Electric Fields and Gravitational fields
1/16
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
17 Terms
What is an electric field
A region of space where a charged particle experiences a force
define electric field strength
the force experienced per unit positive charge at that point
is electric field strength a vector or scalar quantity, what does that mean?
vector - it has direction
Define coulombs law in words
The force between two point charges is proportional to product of charges inversely proportional to square of distance between the charges
state units for electric field strength
N/C or V/m
Explain why an electron placed between 2 oppositely charged parallel plates will experience a constant acceleration towards the +ve plate
Being negatively charged, an electron between the plates will travel away from the negative plate and towards the positive plate in the opposite direction of the electric field. The electron experiences a constant electrostatic force because of the uniform electric field between the plates, so it has a constant acceleration
how can you calculate the acceleration of a charge particle in a uniform field
for horizontal motion: there is no acceleration
for vertical motion: a=F/m = EQ/m
Define electric potential in words
the work done per unit charge in bringing a positive charge from infinity to that point
Define electric potential difference
The work done per unit charge between two points around a particle of charge Q.
Define gravitational field strength
The gravitational force exerted per unit mass on a small object placed at that point within the field
Give Newtons law of gravitation in words
The force between two point masses is :
directly proportional to the product of the masses
and inversely proportional to the square of their separation
What does the negative sign show in Newtons law of gravitation (F= -GMm/r^2)
It shows that gravitational force is an attractive force
State Keplers first Law
The orbit of a planet is an ellipse with the Sun at one of the two foci.
what is an ellipse
A 'squashed' or elongated circle with two foci.
The orbits of all planets are elliptical
State Keplers second law
A line segment joining a planet and the Sun sweeps out equal areas during equal intervals of time.
Use Keplers second law to explain why the speed of a planet is not constant as it orbits the sun
As planets move on their elliptical orbit around the sun, their speed is not constant. When a planet is closer to the sun it moves faster. Between X and Y the planet moves faster than between P and Q. Keplers second law states if the time interval from X to Y is the same as for P to Q the areas must be the same
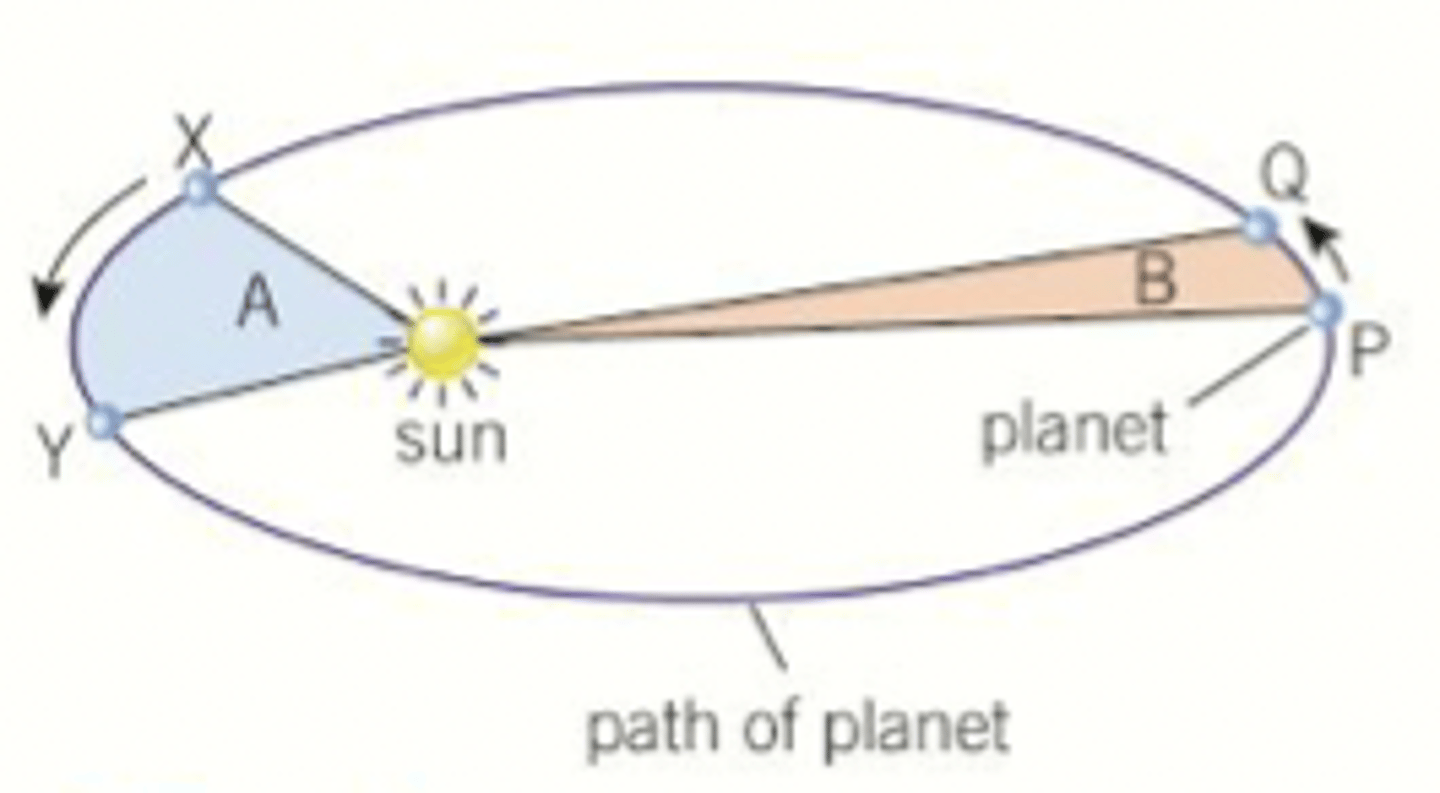
State keplers third law
the square of the orbital period T of a planet is directly proportional to the cube of its average distance r from the sun