Ch 2. BIO101A - Chemistry
1/122
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
123 Terms
matter
anything that occupies space and has mass
element
pure substance that cannot be broken down → simpler substances by chemical/physical techniques
an element that occurs in organisms in very small quantities
trace element
atoms
the smallest units that retain chemical/physical properties of an element
compound
molecule made of fixed ratio of two/more different elements
What is inside the atomic nucleus?
Protons + Neutrons
Where are electrons located?
Orbital paths around atomic nucleus
a distinct form of atoms of an element, with same number of protons, but different number of neutrons
isotope
isotopes have same atomic number but…
different mass number
mass
amount of matter in an object
weight
measure of pull of gravity on an object
giving off of particles of matter and energy by decaying nuclei
radioactivity
radiometric dating
uses clockwork decay of unstable isotopes to age organic material, rocks, fossils
The number of electrons surrounding the nucleus equals the
number of protons in the nucleus
orbital
region of space where electron lives most of the time
1s orbital is in the…
nucleus
1s orbital fits..
2e
2p fits
6 e
3d fits
10 electrons
an electron in outermost energy level of an atom
valence electrons
atoms in outermost energy level that is not filled are…
chemically reactive
completely filled outermost energy levels are…
nonreactive/inert
chemical bonds
link formed when atoms of reactive elements join into molecules
two or more atoms held together by chemical bonds is called a
molecule
ionic bonds
electrical attractions between atoms that gain/lose valence electrons completely
i.e: NaCl
a positively charged ion like Na+ is a…
cation
a negatively charged ion sub as Cl- is an
anion
True or false: Chemical bond exert an attractive force greater distances than any ionic bond
F, vice versa
Bond formed by electron sharing between atoms
Covalent bonds
the measure of tendency of an atom to attract electrons to itself in a chemical bond (to become negative)
electronegativity
non polar covalent bond
electrons are shared equally/nearly equally;
atoms involved have no charge
polar covalent bond
atom attract electrons more strongly → has a partial negative charge, (Δ-),
atom deprived of electrons has a partial positive Δ+
polar associations
when polar molecules align themselves with other polar molecules and with charged ions & molecules
nonpolar associations
association that occurs when non polar molecules clump together
intermolecular
between atoms in different molecules
intramolecular
between atoms in the same molecule
Hydrogen bonds are easier to break than covalent and ionic bonds.
True
Van der Waals forces
Weak molecular forces over short distances
How does an ionic bond form?
An ionic bond forms between atoms when those atoms gain or lose electrons completely.
How does a covalent bond form?
A covalent bond forms when atoms share a pair of valence electrons rather than ganing/losing completely
What is a chemical reaction?
atoms/molecules interact to form new bonds/break old ones
atoms are added/removed → molecules, linkages of atoms are rearranged
water lattice
an arrangement formed when. water molecule in liquid water establishes an avg of 3.4 H bonds with its neighbors
ice lattice
spaces water molecules farther apart than water lattice
the amount of energy as heat required to increase temperature of a given quantity of water
specific heat
calorie
amount of heat energy required to raise 1g of water by 1c
heat of vaporization
allows humans & many other organisms to cool when hot
cohesion
the high resistance of water molecules to separation (via hydrogen bond lattice)
molecules stick to walls of tube forming H bonds w/ polar groups in tubes
adhesion
surface tension
force places surface water molecules under tension → making them more resistant to separation than underlying water molecules
hydration layer
surface coat of water molecules,
covers other polar & charged molecules/ions
The number of moles of a substance dissolved in 1 L of solution is known as the
molarity
solution
solute dissolved in a solvent
bases
proton acceptors that reduce H+ [] of a solution
buffers
substances that compensate for pH changes by absorbing/releasing H+
acids
hydrogen ion (proton H+) donors
bases
H+ acceptors
acid dissociates → water to produce
H+ ion and atom
most bases dissociate in water to
give OH- ions → which accept protons → H2O
emergent properties
trait/characteristic possessed by object due to arrangement/interaction of components
not found in components themselves
emergent property of life #1
increase in size/cell no.
systematic change in form / function over time
energy utilization to do useful work
sun → radiant energy →
chemical energy
unicellular →
bacteria
multicellular
plants, animals
solar energy → chemical energy
photoautotrophs (plants)
humans are
heterotrophs
all (heterotroph) organisms perform…
cellular respiration, while plants do at night
Change in sate → receptor/detector →
___________ → effector → __________________
control center
response restores state
reproduction
generation of new, separate individual
_________ has information, blueprint for making new individual
hereditary system
change in form, structure, function of organisms over geologic time
evolve
atoms → molecules → ____________ → _____________ → organelles → cells → ____________ → organs → organ systems
macromolecules
supramolecular systems
tissues
how many bonds for O to complete outer shell (valence e)
2 bonds
how many bonds for N to complete outer shell (valence e)
3
how many bonds for C to complete outer shell (valence e)
4
how many bonds for P to complete outer shell (valence e)
3,5
Adaptation & natural selection are up to chance
F
Organelles are considered ‘alive’
F
How do viruses live?
Acellular, no metabolism, reproduction, invade host
How many protons in Carbon?
How many shells are filled?
How much electrons in first and second shell?
6 protons
1s2 2s2 2p2
How many protons are in Hydrogen?
How many shells are filled?
How much electrons in first and second shell?
1
1s1
How many protons in Oxygen?
How many shells are filled?
How much electrons in first and second shell?
8 protons
1s2 2s2 2p4
How many protons in Nitrogen?
How many shells are filled?
How much electrons in first and second shell?
7 protons
1s2 2s2 2p5
cells within the body communicate with each other using chemicals known as
receptors/proteins
Electrical attraction of partially (+) charged H on one polar molecule to partially (-) charged atom on 2nd polar molecule
Hydrogen bond
Water has a lower structural organization than most other liquids
F, higher
ionic bonds exert forces in all directions
T
ionic bonds are all the same strength depending on charged substances
F, can vary
Of 92 elements, ______ found in organisms
25
biomolecules
carbon backbone
acts as an organic base accepting H+ in [aq] -> converting from a non-ionized to an ionized form
Amines
an _________ has the carbonyl group at the end of a carbon chain, bonded to a hydrogen atom,
while a ________ has the carbonyl group bonded to two other carbon atoms within the chain.
aldehyde (C1)
ketone (C2)
________________ give organic molecules acidic properties because -OH group releases H+ in [aq] converting from non-ionized -> ionized form
carboxylic acids
Thiols lose a hydrogen atom as it bonds
T
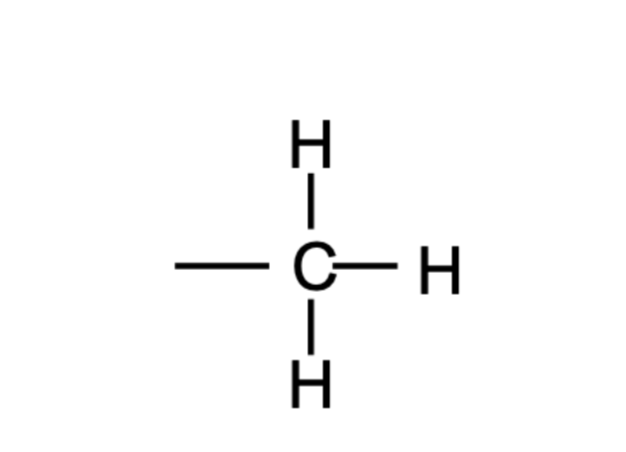
Methyl Group
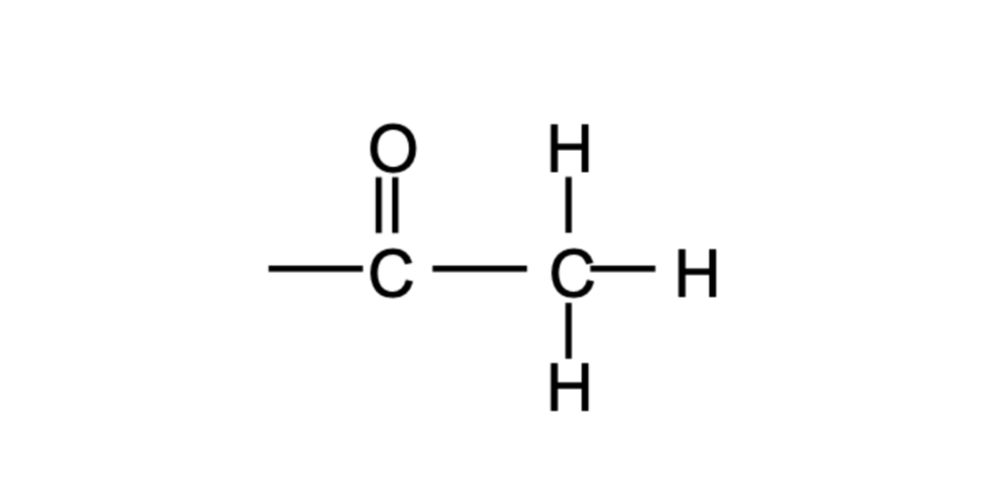
Acetyl Group
same structures, different covalent molecular arrangement
isomer
L-form is biologically active while D-form is not
T
Lipids are made of building blocks, and are considered polymers
F, not polymers
Constructed by forming covalent bonds between basic building blocks
Macromolecules
Dehydration reaction:
Releases or requires energy?
Requires