Pathological Conditions in Oncology
1/87
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
88 Terms
Pathology Definition
the sicence of the causes and effects of diseases, especially the branch of medicine that deals with examing the histlogy for diagnostic purposes
Three overlapping risk factors for cancer and chronic conditions
alcohol
smoking
obesity
what percent of body is water
60%
ICF = 66%
ECF = 33%
What is tissue
a collection of cells and their ecm working together to perform a shared function
what is an organ
a strucutre made up of a group of tissues, working together to perform a specific function
what is interstital matrix
The interstitial matrix is the extracellular matrix that exists between tissues, providing structural and biochemical support to surrounding cells.
what is interstital matrix
made up of fibroblasts, which produce collagen and other components
water as well
is there more filtration on the arterial or venous end of capillaries
more filtration due to higher hydrostatic pressure
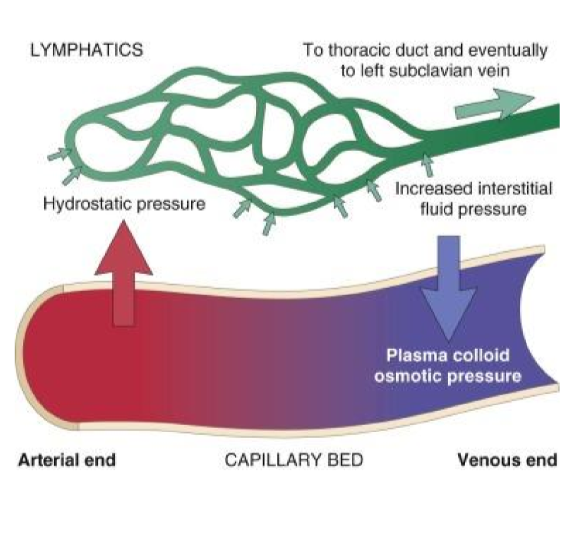
why is there more absorption on the venous ends
There is more absorption on the venous end of capillaries due to lower hydrostatic pressure and and increased colloid proteins pulling water back into the vessels
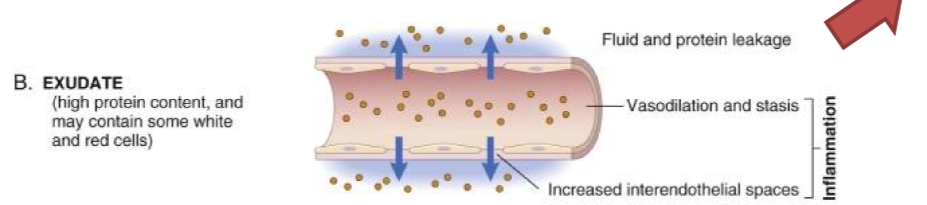
what is exudate
inflammation causes cytokines to be released, resulting in increased vascular permeability, leading to the accumulation of fluid, proteins, and cells in tissues.
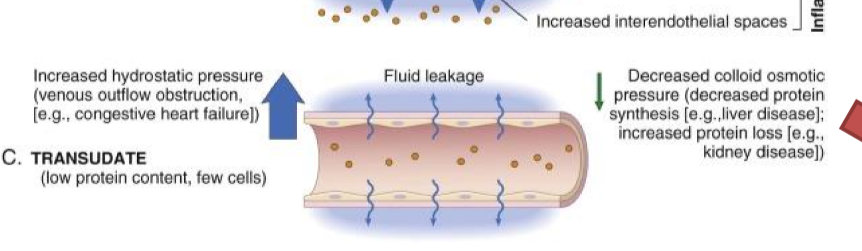
what is transudate
decreased concentration of protein in blood results in fluid leaking out of the vessels into the interstitial space with low protein content.
no proteins released
6 causes of abnormal fluid retention
increased vascular permeability
inreased hydrostatic pressure
decreased protein synthesis
increased protein loss
lymphatic obstruction
sodium retention
What is ascites
A pathological condition characterized by the accumulation of excess fluid in the abdominal cavity, often due to liver disease, heart failure, or malignancies.
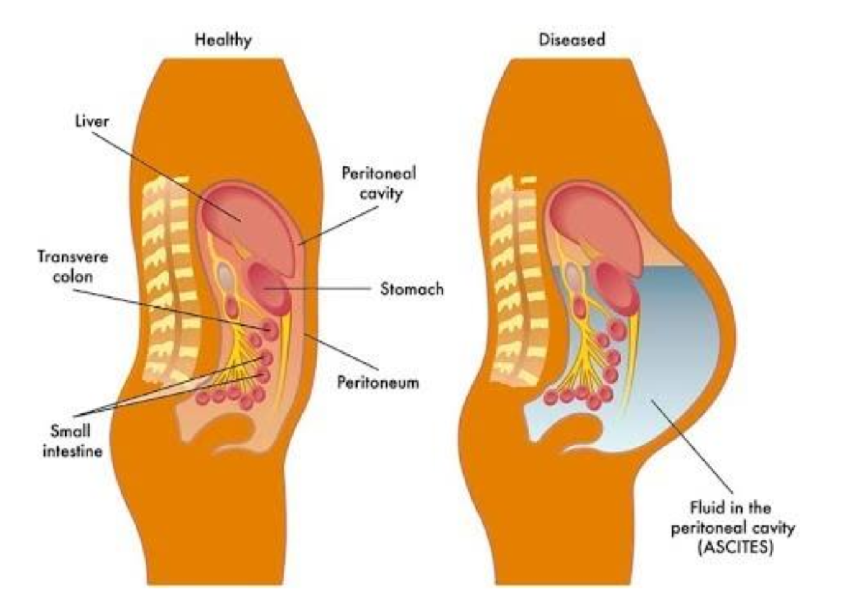
most common cause of ascites
liver cirrhosis
what is cirrhosis
chronic liver disease that results in excessive liver scarring and destruction of hepatocytes
liver has only 1 repair pathway - fibrosis - leading to loss of liver function and complications such as portal hypertension and liver failure.
three symptoms of cirrhosis
jaundice
ascites
splenomegaly
what is esophageal varices (symptom of cirrhosis)
Enlarged veins in the esophagus that occur due to increased pressure in the portal vein, often leading to bleeding.
three leading causes of cirrhosis
viral (Hep B and C)
Alcohol/metabolic
Autoimmune
what cancer are patients with cirrhosis at an increased risk at?
Liver cancer (hepatocellular carcinoma)
more fibrosis repair = increase risk of hepatocytes becoming cancerous
why does cirrhosis limit the interventional approaches to cancer treatment
the liver is important in the metabolism and pharmacokinetics of many drugs
cirrhosis livers have less efficacy to convert drugs and activate them
best treatment for hepatocellular carcinoma
liver transplant: get rid of cancer and potential cirrhosis
hepatic venous outflow obstruction
any condition that impairs the blood flow through the liver or from the liver to the heart
how does HVOO cause ascites
increased in hydrostatic pressure in the hepatic veins leads to fluid accumulation in the abdominal cavity.
Veno-occlusive disease of the liver
liver sinusoidal endothelial cells canbe damaged, leading to venous obstruction and hepatic dysfunction.
Budd-Chiari Syndrome
a condition caused by obstruction of hepatic venous outflow due to thrombosis or compression, often resulting in liver dysfunction and portal hypertension.
hepatocyte death may occur
What is pleural effusion
Pleural effusion is the accumulation of fluid in the pleural space
simple pleural effusion
accumulation of fluid
complicated pleural effusion (empyema)
accumulation of infected fluid in the pleural spaces
Serofibrinous Pleuritis
the inflammation of the pleura
most common causes are infection and autoimmine disorders
two ways serofibrinous pleuritis is associated with cancer
metastatic involvement of the pleura can cause pleuritis
radiation therapy for tumors of the lung and mediasteinum can cause pleuritis
Pericardial Effusion
the abnormal build up of fluid in the pericardial sac around the heart
Radiation-related pericarditis
inflammation of the pericardium due to radiation therapy, often manifesting as pericardial effusion
acute manifestation of radiation injury
what can rapid accumulation of pericardial effusion result in?
cardiac tamponade: fluid compressing the heart
Edema
abnormal buildup of fluid in the tissue and interstitium
three categories of edema
subcutaneous
pulmonary
brain edema
localized subcutatenous edema
edema secondary to surgical procedures or RT that disrupt draining lymphatics
the more nodes removed = more edema
what lymph node procedure minimizes lymphedema
Sentinel lymph node biopsy
Hydrocephalus
A condition characterized by an accumulation of cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) within the ventricles of the brain, leading to increased intracranial pressure and potential brain damage.
two types of cancer that can cause hydrocephalus
brain tumors/metastasis
leptomeninges
radiation leukocephalopathy
damage to the brain's white matter caused by radiation therapy, leading to symptoms like memory loss, confusion, and difficulty walking.
also causes hydrocephalus
late effect
what is the underlying pathogenesis of coronary and cerebral vascular diseases
atherosclerosis
what is atherosclerosis
buildup of fatty deposits (plaque) inside arteries, which can narrow them and reduce blood flow.
what are athersclerotic plaques susceptible to?
rupture/ulceration
exposes thrombogenic substances and leads to thromosis
atheroembolism
plaqure rupture can lead to debris causing microemboli
aneurysm
what is an aneurysm
bulge or ballooning in a blood vessel wall caused by weakness, which can rupture and lead to serious bleeding.
3 modifiable factors for atherosclerosis
hyperlipidedemia, hypertension, smoking
3 non-modifiabe factors for atherosclerosis
genetic abnormalities, family history, age, being male
Stroke (CVA)
happens when blood flow to part of the brain is blocked or a vessel bursts, causing brain cell damage.
two general types of strokes
hemorragic stroke
a weakened blood vessel in the brain bursts, causing bleeding and damage to brain tissue.
ischemic stroke
a blood clot or blockage cuts off blood flow to part of the brain, leading to brain cell death.
hemmorage = burst
ischemic = block
thrombotic vs. embolic ischemic strokes
thrombotic: blood clot develops from blood vessels inside brain
embolic: blood clot/plaque debris develops elsewhere in the body and travels to brain
Signs/Symptoms of a stroke
BE FAST
balance loss
eyesight changes
face drooping
arm weakness
speech difficulty
time to call 911
Transient Ischemic Attacks
are brief episodes of stroke-like symptoms caused by temporary blockage of blood flow to the brain, usually resolving within minutes to hours without lasting damage.
often warning sign for major stroke
what type of strokes do cancers mostly cause
ischemic strokes
4 reasons cancer can induce a stroke (two are tx related)
cancer is a hypercoaguable state
tumors try isolate themselves from immune system, throw out coaguable factors
direct vessel compression from a tumor
vasculopathy from irradiation
chemotherapy association
cisplatin, thalidomide
myocardial infarction
happens when blood flow to coronary vessels of heart are blocked, causing necrosis to the heart muscle.
signs/symptoms of myocardial infarction
chest pain, shortness of breath, sweating, nausea, and pain radiating to the jaw or arm.
why is it important to keep the heart out of the radiation treatment field
RT can induce damage to coronary arteries that accelerate development of atherosclerosis
Pulmonary Embolism
a sudden blockage in a lung artery, usually caused by a blood clot that traveled from the legs (deep vein thrombosis).
symptoms of PE
include shortness of breath, chest pain, cough, and rapid heart rate.
why is PE risk increased in cancer patients
cancer is prothrombotic state: blood is more prone to clote
patients may less active, DVT will throw clots
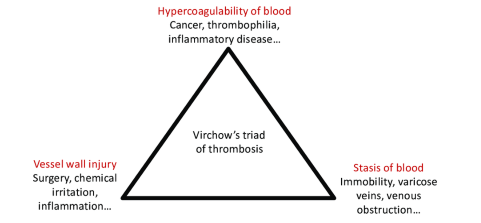
Virchow’s triad of thrombosis
hypercoagubility of blood
vessel wall injury
stasis of blood
fracture
loss of bone integrity resulting from mechanical injury and/or diminished bone strength
pathologic fracture
bone weakened by an underlying disease process (such as a neoplasm)
what is more common: bone metastasis or bone neoplasms
Bone metastasis is more common than primary bone neoplasms, as most bone lesions result from cancer that has spread from other parts of the body.
prostate, breast, thyroid, lung
osteolytic metastasis
a type of bone metastasis characterized by the destruction of bone tissue due to the invasion of cancer cells
increased PTH induces osteoclasts to break down bone
often seen in breast cancer
osteoblastic metastasis
deposition of new abnormal bone growth
often seen in prostate cancer.
osteoporosis
a condition characterized by weakened bones and increased risk of fractures due to loss of bone density.
major causes of osteoporosis
include aging, hormonal changes, and nutritional deficiencies.
cancer therapies that increase osteoporosis in patients
Selective estrogen receptor modulators and androgen deprivation therapy
COPD
(Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease) is a progressive lung disease that causes breathing difficulties due to airflow obstruction.
most commonyl caused by smoking
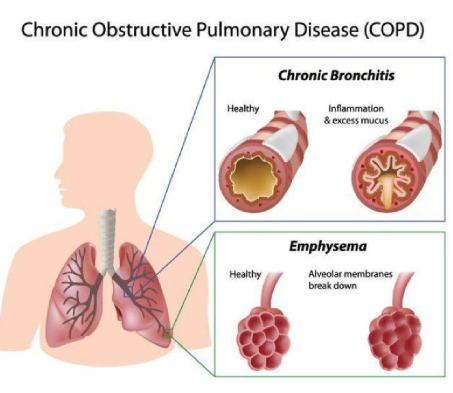
COPD impact on cancer
can lead to increased risk of lung cancer due to compromised lung function and inflammation.
also have worse outcomes: surgical resection of lung cancer requires having sufficient lung reserve in remaining lung
pneumothorax
is a condition where air leaks into the space between the lungs and chest wall, causing lung collapse (atelectasis). It can occur spontaneously or due to injury.
primary spontaneous pneumothorax
spontaneous distruption of pleural lining, often seen in younger patients
secondary pneumothorax
underlying lung disease that disrupts pleural surface
TB, emphysema, pleural cancer, etc
Tension Pneumothorax
is a life-threatening condition where air accumulates in the pleural space, leading to increased pressure that collapses the lung and shifts mediastinal structures. This requires immediate medical intervention to decompress the pleural cavity.
non collapsed lung is impacted, can’t transfer oxygen
Pneumonia
an infection that inflames the air sacs in one or both lungs, which may fill with fluid or pus, causing difficulty in breathing.
lung defence mechanisms
cough
alveolar macrophages
mucociliar elevator
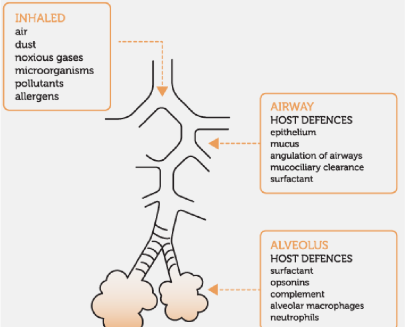
pneumonitis
inflammation of lung tissue, often due to infection, allergens, or chemicals, that can lead to similar symptoms as pneumonia, including cough, fever, and difficulty breathing.
pneumonia vs. pneumonitis
pneumonia = inflammation caused by infection
pneumonitis = inflammation caused by allergens, chemicals or other irritants.
radiation pneumonitis
inflammation of lung tissue resulting from radiation therapy, often occurring in cancer patients, characterized by cough, fever, and shortness of breath.
chronic radiation pneumonitis is called
pulmonary fibrosis
Stridor
a high-pitched wheezing sound caused by an obstruction in the upper airway.
causes of stridor
airway obstruction, infections, tumor in upper airway, foreign bodies
Chondroradionecrosis
death of condrocytes due to radiation therapy to neck
cartilage death = potential airway collapse
rare late complication
GI obstruction
a blockage that prevents the normal passage of contents through the gastrointestinal tract, which can lead to symptoms like vomiting, abdominal pain, and distension.
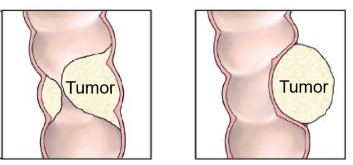
Two types of tumor causes of GI obstruction
intraluminal or extrinsic (mesentery growth) tumors
GI or GYN origin
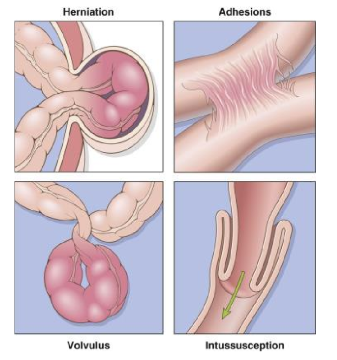
other causes of GI obstruction
herniation
adhesions
volvulus
intussception
why do opiods cause GI obstruction
decreased GI motility since peristalsis is inhibited