BUSN 107 - FINAL EXAM
1/394
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
395 Terms
Change
The transformation or modification of an organization and/or its stakeholders
Opportunities
Favorable times or chances for progress and advancement
Challenge
The call to competition, contect, or battle
Psychology
The science of human behavior
Organizational behavior
The study of individual behavior and groupd dynamics in organizations
Athropology
The science of human LEARNED behavior
Engineering
The applied science of energy and matter
Sociology
The science of society
Medicine
The applied science of healing or treating diseases to enhance an individual’s and well-being
Management
The study of overseeing activities and supervising people in organizations
Task
An organizatoin’s mission, purpose, or goal for existing
Structure
The systems of communication, authority and roles, and workflow
Technology
The tools, knowledge, and/or techniques used to transform inputs into outputs
People
The human resources or an organization
Formal organization
The official, legit, and most visible part of the system
Hawthorne studies
Studies conducted in the 1920s-30s that suggested the importance of the informal organization
Informal organization
The unofficial and less visible part of the system
Skill development
The mastery of abilities essential to successful functioning in organizations
Objective knowledge
Knowledge that results from research and scientific activities
Transnational organization
An organization in which the global viewpoint supersedes national issues
Individualism
A cultural orientation in whichpeople belong to loose social frameworks and their primary concern is for themselves and their families
Expatriate managers
A manager who works in a country other than her or his home country
Guanxi
The Chinese practice of building networks for social exchange
Uncertainty avoidance
The degree to which a culture tolerates ambiguity and uncertainty
Power distance
The degree to which a culture accepts unequal distrubution of power
Collectivism
A cultural orientation in which individuals belong to tightly knit social frameworks and depend strongly on extended families or clans
Time oritentation
Whether a culture’s values are oriented toward the future (long-term orientation) or toward the past and present (short-term orientation)
Masculinity
A cultural orientation in which assertiveness and materialism are valued
Femininity
A cultural orientation in which relationships and concern for others are valued
Diversity
All forms of difference among individuals, including culture, gender, age, ability, religion, personality, social status, and sexual orientation
Glass ceiling
A transparrent barrier that keeps women from rising above a certain level in organizations
Consequential theories
An ethical theory that emphasizes the consequences or results of behavior
Character theories
An ethical theory that emphasizes the character, personal virtues, and intent of the individual
Rule-based theories
An ethical theory that emphasizes the character of the act itself rather its effects
Prodcedural justice
The fairness of the process by which outcomes are given in an organization
Distributive justice
The fairness of outcomes that individuals receive in an organization
Social responsibility
The obligation of a organization to behave ethically in its social environment
Whistle-blowers
An employee who informs authorities of the wrongdoings of their company or coworkers
Attitude
A psychological tendency expressed by evaluating something with a degree of favor or disfavor.
Affect
The emotional component of an attitude.
Social Learning
The process of deriving attitudes from family, peer groups, religious organizations, and culture.
Job Satisfaction
A pleasurable or positive emotional state resulting from the appraisal of one's job or job experiences.
Cognitive Dissonance
A state of tension produced when an individual experiences conflict between attitudes and behavior.
Counterproductive Work Behavior (CWB)
Behavior that violates organizational norms and causes harm to the organization and/or employees.
Organizational Commitment
The strength of an individual's identification with an organization.
Organizational Citizenship Behavior (OCB)
Behavior that is above and beyond the call of duty.
Normative Commitment
Organizational commitment based on an individual's perceived obligation to remain with an organization.
Continuance Commitment
Organizational commitment based on the fact that an individual cannot afford to leave.
Affective Commitment
Organizational commitment based on an individual's desire to remain in an organization.
Emotional Contagion
A dynamic process through which the emotions of one person are transferred to another, either consciously or unconsciously, through nonverbal channels.
Ethical Behavior
Acting in ways consistent with one's personal values and the commonly held values of the organization and society.
Emotions
Mental states that include feelings, physiological changes, and the inclination to act.
Values
Enduring beliefs that a specific mode of conduct or end state of existence is personally or socially preferable to an opposite or converse mode of conduct or end state of existence.
Instrumental Values
Values that shape the acceptable behaviors that can be used to achieve some goal or end state.
Terminal Values
Values that influence the goals to be achieved or the end states of existence.
Machiavellianism
A personality characteristic involving one's willingness to do whatever it takes to get one's own way.
Cognitive Moral Development
The process of moving through stages of maturity with regard to making ethical decisions.
Psychoanalysis
Sigmund Freud's method for delving into the unconscious mind to better understand a person's motives and needs.
Theory X
A set of assumptions managers might apply to individuals who are motivated by lower-order needs.
Theory Y
A set of assumptions managers might apply to individuals who are motivated by higher-order needs.
ERG theory
A theory that organizes human needs into the categories of existence, relatedness, and growth.
self-interest
What is in the best interest of and benefit to an individual.
need for achievement
A manifest need that concerns excellence, competition, challenging goals, persistence, and overcoming difficulties.
need for power
A manifest need that concerns the desire to influence others, change people or events, and make a difference in life.
need for affiliation
A manifest need to establish and maintain warm, close, intimate relationships with other people.
motivation factors
Work conditions that satisfy the need for psychological growth.
hygiene factors
Work conditions that generate dissatisfaction due to discomfort or pain.
inequity
A situation in which a person perceives that they are receiving less than they are giving or giving less than they are receiving.
Entitleds
Individuals who are comfortable with an equity ratio greater than that of their comparison other.
Benevolents
Individuals who are comfortable with an equity ratio less than that of their comparison other.
Instrumentality
The belief that performance is related to rewards.
Valence
The value or importance one places on a particular reward.
Expectancy
The belief that effort leads to performance.
moral maturity
The measure of a person's cognitive moral development.
motivation
The process of arousing and sustaining goal-directed behavior
manifest needs
learned or acquired needs that are easily perceived
Freud proposed a more complex motivational theory, suggesting that a person’s organizational life was founded on
the compulsion to work and the power of love
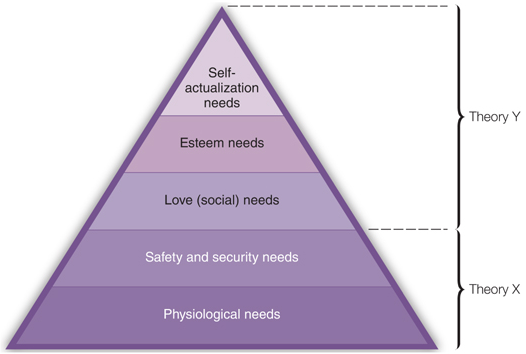
Maslow labeled the five levels of his need hierarchy as
physiological needs, safety and security needs, love (social) needs, esteem needs, and the need for self-actualization.
Maslow’s need hierarchy is the progression hypothesis, which suggests that
as one level of need is met, a person progresses to the next higher level of need as a source of motivation.
Alderfer’s regression hypothesis suggests that when people are frustrated by their inability to meet needs at the next higher level in the hierarchy,
they regress to the next lower category of needs and intensify their desire to gratify those needs.
Herzberg identified motivation factors as
responsibility, achievement, recognition, advancement, and the work itself.
Equity theory
a social exchange process approach to motivation that focuses on the interaction between an individual and the environment
Inequity creates . .
tension, which in turn motivates a person to take action to resolve the inequity.
Adams’s theory provides seven basic strategies for restoring equity:
(1) alter the person’s outcomes
(2) alter the person’s inputs
(3) alter the comparison other’s outcomes
(4) alter the comparison other’s inputs
(5) change who is used as a comparison other
(6) rationalize the inequity
(7) leave the organizational situation.
Positive consequences
Results of a behavior that a person finds attractive or pleasurable.
Reinforcement
A strategy to cultivate desirable behavior by either bestowing positive consequences or withholding negative consequences.
Punishment
A strategy to discourage undesirable behavior by either bestowing negative consequences or withholding positive consequences.
Task-specific self-efficacy
An individual's internal expectancy to perform a specific task effectively.
Goal setting
The process of establishing desired results that guide and direct behavior.
Consensus
An informational cue indicating the extent to which peers in the same situation behave in a similar fashion.
Performance appraisal
The evaluation of a person's performance.
Mentoring
A work relationship that encourages development and career enhancement for people moving through the career cycle.
Distinctiveness
An informational cue indicating the degree to which an individual behaves the same way in other situations
Learning
A change in behavior acquired through experience
Classical conditioning
Modifying behavior by pairing a conditioned stimulus with an unconditioned stimulus to elicit an unconditioned response.
Operant conditioning
Modifying behavior through the use of positive or negative consequences following specific behaviors.
Negative consequences
Results of a behavior that a person finds unattractive or aversive.
Extinction
A strategy to weaken a behavior by attaching no consequences to it.
Management by objectives (MBO)
A goal-setting program based on interaction and negotiation between employees and managers.
Performance management
A process of defining, measuring, appraising, providing feedback on, and improving performance.