Chapter 17 - Brain Stem , Cerebellum and Cranial Nerves
1/36
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
37 Terms
Name the three primary regions of your brainstem.
midbrain, pons, and medulla oblongata.
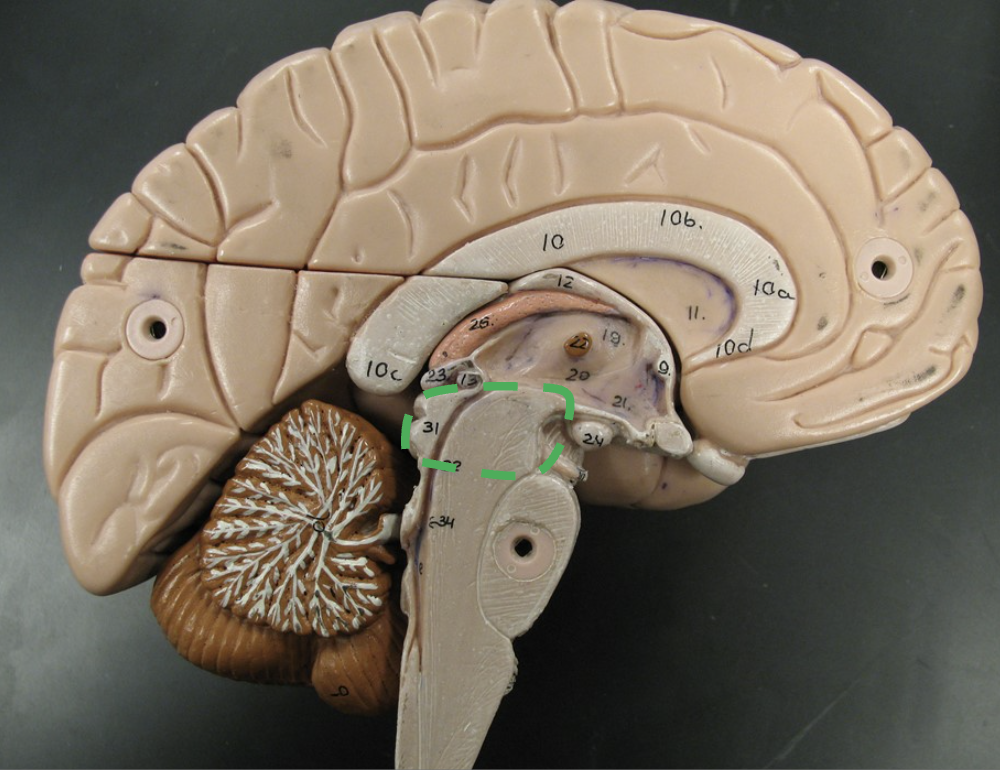
What does the circle indicate, and what is its function?
The Midbrain
Responsible for processing auditory and visual information, as well as motor control.
*Inferior (below) diencephalon
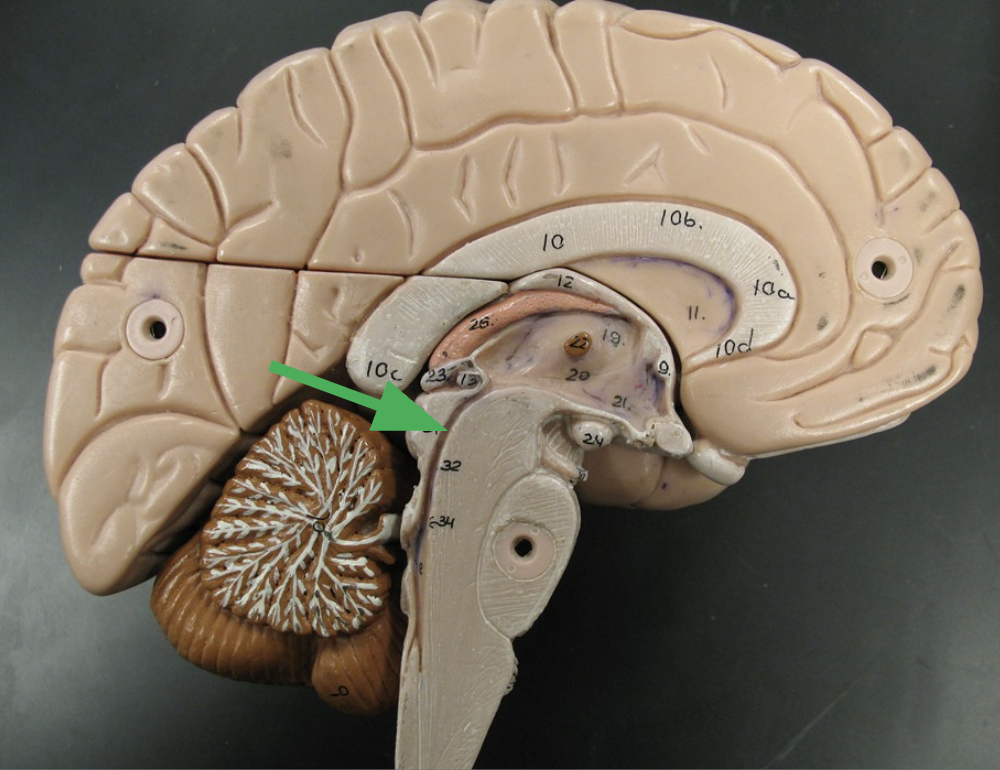
What does the arrow indicate?
What happens in this area?
Cerebral aqueduct
Connects the third and fourth ventricles, allowing cerebrospinal fluid to flow between them.
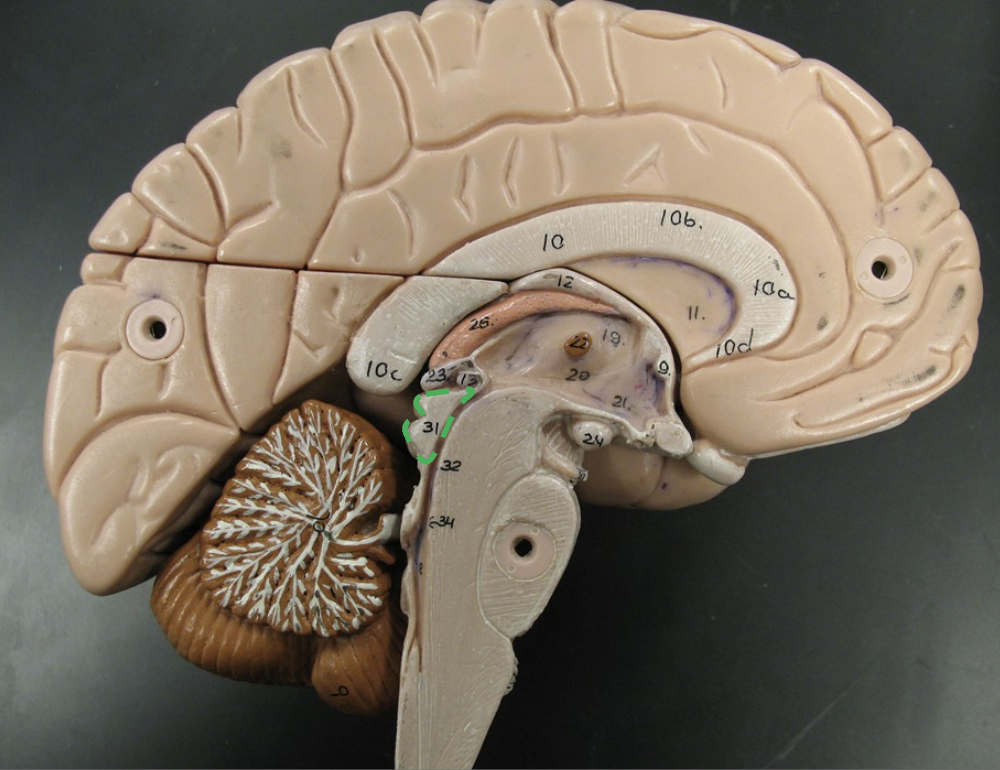
what does the circle indicate?
Tectum part of the midbrain
involved in auditory and visual reflexes, containing the superior and inferior colliculi.
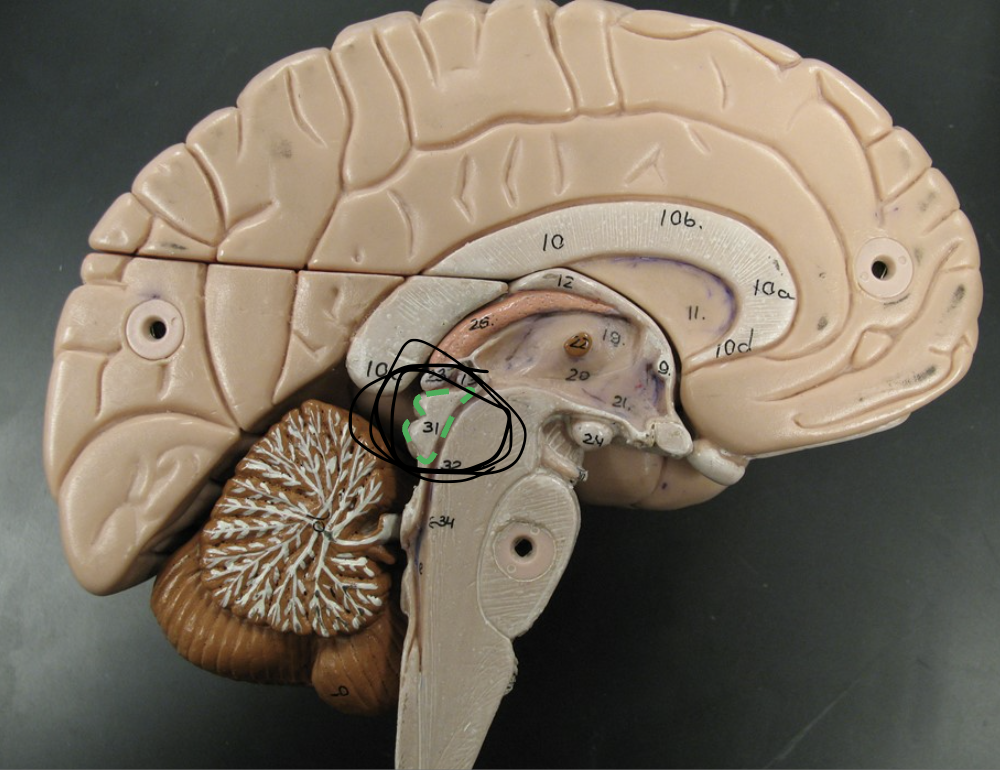
What are the 4 bulges posterior from the tectum called? (You only see 2 because this is a sagittal section.)
Corpora quadrigemina
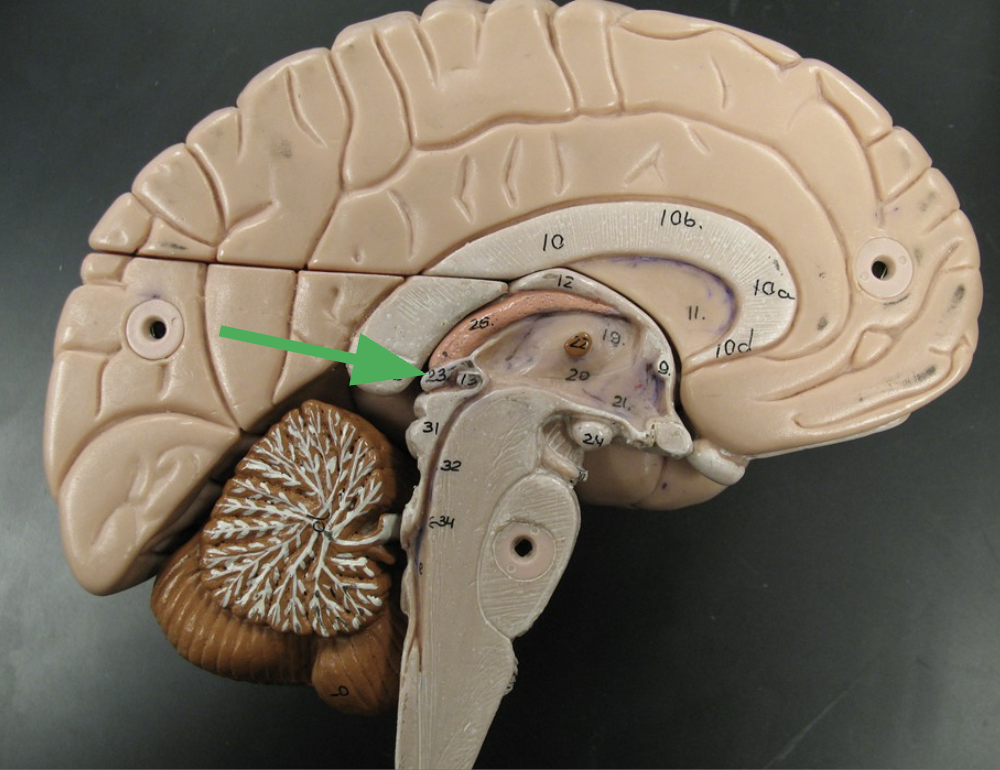
Superior Colliculus
Visual reflexes coordinating head and eye movements.
Inferior colliculus
Auditory reflexes, e.g., turning your head or body towards a loud noise
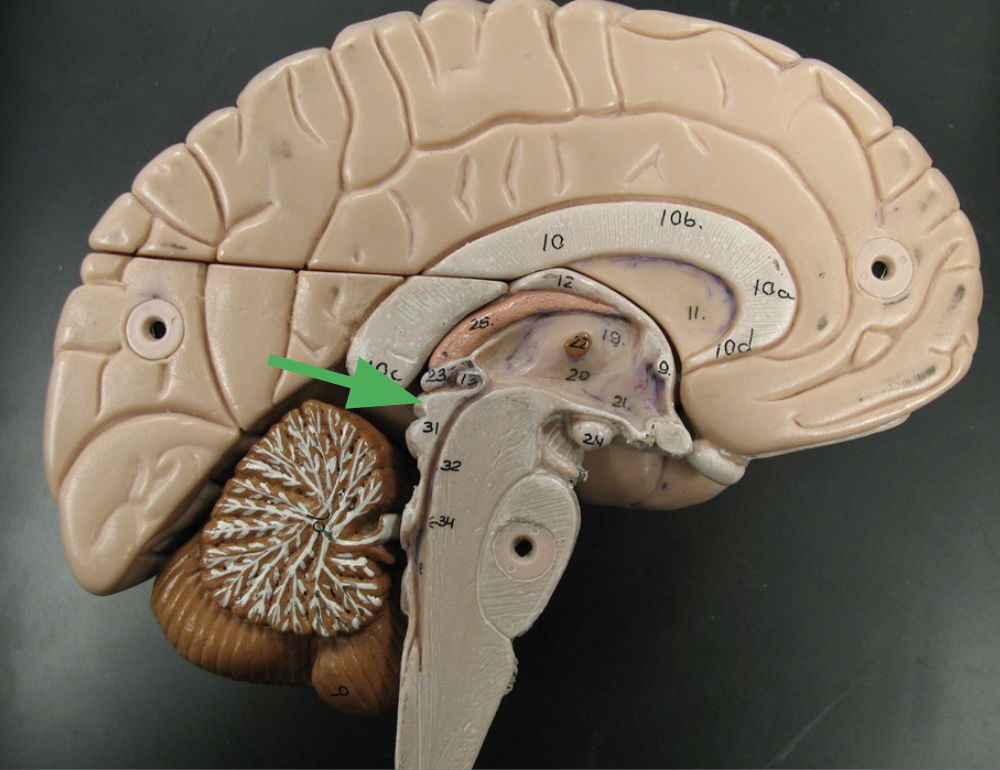
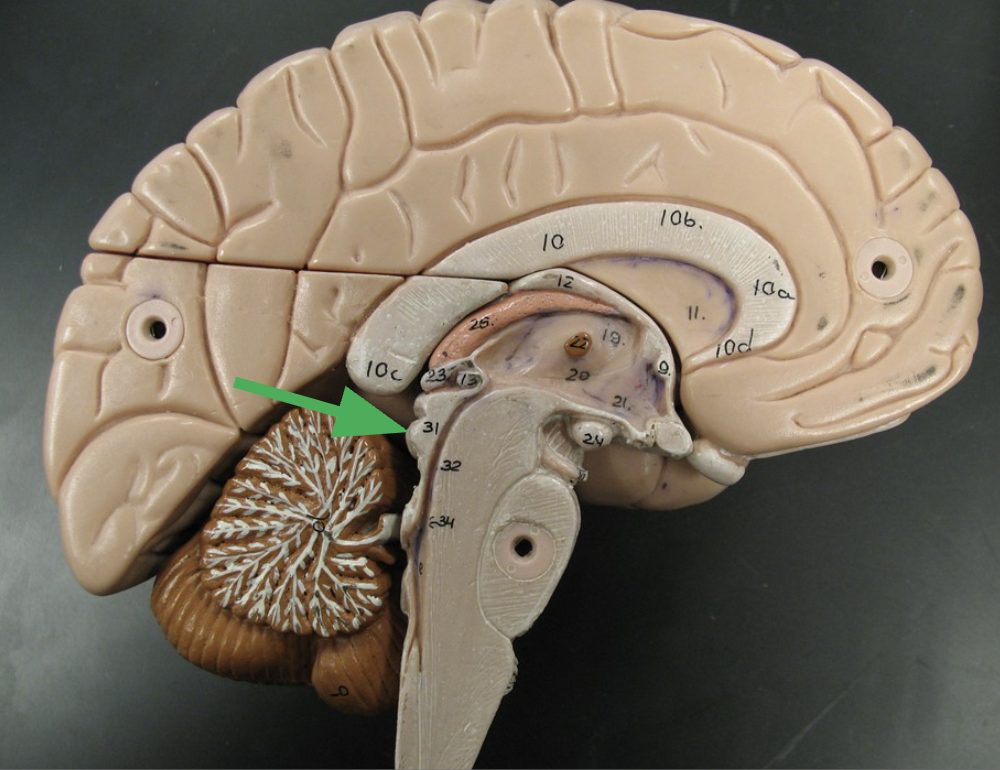
Oculomotor Nerve, Cranial Nerve 3
Controls most eye movements, pupils' constriction, and maintains an open eyelid.
Pineal glad
Production of melatonin
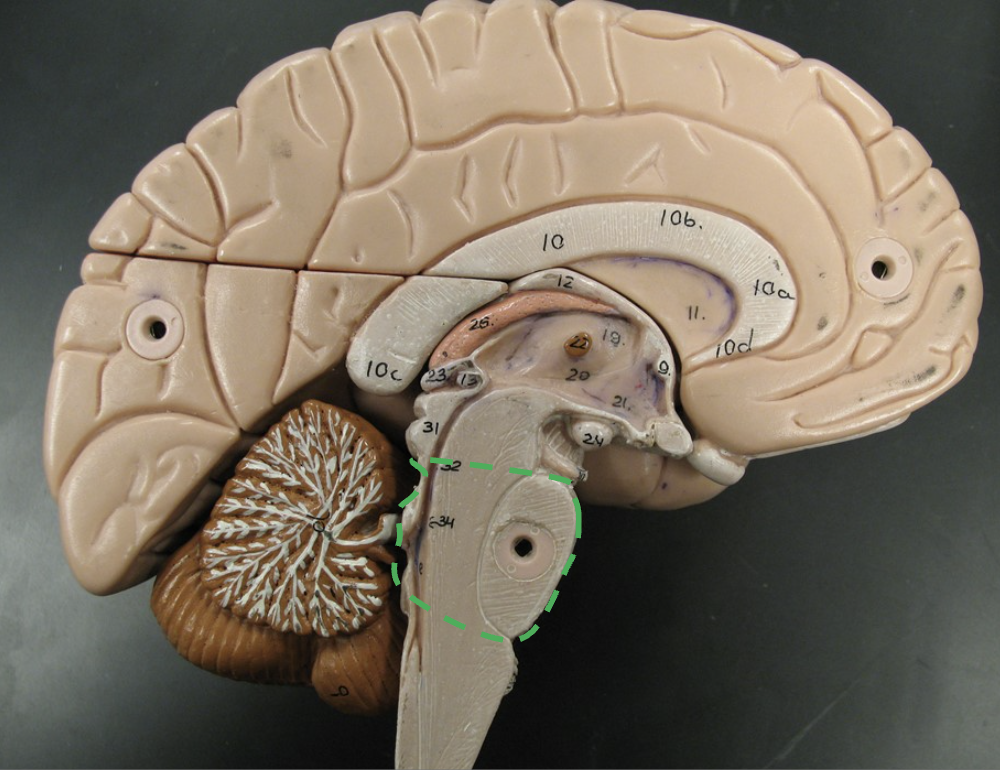
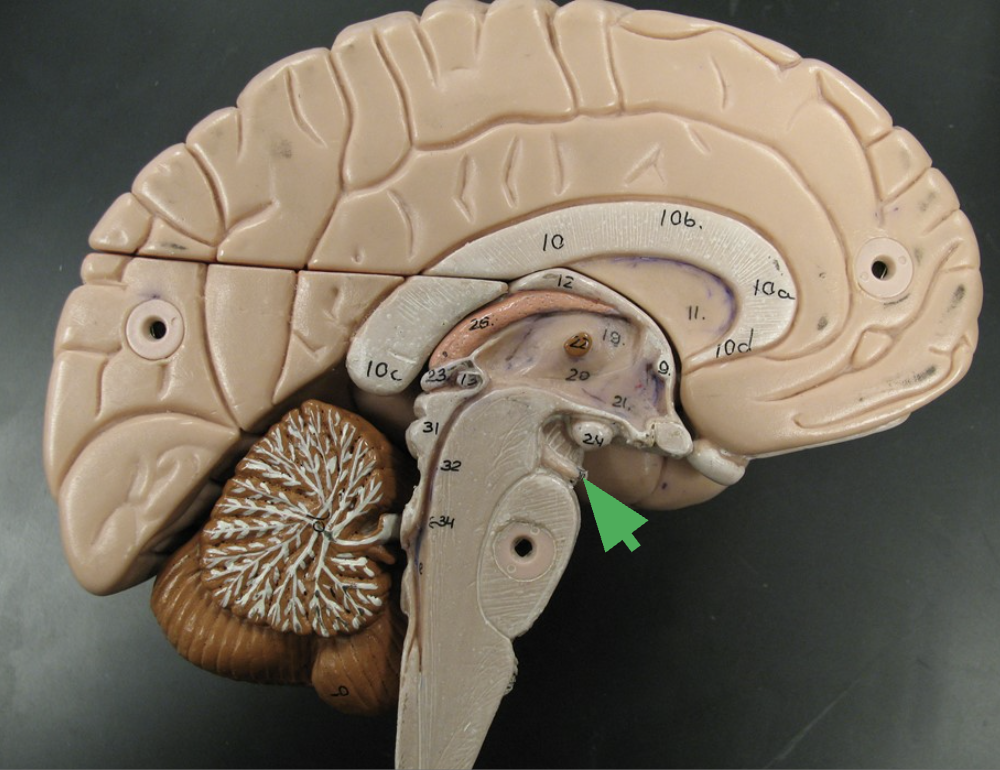
What section of the brainstem is this? What does it connect?
Pons “bridge”
connects diencephalon and cerebrum to the cerebellum and medulla oblongata
What does the pons do?
Nuclei involved in functions including chewing, swallowing, and breathing
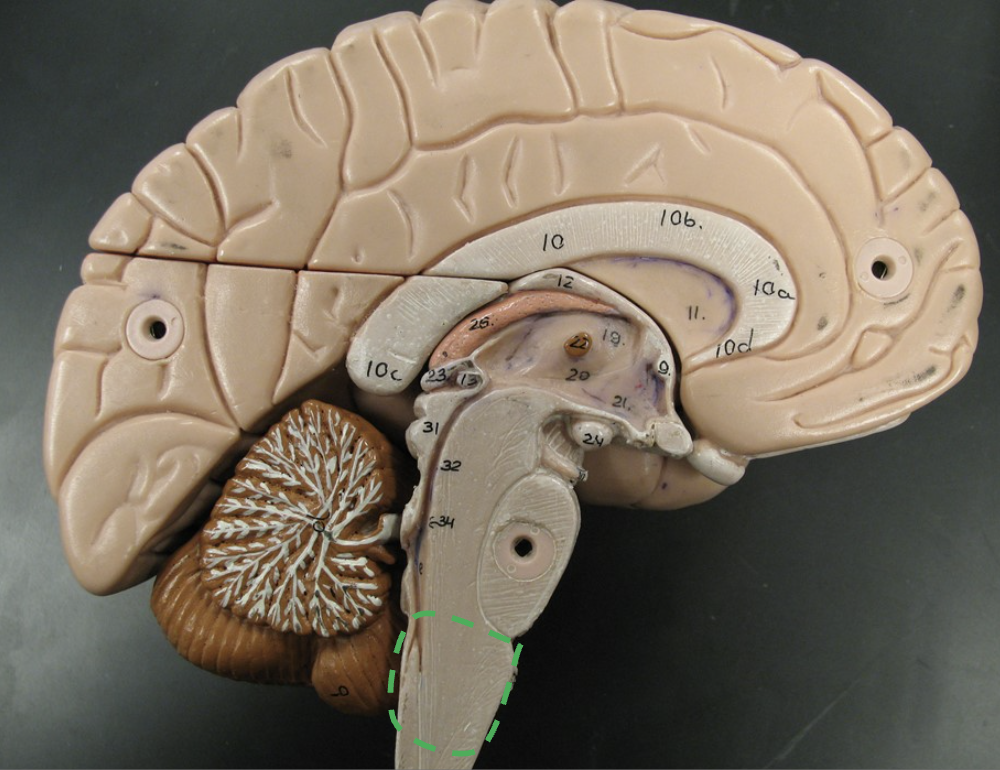
Medulla oblongata
What does the medulla oblongata do?
Nuclei are involved in heart rate, blood pressure, breathing, sneezing, and vomiting.
What does the medulla oblongata contain?
Contains motor tracks ventrally and sensory tracks dorsally.
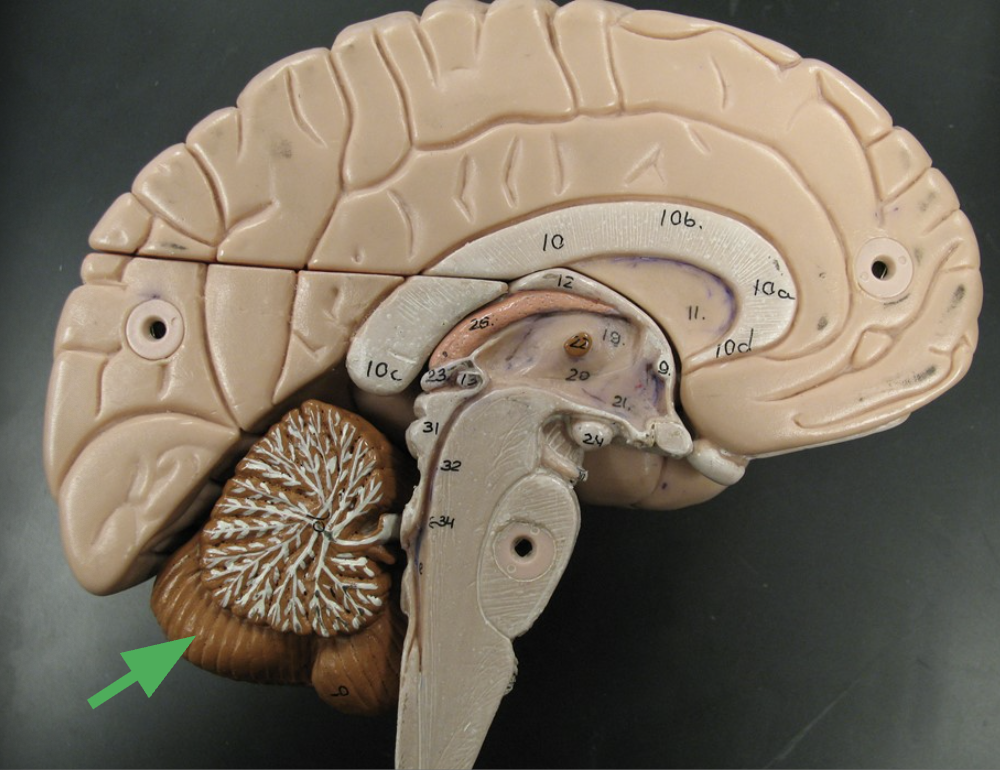
What is the arrow indicating?
1 of the 2 cerebral hemispheres
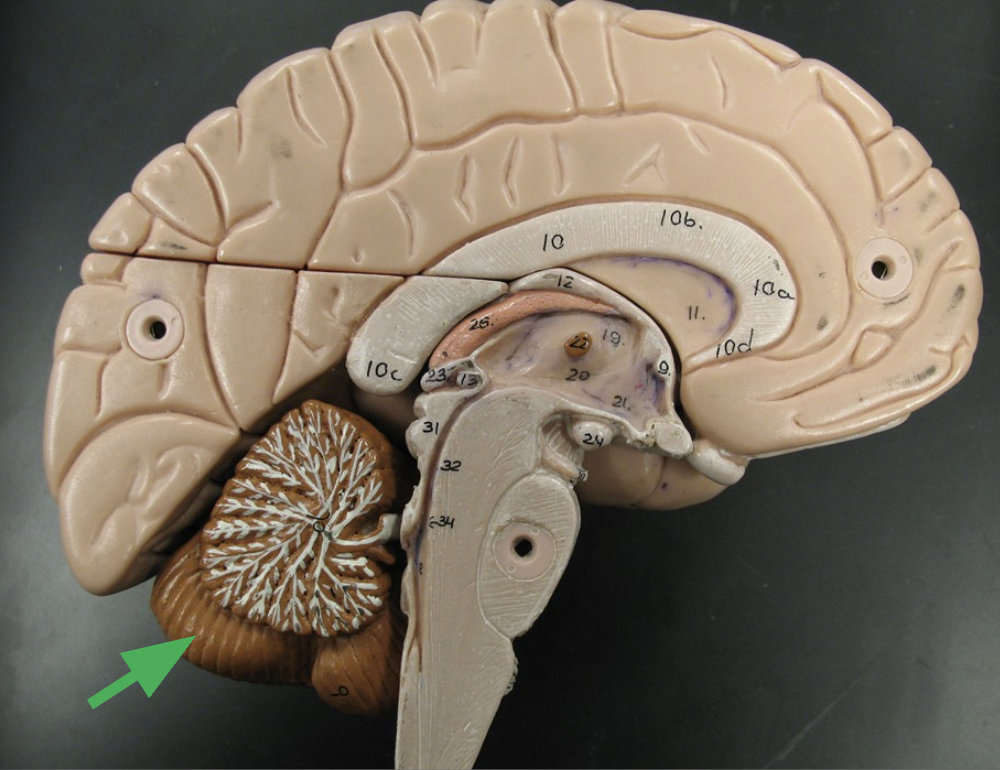
what are the folds in the cerebellum called?
Folia
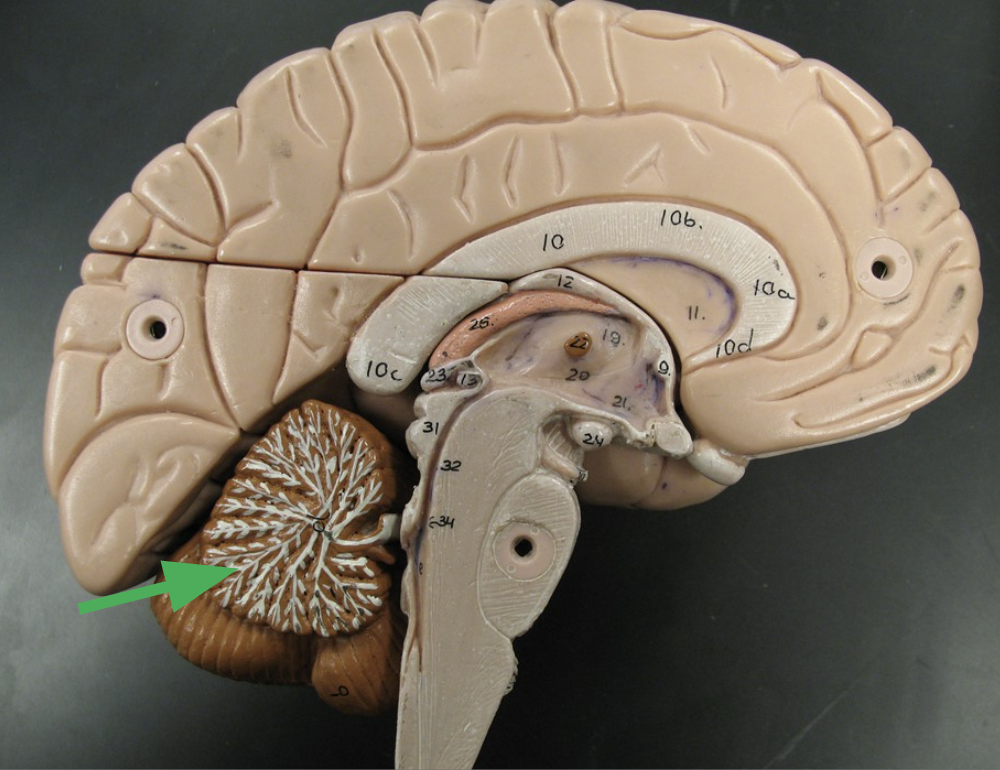
What is this white matter called?
Arbor vitae
*reminded anatomist of a tree of the same name
What is the cavity called between the brainstem and cerebellum?
Fourth ventricle
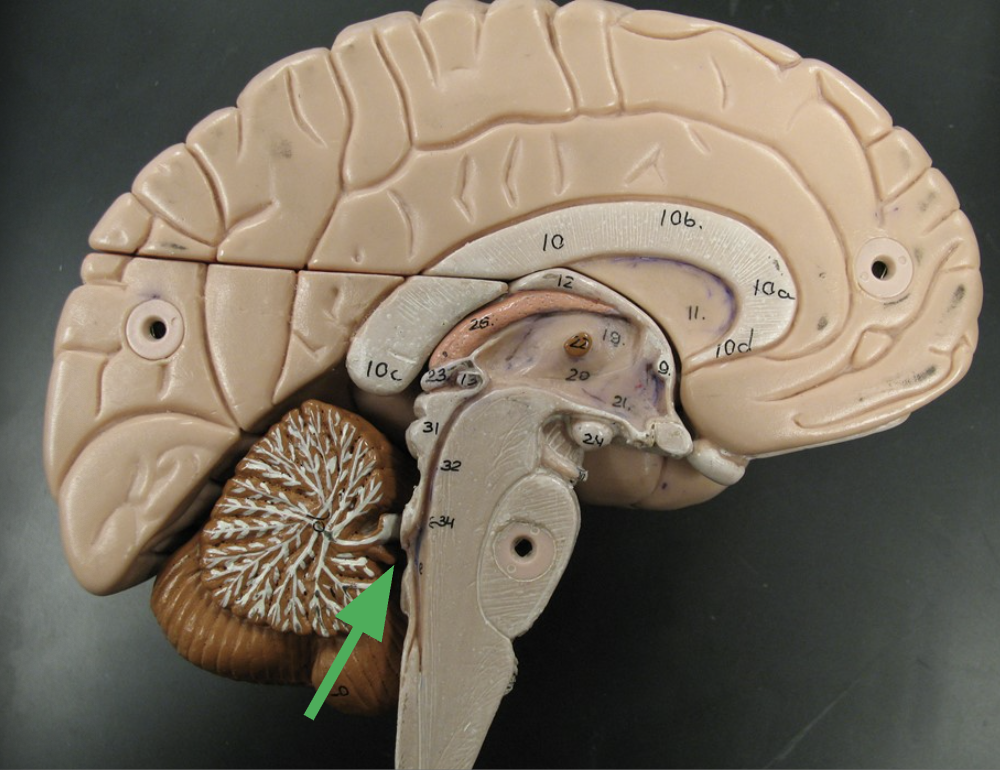
What is in the fourth ventricle, and how does it move?
Cerebrospinal fluid (CSF)
Receives cerebrospinal fluid from third ventricle from cerebral aqueduct.
Moves inferiorly to the central canal of the spinal cord.
Then laterally and posteriorly into subarachnoid space.
What is the space between the cerebellum and the occipital lobe of the cerebrum?
Transverese Fissure
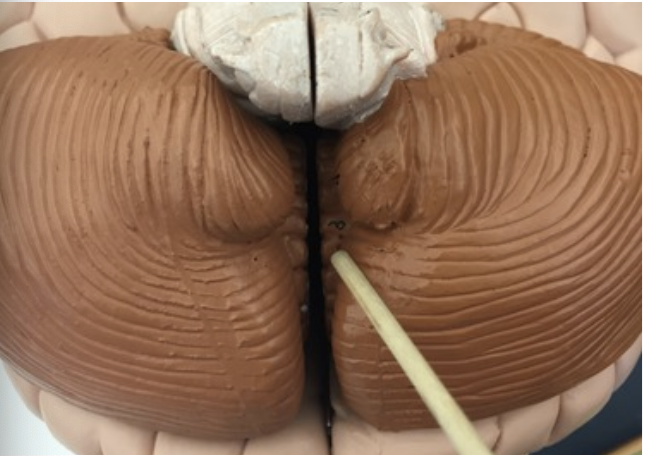
what is the arrow pointing at?
Vermis
Nervous tissue between both cerebellar hemispheres
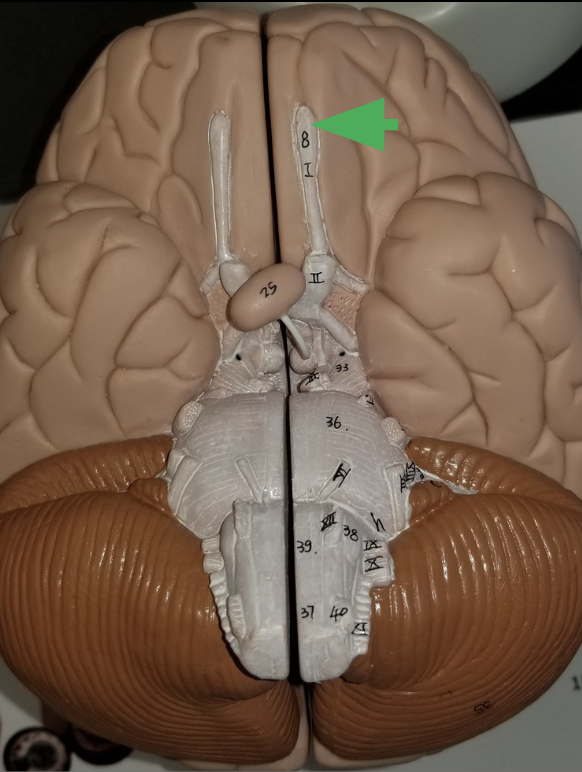
what does the arrow indicate?
Olfactory bulb
What is the function of an olfactory bulb?
Receives input from olfactory neurons coming from nasal cavity
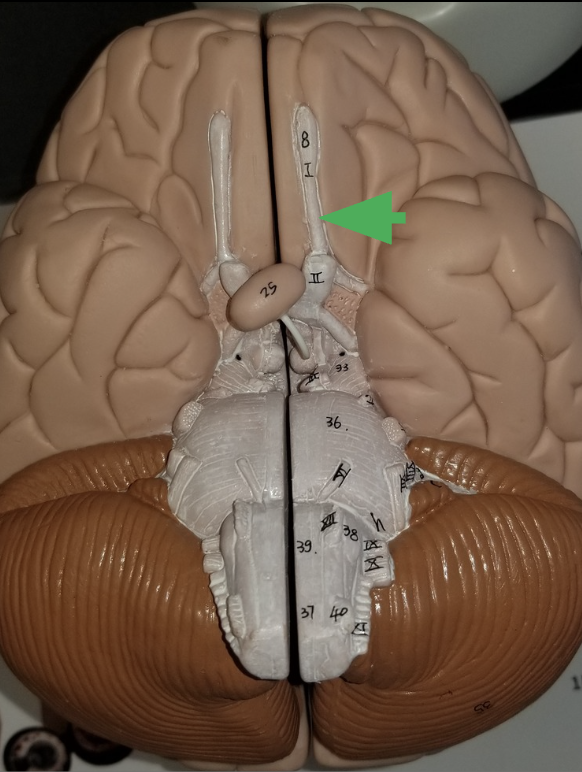
Olfactory Track
What does the olfactory tract do?
carries information from the olfactory to the cerebrum, where it can be sorted, interpreted, and processes
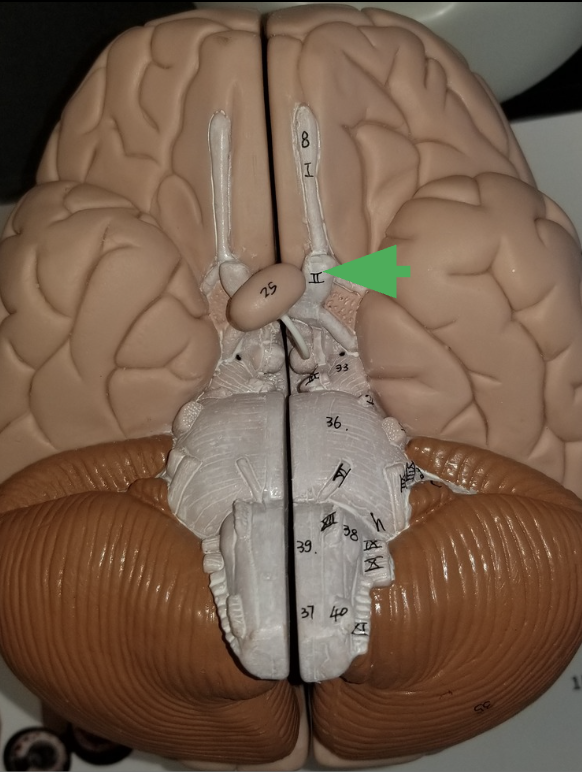
Optic Nerve (cranial nerve 2)
What does the optic nerve do?
carries axons from retina of the eye
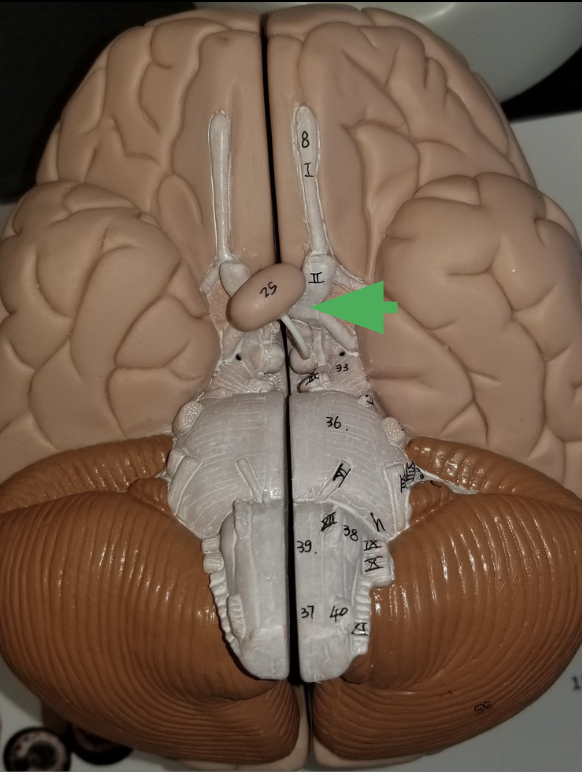
what does the arrow indicate ?
Optic chiasm
What happens in the optic chiasm?
where some axons in each optic nerve cross over to the other side
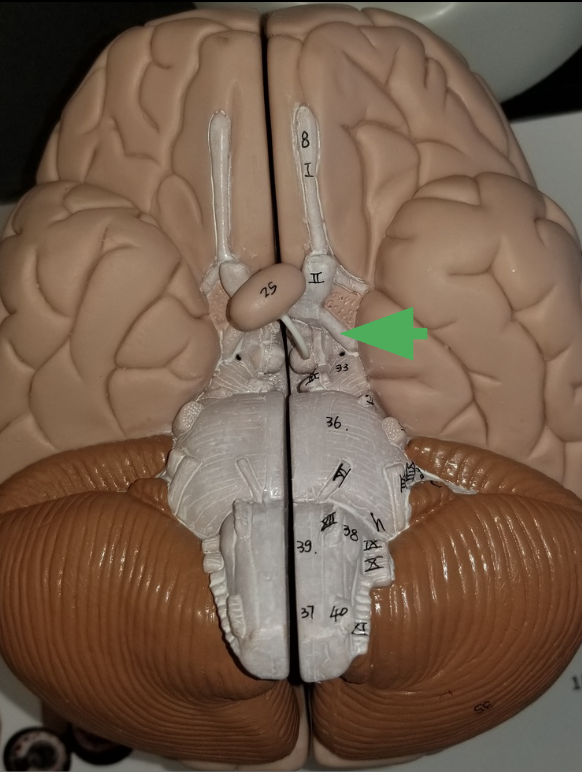
What does the arrow indicate?
Optic Track
What does the optic track do?
carry axons from optic nerves ro the thalamus
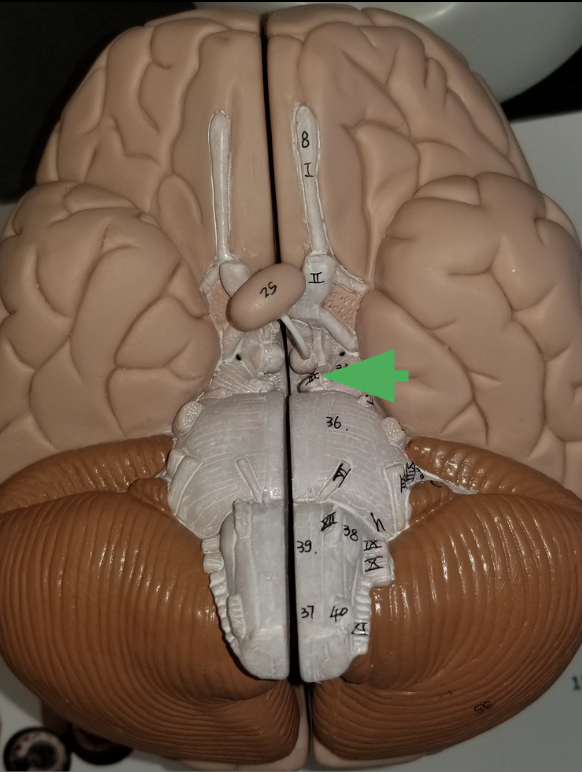
What is the arrow pointing at?
Oculomotor nerve
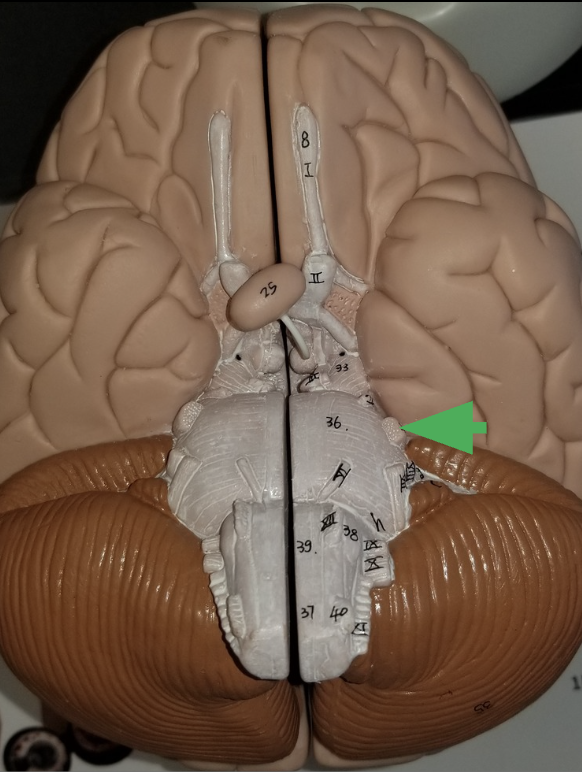
What is the arrow indicating?
Trigeminal nerve (cranial nerve 5 /V )
What does the trigeminal nerve do?
Carries sensory information from the face
Carries motor commands to chewing muscles
Bonus Question: What are the twelve cranial nerves?
*scroll
Oh - olfactory
Oh - optic
Oh —oculomotor
To—Trochlear
Touch—trigeminal
And—abducens
Feel—facial
Very—vestibulocochlear
Green—glossopharyngeal
Vegetables—vagus
AH - Accessory
HA - Hypoglossal
Match the 12 nerves with either sensory, motor, or both.
*scroll
S = sensory M = motor B = both
Some
Say
Marry
Money
But
My
Brother
Says
Big
Brains
Matter
More
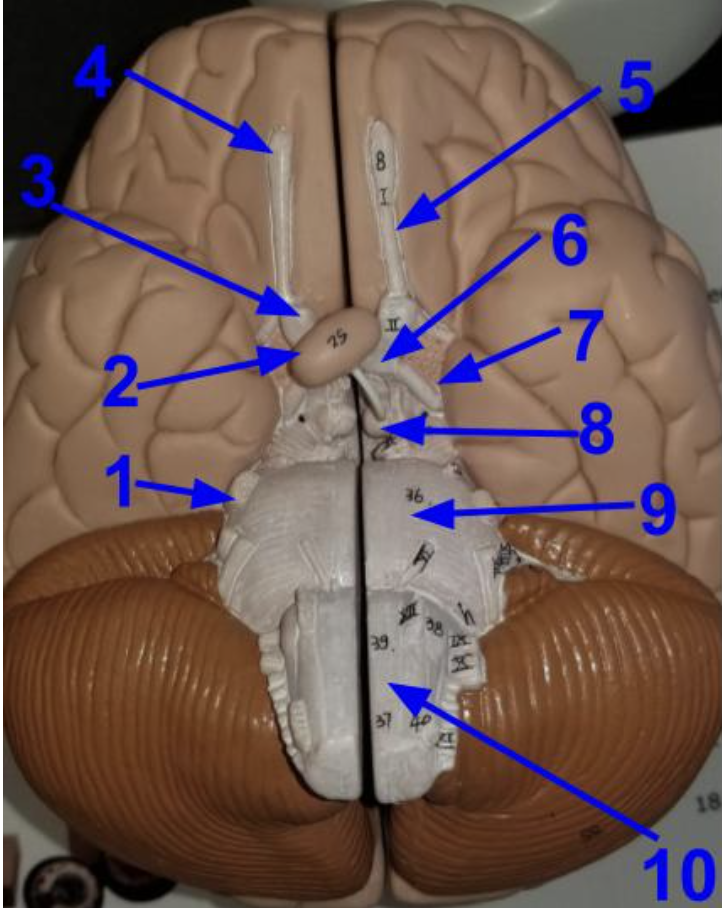
Name the structures
