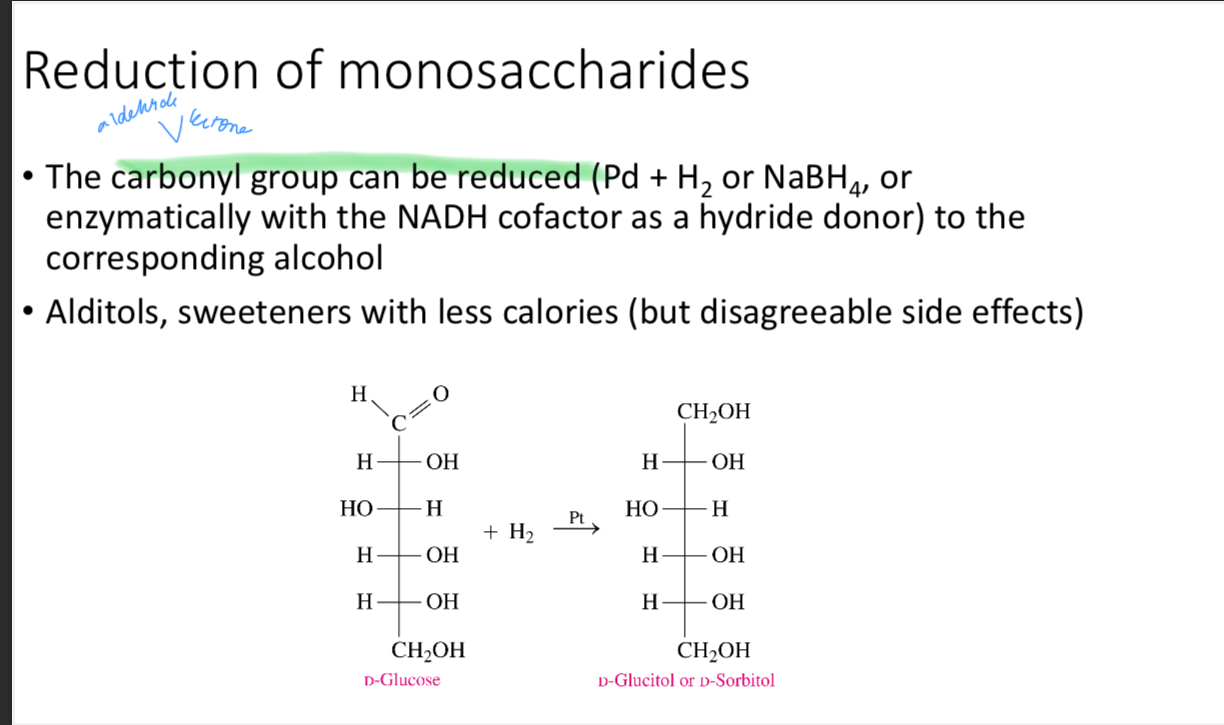
What are alditols
Sweeteners with less calories
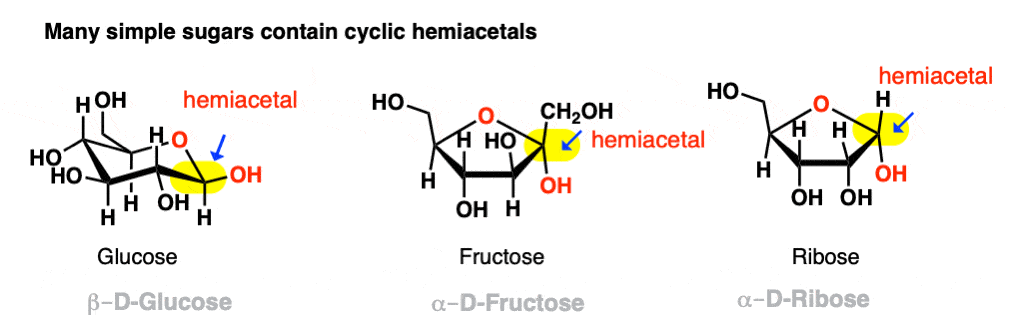
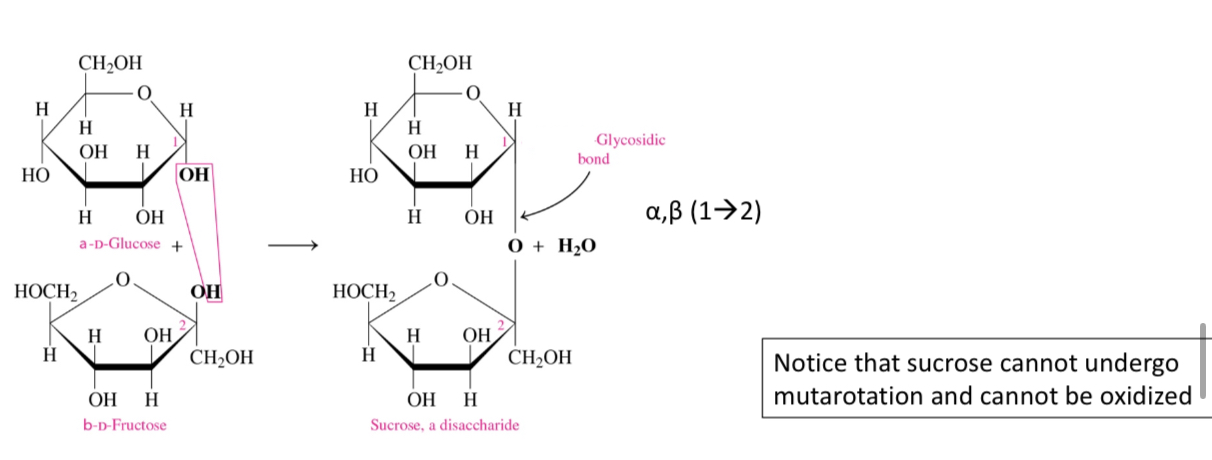
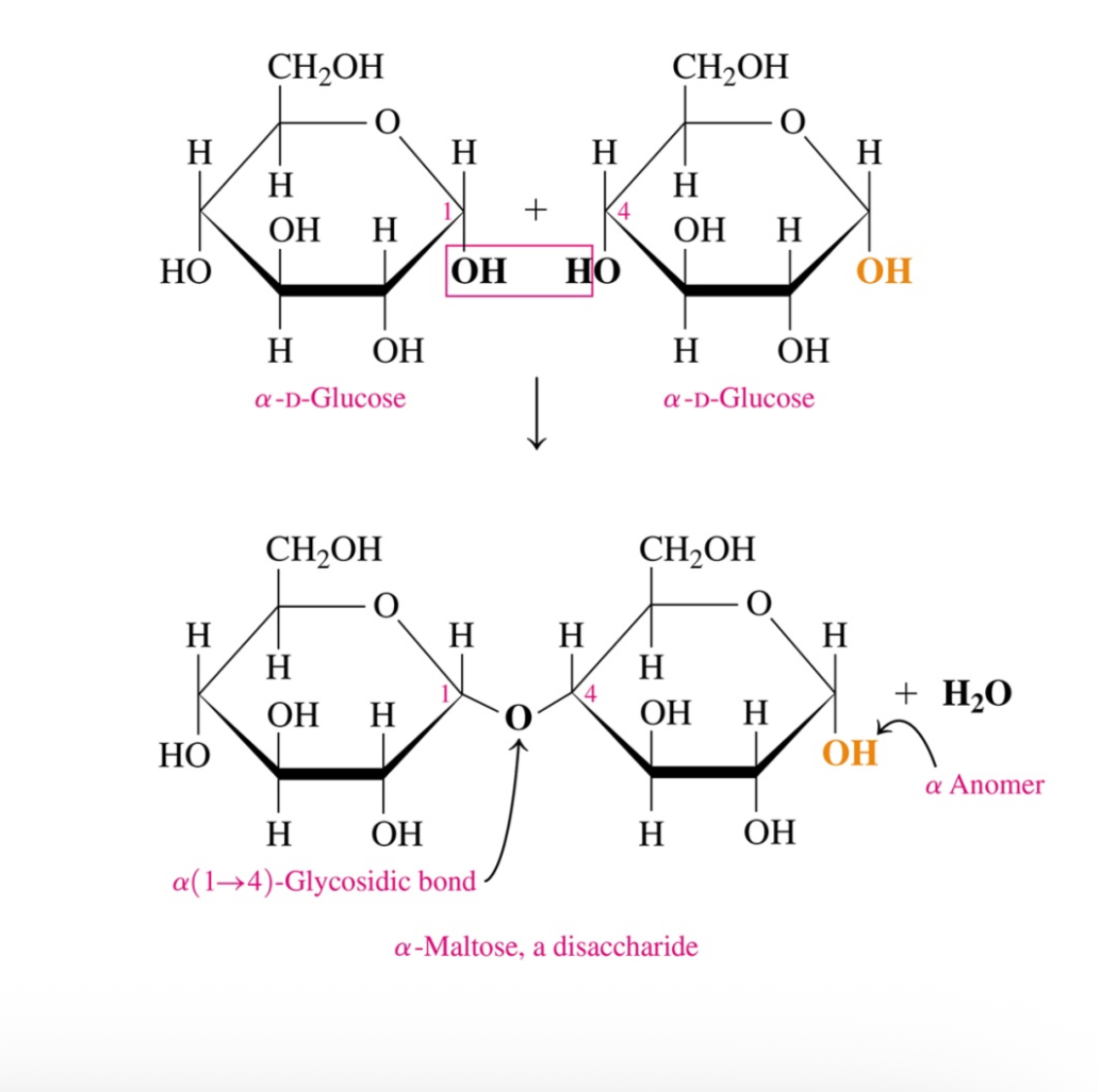
How are disaccharides formed
they are formed through the conensation of two cyclic monosaccharides
Hemiacetals tam anlamadım ama özetle bu
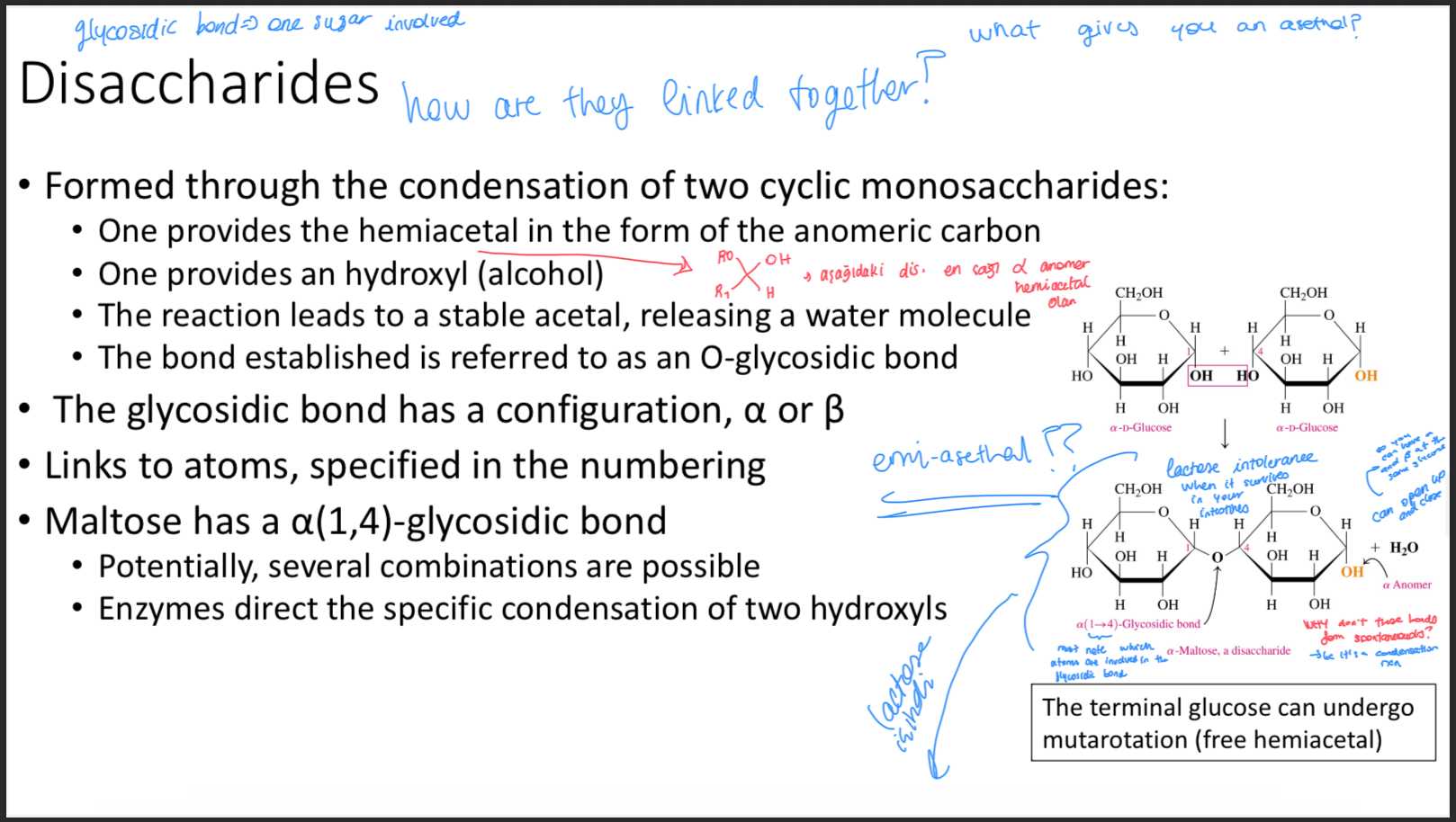
İyi çalış bu slaytı
Slayt
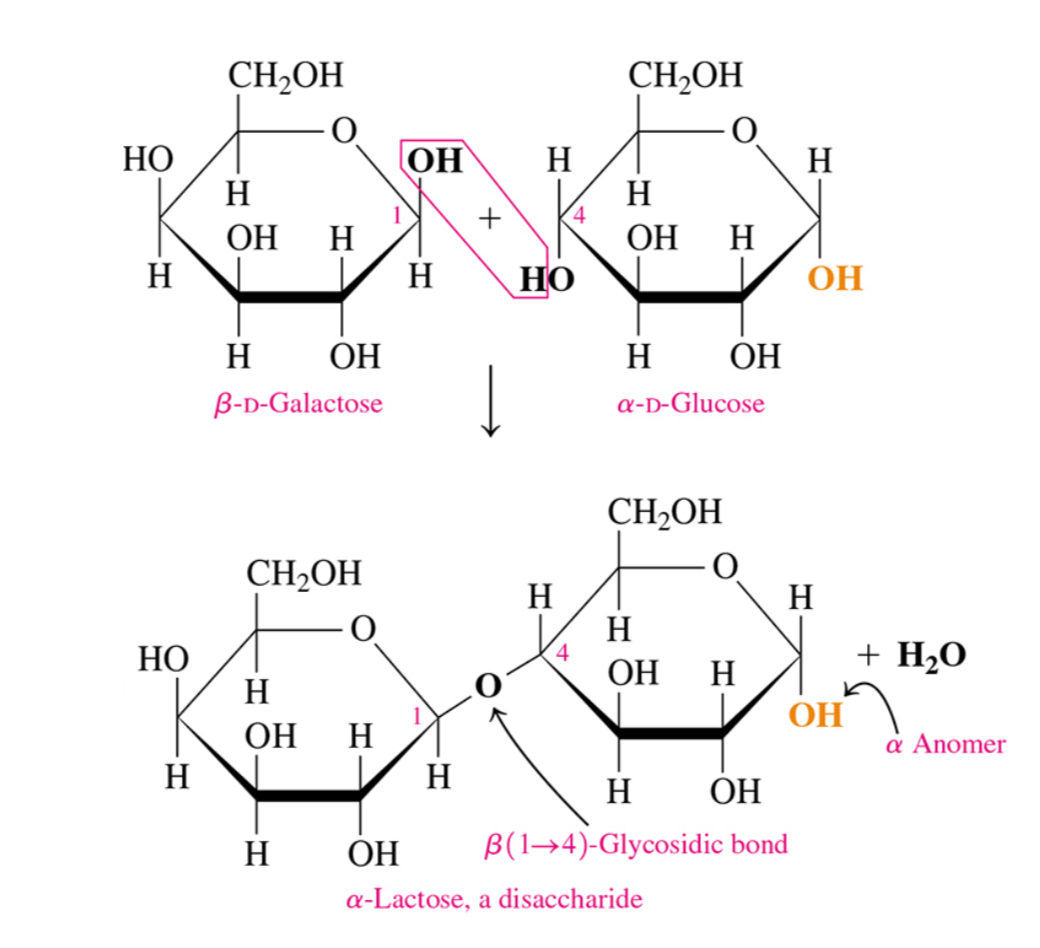
Two disaccharides
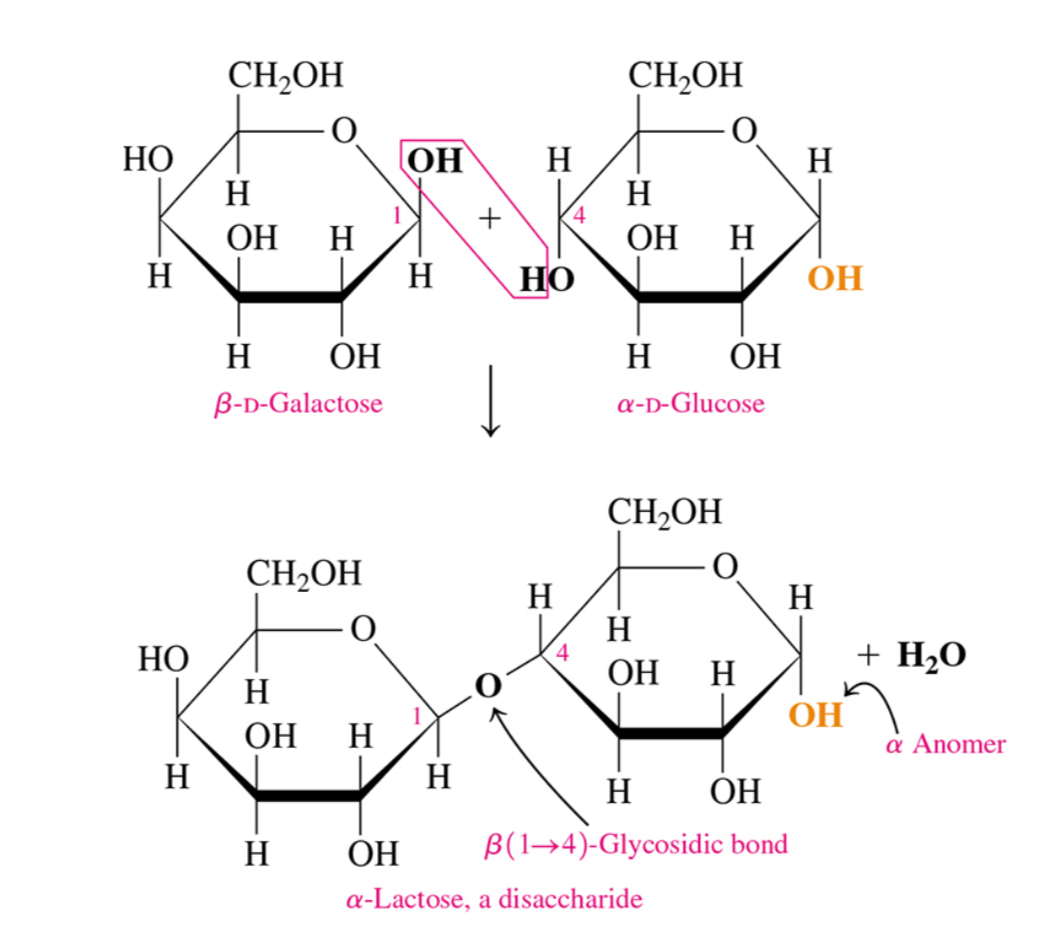
Lactose and sucrose
What is lactose found in
Breast milk
Hydrolysis of lactose
Is hydrolyzed by lactase in the intestine to galactose an glucose that are absorbed by the villi
How does lactose intolerance develop
Lactase enzyme is dose-inducible so if absent or low activity, lactose intolerance develops
What are lactose and sucrose composed of
Lactose= beta-D-galactose and alpha-D-glucose
Sucrose= alpha-D-glucose and beta-D-fructose
Why can’t sucrose undergo mutarotation
Because both its anomeric carbons are involved in the glycosidic bond
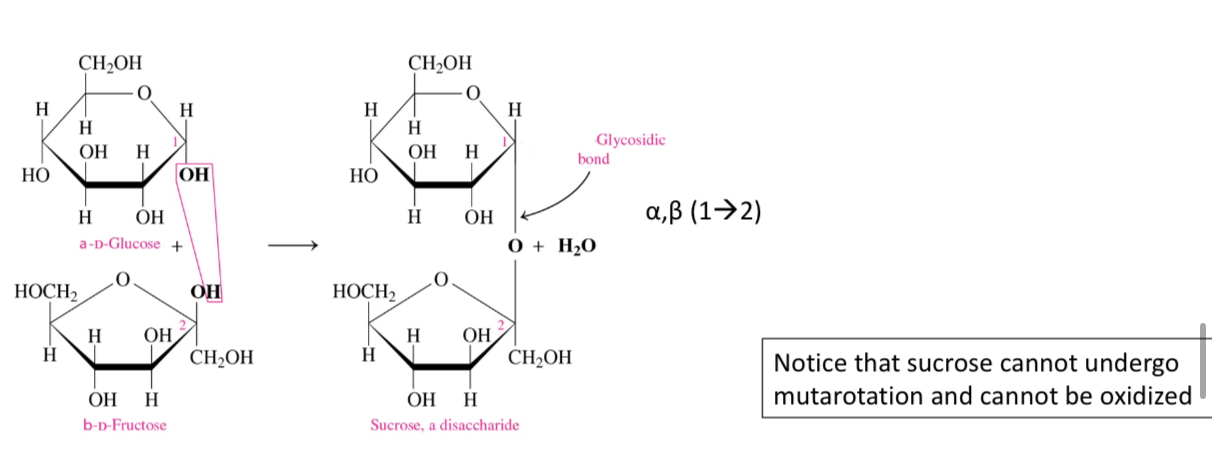
Why can’t sucrose undergo oxidation
Because it has no free aldehydes or ketone group
GLUCOSE VE SUCROSE NASIL OLUŞUR ŞEKİLLERİ O FORMÜLLERİ FALAN BİL
Yani soruğunda yazabil
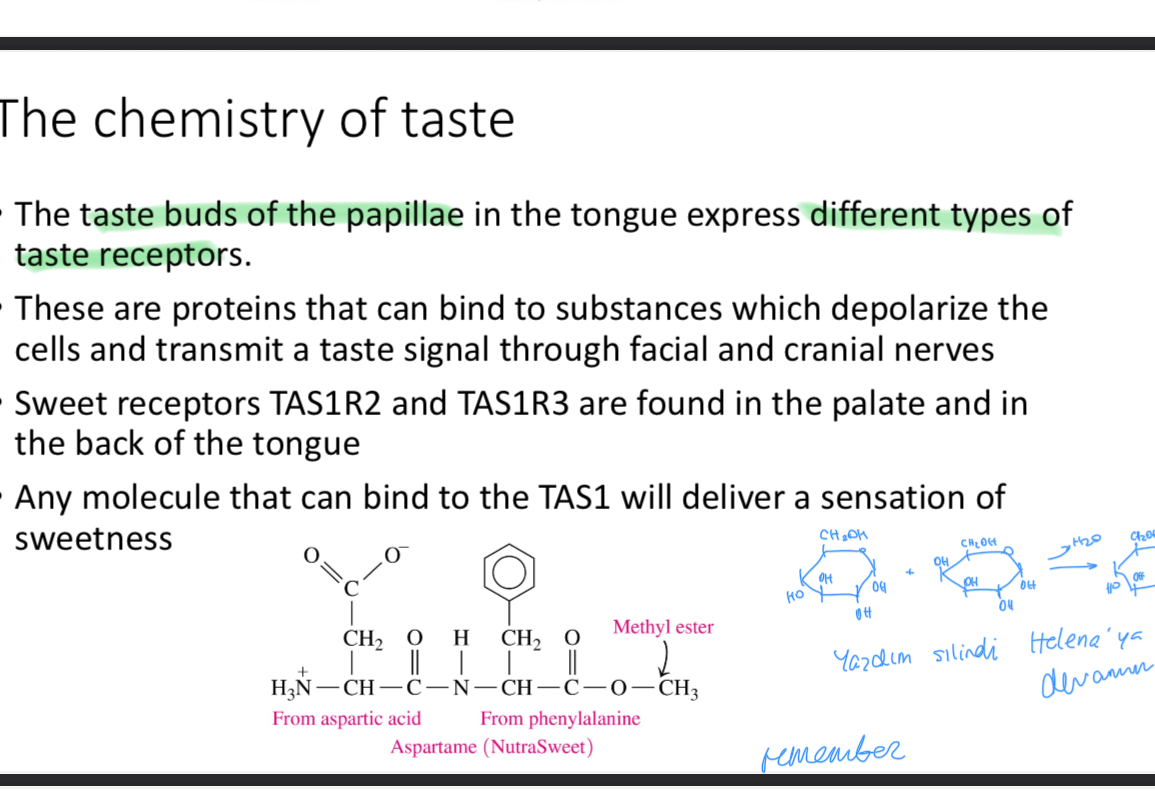
The chemistry of taste
What is a polysaccharide
Many monos. Joined together via O-glycosidic bond
What is a homopolysaccharide
Single repeating unit and zıttı da heteropolysaccharide
What is the formation of specific O-glycosidic bonds directed by
It’s directed by enzymes that not only catalyze the condensation reaction but also direct the specific coupling between one anomeric carbon and one specific hydroxyl
Why is the most common homopolysaccharide is glucose polymers
Because organisms fight har for their energy source and when an excess is available it is store in a polymeric molecule. When energy is scarce, individual units can be removed from polymer to extract the required energy (also for structural reasons like cellulose)
4 polysaccharides
Amylose
Amylopectin
Cellulose
Glycogen
Amylose:
poly-alpha (1,4) glucose
Linear chains usually between 300-600 but up to 4000 repeating units
Found in plants, about 20-30% starch
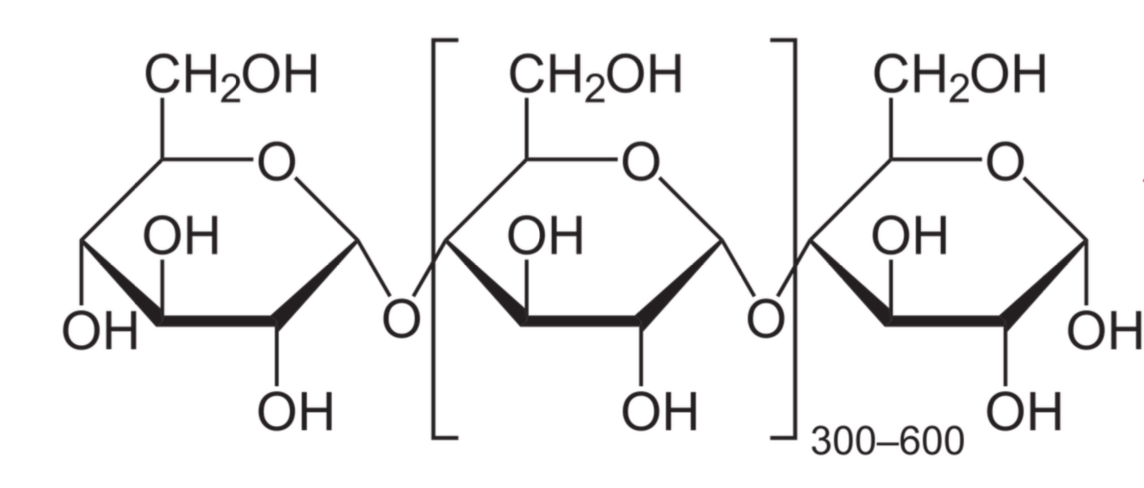
How is amylose broken down into smaller oligosaccharides
Through hydrolysis catalyzed by enzymes called alpha-amylases (in the saline secrete by the pancreas)
Amylopectin:
poly-alpha (1,4) glucose with alpha(1,6) branches
Branching occurs every 30 glucose units
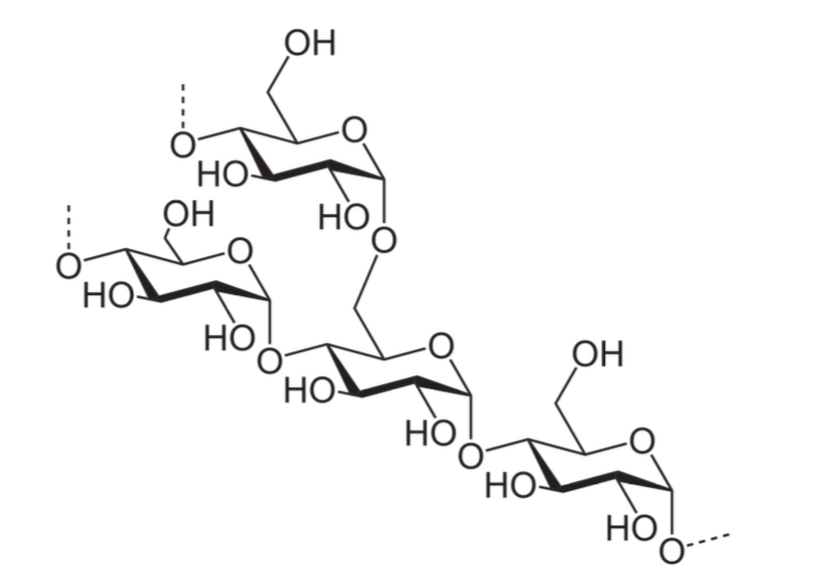
How does an amylopectin form starch
Amylopectin associates with amylose via non-covalent hydrogen bonding interactions to form starch
Are amylose amylopectin cellulose glycogen all homopolysaccharide
Yes
Cellulose:
Poly-beta(1,4) glucose
N is between hundreds and thousands
Cotton fiber is 90% cellulose
What is the cell wall of green plants composed of
Cellulose
Is cellulose digestible
No, most animals lack the enzyme required for the hydrolysis of the beta(1,4) glycosiic bond
How do animals store glucose
Animals store glucose in a polymer called glycogen
Glycogen:
poly-alpha(1,4) glucose with alpha(1,6) branches
Branching occurs every 8-12 residues
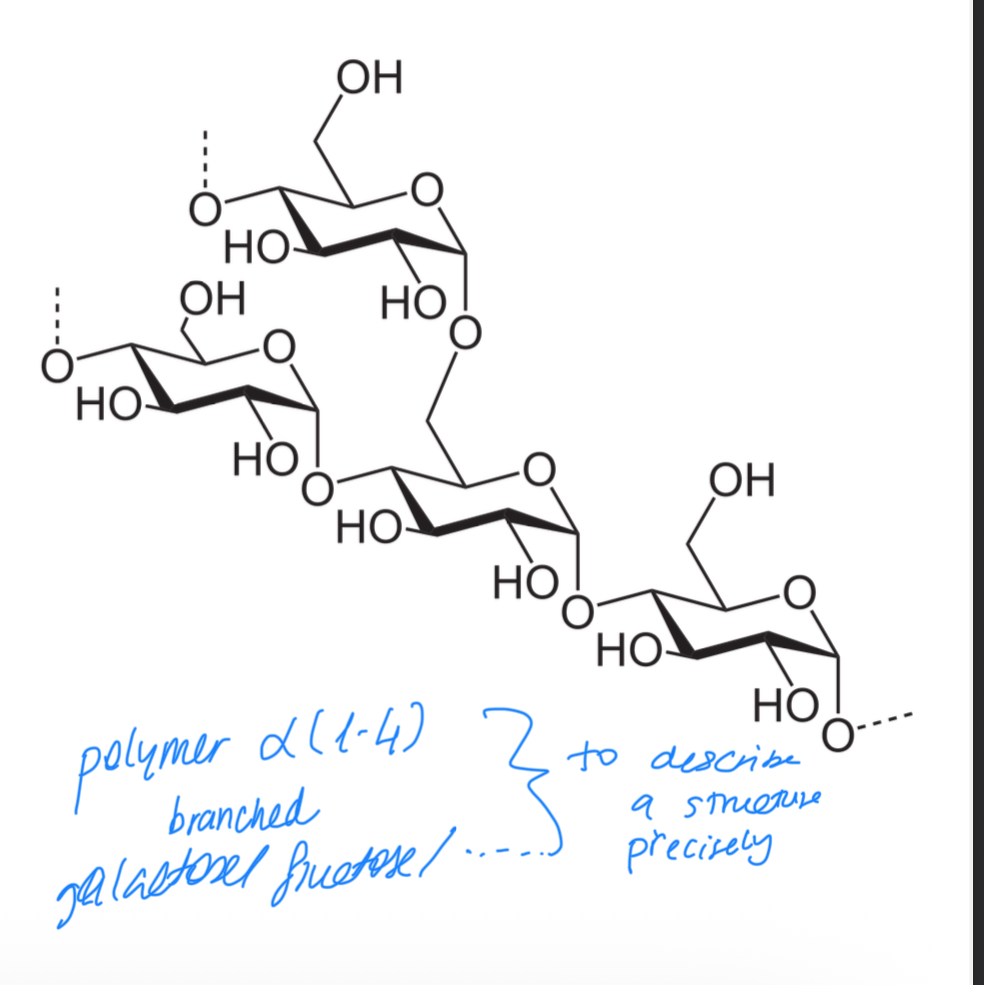
Which two homopolysaccharide are branched
Amylopectin and glycogen (glycogen has more frequent branching)
Why branching on glycogen?
When glucose is needed, monosaccharides are detached at the non-reducing end of the chain
What are the products when a hemiacetals reacts with an alcohol
Acetal and water
The slide explains that glycosidic bond formation is a condensation reaction that is thermodynamically unfavorable in water, so it does not occur spontaneously. To make polysaccharides, cells use activated sugar nucleotides (like UDP-glucose), whose high-energy phosphoanhydride bonds provide the energy needed to drive glycosidic bond formation.
Briefly,
Glycosidic bonds don’t form spontaneously in water — cells must spend nucleotide energy to make them.
Homopolysaccharides are typical energy storage molecules, what are heteropolysaccharies’ functions
structural
Increasing solubility of proteins
Shielding proteins from the immune system
Stabilizing extracellular proteins
Specific function, such as anticoagulants
Determine medically-important features, such as blood groups
Glycans (polysaccharides conjugated to other molecules) can associate with proteins to yield glycosylated proteins
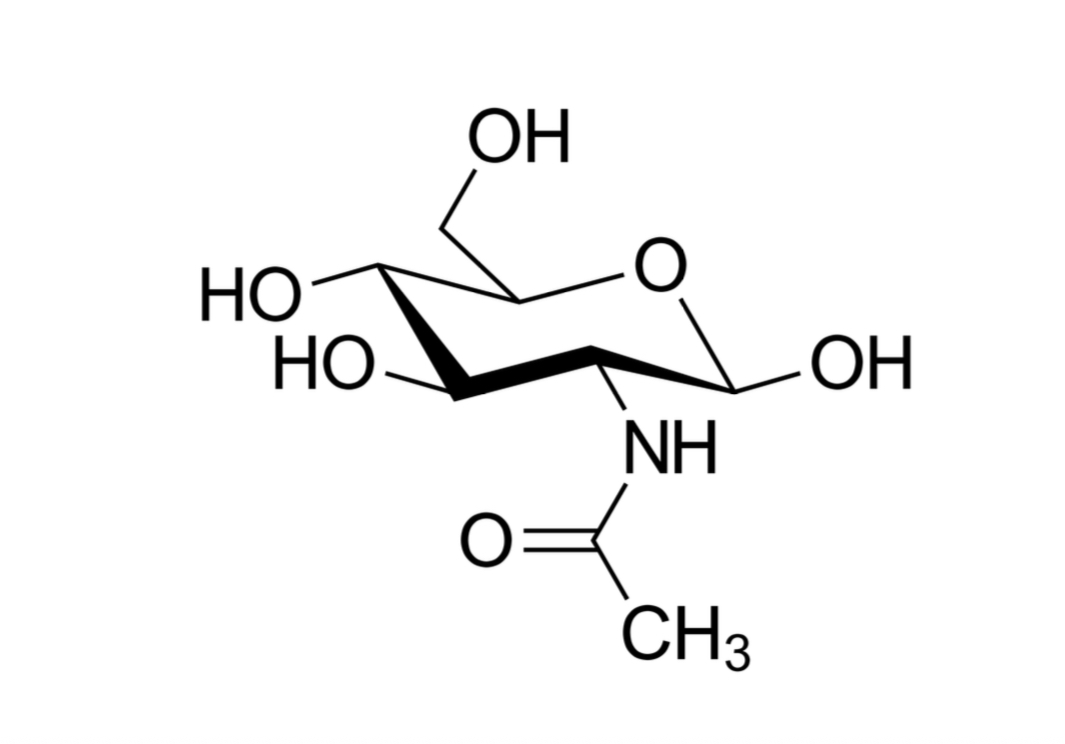
Which kind of protein undergoes glycosylation
extracellular proteins, produced inside the cell and the secreted or translocated to the cell membrane
What is N-glycosylation
Glycans attached at the N (nitrogen) atom of Asn (Asparagine) residues that are found in consensus sequences
What is O-Glycosylation
Glycans attached to Ser or Thr residues. Very heterogeneous (bura da yine ser ve thr nin oksijenine bağlı diye o)
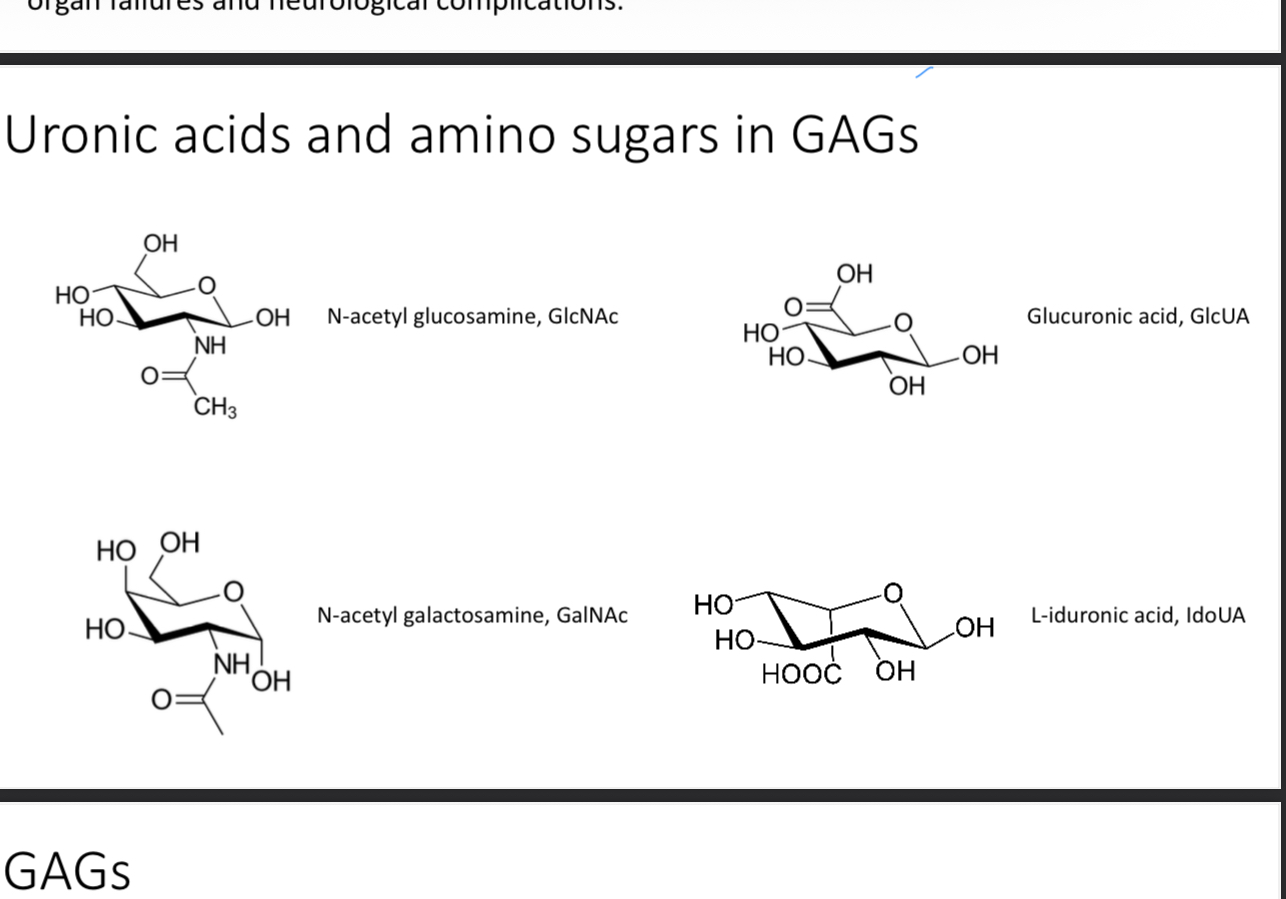
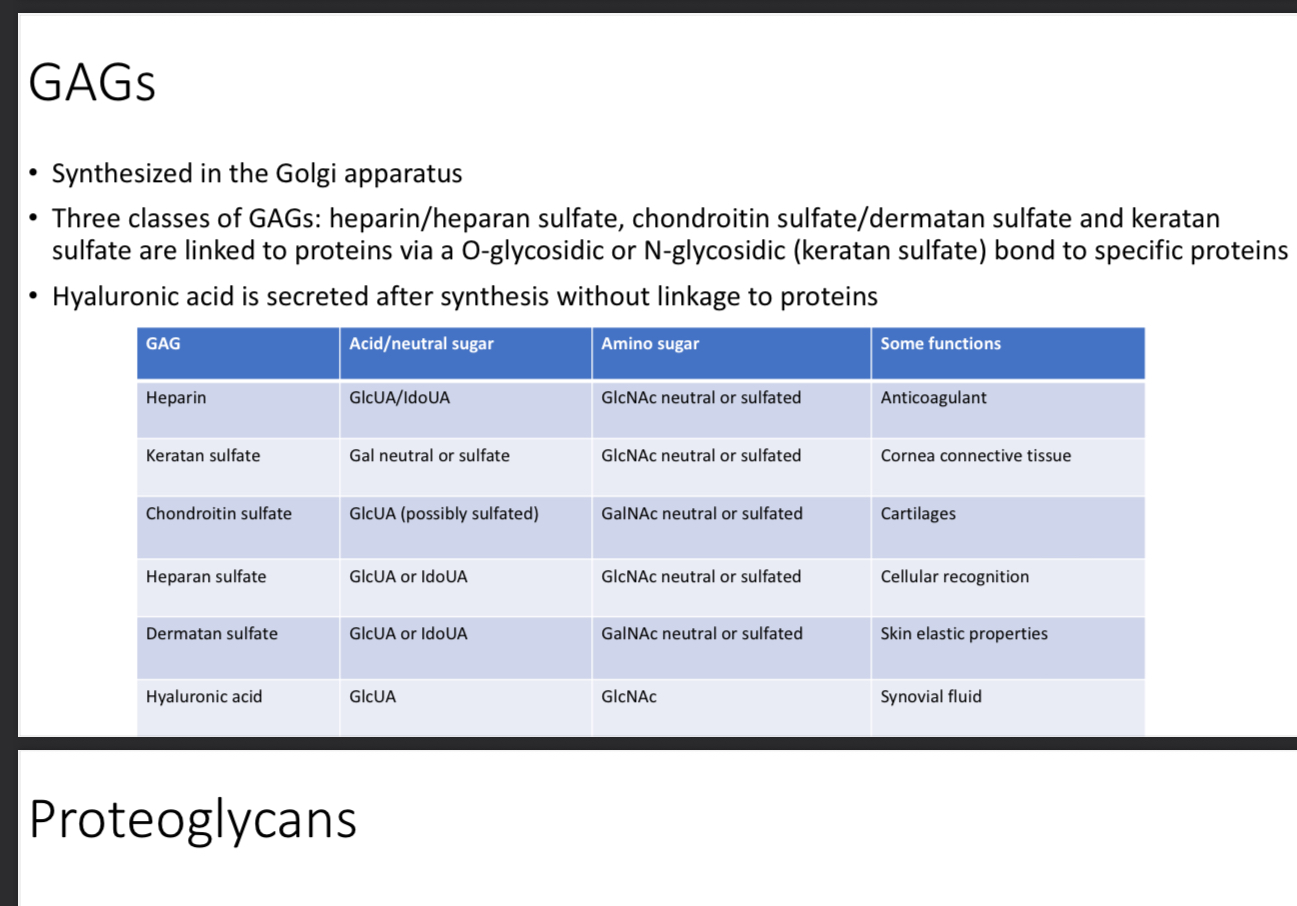
What are glycosaminoglycans (GAGs) Aka mucopolysaccharides
linear polymers of repeating disaccharides (ama galiba glycan olanlar)
What is the disaccharide composed of In glycosaminoglycans
Uronic acid (sugar with -COOH function) and amino sugar (sugar with amino group replacing one of the -OH)
What is the exception to the previous question
Keratin where galactose is in place of the acid
How can sugars be modified
By formation of sulfate esters
It means that a hydroxyl group (–OH) on a sugar is chemically modified by attaching a sulfate group (–SO₃⁻) to it. Yani o eklenirse sugar olmaktan çıkıyo diye anladım
Structural function of glycosaminoglycans
Function is mostly to maintain flexibility, composition of connective tissue, act as lubricants for joints
Uronic acids and amino sugars in GAGs
Where are GAGs synthesized
Golgi apparatus
Anlamadım
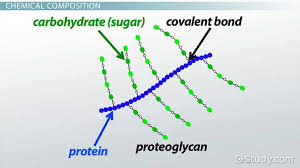
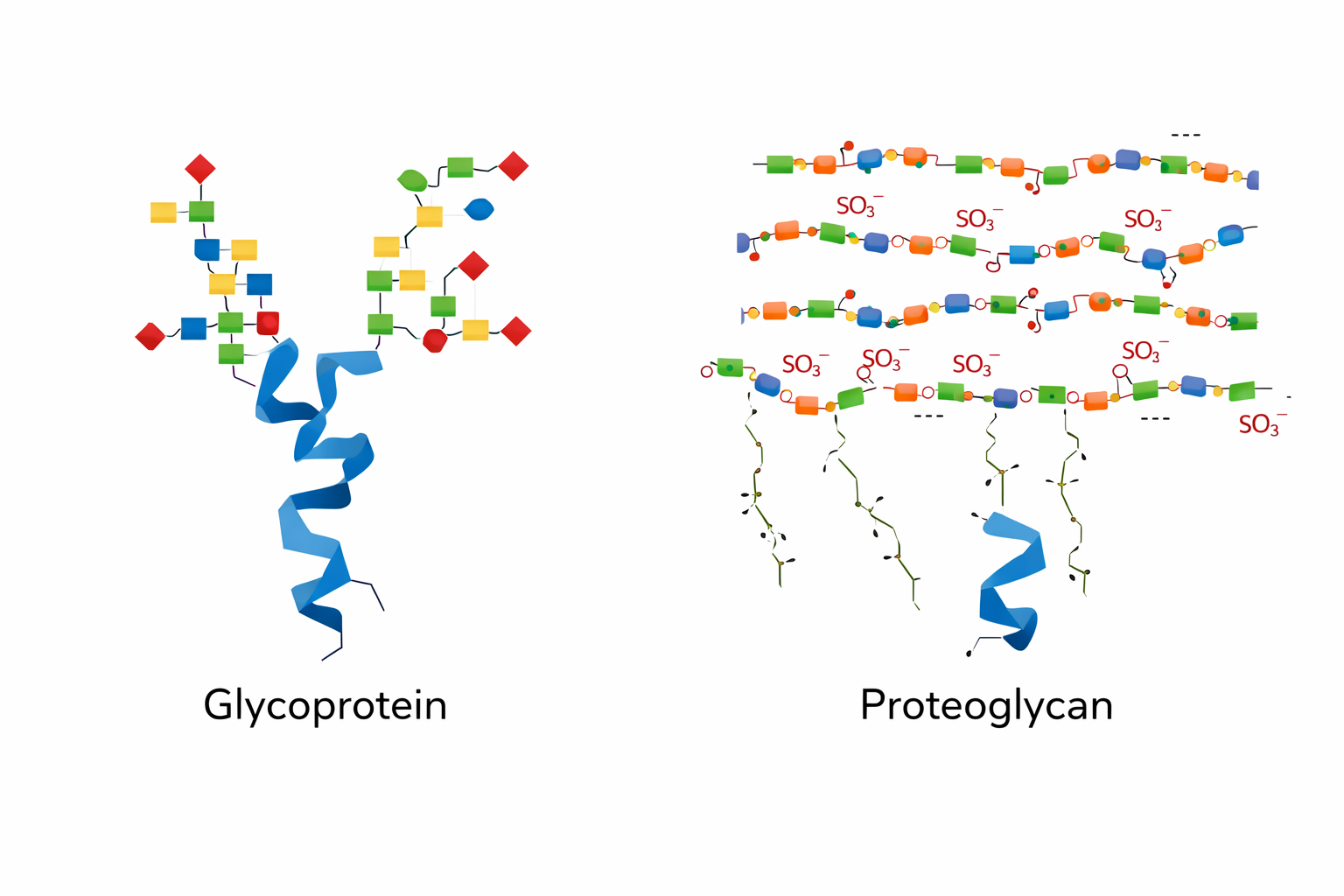
What are proteoglycans
heavily glycosylated proteins with one or more GAGs attached to to the core polypeptide
What is the principal component of the extracellular matrix in animals
Proteoglycans
Difference between glycoproteins and proteoglycans
Glycoproteins are mostly protein with short, branched carbohydrates; proteoglycans are mostly carbohydrate with long glycosaminoglycan (GAG) chains attached to a small protein core.
What is cartilage composed of (Kıkırdak)
Collagen GAGs and proteoglycans
Bu sunumun 24 ve 25. Sayfalarını hiç anlamaım bak
!!!!