Physics - 1 Conservation and Dissipation of Energy
1/52
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
53 Terms
How many energy stores are there?
8
What are the 8 energy stores?
- magnetic
- thermal
- chemical
- kinetic
- electrostatic
- elastic potential
- gravitational potential
- nuclear
How many energy transfers are there?
4
What are the 4 energy transfers?
- mechanical work
- electrical work
- heating
- radiation
Sankey diagram
Represents useful and wasted energy with arrows
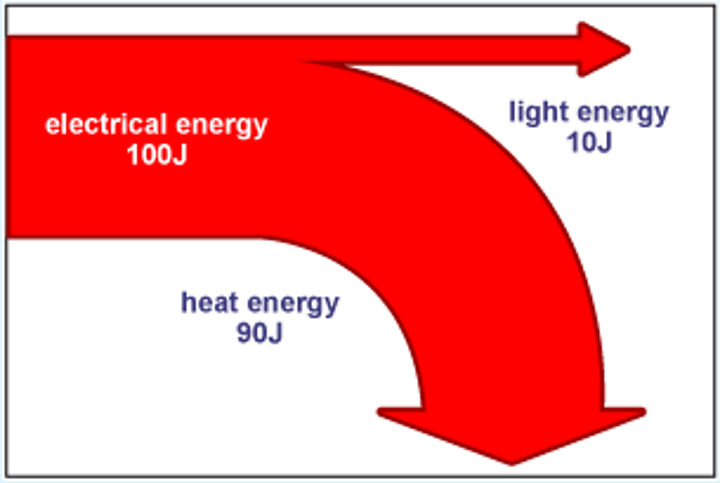
What is the law of conservation of energy?
energy cannot be created or destroyed, only transferred
Work
applied force that causes an object to move
'Work done' is another way of saying...
energy transferred
Equation for work done:
work done = force x distance
What is work measured in?
J (or Nm)
Where does work done to overcome friction mostly go?
into thermal energy stores via heating
What does friction do?
oppose motion
Why do brakes work? [2]
- friction opposes the motion of the wheel
- the kinetic energy of the wheels and vehicle is transferred by heating to the thermal stores of the brakes and the wheels
In equations, gravitational energy store is:
Eₚ
The force you need to lift an object is equal and opposite to the...
gravitational force of the object
Equation for gravitational potential energy:
Δgravitational potential energy = mass x gravitational field strength x Δheight
gravitational potential energy is measured in:
Joules, J
Equation for weight:
weight = mass x gravitational field strength
kinetic energy
the energy an object has due to its motion
Equation for kinetic energy:
kinetic energy = ½ x mass x speed²
Kinetic energy is also written as:
Eₖ
Symbol equation for kinetic energy:
Eₖ = ½mv²
Elastic potential energy
the energy of stretched or compressed objects
Spring constant
a parameter that is a measure of a spring's resistance to being compressed or stretched
Hooke's Law
extension is directly proportional to force until the spring reaches its elastic limit
Hooke's Law equation:
Force = spring constant x extension [F=ke]
Equation for elastic potential energy:
elastic potential energy = ½ x spring constant x extension²
Symbol equation for elastic potential energy:
Eₑ = ½ke²
What is spring constant measured in?
N/m
Useful energy
energy transferred to where it is wanted in the form it is wanted.
Wasted energy
energy that is not usefully transferred
dissipated energy
wasted energy that has 'spread out'
What are examples of wasted energy? [2]
- thermal energy (friction etc)
- sound waves
Combating friction in machinery [3]:
- lubrication
- removing irregularities (smoother)
- using smoother materials
Input energy
energy supplied to a device
Useful output energy
useful energy transferred by the device
Equation for efficiency:
efficiency = useful output energy ÷ total input energy
Efficiency limits
No device can be more than 100% efficient because you can never get more energy from a machine than you put into it
How could we investigate efficiency?
attach a joulemeter into the circuit of an electric winch and use a mass's increase in GPE to figure out its efficiency
Improving efficiency [4]:
- lubricate moving parts in machinery
- use wires with little electrical resistance
- streamline moving objects to reduce air resistance
- cut out noise (tighten loose parts to decrease vibration)
Light bulb [U:W]
- useful: light emitted from glowing filament
- wasted: energy transfer from filament heating surroundings
Electric heater [U:W]
- useful: energy heating surroundings
- wasted: light from glowing filament
Electric toaster [U:W]
- useful: energy heating bread
- wasted: energy heating toaster case and surroundings
Electric kettle [U:W]
- useful: energy heating water
- wasted: energy heating kettle and surroundings
Hairdryer [U:W]
- useful: kinetic energy of air from fan, energy heating air from filament
- wasted: sound of fan motor, energy heating hairdryer
Electric motor [U:W]
- useful: kinetic energy of object driven by motor, GPE of objects lifted
- wasted: energy heating motor, sound waves from motor
How does a clockwork radio function?
a spring is wound inside, increasing its elastic potential energy. This energy is transferred to its KE store as it turns an electric generator.
Power is...
the rate at which energy is transferred
The more powerful an appliance...
the faster it transfers energy
Power is measured in:
Watts, W
1 Watt =
1 J/s
Equation for power:
power = energy transferred OR work done ÷ time taken for transfer
Symbol equation for power:
P = E OR W ÷ t