ECON 303 - Lesson 11
1/14
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
15 Terms
How would you best explain the ‘one market / one price approach’ underlying the one-period closed economy model? Select one – the most appropriate answer.
The economic system is examined as just one market where leisure is exchanged for consumption goods, and the resulting real wage is the equilibrium price on this market.
Macroeconomic equilibrium is derived from the fact that labor market closely interacts with other markets that results in fair competitive prices in all markets.
The economic system is interpreted as just one market where goods are exchanged for money.
There is one equilibrium price in each market in an economic system.
Macroeconomic equilibrium is set on the labor market and the resulting prices of goods on other markets are considered as equilibrium prices.
The economic system is examined as just one market where leisure is exchanged for consumption goods, and the resulting real wage is the equilibrium price on this market.
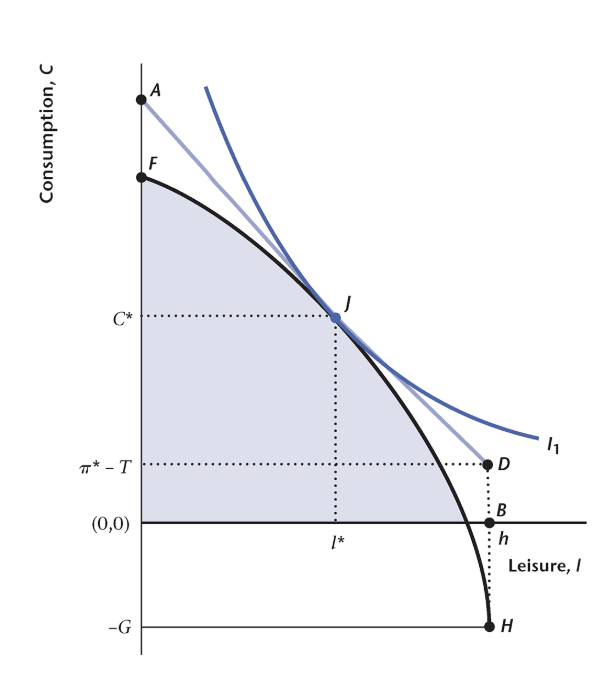
Consider the diagram below given findings of one-period closed economy model. Assume now that for some reason the aggregate household utility function changed and the new equilibrium (point J) shifts to the South-East along the PPF curve. What subsequent change in this economic system do we expect to take place? Select one – the most appropriate answer.
Private consumption increase.
Real wage increase.
Output rise.
Labor supply increase.
Public consumption decline.
Labor supply increase.
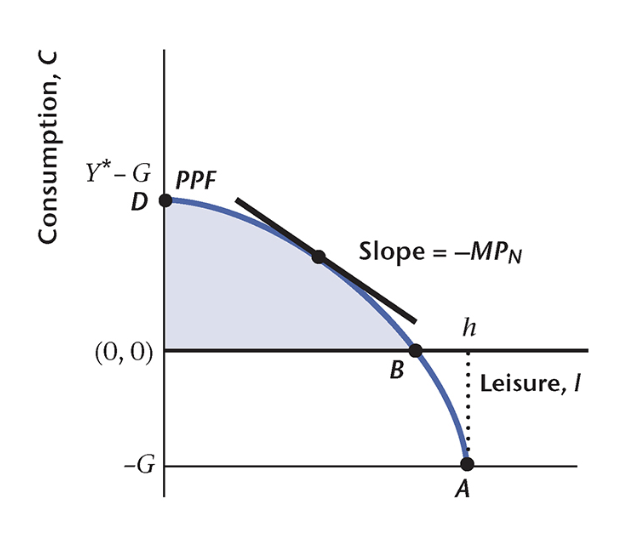
How would you best describe the distance between points B and h on the diagram below? Select one – the most appropriate answer given provisions of one-period model of a closed economy.
Number of hours used to produce C.
Aggregate labor supply in this economy.
Number of hours spent to produce G.
Number of hours used to produce Y.
Aggregate leisure in this economy.
Number of hours spent to produce G
Assume an economic system that is described by one-period closed economy model. The government purchases some part of the output and finances this expenditure by collecting a flat rate tax. Suppose that the government considers substituting a lump sum tax for the existing flat rate tax given that the actual revenues collected remain unchanged. What is the most likely effect of this substitution on the economy? Select one – the most appropriate answer.
Public consumption will go down.
Public consumption will rise.
Output will diminish.
Private consumption will decrease.
Labor supply will go up.
Labor supply will go up.
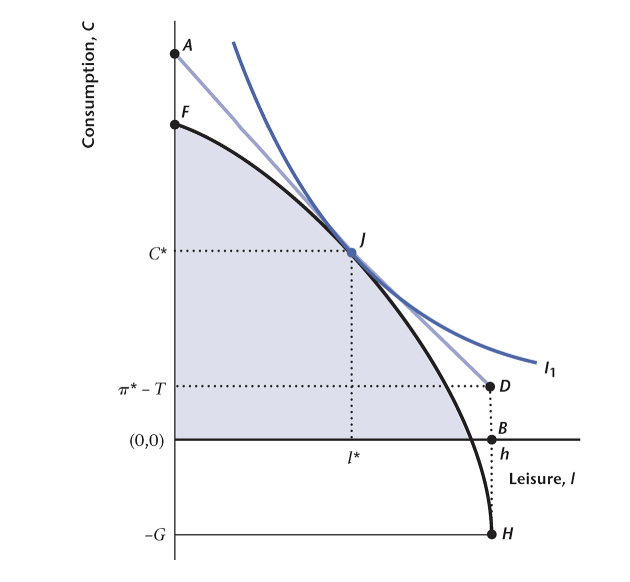
Consider the diagram below given findings of one-period closed economy model. Assume now that the real wage goes down. How is the distance between D and B expected to change? Select one – the most appropriate answer.
It may either increase or decrease.
It will rise.
It will go down.
It will remain constant.
It will depend on the marginal product of labor.
It will rise.
What is the major role of government in macroeconomic models? Select one – the most appropriate answer.
Crowding out private consumption.
Creating public income.
Substituting private consumption.
Purchasing part of the output.
Regulation of private sector.
Purchasing part of the output.
When macroeconomists describe competitive equilibrium as Pareto optimal, they mean that … . Select one – the most appropriate answer given provisions of one-period closed economy model.
The economy must be restricted because when firms want to maximize their profits social efficiency is impossible.
Correct!
Unconstrained markets can maximize households’ utility.
A fictional social planned should intervene to produce socially efficient outcomes.
Government should regulate the economy so that this situation is possible.