Human reproduction
1/51
Earn XP
Description and Tags
zoology
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
52 Terms
bulbourethral gland also called
cowpers gland
testis width and length
width= 2-3cm
length= 4-5cm
testis descend into scrotum from abdominal cavity through inguinal canal during
7th month of pregnancy
scrotum provides ____ temp lower than abdominal cavity
2-2.5 degrees lower temp necessary for spermatogenesis
Gonadotropins are
LH and FSH
how many testicular lobules present
250 compartments in each testis
seminiferous tubules number
1-3 in each testicular lobule
pathway of sperm
rete testis—-vasa efferentia—-epididymis—-vas deferens—-ejaculatory duct—-urethra
male accesory ducts__ and ___ sperms
store and transport
seminal plasma contains
fructose, calcium and enzymes
urethra passes through which tissue in peni*
corpus spongiosum
Seminal vesicle, prostate and bulbourethral
location
percent of semenn contributed
secretion
sv- dorso-lateral to urinary bladder
pro= base of urinary bladder
bul= below prostate
60-70%, 20-25%, 5-10%
fructose and prostaglandis
calcium
mucus for lubrication
interstitial space outside seminiferous tubules contain
interstitial cells or leydig cells
small blood vessels
immunocompetent cells
leydig or interstitial cells produce androgens by signals from
anterior pituitary gland luetenising hormone or interstitial cell stimulating hormone
Primary germ cell or spermatogonia 1. Epithelium and function
simple cuboidal epithelium
undergo meiotic division and forms sperms
sertoli cell 1. Epithelium and function
simple columnar
provide nourishment to developing sperms
phagocyte surrounding excess cytoplasm and organelles
phagocyte abnormal sperms and dead sperms
secrete inhibin hormone which inhibits FSH
secretes Androgen binding protein which binds and concentrates androgens inside Seminiferous tubules
certain factor called sperm maturation factors responsible for spermiogenesis or spermatid to sperm is secreted by
sertoli cells
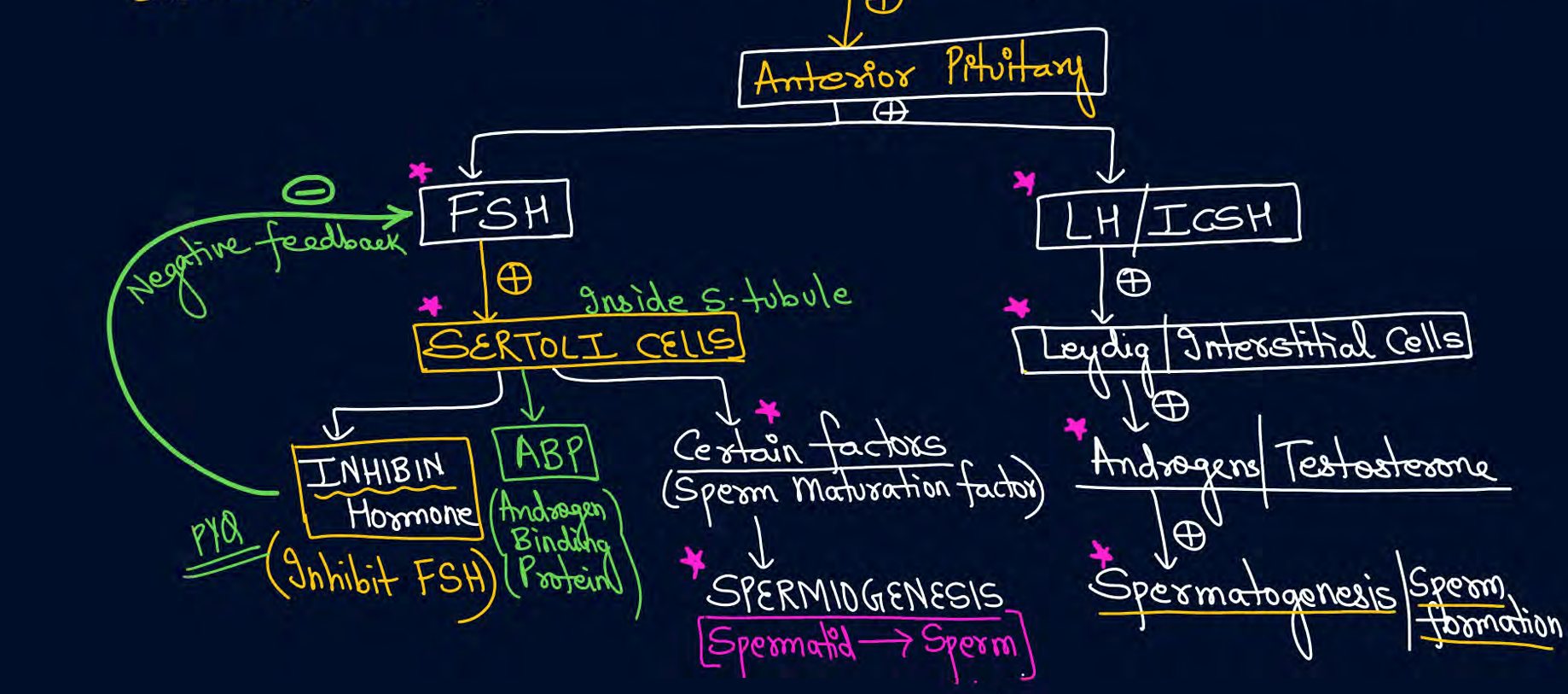
explain hormonal regulation in males
GnRH from hypothalamus acts on anterior pituitary
FSH and LH released from anterior pituitary
FSH acts on sertoli cells and helps in releasing certain factor from which inhibin gives negative feedback
LH acts on interstitial cells and releases androgens for spermatogenesis
Fallopian tube length and epithelium
length 10-12cm
ciliated columnar epithelium
infundibulum shape, position and function
funnel shaped
closer to ovary
has finger like projections called fimbrae which collects ovum or 2’ oocyte from ovary
ampulla shape and function
widest part
site of fertilisation
ampulla or ampullary isthmic junction
isthmus size and function
narrow lumen
opens into uterus
uterus and ovary is attached to pelvic walls by
ligaments
perimetrium, myometrium, endometrium
structure and function
perimetrium- external, thin, membranous
myometrium- thick smooth muscles for contractions
endometrium- lines uterine cavity and glandular. Implantation occurs here
length of ovary and lined by ___ epithelium
2-4 cm'
germinal epithelium (simple cuboidal epithelium)
germinal epithelium of ovary encloses____ which is divided into 2 parts namely and their function
stroma divided into outer cortex—follicle development
and inner medulla—contains blood vessels,nerves etc
clitoris is ____ tissue present at upper portion of ____
erectile tissue
labia minora
In some women hymen persists even after coitus
true false
true
mammary gland lies on _____ muscle
pectoralis major
each mammary gland has ____ lobes
15-20 mammary lobes
___contains cluster of milk secreting cells called alveoli
mammary lobes
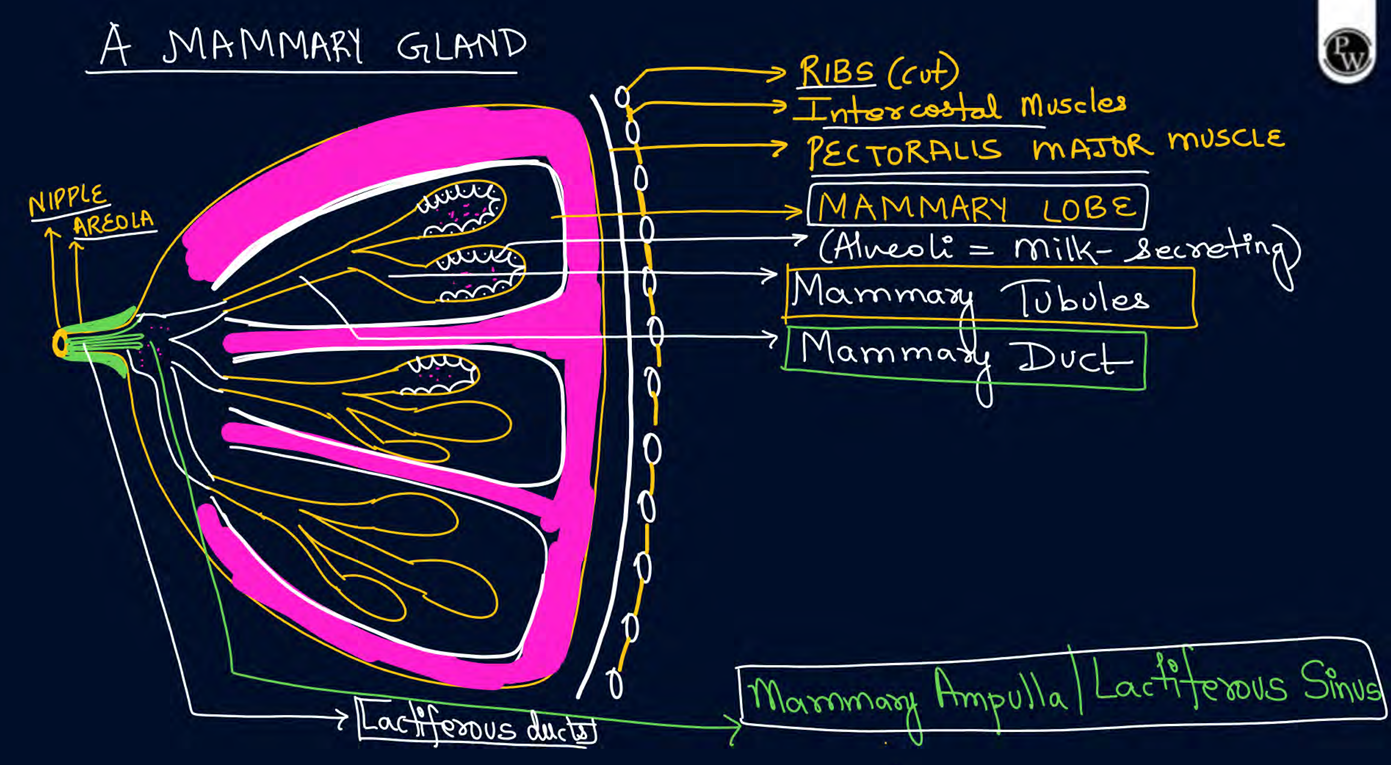
pathway of milk in mammary gland
mammary lobes—mammary tubule—mammary duct—-mammary ampulla—-lactiferous duct
milk secretion or production is by hormone
prolactin from anterior pituitary
and HpL from placenta
milk ejection is done by hormone
oxytosin
secreted by hypothalamus and released by posterior pituitary
breast development at puberty by hormone
estrogen
increase in alveoli during pregnancy by hormone
progesterone
bulbourethral gland also called
bartholin gland
spermatogenesis from male primary germ cell or spermatogonia with ploidy
spermatogonia(2n)—
-form many spermatogonia using mitosis in multiplication phase—
—form primary spermatocyte(2n) by growth/differentiation—
—2 secondary spermatocyte(n) by meiosis1—
—four spermatids(n) by meiosis2—
—differentiate to form sperms(n)
spermiogenesis is process of
differentiation of spermatid into sperms
spermatogenesis is process of
spermatogonia to sperms
spermiation is process of
after spermiogenesis, the sperm heads become embedded in sertolli cells, and are finally released into the lumen of seminiferous tubule

B

C

C
sperm acrosome location, modification of, function
anterior part of head
modified golgi body
certain enzymes that help in fertilisation with ovum (spermlysins)
in human sperm nebenkern is
and function
spirally arranged mitochondria in middle piece of sperm
energy provider for swimming
Flagella extends from middle piece to end of tail
true false
false
flagella only present in tail till end
in middle piece, axoneme/axial filament present which is also of 9+2 arrangement
structure of sperm
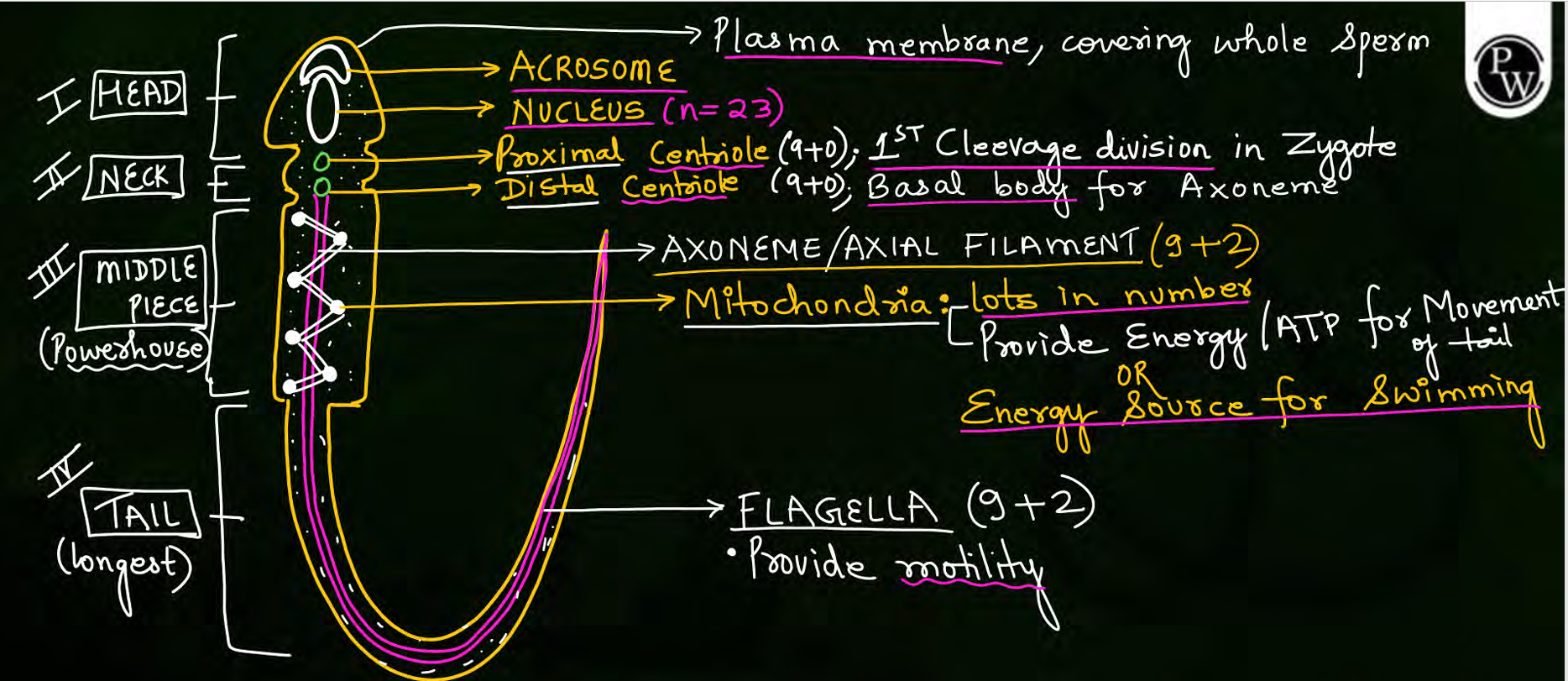
proximal and distal centriole present in neck of sperm1. arrangement and 2. function
9+0 arrangement
proximal= 1st cleavage division in zygote
distal= basal body in axoneme
sperms present in 1ml semen
sperms present in 1 ejaculation of semen
100 million
2-3 ml so 200-300 million
In one ejaculation how many sperms in percentage 1) should have normal shape and size
2) vigorous motility
Atleast 60% should have normal shape and size
40% should have vigorous motility
oogenesis in female process starting from oogonia
oogonia or primary germ cell undergoes mitosis to form more oogonia
oogonia undergoes differentiation to form primary oocyte.
primary oocyte undergoes meiosis 1 to form first polar body and secondary oocyte
secondary oocyte undergoes meiosis 2 only if fertilization takes place
secondary oocyte undergoes meiosis 2 to form ovum and second polar body