PHC6410 Exam 1
1/136
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
137 Terms
primordial prevention
-general population
-injury prevention, promote a healthy diet, physical activity, no substance use
prevents the development of risk factors
primary prevention
-at risk
-reduces incidence rate of a disease
--examples: wearing face masks, handwashing,improving diet
prevents the onset of disease through risk reduction
secondary prevention
-high risk and confirmed cases
-prevent more serious disease/reduce severity, limit disability
-screening for cdv risk, enhance adherence to medical recommendations like medication/low fat diet
early detection and treatment
tertiary prevention
-cancer, AIDS
-disease management/ CVD patient
rehab, reduces consequences, prevents recurrence
how do we develop theory
precise about wording and measure what we are testing
constructs
conceptual components, building blocks, or primary elements of a theory
variables
operational definitions of constructs or how the constructs are measured/implemented
how is theory used in health promotion?
Provides conceptual context for understanding behavior, guides research that seeks to identify determinants of health-related behavior, and guides program planning methods can be incorporated into health promotion practice
mediators
actors associated with outcome of interest and when changed can increase the likelihood of beahavior change
change processes
health promotion professionals make changes in individuals, organizations with whom they work to accomplish specific outcomes
program development functions
Identifying a need for a program, developing components and plans, implementing interventions, conducting evaluation
what are health promotion’s goals
Providing services and activities that improve behavior and health
Strengthen the environment to support personal health behavior
Facilitate healthful behavior
health related behavior
-everyone , managers, public officials
-engage in behaviors that expose others to possible infection, congregating in large groups
affects health and health behavior of other people and not the person who engages in the behavior
health protective behavior
-everyone, public health profesisonals
-wearing face masks, testing for disease, vaccines
out of concern for one’s own health or the health of others
prevention
makes changes to the environment, behaviors, or other risk factors to prevent or mitigate impacts of health conditions
primary prevention for checking and controlling blood pressure
reduction in heart attack incidence
secondary prevention of controlling blood pressure
screening people with a family history of hypertension
tertiary prevention of checking/controlling blood pressure
trying to prevent the recurrence of a heart attack
How do you develop hypotheses?
be precise and measure ideas that you are testing
what is a model
representation of a behavior that may or may not be testable and is an application of a theory
evaluation
assessing the strengths and weaknesses of programs, policies, personnel, products, and organizations to improve their effectiveness
Do we need a program, policy, product, or service first before we consider evaluation?
no
role of evaluation in public health
developing, improving, and identifying quality health programs and interventions; before, during, and after your program
evaluation research
-perfect world research
-determine cause and effect
-internal validity
impact of a new intervention among a defined population, generating new knowledge, establishes the feasibility, efficacy, and costs of an intervention
program evaluation
-practice based, does the program work when delivered under normal conditions?
-external validity and generalizability
-EFFECTIVENESS
produces valid evidence that a tailored, replicable program is accepted and delivered
efficacy
-behavioral impact/research
did the new intervention produce changes among a population sample under optimal program practice conditions
effectiveness
-program evaluation/existing programs
-real world setting
did the established intervention produce a significant change in a large sample population under normal program practice conditions
formative evaluation
-forming the program
-creates rapid feedback before widespread implementation
-improve the way a program is delivered
provides quantitative and qualitative insight during the developmental and early implementation phases
summative evaluation
to understand the end products. how did behavior change?
summing up the program
draw conclusions and make decisions about impact, outcomes, or other benefits of a health program
process evaluation
-ongoing check on a plan’s implementation and documentation of the process
-compares the actual implementation components of a solution with the intended
documents the degree to which the program was implemented as planned
implementation fidelity
degree to which an intervention was delivered as intended
quality assurance
systematically monitoring to ensure an intervention meets predefined standards
short term evaluaition
-up to 1 or 2 years
immediate effects and behavior
intermediate evaluation
-1 or 2 years, up to 5 years
what short term effects lead to such as health status
long term evaluation
longer than intermediate and measures overall morbidity/mortality and changes in conditions
what makes up the CDC’s social ecological model
individual, relationship, community, social
prevention strategies at individual social ecological model
-conflict resolution, life skills training, social emotional learning
promote attitudes beliefs and behaviors
prevention strategies at relationship social ecological mdoel
family focused prevention programs, mentoring, peer
prevention strategies at community social ecological model
improve social environment and address social conditions
prevention strategies at societal social ecological model
prevent societal norms and strengthen structural determinats of health
intrapersonal factors
-interventions are education, training, skills
-harm reduction education, safety info, peer led
knowledge, behaviors, attitudes, self concept
intrapersonal factors
-interventions are education/training to those who interact and modifying home and family environments
-campaigns to change social norms, increase accessibility to sex worker led groups
social network with family, group, and friendships; expectations of how one should behave
Institution/organizational levels (school/work)
-modifications to environments, policies, or services
-workplace policies, connection to support services
rules, regulations, policies, and informal structures
community factors
-coalition building, sex worker organizations’ community building efforts
relationships among orgs, institutions, and informal networks
public policy
-decriminalization of sex work, improved law enforcement
state, local laws, and regulations
health program
-has educational services, prevention and populaiton focused
organized set of activities to provide a health focus intervention for a specific audience
health service
organizational structure through which providers interact w clients or patients to meet their health needs
project
time limited effort to provide a specified set of organized services or interventions
policy
decisions, plans, and actions achieve specific healthcare goals
product
-food, drugs, assistive tech, med devices or imaging, ppe
refer to a program
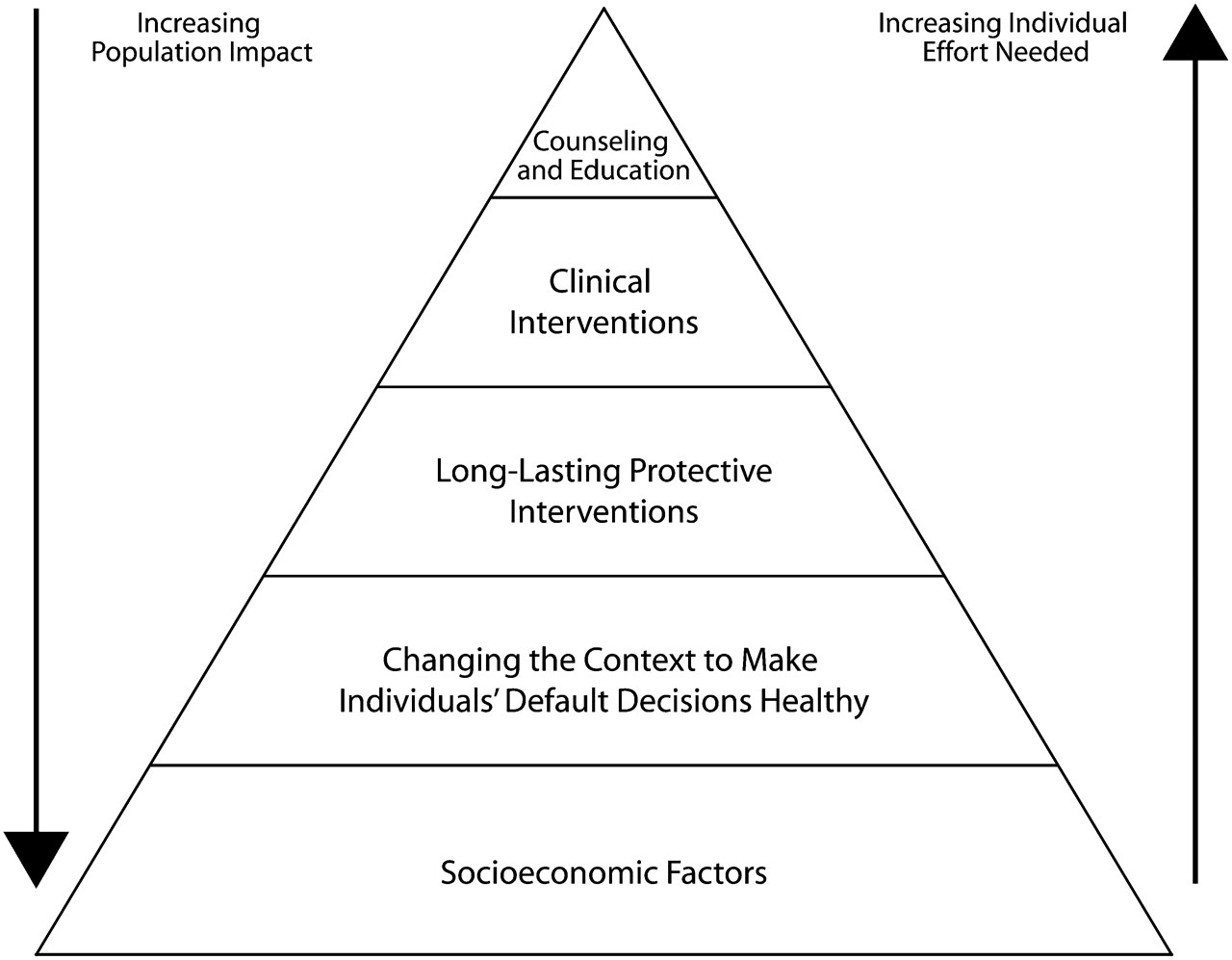
What is the public health impact pyramid levels from most individual effort needed to increasing population impact
counseling, clinical interventions, long lasting protective intervention, changing the context, and socioeconomic factors
critiques of social ecological models
complex for bringing up many protective/risk factors, resource-intensive unclear which factors are at each level
What is behavior mediated by?
-Knowledge isn’t sufficient for behavior change
-perceptions, motivation, emotions, skills, and factors
cognitions since your thoughts and knowledge affect actions
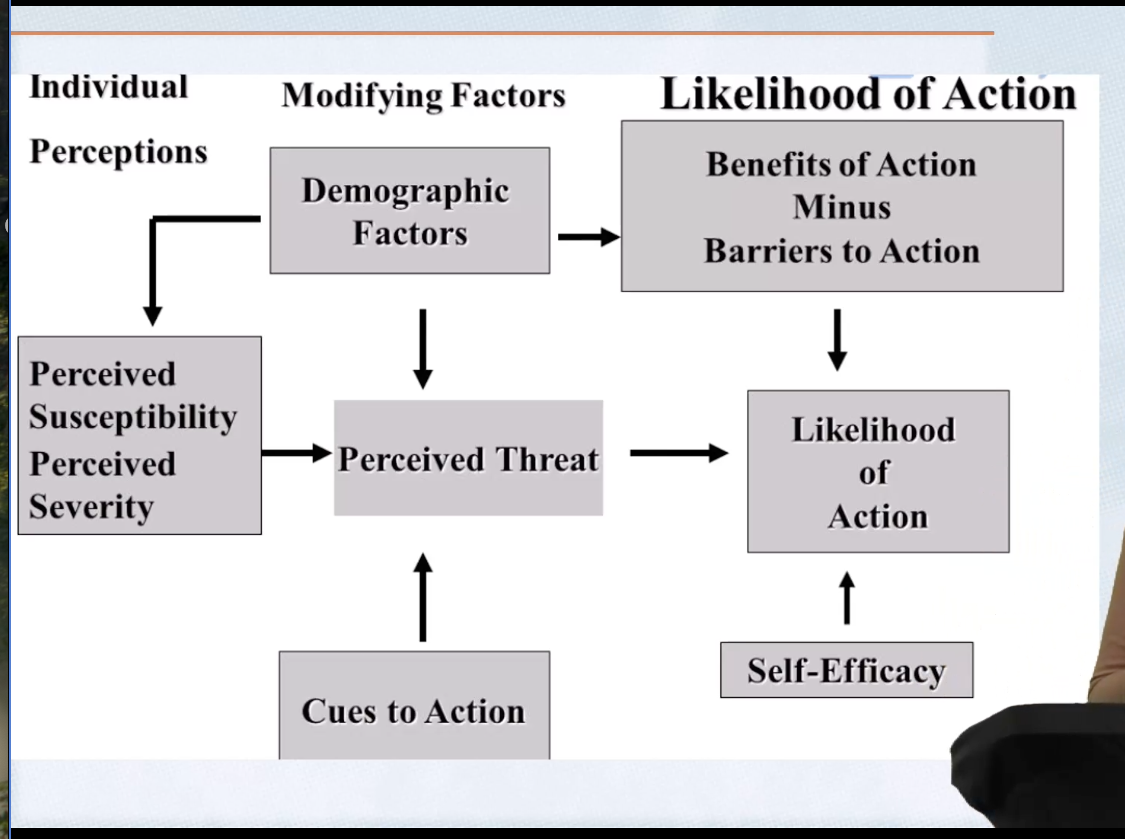
Health Believe Model (HBM)
-an expectancy-value theory
-people expect that working out will prevent them from getting heart disease
people behave in ways they expect will maximize the likelihood of achieving something they value
assumptions of health belief model
desire to avoid illness or get well; a specific health action available will prevent illness
constructs of HBM
perceived susceptibility, seriousness, benefits, barriers
percieved susceptibility
how likely do you think you are to have a health issue
perceived severity/ seriousness
how serious a problem do you believe a health issue is
perceived threat
susceptibility and severity/seriousness
perceived benefits
how well does the recommended behavior reduce the risks associate with a health issue
perceived barriers
potential negative aspects of doing a recommended behavior
cues to action (HBM)
-media, education, person’s symptoms
-essentially a catalyst
factors that cause you to change or want to change
self efficacy
one’s confidence that can successfully execute the behavior required to produce outcomes
Increased perceived threat means there also needs to be a high
self efficacy
what is the strongest association with lack of protective behavior?
-percieved susceptibility has some association
perceived barriers
when is HBM most useful for?
-specific threat associated with a health behavior
-ex. getting a vaccine
-not for something we do regularly
predict preventive health behaviors that are short term , examining specific constructs across studies
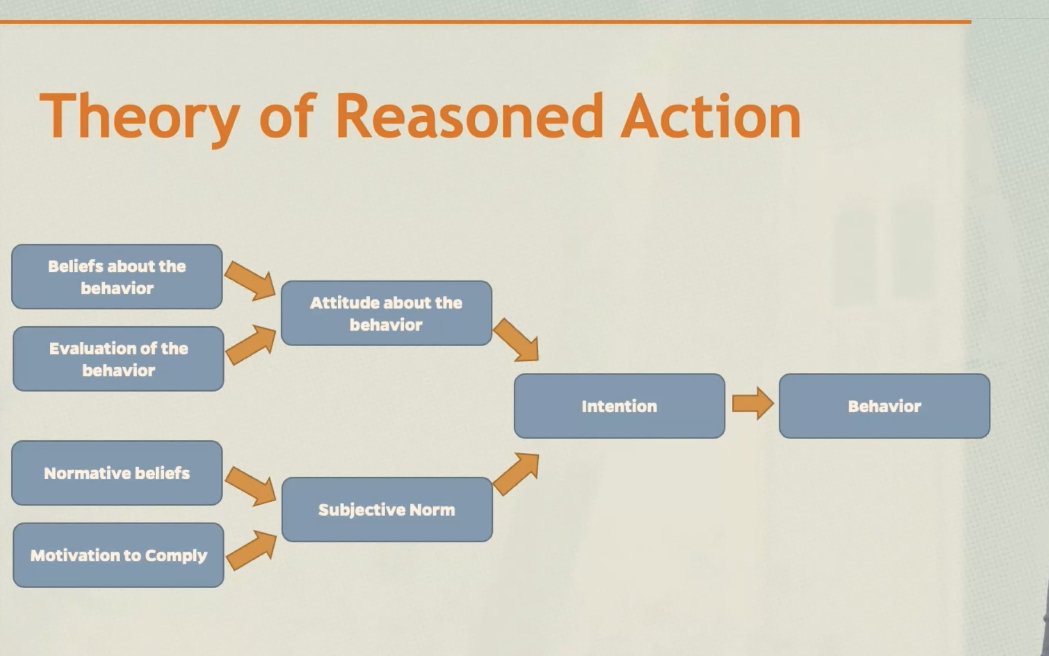
theory of reasoned action
individual will perform a behavior based on their intent to perform the behavior, attitude, and subjective norms
beliefs about a behavior (TRA)
what the person thinks the consequence of a behavior will be
evaluation of a behavior (TRA)
value attached to the outcome and judgements on whether it is positive or negative
what two factors influence subjective norms
-acceptable to their friends (opinions of others), perception of their beliefs
normative beliefs and motivation to comply
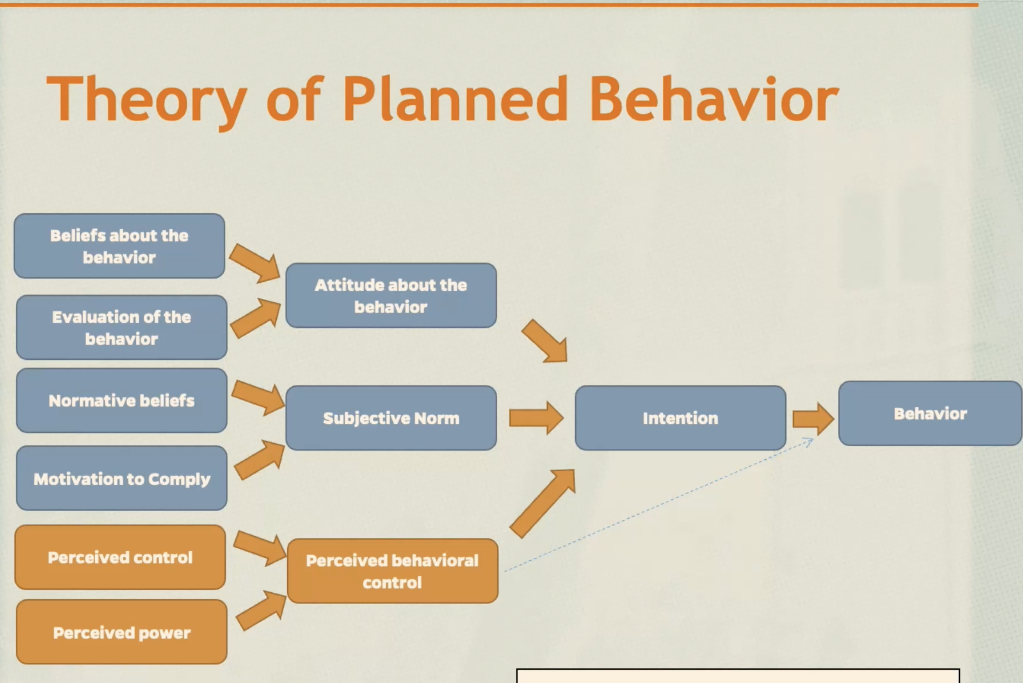
Theory of Planned Behavior
adds the factor of perceived behavior control like the ability to engage or have control over a behavior
perceived control
facilitating control beliefs; factors making it easier or harder to participate in a behavior
integrative model of behavior
adds self-efficacy, environmental factors, and skills/abilities
intervention
organized set of activities designed for a specific audience targeting behavioral or health changes
method
technique or process of influencing changes in determinants of behaviors and conditions
anticipated regret
stimulating people to focus on how they may fell after engaging in an unintended risky behavior
information about other’s approval
provide info about what others think about the person’s behavior and whether they will approve or disapprove
guided practice
prompting people to rehearse and repeat the behavior various times to discuss the experience and provide feedback
precontemplation stage
-may have wanted to change but have been demoralized
-Disadvantages are greater than advantages
-consciousness raising, dramatic relief
have no interest in changing their behavior or have no awareness
contemplation
-be open to information and may actively seek information about it
-long periods of time in this stage
-self reevaluation, environmental reevaluation
people are ware that change might be beneficial and are considering it
preparation for action
efforts to change have not been recent or sustained
-often lack the skill and resources needed to establish change
-social liberations, self liberation
have a plan to take action in the future
action
-stopping smoking for all
substantial behavior change that can reduce risk of disease and promotes health
maintenance
>6 months
helping relationships, reinforcement management, stimulus control
prevent relapse and keep the gains they have made
how do people move from one stage to another?
advantages of changing outweigh the disadvantages
interventions for precontemplation > contemplation
consciousness raising, dramatic relief, environmental reevaluation
dramatic relief
experiencing and expressing feelings about one’s problems and solutions
contemplation > preparation interventions
self reevaluation
self reevaluation
looking at life with and without the healthy risk behavior
preparation > action intervention
self liberation (choosing and committing to act in ability to change)
action > maintenance intervention methods
reinforcement management, helping relationships, counter conditioning, stimulus control
critiques of TTM
unclear stages, stage progression doesn’t always lead to behavior change, doesn’t consider external factors, may not capture complexities of behaviors
what were the bobo doll experiment replications
observational learning through recordings/tv and impact of observed rewards/punishments
social learning theory
behavioral + cognitive
vicarious learning
observing the behaviors of others
vicarious reinforcement
engage in behavior we’ve seen others being rewarded for
social cognitive theory
association between personal factors, environmental factors, and human behavior
behavioral capability
whether one has the skills necessary to perform a behavior
self efficacy
person’s belief in their ability to engage and maintain a behavior
outcome expectations
regarding the outcomes of a behavior
how to build behavioral capability
education, modeling, skills training, skills practice, role playing